Hematology 8: Granulocytes and Monocytes
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Introduction to Leukocytes and where they mature
•Differentiate, proliferate, and mature in the _bone marrow_
•Except for T lymphocytes - mature in thymus
granulocytes (Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs)
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
Neutrophils
•Most abundant bacterial defense
•Eosinophils
•Allergy, parasitic infections
Basophils
Histamine release, inflammation
agranulocytes (mononuclear cells)
monocytes, lymphocytes
Myeloblast
Large nucleus, no granules - earliest recognizable precursor, scant light blue cytoplasm, Golgi apparatus, nucleus is round or oval and lacy and with evenly stained chromatin, nucleoli
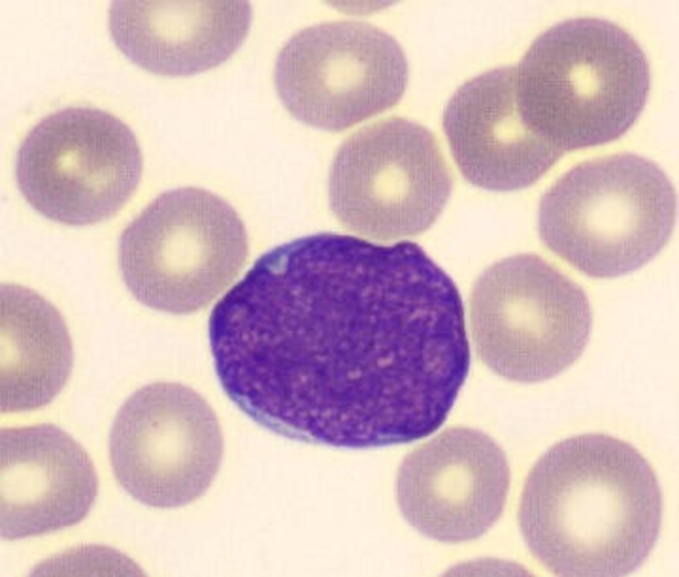
Microscopic Features of myeloblast
•3-4x larger than a mature RBC
