Reporting and Analyzing Receivables in Financial Accounting
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Accounts Receivable
Amounts customers owe on account that result from the sale of goods and services.
Notes Receivable
Written promise (formal instrument) for amount to be received.
Other Receivables
Nontrade receivables such as interest, loans to officers, advances to employees, and income taxes refundable.
Recognizing Accounts Receivable
Service organizations record a receivable when they perform services on account.
Merchandisers Recording
Merchandisers record receivables at point of sale of merchandise on account.
Sales Returns
Sales returns reduce receivables.
Journal Entry for Sale
Assume that Jordache Co. on July 1, 2022, sells merchandise on account to Polo Company for $1,000 terms 2/10, n/30.
Journal Entry for Return
On July 5, Polo returns merchandise worth $100 to Jordache Co.
Journal Entry for Payment
On July 11, Jordache receives payment from Polo Company for the balance due.
Credit Card Sale
Assume that you use your JCPenney Company credit card to purchase clothing with a sales price of $300 on June 15.
Interest Revenue Entry
JCPenney charges interest of 1.5% per month on the balance due.
Adjusting Entry for Interest
JCPenney makes an adjusting entry to record interest revenue on June 30 as follows.
Do It! 1 - Sale Entry
On May 1, Wilton sold merchandise on account to Bates for $50,000 terms 3/15, net 45.
Do It! 1 - Return Entry
On May 4, Bates returns merchandise with a sales price of $2,000.
Do It! 1 - Payment Entry
On May 16, Wilton receives payment from Bates for the balance due.
Sales Discounts
Seller may offer a discount to encourage early payment.
Balance Due Calculation
If you still owe the $300 from the June 15 transaction at the end of the month.
Interest Calculation
Interest revenue calculated as ($300 × 1.5% × ½).
Terms of Sale
Terms 2/10, n/30 means a 2% discount is available if paid within 10 days, otherwise full amount is due in 30 days.
Accounts Receivable
Valued at net realizable value.
Uncollectible Accounts Receivable
Sales on account raise the possibility of accounts not being collected.
Bad Debt Expense
Seller records losses that result from extending credit.
Direct Write-Off Method
No matching; receivable not stated at net realizable value; not acceptable for financial reporting.
Allowance Method
Better matching; receivable stated at net realizable value; required by GAAP.
Sale on Account
Journal entry for credit sale of $100.
Collection on Account
Collect $333 on account.
Bad Debt Expense Adjustment
Adjustment of $15 for estimated bad debts.
Write-Off Uncollectible Receivable
Write-off of uncollectible accounts of $10.
Direct Write-Off Method Example
Assume that Warden Co. writes off M. E. Doran's $200 balance as uncollectible on December 12.
Allowance Method Features
Estimate uncollectible accounts receivable; debit Bad Debt Expense and credit Allowance for Doubtful Accounts.
Recording Estimated Uncollectibles
Hampson Furniture has credit sales of $1,200,000 in 2022, estimating $12,000 will be uncollectible.
Write-Off of an Uncollectible Account
On March 1, 2023, Hampson Furniture writes off $500 owed by R. A. Ware.
Recovery of an Uncollectible Account
On July 1, R. A. Ware pays the $500 amount that Hampson Furniture had written off.
Net Realizable Value Reporting
ABC Corporation Balance Sheet (partial).
Note Disclosure of the Allowance Method
Disclosure related to the allowance method.
Percentage-of-Receivables Basis
Basing estimates on outstanding receivables where management establishes a percentage relationship between amount of receivables and expected losses from uncollectible accounts.
Bad Debt Expense
The amount of bad debt expense to be recorded is the difference between the required balance and the existing balance in the allowance account.
Aging of Accounts Receivable
A method used to estimate uncollectible accounts by categorizing receivables based on how long they have been outstanding.
