GCSE Computer Science - paper 1
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
processes data and instructions by following the:
FETCH- DECODE- EXECUTE cycle
Control Unit (CU)
¬ executes program instructions by following FDE cycle
- controls data flow inside CPU to registers and outside CPU
- Overall control of CPU
Program Counter (PC)
holds memory address of the instruction for each cycle
cache
¬ very fast memory but slower than registers.
- Stores regularly used data to access quickly.
- low capacity but expensive
- different levels (l1 quickest but lowest capacity)
von neuman architecture
data and instructions stored together in memory
Memory Address Register (MAR)
holds the memory address about to be used by the CPU, which can point to specific data or CPU instructions
Memory Data Register (MDR)
holds the data or instructions fetched from memory or waiting to be written to memory
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
¬ carries out calculations and logical operations.
- contains accumulator which is used to store intermediate results and calculations
clock speed
¬ the speed which instructions are executed in cycles per second.
- measured in hertz
- 500MHz = 500 mill instructions
- 3GHz = 3 bill instructions
embeded systems
computers built into a larger system that perform specific tasks with one circuit board
accumulator
intermediate results of logic and arethmetic results are stored
core
¬ process data independantly
- more cores = instructions processed faster
Random Access Memory (RAM)
¬ main memory
- volatile (loses data when off)
- more RAM = better performance
- stores: applications, GUI, OS
Read Only Memory (ROM)
¬ CPU reads instructions from ROM
- non-volatile (keeps data when off)
- smaller capacity
- stores: BIOS
Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM)
used as main memory
Static Random Access Memory (SRAM)
¬ used for cache memory
- small capacity
- fast access
virtual memory
¬ memory temporarily created on storage drive
- used when RAM is full
Fetch-Decode-Execute cycle (fetch)
1# copy memory address from PC to MAR
2# copy instructions stored in MAR to MDR
3# increment PC to point to address for next instruction
Fetch-Decode-Execute cycle (decode)
4# instruction in MDR decoded by CPU
Fetch-Decode-Execute cycle (execute)
5#instruction performed
# load data, calculations, logic operations, hault program
flash memory
¬ programmed electronically
- non- volatile
- used in: SD cards, USB sticks...
- fast
- portable
- no moving parts
- more expensive
- capacity smaller than HDD
primary storage
¬ memory areas where CPU can access quickly
- fastest read / write speeds
- mostly volatile
- registers
- cache
- ROM
- RAM
secondary storage
¬ where data is stored when not in use
- non- volatile
- (HDD, SSD)
- read / write speeds much slower than primary storage
tertiary storage
¬ used for archives and back ups for large amounts of data
- non- volatile
- stores data long term
magnetic storage
- demagnetised (0)
- magnetised (1)
- moving parts to read / write disk
- LARGE capacity (3TB)
- low cost
- fast read / write time
- not very portable
- can be damaged (heat, magnetic field)
- generally reliable
Solid State Drive (SSD)
¬ used for internal storage
- no moving parts
- use flash memory
- back up and transport data
- much faster read/ write times than HDD
- up to 500GB
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
¬ traditional internal storage for laptops / PCs
- made from stack of magnetised metal disks
- data stored magnetically in sectors within circular tracks
- heads on arms access sectors on disk
- portable HDDs back up and transport large data amounts
- long lasting (reliable)
- can be damaged by dropping
HDD advantages
# cheaper
# higher capacity
# longer read / write life
SSD advantages
# faster
# don't need defragmentation
# more shock- proof
# don't make any noise
optical discs
¬ data is held on a reflective disk
- laser beam shined on disk
- reflect (0)
- doesn't reflect (1)
- CD = 700MB
- DVD = 4.7GB
- Blu-Ray = 25GB
- CD-ROM = read- only
- CD-R = write- once
- CD-RW = rewritable
- cheap per GB
- portable
- robust (can easily be scratched though)
- slow transfer speed compare to SSD
Operating System (OS)
¬ runs and maintains a computer system
- provides a UI (GUI)
- command line interface is text based, specific commands and knowledge needed to understand
- can run multiple tasks
- handles files and disk management (defrag)
- allow single-user or multi-user (i.e windows 10 = 1, bank ATMs = multiple)
defragmentation
¬ reorganises data on HD by putting fragmented files together