•High nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio
•Round Nucleus with immature chromatin (not clumped)
•Prominent nucleoli
•Cytoplasm is scant, gray to pale blue and lacks granules
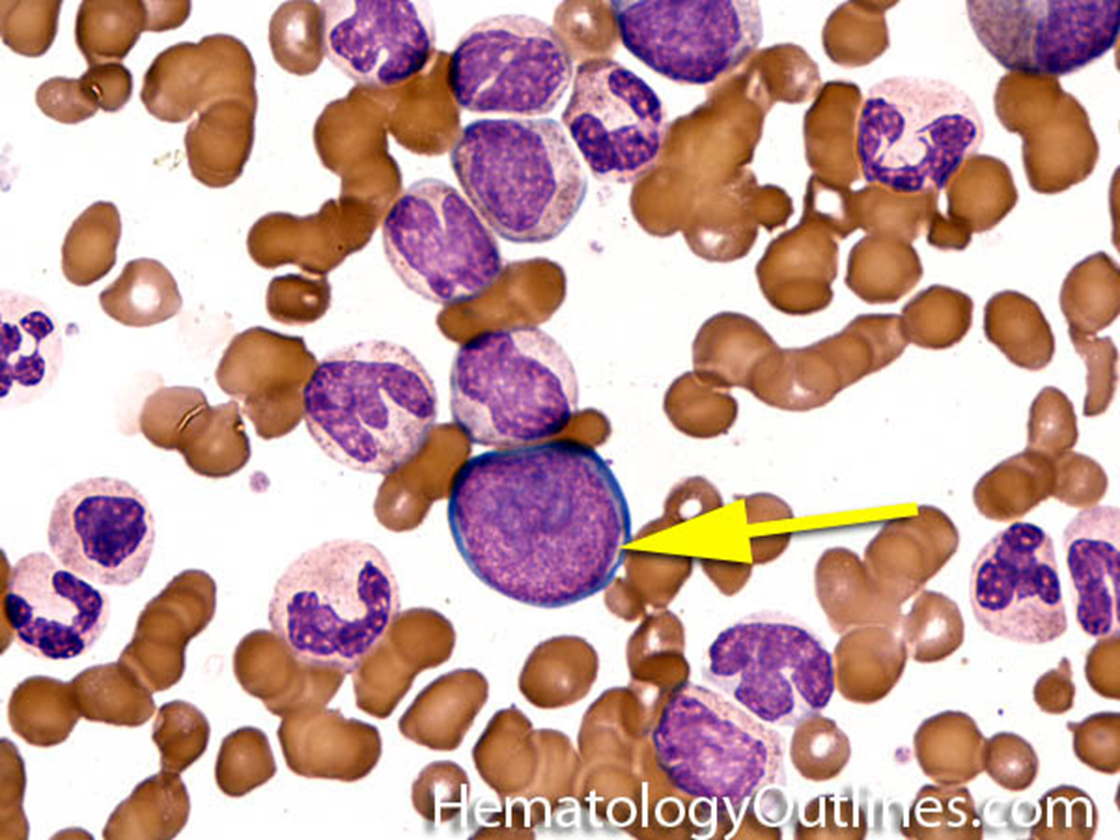
promyelocyte
azurophilic granules appear - reddish purple primary granules (glitter) start to see, large N-C ratio, more cytoplasm, nucleus centrically located, chromatin coarser than blast, still open and lacy, several nucleoli
Microscopic Features of promyelocyte
2-3x larger than a mature RBC
High nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio (but more cytoplasm than Myeloblast)
Round Nucleus with immature chromatin (not clumped)
Nucleoli are present but less prominent than Myeloblasts
Cytoplasm with primary (azurophilic) granules
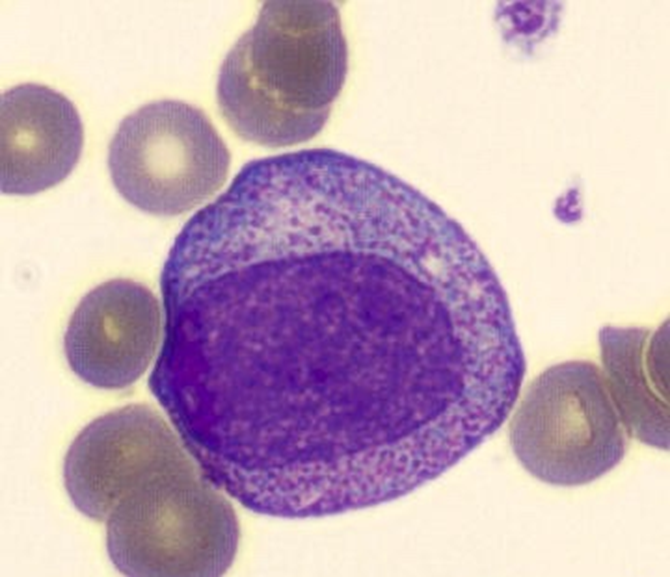
myelocyte