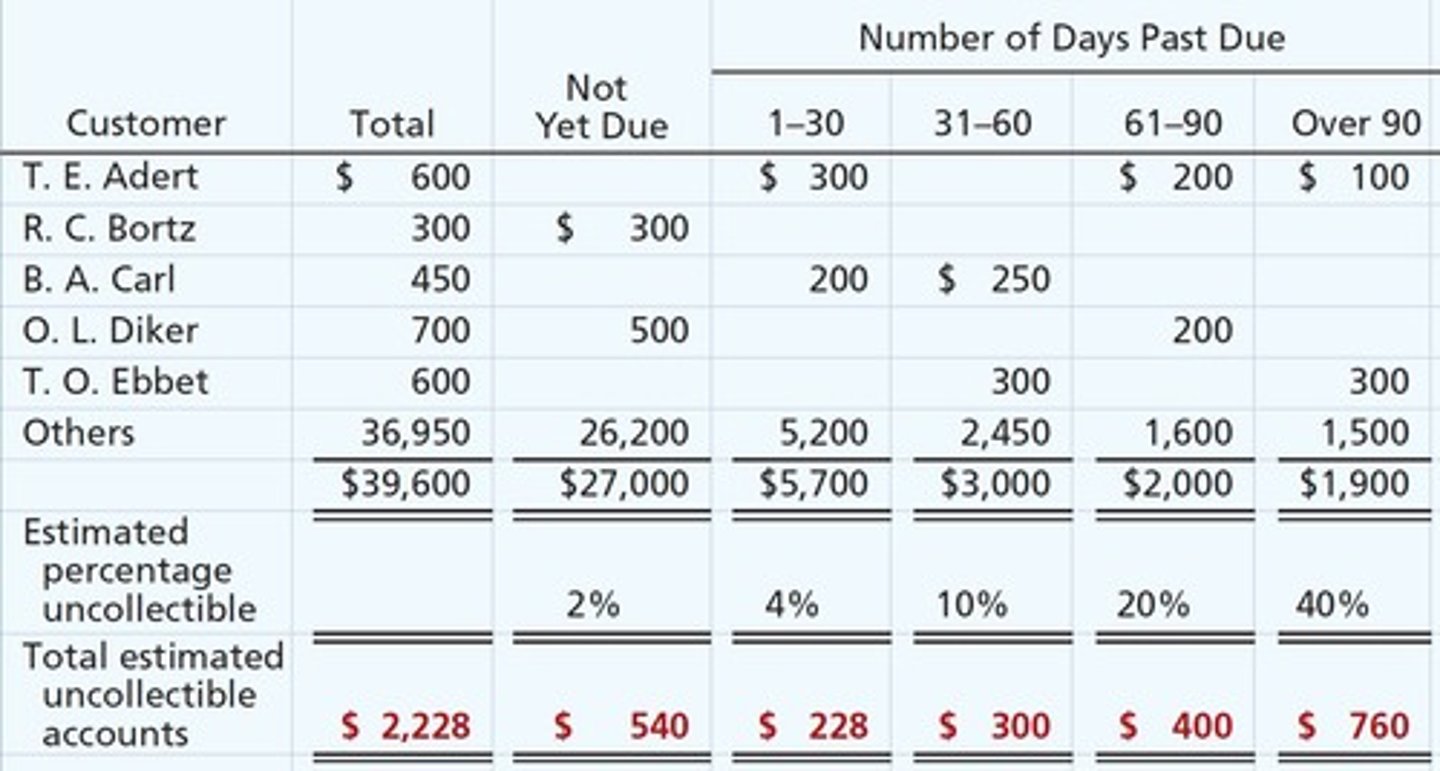
Adjusting Entry for Allowance
An entry made to adjust the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts based on estimates of uncollectible receivables.
Unadjusted Trial Balance
A report that shows the balances of all accounts before any adjustments are made.
Service Charge Expense
The fee charged by a factor for purchasing receivables, typically ranging from 1% to 3% of the receivables sold.
Factoring
A method of disposing of accounts receivable where receivables are sold to a finance company or bank.
National Credit Card Sales
A method of disposing of accounts receivable where retailers pay card issuers a fee of 2% to 4% of the invoice price.
Promissory Note
A written promise to pay a specified amount of money on demand or at a definite time.
Cash from Factoring
The cash received from factoring receivables, minus any service charge.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
An account that estimates the amount of receivables that may not be collected.
Example of Bad Debt Expense Entry
Bad Debt Expense of $5,000 is recorded as [(10% × $30,000) + $2,000].
Example of Sale of Receivables
Hendredon Furniture factors $600,000 of receivables, with a service charge of 2%, resulting in a cash receipt of $588,000.
Example of National Credit Card Sale
Anita Ferreri purchases $1,000 of equipment, with a service charge of 3%, resulting in a cash receipt of $970.
Cash Needed for Payroll
Peter M. Kell Wholesalers Co. factors $125,000 of receivables to raise $120,000 in cash, incurring a 1% service charge.
Credit Investigation
A process undertaken by the issuer of a credit card to assess the creditworthiness of a customer.
Collection of Receivables
The process where factors collect payments directly from customers after purchasing receivables.
Advantages of National Credit Cards
Retailers benefit from quicker cash receipts, credit investigations, and the management of customer accounts by the issuer.
Example of Adjusting Entry with Debit Balance
If the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has a debit balance of $500, the adjusting entry for an estimate of $2,228 results in a Bad Debt Expense of $2,728.