- if files are all together, read / write times much quicker and easier to find
full back up
¬ copy of every file on system
- use lots of storage space
- faster to restore from
- slow process
incremental back up
¬ files created / edited from last back up are copied
- less storage space
- much quicker to create
- full system restore slow
compression software
¬ reduces file size for less disk space used
- need to be extracted before use
encryption software
¬ scrambles data
- stop third parties from accessing
- data decrypted using special key
open source software
- python,
✔ source code provided with software
✔ usually free download
✔ able to edit and distribute changes
✔ social support forums
✔ good for companies with small budgets
-----------------------------------------------
✘ expert needed for debugging
✘ may need additiona support bought
✘ open to malicious code
✘ may take a while to fix
✘ no warranties
propietary software
- windows word
✔ free customer support
✔ professional standards
✔ tailored to market needs
✔ issues more likely to fix quicker
✔ may contain more features
--------------------------------------
✘ expensive
✘ rely on one company
✘ not personalised to customers
✘ may be limited updates
network
two or more computers connected together to share information and resources
Local Area Network (LAN)
¬ covers small geographic area
- hardware owned by organisation who use it
- can share resources
- centralised management
- network manager needed
- security issues
- used in schools and homes
Wide Area Network (WAN)
¬ covers large geographical areas
- cables owned by others (BT, Vodafone...)
- connects LANs
- may be town, internet, different countries
cloud storage
¬ stores files and programs online
- infro can be shared
- may need to pay but unlimited
- speed depends on network
- only work on internet
- backup handled by provider (google, dropbox...)
- easier to hack
- google drive, dropbox...
bandwidth
amount of data transferred in a given time
network traffic
badwidth shared so slows network
latency
time delay between sending and receiving
what affects wireless network performance
# distance from Wireless Access Point (WAP
# physical objects (walls)
# interference from other devices
# weather
Wireless Access Point (WAP)
allows devices to connect to WAN using WiFi
router
connects two networks together (LAN and WAN) transmits data between them (packets)
Network Interface Card (NIC)
used to connect device to network by gaining MAC address
ethernet
twisted pair to reduced interference
fibre optic
data transmitted as light , fast but expensive. Longer distance = less interference
switch
connects to devices by getting MAC address to send data to correct device using internal index, reducing data collisions
coaxial cable
single copper wire covered in plastic for insulation with metal mesh to stop interference. Connect tv for freeview
hotspot
location to connect to WAP
WiFi
¬ standard use for wireless networks
- two radio frequencies (2.4GHz / 5GHz)
- split into bands covering small frequency range
- affected by interference from networks using close channels
client server
¬ network managed by a server
- files stored centrally
- stores user profiles, passwords, and access information
----------------------------------------------------
1# clients send request to server
2# processes request and responds
peer to peer
¬ all devices equal
- devices connect directly to each other
- used at home to share files between devices or connect to printer
client server (advantages and disadvantages)
✔ easy to manage network security
✔ easier to track files (central)
✔ servers reliable and always on
✔ easy to update software
---------------------------------------------------
✘ need it specialist to maintain
✘ expensive to set up
✘ may become overloaded if too many clients accessing at once
✘ dependant on server (if server down, clients lose access to work)
peer to peer (advantages and disadvantages)
✔ easy to maintain
✔ not deoendant on server
-------------------------------------------------
✘ no central management
✘ file copies between devices = duplicates
✘ easy to lost track of what stored and which files up to date
✘ if one machine fail = data lost
✘ machines slow if other devices access
internet
worldwide collection of interconnected networks
Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
an address used to access web servers and resources
Domain Name Server (DNS)
a server that stores website domain names and IP addresses (like an address book for them)
domain name
the name of the website (google / youtube...)
