Unit 1 AP Precalculus
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
When Graph Concaves Up
AROC is Increasing
When Graph Concaves Down
AROC is Decreasing
Positive ROC (Rate of Change)
When both quantities on the x and y axis increase
Negative ROC (Rate of Change)
When y-value increases and x-value decreases
Even Function
Symmetric over the line x = 0 and satisfies the property f(-x) = f(x)
Odd Function
Symmetric over the point (0, 0) and satisfies the property f(-x) = -f(x)
AROC
Y2-Y1 / X2-X1
Rate of Change Positive
Graph is Increasing
Rate of Change Negative
Graph is Decreasing
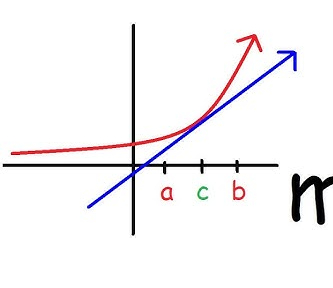
IROC
Find Tangent Line and Do f(b) - f(a) / b - a
Change in AROC for Linear Functions
0
Change in AROC of Quadratic Functions
Constant
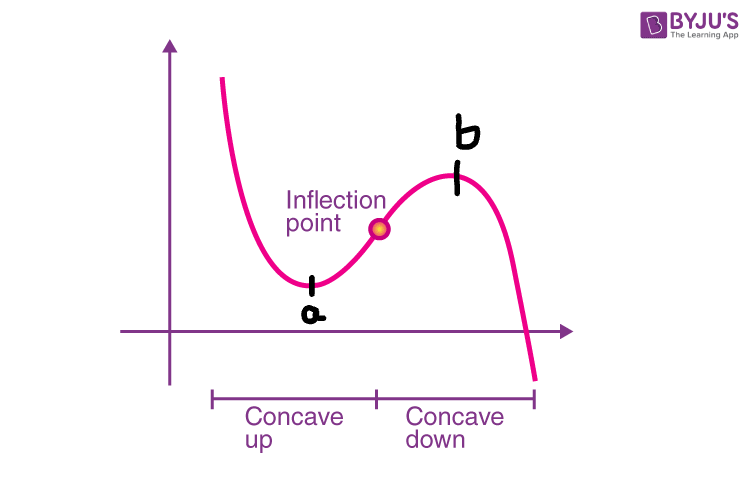
POI (Point of Inflection)
X = b - a | Y = f(b) - f(a)
Odd Multiplicity
Cross the X-axis
Even Multiplicity
Touch/Bounce Off the X-axis
If (a + √b) is a Zero, then
(a - √b) is a Zero
If (a + bi) is a Zero, then
(a - bi) is a Zero
Relative / Local Extrema
Y-values on graph change from increasing to decreasing or vise versa. OR and endpoint when the domain is restricted.
Absolute / Global Extrema
The highest / lowest local extrema so long as the graph does not continue forever.