Porous materials continued/macroporous
5.0(1)Studied by 15 people
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:36 PM on 12/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
what are the self-assembly pathways of Mesostructured Phases
Mesostructured Phases, Mediated electrostatic pathway, Hydrogen bonding
2
New cards
what are the Interactions between the surfactant and inorganic framework

3
New cards
what does the thermal stability of mesostructured metal-oxide phases depend on
the degree of charge-matching at the organic-inorganic interface, the strength of interactions between inorganic species and surfactant head-groups, the flexibility of the M-O-M bond angles in the constituent metal oxides, the Tammann temperature of the metal oxide, and the occurrence of redox reactions in the metal-oxide wall.
4
New cards
what does charge matching depends on.
electrokinetic behavior
5
New cards
Why might harsh conditions be needed for surfactant removal, and why is the potentially bad.
The presence of strong covalent bonds between metal-oxide species and surfactant head-groups (metal-N) means that harsh conditions (combustion) are needed to remove the surfactant, which can lead to the collapse of the mesostructure
6
New cards
For inorganic-organic interactions, what type of interaction is preferred.
Hydrogen Bonding preferred over electrostatic interactions
7
New cards
What may result in the formation of only lamellar or dense metal-oxide phases.
Rigid M-O-M bond angles that are unable to accommodate the curvature of the
inorganic-organic interface
inorganic-organic interface
8
New cards
how is Tamman temperature defined
0.5-0.52Tm
Tm is the melting point in Kelvin
Tm is the melting point in Kelvin
9
New cards
what happens at the Tamman temperature
The mobility of metal ions or atoms in a crystalline metal oxide increases rapidly
10
New cards
how may redox reactions cause the structural collapse of the mesophases
with redox reactions occurring in the metal-oxide wall during surfactant removal or catalytic reaction
11
New cards
What reaction does VPO catalyize
Industrial n-butane oxidation to maleic
anhydride
anhydride
12
New cards
what is the definition of a macroporous material
pores above 50 nm
13
New cards
draw how are macroporous materials made.
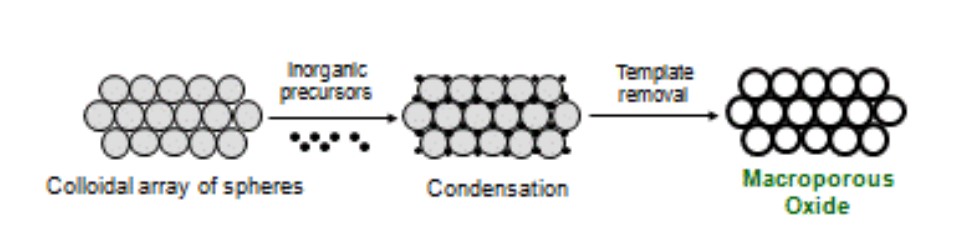
14
New cards
what are the different types of macroporous wall structures
amorphous, functionalized, zeolite, crystalline, mesoporous, and active catalytic species.
15
New cards
draw the sol-gel approach for 3D macroporous oxides
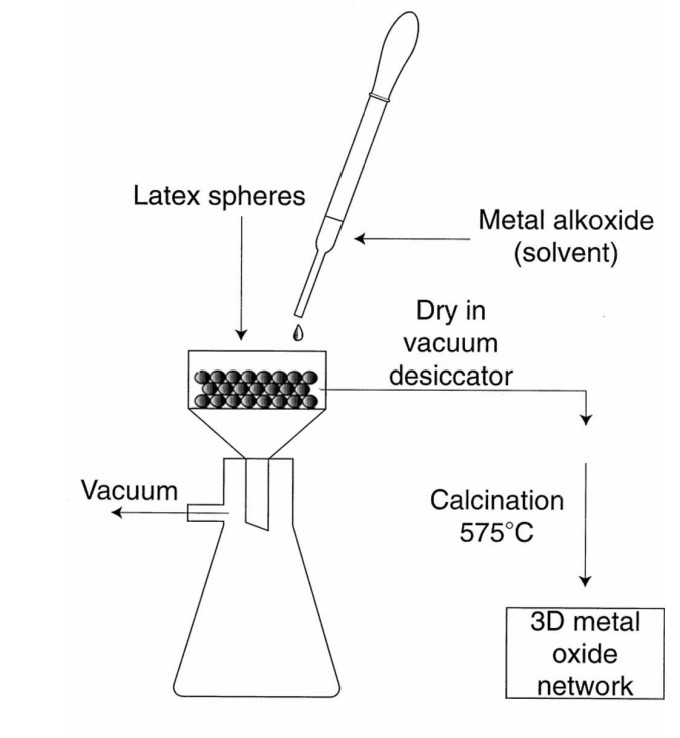
16
New cards
How are macroporous polymers made
spherical silica particles -> Colloidal crystal of silica particles after pressing and heating -> divinylbenzene -> Ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate
17
New cards
draw how are macroporous polymers made

18
New cards
what is the salt precipitation method.