reduced size of nucleus, is oval or round or slightly flattened to one side, cytoplasm less blue, clear light area next to nucleus = golgi apparatus, has secondary granules
Microscopic Features of myelocyte
•2-3x larger than a mature RBC
•Intermediate N:C ratio (more cytoplasm than promyelocyte)
•Eccentrically placed oval Nucleus (No nucleus indentation) with more mature chromatin (clumped)
•Perinuclear clearing is common
•Nucleoli are absent (Note: absent nucleoli from this stage onward)
•More cytoplasm with only rare or absent primary (azurophilic) granules
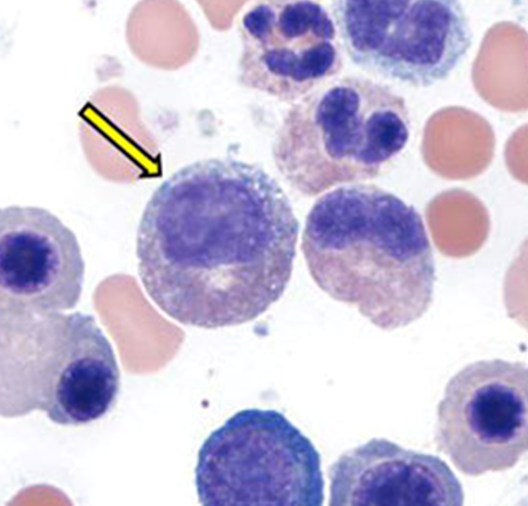
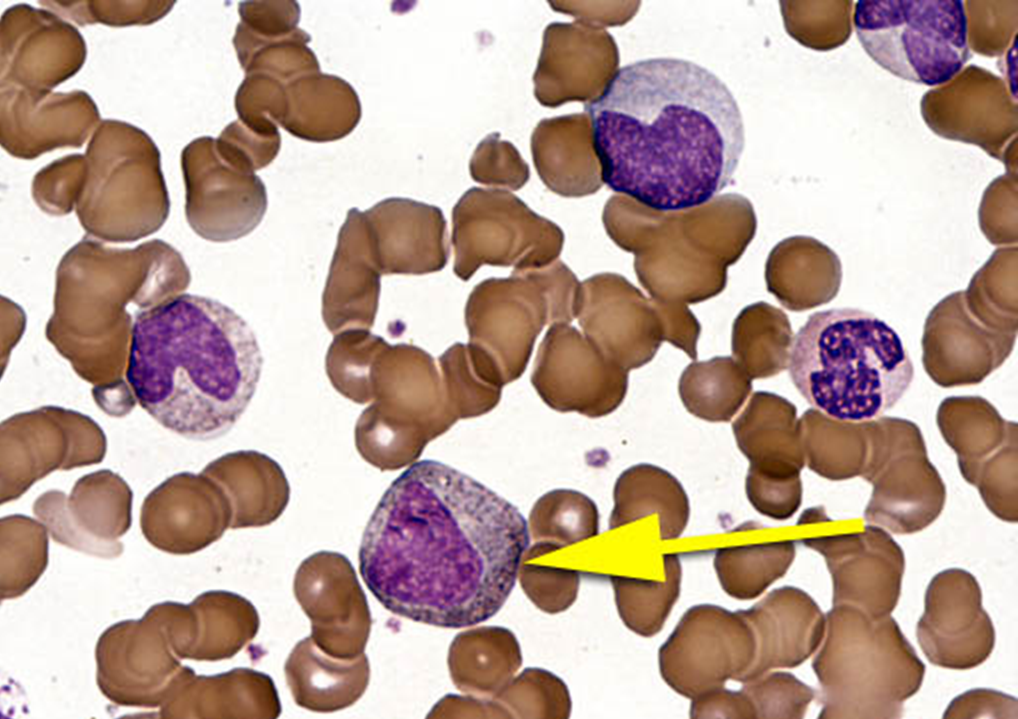
metamyelocyte
nuclear chromatin coarse and climbed, no nucleoli visible, nuclear indentation kidney bean shape, tertiary granules synthesized, predominance of secondary granules
can start to differentiate between eosinphil, neutrophil or basophil?
