A&P: Anatomical Organization
1/69
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Anatomy
Study of the structure of body parts and their relationship to one another.
Physiology
Study of the function of the body’s machinery; requires understanding of anatomy.
Gross Anatomy
Study of body structures visible to the naked eye, approached systematically or regionally.
Microscopic Anatomy
Study of body structures using a microscope, including cytology and histology.
Cytology
Examination of the structural features of cells.
Histology
Examination of tissues.
Developmental Anatomy
Study of structural changes from conception to adulthood, including embryology.
Physiology
Study of the function of the body’s machinery.
Six levels of organization
Chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal.
Necessary life functions
Boundaries, movement, responsiveness, digestion, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, growth
Boundaries
Separation of internal and external environments. Regulates the exchange of material.
Movement
Get the materials needed or to escape biological threats such as predation or hostile environments.
Responsiveness
Detect and respond to changes internally and externally (sensation). Allows organisms to adapt to their environment and maintain homeostasis.
Digestion
Ability to break down energy to be used by the cells to function. Need to ingest high energy bonds to take macromolecules. Provides the organism with essential nutrients.
Metabolism
Ability to use the energy provided by digestion for cellular processes. Chemical reactions that occur within the organism. Energy production, synthesis of cellular components, and regulation of physiological processes.
Excretion
Removal of waste and metabolic byproducts.
Reproduction
Production of offspring. Passes on genetic material and continues the population.
Growth
Necessary for development, repair, and maturation.
Homeostasis
Ability to maintain stable internal conditions within a narrow range of values.
Feedback System
Process involving a receptor, control center, and effector to maintain homeostasis.
Negative Feedback
Mechanism that decreases stimulus to return a variable to its set range.
I.e, sweating, regulation of glucose
Positive Feedback
Mechanism that increases stimulus, less common than negative feedback.
I.e, blood clotting, lactation, childbirth
Anatomical Position
Standard position of the body used as a reference in anatomy.
Antecubial
Anterior side of elbow.
Axillary
Armpit.
Brachial
Upper arm.
Calcaneal
Heel.
Carpal
Wrist.
Cephalic
Head.
Cervical
Neck and cervix.
Coxal
Fusion of ilium (hips), ischium (hip and pelvic), and pubis (pelvic area).
Digital
Fingers and toes.
Femoral
Thigh.
Gluteal
Butt.
Lumbar
Lower back.
Inguinal
Groin.
Occipital
Back of the head.
Olecranal
Point of elbow.
Oral
Mouth.
Orbital
Eye socket.
Patella
Knee cap.
Sacral
Related to the sacrum (tailbone).
Tarsal
Ankle.
Vertebral
Spine.
Umbilical
Around the belly button.
Superior
Above.
Inferior
Below.
Anterior
In front of.
Posterior
Behind.
Medial
Toward the midline of the body.
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body.
Intermediate
Between two structures.
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment.
Distal
Farther from the point of attachment.
Superficial
Towards the surface.
Deep
Away from the surface.
Axial Region
Central region of the body, including the head, neck, and trunk.
Appendicular Region
Region consisting of the limbs (arms and legs).
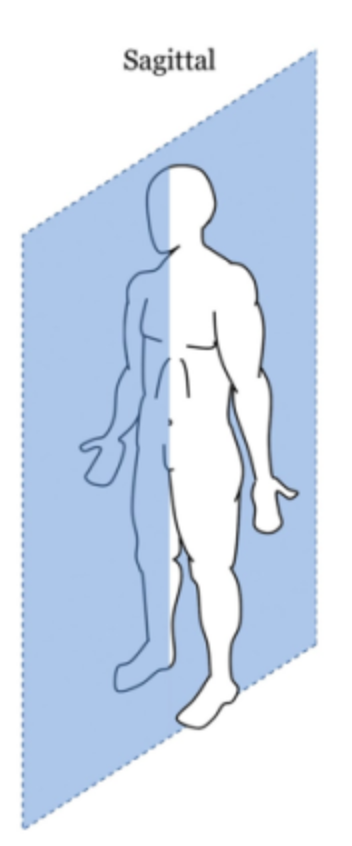
Sagittal Plane
Divides the body into right and left halves.