Example of Adjusting Entry with Credit Balance
If the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has a credit balance of $528, the adjusting entry for an estimate of $2,228 results in a Bad Debt Expense of $1,700.
Promissory Notes
May be used when lending or borrowing money, when the amount of transaction and credit period exceed normal limits, or in settlement of accounts receivable.
Notes Receivable
To the payee, the promissory note is a note receivable. To the maker, the promissory note is a note payable.
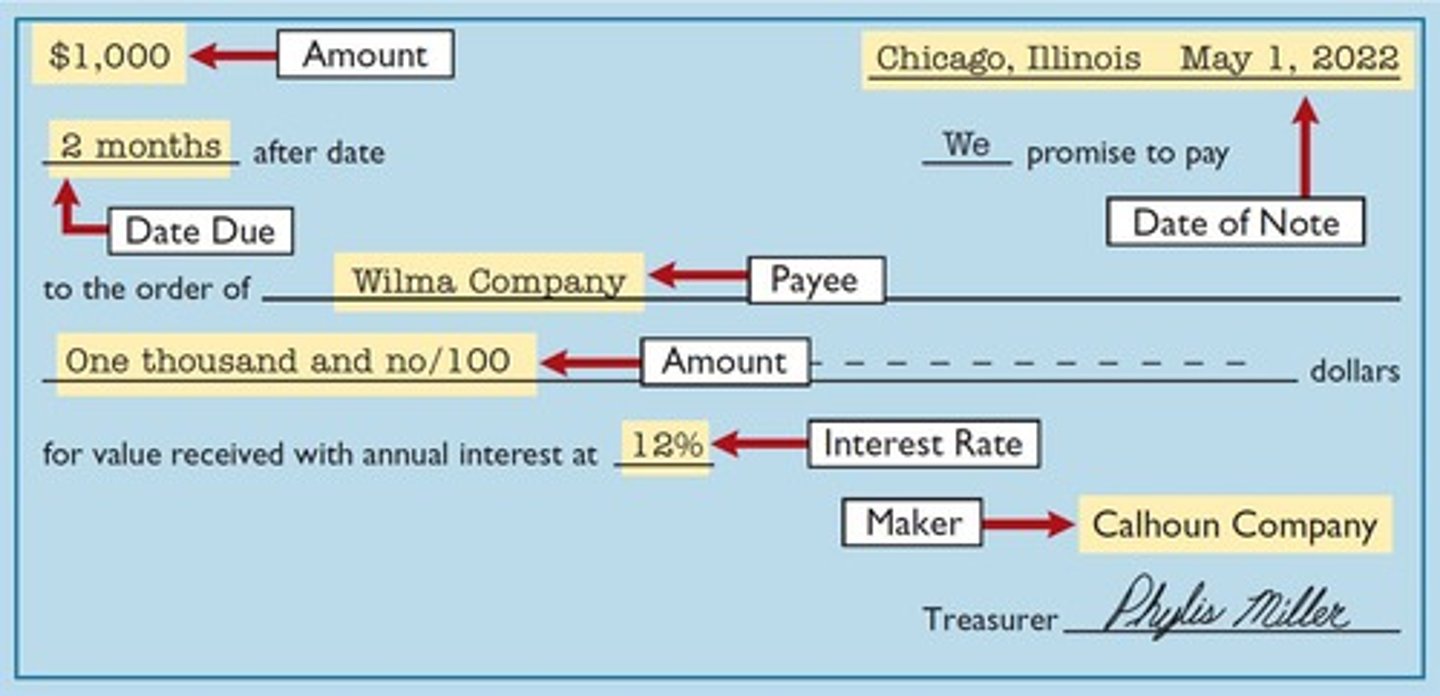
Maturity Date
Maturity date of a promissory note may be stated in one of three ways: on demand, on a stated date, or at the end of a stated period of time.
Note Terms
Note terms are expressed in months or days.
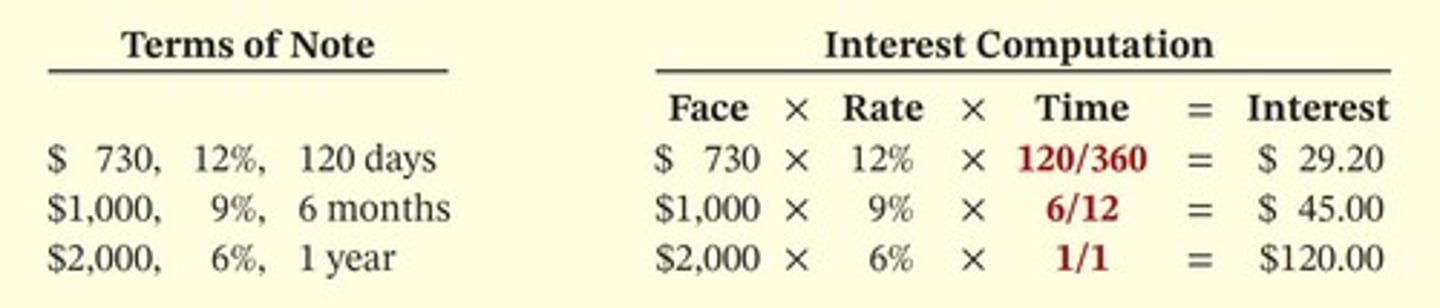
Computing Interest
Face Value of Note × Annual Interest Rate × Time in Terms of One Year = Interest. When counting days, omit the date note is issued, but include the due date.