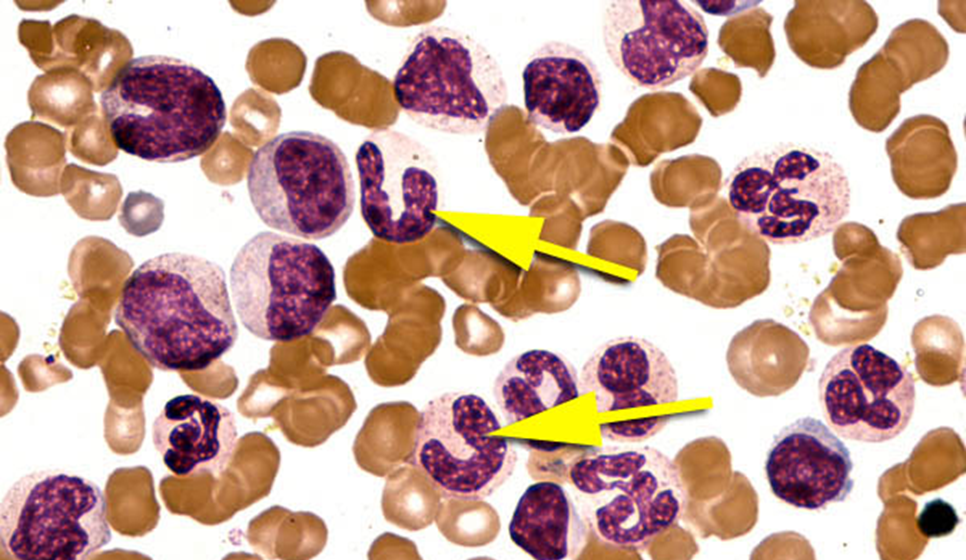
Band neutrophil
Horseshoe shaped nucleus, indentation of nucleus of more than half the diameter, cytoplasm is pink to tan, granules all granules present, granules don’t stain as prominent
first stage normally found in peripheral blood vessels
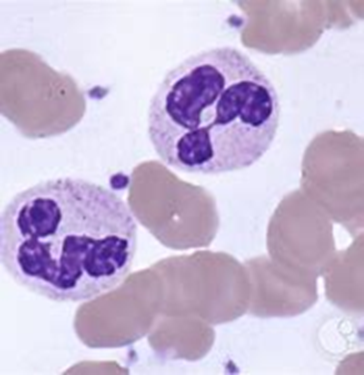
segmented neutrophils
nucleus segmented with three to five lobes, condensed chromatin, cytoplasm is pink or tan to clear color, contains secondary granules, tertiary granules, smaller cytoplasm
positive for CD11b
leukocytosis
increase in leukocytes
leukopenia
decrease in leukocytes
neutrophil function and kinetics
first responders, most abundant WBC - 70%, migrate from peripheral blood into tissues in response to chemotactic stimulation induced by a foreign agent, where they engulf and destroy the invader.
first sign of underlying pathology
Alteration in concentration of PB leukocytes is often
Granulocytopenia
↓ in all types of granulocytes
Neutropenia:
•↓ only in neutrophils
Agranulocytosis:
•absence of granulocytes, high risk of developing infection
Granulocytosis:
•↑ in all granulocytes
Neutrophilia
↑ in neutrophils
Reactive response to bacterial infection, metabolic intoxication, drug intoxication, tissue necrosis
three roles of innate immune response neutrophil function
Adherence & Migration (chemotaxis)
Phagocytosis
Direct bacterial killing
Neutrophil Adherence and Migration
Neutrophil-endothelial cell adhesion facilitates diapedesis.
Once in tissues, neutrophils migrate towards infected site through chemotaxis.
