Lecture #11 | Identification of Cellular Oncogenes: Src
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
c-Src function
Links extracellular cues to intracellular signaling pathways
able to activate downstream signaling pathways
required for a normal cells activity but modulations can lead to the transformed phenotype
Protein structure of c-Src
Member of a family of tyrosine kinase
Has two conserved, non catalytic domains that mediate protein-protein interactions
SH3: recognizes Pro-X-X-Pro
SH2: Binds P-Tyr
SH1: has a catalytic cite
Not found in just Src proteins, but first identified
Myrsitic functional group that tells kinase to attach to inner plasma membrane
Tyr at 527 position
Difference between v-Src gene and c-Src structure
v-Src gene lacks the C-terminal domain of c-Src, which contains Tyr at 527 position
SH2 domain
Binds phospho-tyrosine (yellow dots)
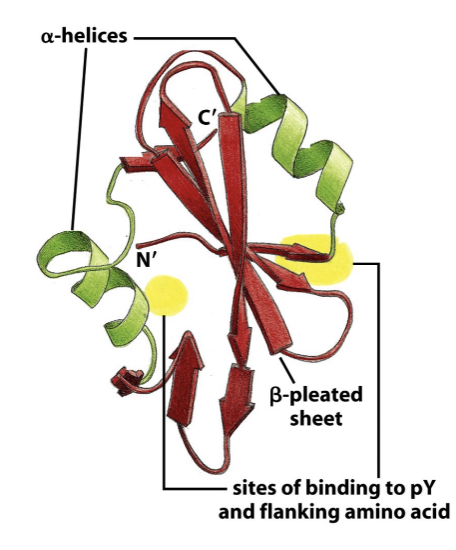
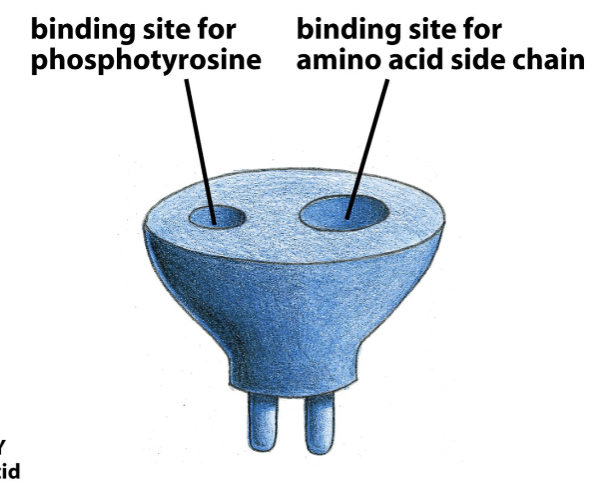
Why is v-Src more oncogenic that c-Src
C-terminal domain has a Tyr that is phosphorylated
v-Src lacks phosphorylated Tyr
Phosphorylation of Tyr acts as an inhibitor signal (negative regulator)
Inactive conformation of c-Src
SH2 domain binds to phosphorylated Tyr 527 in C-terminus
proline linker region binds Sh3 domain, causes a folding in
Tyr at active site is hidden
SRC cant phosphorylate substrates → cannot act as a kinase, folding makes inactive protein
How is c-src activated?
De-phosphorylation of Y527.
Other P-Y binding to the SH2 domain.
Other Pro-X-X-Pro peptide binding to the SH3 domain.
Auto-phosphorylation of Y416 in the activation loop.
Phosphorylation of Y416 relieves a steric barrier and allows the kinase to adopt a fully active form.
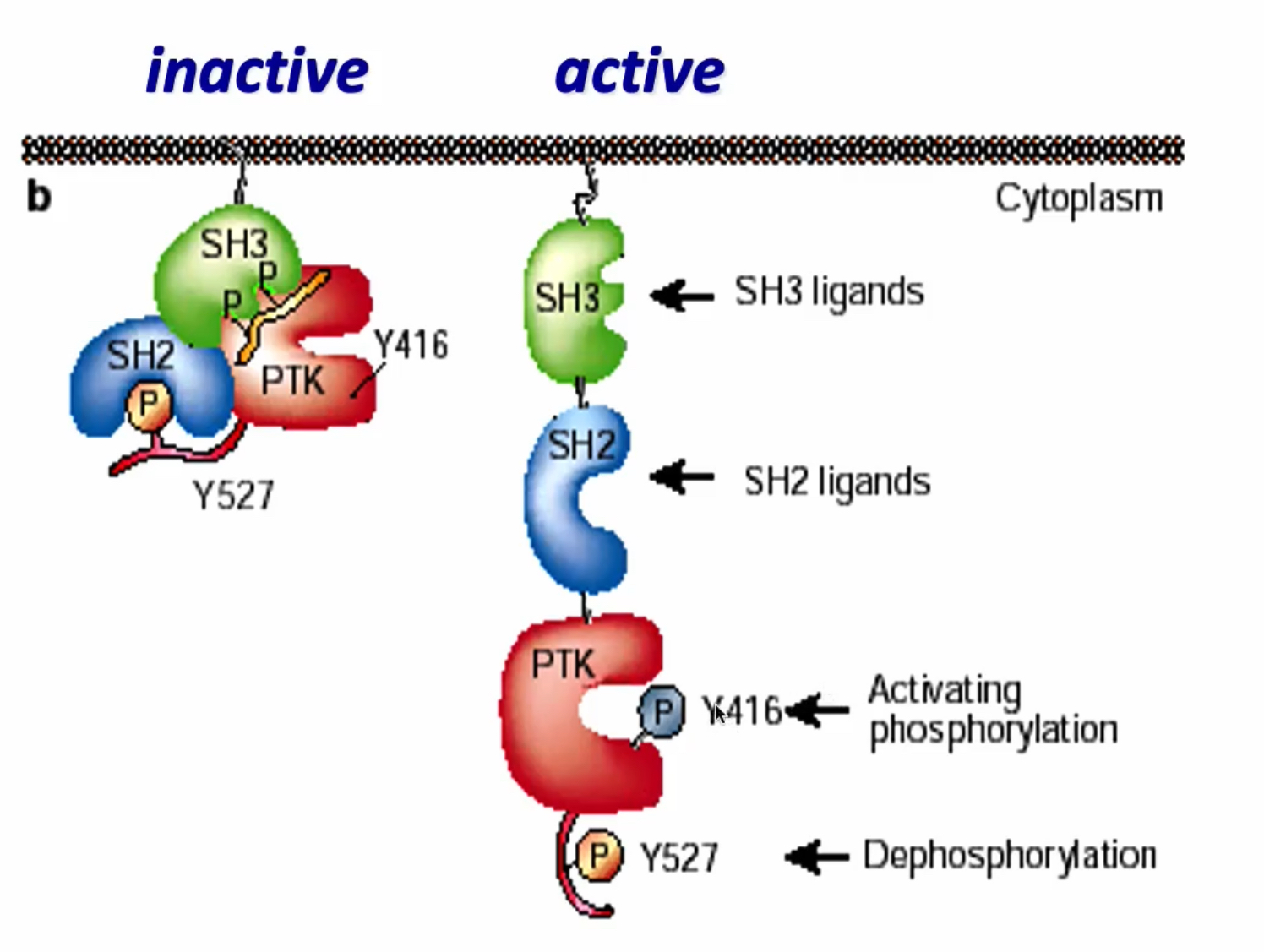
What happens if there is no Y527 like in v-Src?
No able to be inhibited, cannot be shut off and will always be regulating gene transcription
keeps in creasing number of cells present
In addition to removing C-terminus, how else is c-Src activated?
Mutated Tyr 527 is actually a Phenylalanine