hosting
register a unique domain name and pay to place content on webserver
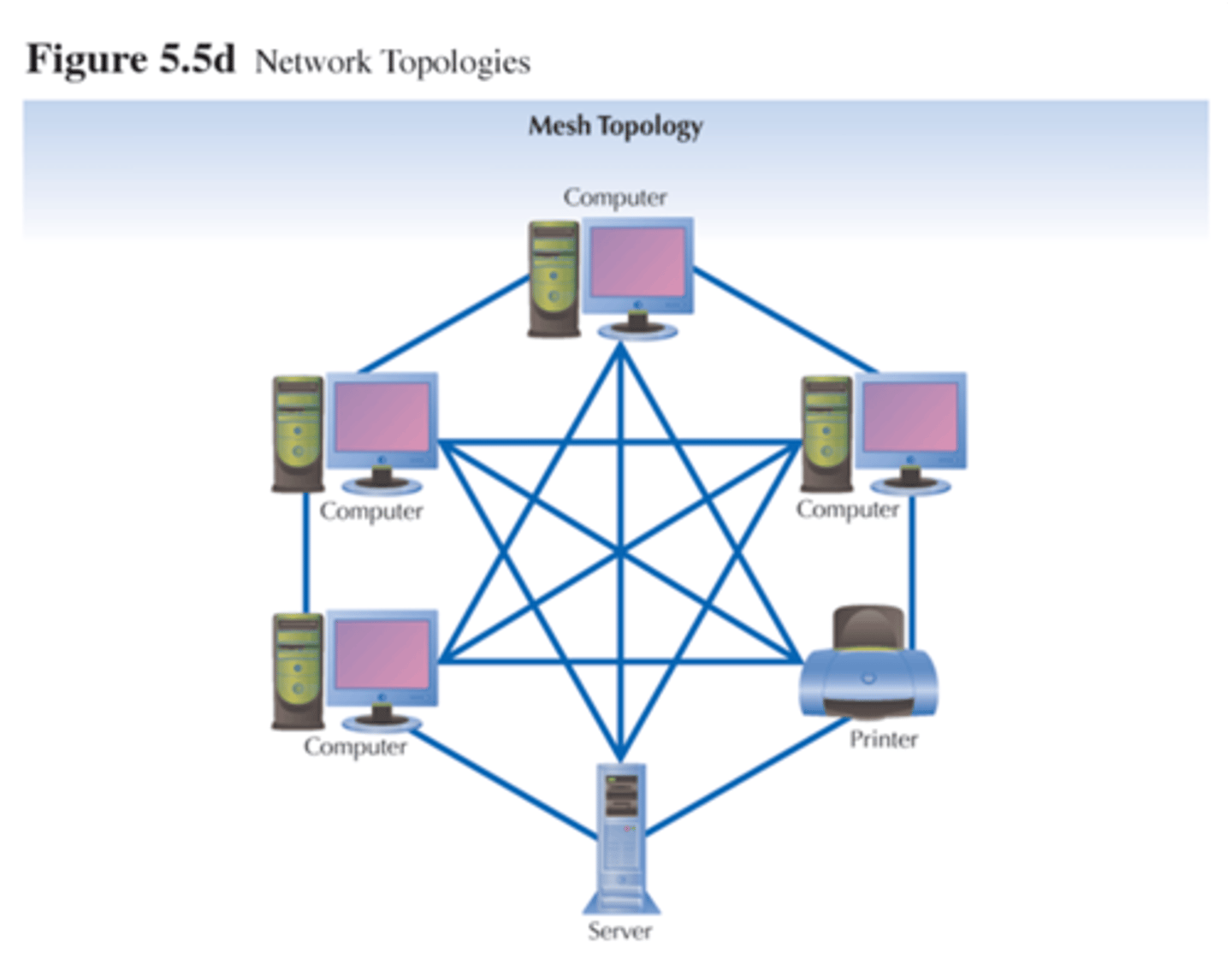
mesh network
¬ devices connected directly to each other
- send data along fastest route
- expensive, lots of cables needed
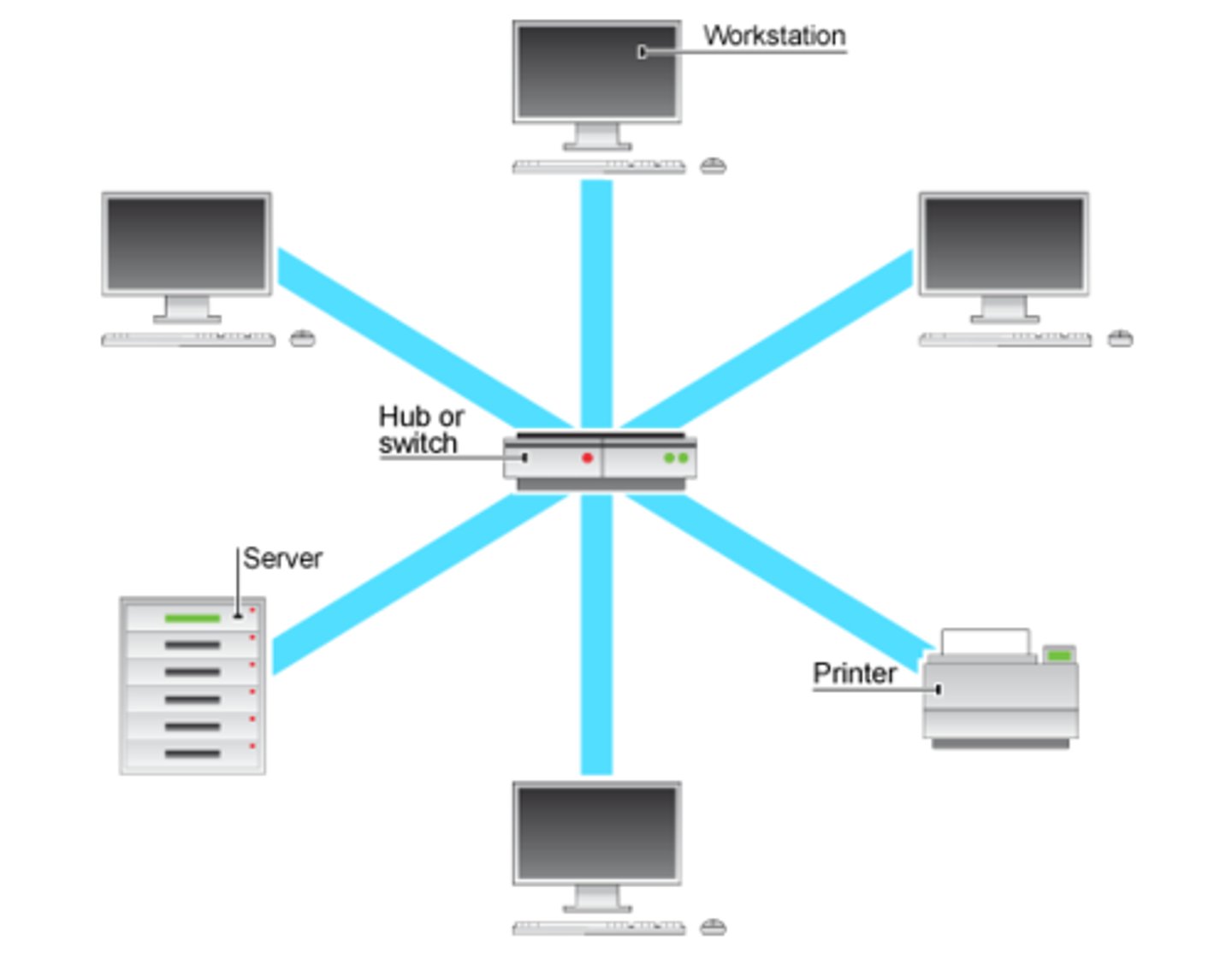
star network
¬ connected to central switch or server
- device / cable failure doesn't affect rest of network
- easy to add more devices
- better performance
- problem with server affects whole network
- every device needs cable to server
virtual network
¬ software based network
- can exist on same physical network
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) sends data securly over large network (internet)
- has own security (specific login details, firewall)
the cloud
✔ users can access files from any connected device
✔ easily increase storage capacity
✔ no expensive hardware
✔ IT staff not needed
✔ provides security and backups
✔ updated automatically
---------------------------------------------------
✘ need internet connection
✘ dependant on host for security and backups
✘ data vulnerable to hackers
✘ unclear ownership
✘ subscription fees may be expensive
protocol
set of rules how devices communicate and how data is transmitted across a network from start to end and how it should be organised
MAC address
a unique identifier assigned to a device that can't be changed.