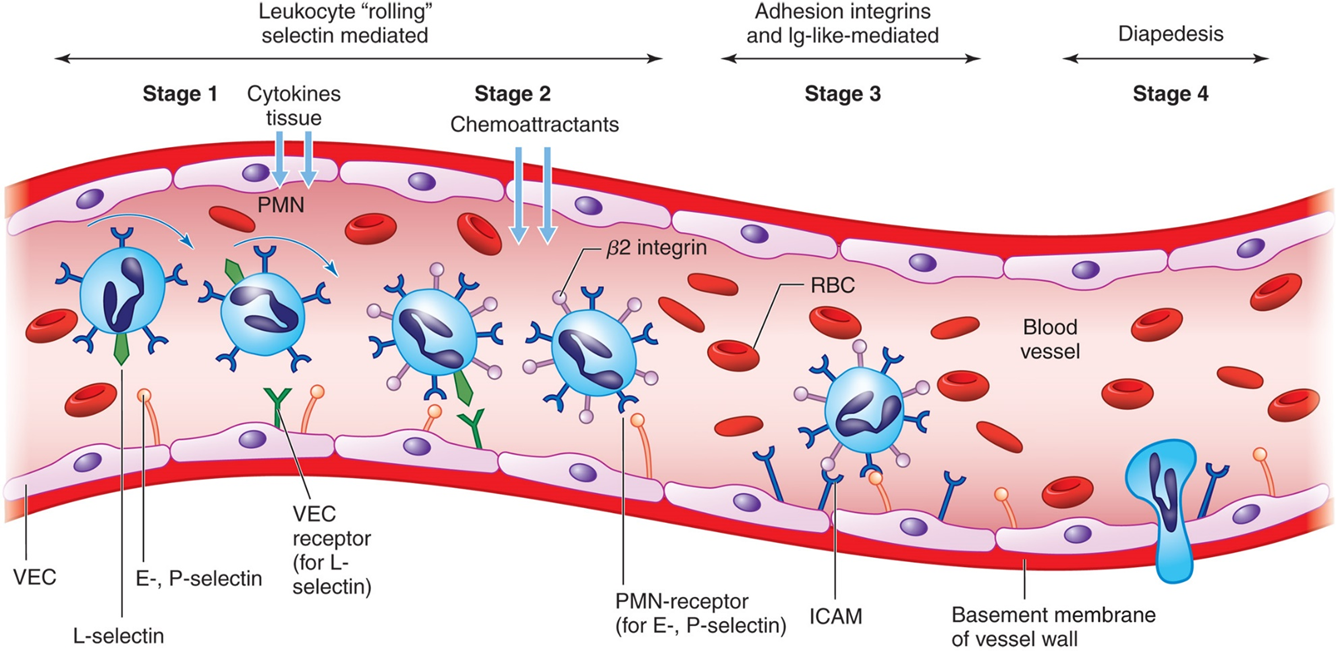
phagocytosis
Neutrophil eats cell with psuedopodia pushing membrane out - actin mediated
steps of phagocytosis
recognition and attatchment: Neutrophils recognize and bind pathogens.
Engulfment:
Neutrophil extends pseudopods, enclosing the pathogen within a phagosome.
phagosome maturation: phagosome fuses with lysosome - forming phagolysosome
microbial killing mechanism - reactive o2 and n species and enzymes degrade
pathogen is broken down into fragments and expelled
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)
Composed of DNA and proteins
Function to eradicate microbes independent of phagocytosis
Trap, neutralize, and kill bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites
prevent hte spread of microbes
Eosinophil Development & Maturation
Myeloblast → Large nucleus, no granules.
Promyelocyte → Azurophilic granules appear.
Myelocyte → Secondary granules form, no more mitosis. **here can tell it is eosinphil because stains red!!!
Metamyelocyte → Nucleus starts to indent.
Eosinophilic Band → Horseshoe-shaped nucleus.
Eosinophil → Mature, functional cell.
eosinophillic myelocyte
contains large, eosin staining crystalloid granules, granules larger than neutrophils and more of them
lots of cytoplasm, nucleus usually one lobe, maybe nucleoli, secondary granules
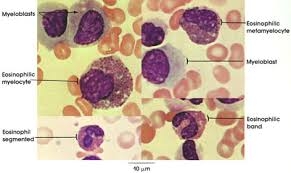
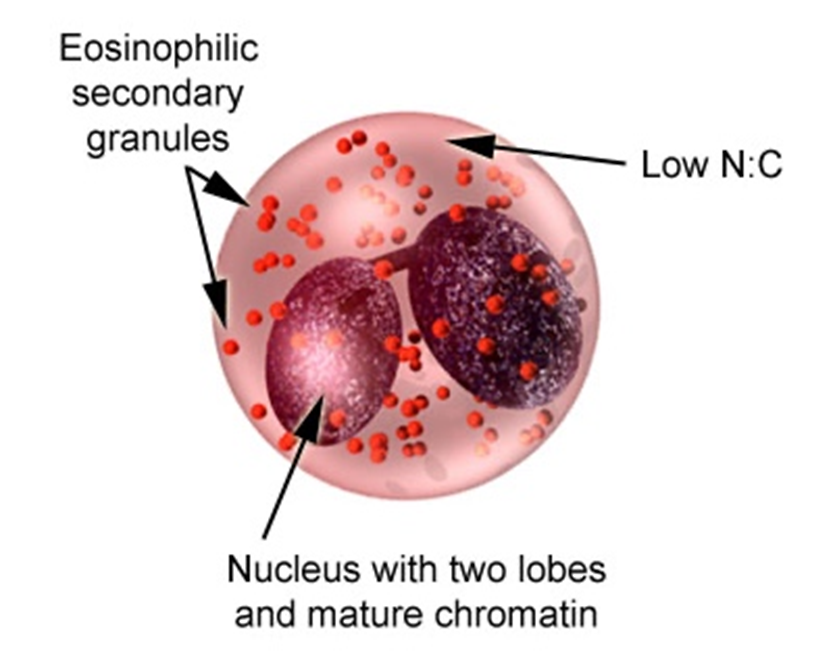
eosinphil
nucleus - no more than 2 or three lobes, no nucleoli
reddish cytoplasm completely filled with granules - crystaloid, uniform in size, evenly distributed, secondary granules
eosinophil defense function
Parasitic infections (helminths), too large to be phagocytosed so releases granules of major basic protein from granules on parasites
Allergic reactions and hypersensitivities (asthma, anaphylaxis
basophil maturation
Similar to neutrophil maturation
Gradual indentation and segmentation of the nucleus,
defining stage at basophilic myelocyte, stains purple
basophils function
Release histamine in granules & heparin → important in allergic responses
more involved in inflammatory responses
Releases enzymes that are vasoactive, bronchoconstrictive, and chemotactic
basophil morphology
