Human Kinship
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Kinship
Kinship is the web of social relationships formed among individuals who are related by descent, marriage, or shared social and economic interests
Human kinship is biologically based, but it is also culturally constructed, because:
Kinship categories reflect not only biological relationships, but also relationship formed via marriage, shared interests, co-residence, fictive relations, etc
Ex.) who are uncles and aunts?
Societies differ in how they classify their relatives into various kinds
Ex.)
English: brothers and sisters
Chinese:兄 (older brother); 弟 (younger
brother); 姐(older sister); 妹(younger sister)
Types of kin groups
family
descend groups
fictive kin
Family
A family is a group of people affiliated by blood, marriage, co-residence, or shared consumption
Types of family
nuclear family
extended family
matrifocal family
avuncular family
The nuclear family
A nuclear family consists of a married couple with their unmarried children, normally living together in the same household
The nuclear family in the industrial societies
the most common kin group and a cultural preference
this type of family is closely related to social mobility caused by industrialism
Neolocality: living situation in which married couples establish a new place of residence
The nuclear family in foraging societies
For foragers with a highly mobile life, the nuclear family is the most significant and stable kin group (one may shift one’s band membership)
Extended families
An extended family usually consists of a group of related nuclear families and includes three or more generations of family members
Extended families often function as an economic strategy. Higher proportion of extended family are often found among
Pre-industrial or non-industrial societies
Ethnic groups or low-income populations of
industrial societies
Matrifocal family
Family group consisting of a mother and her children, with a male only loosely attached or not present at all.
Avuncular families
A household headed by a senior woman, her children, and her brother(s).
Ex.)
Nayars of Malabar Coast of India
Mosuo people in southwest China
Factors that have caused the different types of famlies amogn human populations:
different social and economic contexts
cultural and emotional preferences
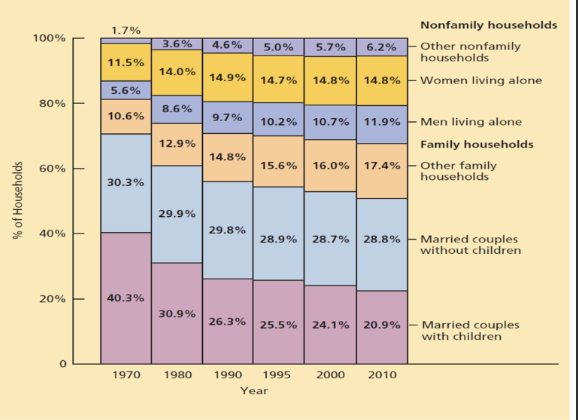
Understanding changes—USA
Nuclear families account for only 21% of American households in 2010
Declining importance of kinship and narrower kin attachments (especially among the middle class) in recent decades
Diverse forms in recent decades:
single-parent families
heterosexual couples raising adopted children
gay couples raising children
birth mothers vs adoptive mothers; sperm dads vs adoptive father
Will the new forms change our conception of family?
Descent groups
A kin group whose members believe themselves to be descended from a common ancestor
Types of descent groups
unlineal descent groups
lineage
patrilineal
matrilineal
clan
Non-unilineal
Ambilineal descent groups
Unilineal descent groups
A group of relatives/families, who traces their genealogical links through only one sex (male of female)
Lineage: unilineal group whose members can actually trace how they are related (demonstrated descent)
Clan: unilineal group whose members may not always be able to trace how they are related, but who still believe themselves to be kinfolk (stipulated descent)
Lineage
unilineal group whose members can actually
trace how they are related (demonstrated descent)patrilineal
matrilineal
Clan
unilineal group whose members may not always be able to trace how they are related, but who still believe themselves to be kinfolk (stipulated descent)
Patrilineal lineage
individuals trace their genealogical links and kinship relationship through their fathers
Matrilineal lineage
individuals trace their genealogical links and kinship relationship through their mothers
Ambilineal descent groups (non-unilineal)
descent groups with flexible descent rule
Individuals can make choices about whom to live with, whose land to use, and so forth.
Fictive kin
Kinship relations based on neither blood nor marriage ties, but on a variety of forms of familiarity such as shared residence, shared economic ties, nurture relationship, etc
Fictive kin relations exist in both the family and descent
groups; they are not an independent, separate category