a colloidal crystal is soaked in a metal salt solution, which remains in the void space after filtration. This composite is soaked in an oxalic acid solution to convert the salt into a more thermally stable oxalate. Carbon is removed by calcination, leaving a 3DOM framework
19
New cards
what are some other methods to make macroporous materials
chemical vapor deposition, nanocrystal deposition, oxide reduction method, electrodeposition, spraying techniques
20
New cards
What are the reasons for choosing monodispersed colloidal spheres as templates
Theoretical treatments of heterogeneous systems frequently utilize the spherical symmetry
Most theoretical models that deal with the properties of colloidal particles and the interactions between them are usually based on the spherical shape
The sphere represents the simplest form that a colloidal particle can easily adopt during the nucleation or growth process, as driven by minimization of interfacial energy.
For macroporous synthesis, homogeneous monodispersed spheres are ideal templates to prepare interconnected pore structures.
Most theoretical models that deal with the properties of colloidal particles and the interactions between them are usually based on the spherical shape
The sphere represents the simplest form that a colloidal particle can easily adopt during the nucleation or growth process, as driven by minimization of interfacial energy.
For macroporous synthesis, homogeneous monodispersed spheres are ideal templates to prepare interconnected pore structures.
21
New cards
What does the Stover process involve
the hydrolysis and polycondensation of TEOS under alkaline conditions in ethanol.
22
New cards
What happens when aqueous sodium silicate solution is added to ethanol (in the Stober process)
Particle formation takes place
instantaneously
instantaneously
23
New cards
What is responsible for the rapid nucleation and growth of the spherical silica particles in the Stober Process
The silica concentration over silica solubility ratio (supersaturation)
24
New cards
draw an overview of the Stober silica micron spheres
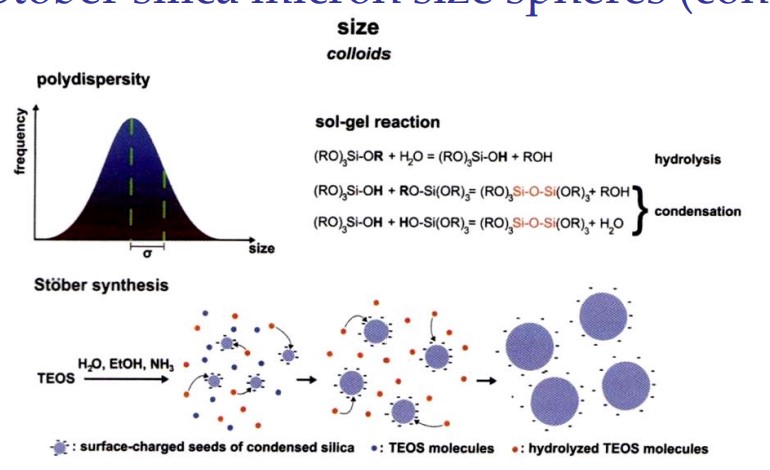
25
New cards
What are the ingredients for an emulsion polymerization to produce monodispersed spheres
a water-soluble initiator, an emulsifier, and a monomer that is only slightly soluble in water.
26
New cards
What are the phases in the emulsion system
aqueous phase
monomer droplets
micelles
monomer droplets
micelles
27
New cards
What are the events of the monomer molecule
The monomer is added to the water, and most of it goes into droplets of monomer because of the low water solubility. The monomer eventually leaves the droplet and goes into the media. The monomer diffuses into the micelle. The monomer becomes part of the polymer.