lose of hydroxyl group that looses the cite of the phosphorylation
so deletion of c-terminus or mutation of Tyr 527 can convert proton-oncogene to oncogene
Key Principle of Signal Transduction (ST) Pathways
Nearly all kinases are actively regulated.
They often have autoregulatory regions that are part of the same polypeptide or associated with other inhibitory proteins.
GF receptors
Growth factors bind to growth factor (GF) receptors and initiate the ST pathway, resulting in :
activation of immediate early genes
delayed early genes
What happens when growth factors bind to growth factor receptors?
GF receptors dimerize and autophosphorylate
Proteins with SH2 domains phosphorylated growth factor receptors
two together helps magnify and stabilize the response
c-Src under normal conditions
activated by membrane-bound receptors in response to growth factors and other signals, including tyrosine and non-tyrosine kinase receptors.
Src binds via SH2 domains to P-Tyr on the receptor, disrupting the intramolecular inhibition (SH2–Tyr527 binding).
Targets of Src
Proteins involved in signal transduction, cell cycle control, and cellular proliferation (e.g., IRS1, JAK, CDK1).
Proteins involved in cell morphology and adhesion (e.g., cortactin).
Transcription factors (e.g., estrogen and androgen receptor).
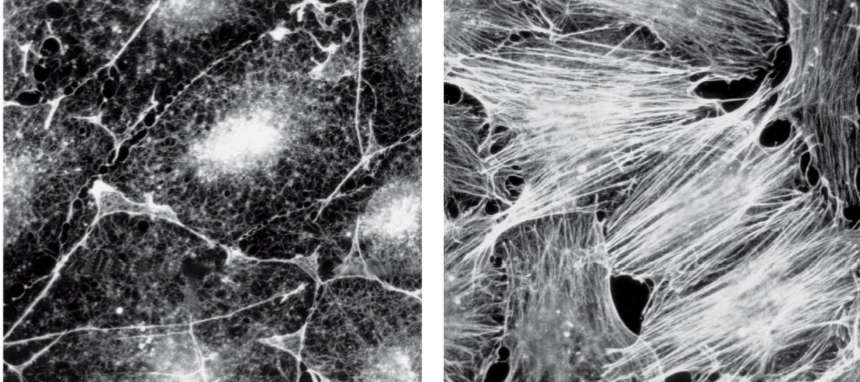
Ex: how cell morphology is altered by growth factors in the serum via c-Src
Cell morphology is altered by growth factors in the serum via c-Src.
Cortactin, an actin-binding protein, is a Src substrate; phosphorylation by Src promotes actin polymerization.
What happened in the 1980s with human tumors?
Oncogenes were identified directly from human tumors using transfections (introducing foreign DNA into mammalian cells).
NIH3T3 transformation/Foci assay
Method of identifying cellular oncogenes by introducing DNA from human tumors into normal mouse cells
integration of tumor into mouse fibroblast
Can create a library of viruses expressing DNA and see protein interactions