hydrocarbons
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
what are the properties of alkanes?
saturated hydrocarbons
insoluble in water
generally unreactive
why does the boiling point of alkanes increase as the length of the chain increases?
longer chain alkanes have more electrons than shorter chain alkanes which increases the strength of the london forces
longer chain alkanes have a greater surface area so there are more points along the chains where london forces can be formed
why do branched alkanes have a lower boiling point than straight chain alkanes?
the branches prevent alkane molecules from getting closer together - and london forces are strongest over short distances
what is the cracking of alkanes?
converts long chain hydrocarbons into short chain hydrocarbons and produces alkenes which are highly reactive material
how is thermal cracking carried out?
requires a high temperature and high pressure
450-900^celcius
70 atm
makes short chain alkanes, alkenes and water
what is a free radical?
a species with an unpaired pair of electrons
how is thermal cracking carried out?
450^celcius
1-2 atm
aluminium oxide catalyst
products are often branched chain alkanes - useful for petrol as they combust efficiently
also produces cyclic alkanes and aromatic compounds
describe the process of free radical substitution of alkanes
step 1: initiation
Cl2 (UV)→(heat) 2Cl*
step 2: propagation
Cl* + C2H6 → *C2H5 + HCl
C2H5 + Cl2 → C2H5Cl + Cl*
step 3: termination step
Cl* + Cl* → Cl2
C2H5 + Cl* → C2H5Cl
*C2H5 + *C2H5 → C4H10
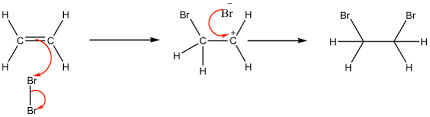
outline the mechanism for the electrophilic addition of alkenes (ethene and hydrogen bromide)
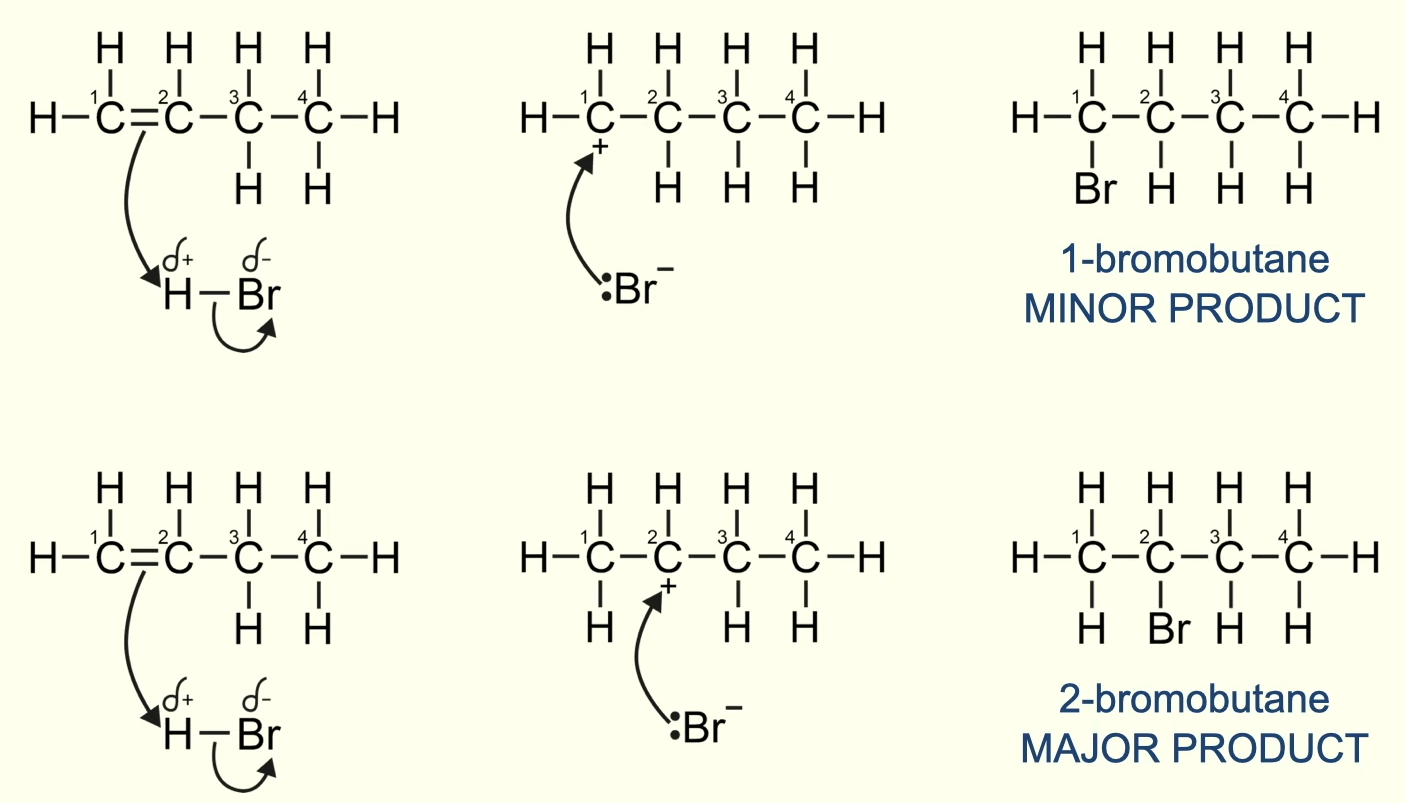
why is 1-bromobutane the minor product and 2-bromobutane the major product?
the carbocation intermediate is an unstable molecule
carbon two is more stable as it forms a secondary carbocation (bonded to two alkyl groups) and exists for a longer period of time
how to test for an unsaturated molecule?
mix with bromine water and shake - if unsaturated molecule is present bromine will add across the double bond and the solution will go from orange to colourless