Week 1 - False Confessions & Interrogating
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
what is the difference between forensic psychology vs. forensic science?
forensic scientists analyze physical evidence left behind by an unknown subjects (the “unsub”)
forensic DNA
latent fingerprints
bite marks, ballistics, fibers, toolmarks
primary goal: link physical evidence to a specific suspect
—
forensic psychologists deal with . . .
lie detection - is it possible? who can do it?
are fingerprint experts as accurate as they think they are?
why do people sometimes falsely confess to a crime?
is eyewitness identification reliable or unreliable?
can we predict who will commit violent behavior?
how useful are criminal profiles?
what are the three different courts mentioned in lecture? what were the different aspects of criminal court related to the class?
Family Court
Civil Court
Criminal Court
Competency and Insanity Evaluation
False confessions
Eyewitness Identification
Predicting violent behavior
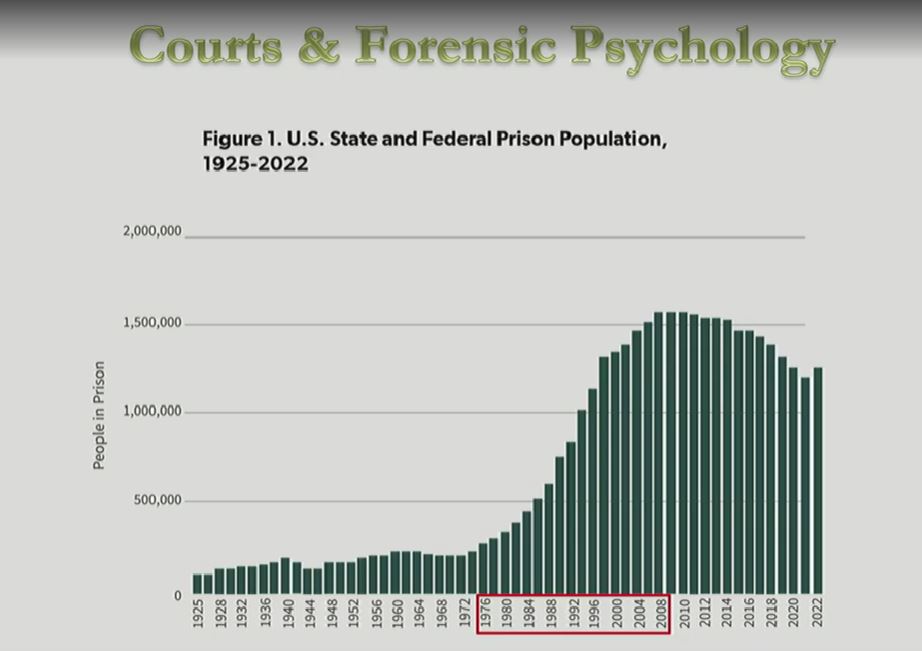
what is interesting about the U.S. State and Federal prison population graph shown in lecture? what is the explanation for this aspect of the graph?
There was exponential growth in the prison population within the U.S. from the 70s to 2008.
This growth can be attributed to the “War on Drugs”
rather than being caused by a growth in population this came from a societal change
what is the “Innocence Project”?
The Innocence Project has used DNA testing to exonerate hundreds of innocent people who were wrongfully convicted and sent to prison
Forensic DNA first used in mid 1980s
first DNA exoneration of an innocent prisoner occurred in 1989
since then, more than 375 innocent prisoners have been exonerated
spent an average of 14 years in prison before being exonerated
how many death row inmates were innocent in 2004? how does it compare to 10 years later?
4.1% (from 1973 to 2004)
1.6% (10 years later)
is eyewitness memory reliable?
yes, it is reliable. people believe it isn’t reliable because a common mistake that is made is using contaminated eyewitness testimony
that just means it has been a long time since the event occurred
who is Hugo Munsterberg? what did he believe? what did wilhelm wundt believe in?
awarded Ph.D. in 1885
Student of Wilhelm Wundt (founder of experimental psychology)
Munsterberg believed in an applied psychology where the field is used for practical concerns (e.g., to the legal setting)
Wundt believed in a basic psychology where it is a pure science that is detached from practical concerns
what information is important for assessing the reliability of a lie detection test?
1. Percentage of guilty people detected as guilty (hit rate)
2. Percentage of innocent people falsely detected as guilty (false alarm rate)
if a lie detection test has 100% accuracy in detecting people as guilty, what percentage of innocent people will be mistakenly detected as guilty?
Not enough information given. It doesn’t tell you what percentage of innocent people are mistaken as guilty
what is the difference between an interrogation and an interview?
Interrogation:
Subject is a person suspected of having committed a crime
Goal is to . . .
Establish if the suspect is the perpetrator
elicit accurate information
Interview:
subject is witness to a crime
goal is to elicit accurate information to facilitate the investigation
problem: witnesses induced to provide false information
what is a custodial interrogation?