segmented nucleus, no nucleolus, many dark purple granules, more cytoplasm - stained purple
monocytes
Primary role is host defense, which is fulfilled in tissues as macrophages
Produced in BM from progenitor cell (CFU-GM)
Monocytes and macrophages
Activated by
•T lymphocytes
•endotoxin
Monocyte Maturation
Monoblasts cannot be differentiated from the myeloblast in normal B M
Stages:
Monoblast
Promonocyte
Monocyte
Macrophage
monoblast
nucleus ovoid or round or slightly indented, pale purple blue, finely dispersed lacy chromatin, nucleoli, cytoplasm abundant blue and gray, sometimes see vacuoles
promonocyte
first morphologically recognizable cell, nucleus irregular and indented, fine chromatin network, coarser than monoblast, many nucleoli, cytoplasm blue gray
monocyte cell morphology
nucleus bean or horshoe shaped, numerous folds, chromatin loose and linear, cytoplasm blue gray, vacuoles frequently seen
macrophage
Monocyte leaves PB and enters tissues
Matures into macrophage
nucleus is round with reticular appearance, cytoplasm blue gray, irregular shape, many vacuoles
what tissues do macrophages live in?
are widely distributed in the body, specific name depending on their anatomic location
liver ?
lungs = alveolar macrophage
skin - langerhans cell
brain- microglia
Monocyte Function
Active in innate and adaptive immunity
Ingest and kill microorganisms
Inhibit the growth of intracellular microorganisms
Requires activation by T cells via cytokines
Killing is nonspecific
Can also be activated by endotoxins or opsonins
they are also important scavengers, remove toxic substances from blood,
what do macrophages phagocytize?
microorganisms
dead /dying cells
cells tagged with antigen - opsonized
particulate matter - foreign
cellular debris
denatured proteins
antigen-antibody complexes
clotting factors
what is the significance of macrophages being antigen presenting?
Initiate and regulate the adaptive immune response
Produce cytokines
Stimulate proliferation and differentiation of lymphocytes
granulocytes
Neutrophils
Most abundant bacterial defense
Eosinophils
Allergy, parasitic infections
Basophils
Histamine release, inflammation
agranulocytes
•Mononuclear cells
•Monocytes
•Differentiate into macrophages
•Lymphocytes
•B cells
•T cells
•NK cells