- 64 bit binary number
- converted into hexadecimal
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
# how devices connect on network
# checks data sent and delivered correctly
# splits data into packets
Internet Protocol (IP)
#responsible for packet switching
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
# sends emails
# transfer emails between server
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
# communicate with web servers
# used by web browsers to access websites
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS)
# secure version of HTTP
# encrypts all information sent and received
Post Office Protocol (POP3)
# retrieves emails
# server holds email until downloaded then is deleted
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
# access, edit and move files
Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
# access emails from server
# copy stays on server until you delete
Layer 1 (Data Link Layer)
# ethernet protocol
- how bits are sent as electrical signal over cables
- passes data over physical network
Layer 2 (Network Layer)
# IP protocol
- used by router
- makes connections between networks
- directs data packets and traffic handling
Layer 3 (Transport Layer)
# TCP protocol
- splitting data into packets
- controlling data flow
- check packets are sent and delivered correctly
Layer 4 (Application Layer)
# HTTP, FTP, SMTP protocols
- turning data into websites and other applications
Packet switching
1# sending device splits data in packets to send across network, each with packet number to show order of data
2# router reads packet header and decides where to direct packet according to IP rules
3# network traffic affects packet path so different routes taken, if too many sent router prioritises
4# packets arrive in wrong order from different journeys, receiving device puts in right order with packet number
5# receiving device checks all packets received, if no then time out message sent
6# receipt sent to sending device if all date there
SQL injection
malicious code inserted into database field on website to corrupt or steal data
phishing
emails or texts from well known companies with links designed to steal money and details
malware
deletes files, lock files, moniter actions, alter permissions, open backdoors
viruses
installed without user knowledge and will replicate
worms
like viruses but self replicate and spread quickly. find weakness in network security
trojans
desguised as software and users install without realising purpose
passive attack
someone moniters data travelling on a network and intercepts sensitive information using packet sniffers
active attack
an attack to a network using malware
insider attack
someone within an organisation exploits their network access to steal information
brute force attack
try to guess passwords and usernames by trial and error by using software to produce likely passwords
denial of service attack (DOS)
a hacker tries to stop users accessing part of a network or website by flooding a network with useless traffic and making it slow and inaccessable
social engeneering
# phishing, over phone
influencing people to give over sensitive information by pretending to be companies over phone
network policy
a set of rules and procedures the organisation follows to ensure their network is safe from attacks and unauthorised access
penetration testing
specialists stimulate potential attacks on their network to identify possible weaknesses
network forensics
investigations to find cause of attacks by having a system of capturing data packets as they enter a network
passwords
prevent unauthorised access by using many characters and a combination of letters numbers and symbols and changing regularly
user access level
which part of the network different groups of people can access, business managers likely to have high access level to access more sensitive data to help prevent insider attacks