28
New cards
draw an experimental procedure to assemble colloidal particles
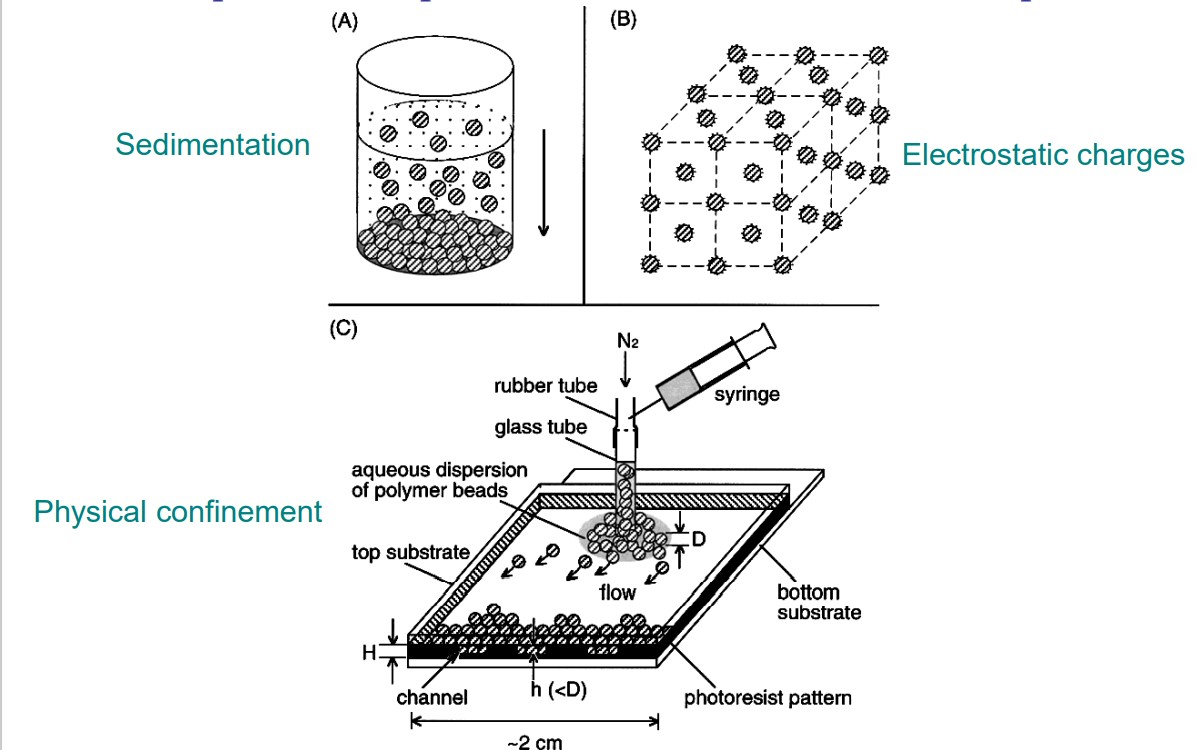
29
New cards
what are the potential applications for ordered macroporous films and membranes
heterogeneous catalysis, bioseparations, as well as membrane supports for the separation of diverse molecules.
30
New cards
what makes macroporous structures highly attractive for a variety of separation and catalytic applications involving large molecules.
high surface area (up to few hundreds m2
/g) and unimodal large pores
/g) and unimodal large pores
31
New cards
what are the steps for the macro-scale templating approach
The interstitial voids of the monodisperse sphere arrays are filled with precursors of various classes of materials, such as ceramics,
semiconductors, metals, monomers, etc.
In the second step, the precursors condense and form a solid framework around the
spheres
Finally, the spheres are removed by either calcination or solvent
extraction.
semiconductors, metals, monomers, etc.
In the second step, the precursors condense and form a solid framework around the
spheres
Finally, the spheres are removed by either calcination or solvent
extraction.
32
New cards
what mainly determines the success of forming macroporous ordered structures
van der Waals interactions,
Wetting of the template surface,
filling of the voids between the spheres,
volume shrinkage of the precursors during the solidification process.
Wetting of the template surface,
filling of the voids between the spheres,
volume shrinkage of the precursors during the solidification process.
33
New cards
how is the wall thickness of macroporous structures controlled
the hydrolysis/condensation rates of the inorganic precursors,
the packing of the PS spheres,
forming core-shell structures at the sphere surface (i.e. deposition of polyelectrolyte multilayers at the sphere surface)
the packing of the PS spheres,
forming core-shell structures at the sphere surface (i.e. deposition of polyelectrolyte multilayers at the sphere surface)
34
New cards
Si-W clusters on Macroporous SiO2 were used to do what
Epoxidation of cyclooctene to epoxide
35
New cards
how were the Si-W clusters dispersed throughout the walls of the 3DOM material
they were intact and nearly molecularly dispersed
36
New cards
How were the catalytic activities of supported and unsupported cobalt-substituted POM clusters tested
by studying the conversion of cyclohexene-to-cyclohexene oxide in the presence of isobutyraldehyde