Valuing Notes Receivable
Report short-term notes receivable at their cash (net) realizable value. Estimation of cash realizable value and recording bad debt expense and related allowance are similar to accounts receivable.
Disposing of Notes Receivable
Notes may be held to their maturity date. The maker may default, and the payee must make an adjustment to the account. The holder speeds up conversion to cash by selling the note receivable.
Honor of Notes Receivable
A note is honored when its maker pays it in full at its maturity date.
Dishonor of Notes Receivable
A dishonored note is not paid in full at maturity. Dishonored note receivables are no longer negotiable.
Interest Revenue Calculation
For a $10,000 note at 9% interest over 5 months, the interest revenue is calculated as $10,000 × 9% × 5/12 = $375.
Accrual of Interest Receivable
For a $10,000 note at 9% interest over 4 months, the adjusting entry is Interest Receivable $300 and Interest Revenue $300, calculated as $10,000 × 9% × 4/12 = $300.
Entry for Honoring Note
When honoring the Higley note on November 1, the entry is Cash $10,375, Notes Receivable $10,000, and Interest Revenue $375.
Dishonor Entry with Hope of Collection
If Higley Co. cannot pay, the entry is Accounts Receivable $10,375, Notes Receivable $10,000, and Interest Revenue $375.
Dishonor Entry without Hope of Collection
If there is no hope of collection, the entry is Allowance for Doubtful Accounts $10,000 and Notes Receivable $10,000.
Gambit Stores Entry
For a $3,400, 90-day, 6% note from Leonard Co., the entry at maturity is Cash $3,451, Notes Receivable $3,400, and Interest Revenue $51.
Statement Presentation of Receivables
The way receivables are displayed in financial statements.
Managing Receivables
Five steps in managing accounts receivable: Determine to whom to extend credit, establish a payment period, monitor collections, evaluate the liquidity of receivables, and accelerate cash receipts from receivables when necessary.
Credit Policy
A guideline that determines how strict or loose a company is in extending credit to customers.
Payment Period
The time frame established by a company for customers to make payments.
Accounts Receivable Aging Schedule
A report prepared at least monthly to estimate timing of future cash inflows and identify problem accounts.
Accounts Receivable Turnover
A measure of how many times, on average, a company collects receivables during a period.
Average Collection Period
The average number of days it takes to collect receivables; should not exceed the credit term period.
Accelerating Cash Receipts
The process of speeding up the collection of cash from receivables.
Factors for Selling Receivables
Reasons receivables are sold: size, may be the only reasonable source of cash, and billing and collection are often time-consuming and costly.
GAAP
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, a framework for financial reporting in the United States.
IFRS
International Financial Reporting Standards, a set of accounting standards developed by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Impairment
A term used to indicate that a receivable may not be collected.
Segregation of Receivables
The practice of reporting receivables with different characteristics separately.
Uncollectible Accounts Estimation
The approach for estimating accounts that are unlikely to be collected, which differs between IFRS and GAAP.
Factoring Transaction
A financial transaction where receivables are sold to another party; IFRS and GAAP have different criteria for recording this.
Partial Derecognition of Receivables
The ability under IFRS to remove part of a receivable from the balance sheet, which is not permitted under GAAP.
Lebron James Company Case
A scenario where net credit sales, beginning and ending accounts receivable balances are provided to compute accounts receivable turnover and average collection period.

Credit Risk
The risk of loss due to a customer's failure to make payments on any type of debt.
Liquidity of Receivables
The ease with which receivables can be converted into cash.
Sales Returns and Allowances
Reductions in sales revenue for products that are returned or allowances given to customers.
Sales Discounts
Reductions in the amount owed by customers if payment is made within a specified period.
FASB
Financial Accounting Standards Board, the body responsible for establishing accounting standards in the U.S.
IASB
International Accounting Standards Board, the organization responsible for developing and maintaining IFRS.