Freedom of movement is significantly restricted
a reasonable person would have felt he or she was not at liberty to end the interrogation and leave
what are Miranda Rights? (Miranda v. Arizona, 1966)
The rights:
to remain silent
to have an attorney present during questioning
to have an appointed attorney when financial need exists
to acknowledge understanding of rights
the goals:
to discourage police from using coercion
to prevent involuntary confession
do suspects make use of their Miranda Rights?
Innocent people feel they have nothing to hide and often waive their Miranda rights
Having waived their right to silence, an innocent suspect can end up making a false confession (in response to coercive police interrogation tactics
80% waive their Miranda rights and are subject to interrogation; more than 90% of juveniles waive their rights
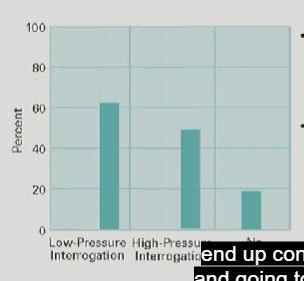
describe the study about the power of confession discussed in lecture.
Mock jurors read trial testimony that included a defendant’s confession
Three conditions:
1. low-pressure interrogation (60% guilty votes)
2. high-pressure interrogation (50% guilty votes)
3. no confession (19% guilty votes)
Result:
mock jurors don’t care about coerced confessions
fundamental attribution error: tendency to overemphasize dispositional factors while minimizing situational factors to explain an individual’s behavior
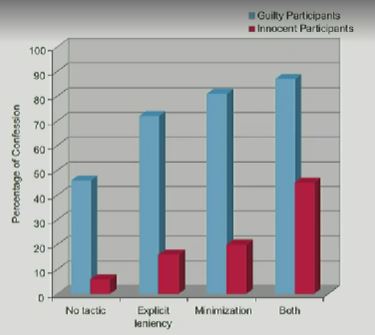
describe the experiment about false confessions discussed in lecture.
Researchers paired subjects with a confederate for a problem-solving study and instructed them to work alone on some trials and jointly on others
in guilty condition, the confederate sought help on an individual problem, inducing the subject to violate the experimental rule; in the innocent condition, the confederate did not make this request
Results:
False confessions from innocent participants became much higher for minimization and explicit leniency techniques (false alarm rate)
what is the receiver operating characteristic? (ROC)
if a plot point falls on the center diagonal line, what does that tell you about your confession test?
Plotted graph of hit rate (y-axis) to false alarm rate (x-axis)
A test that has the SAME hit rate as the false alarm rate is a SHITTY test since it tells you nothing
hit rate = false alarm rate (no information)
hit rate > false alarm rate (better information)
what effect does sleep deprivation have on false confessions?
Experiment:
Participants completed computer tasks and were told not to press the “Escape” key
Two groups:
1. Well Rested
2. All Nighter
Results:
Group 2 were 4.5 times more likely to falsely confessing to pressing the escape key
what are the four types of false confessions?
1. Coerced Instrumental
end interrogation by acquiescence
2. Coerced Authentic
confessor becomes persuaded that he or she is guilty
3. Voluntary Instrumental
protect someone else, gain notoriety
4. Voluntary Authentic
confessor is delusional or mentally ill
who was John Mark Karr? what type of false confession does this case follow?
famous false confession case to 1996 murder of JonBenet Ramsey
voluntary authentic (he mentally ill af)
who was Peter Reilly? what type of false confession does this case follow?
18 year old Peter Reilly found dead mother in home. After 8 hours of interrogation, he confessed to murdering her
coerced authentic (police got him to believe it)
what are the types of factors important to eliciting a false confession?
Personal risk factors
adolescence
cognitive / intellectual disabilities
Situational risk factors
duration
the vast majority of interrogations last from 30 min to 3 hrs
in false confessions, interrogations lasted an average of 16.3 hours
interrogation tactics
lying (ex. claiming that you failed a detection test)
minimization
what are the two things required for a confession to be admissible?
Be given voluntarily
Be given by a person who is competent
what are some potential solutions to prevent false confessions?
video recording of interrogations
limit the duration of the interrogation
Ban the “false evidence ploy”
Illinois and Oregon recently banned the use of police deception during the interrogation of juveniles, OK against adults tho
special protections for vulnerable suspect populations (juveniles and people who are cognitively impaired or psychologically disordered)
From the years 1973-2004, what percentage of death row inmates were. . .
1. Executed
2. Still on death row
3. Removed from death row but not exonerated
4. Exonerated
Executed = 12.6%
Still on death row = 46.1%
Removed from death row but not exonerated = 35.8%
Exonerated = 1.6%
what percentage of wrongful convictions were due to. . .
eyewitness misidentification
improper forensics
false confessions
information / snitches
72% (Eyewitness Misidentification)
47% (Improper Forensics)
27% (False Confessions)
15% (Snitches)