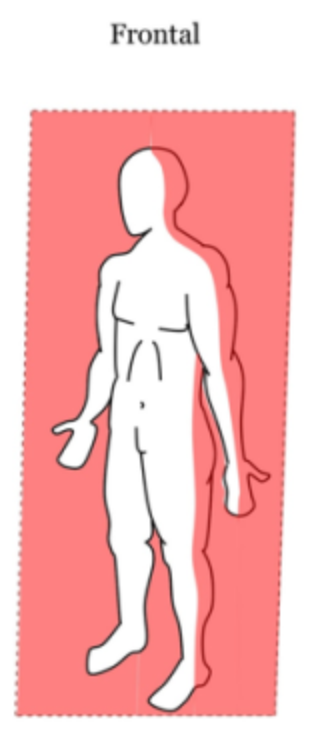
Frontal Plane
Divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) halves.
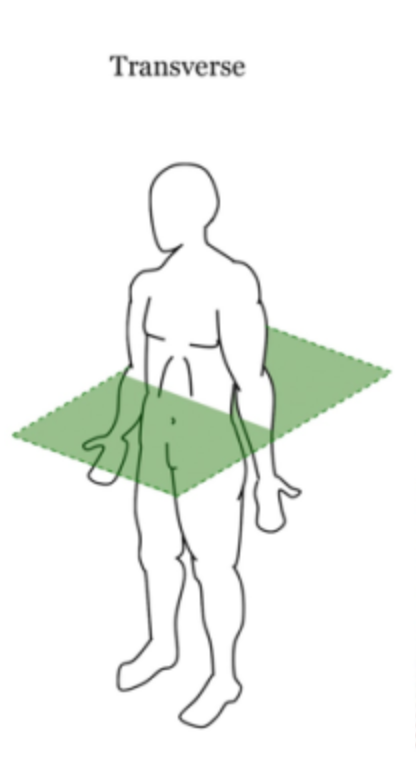
Transverse Plane
Divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) halves.
Dorsal Cavity
Contains the cranial and vertebral cavities.
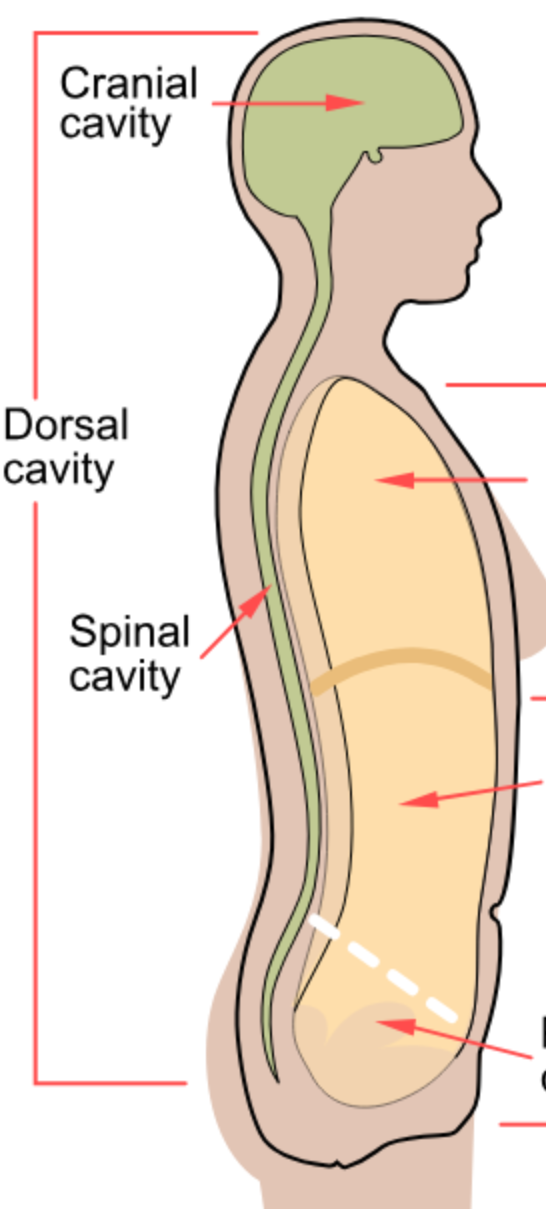
Ventral Cavity
Larger cavity divided into thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
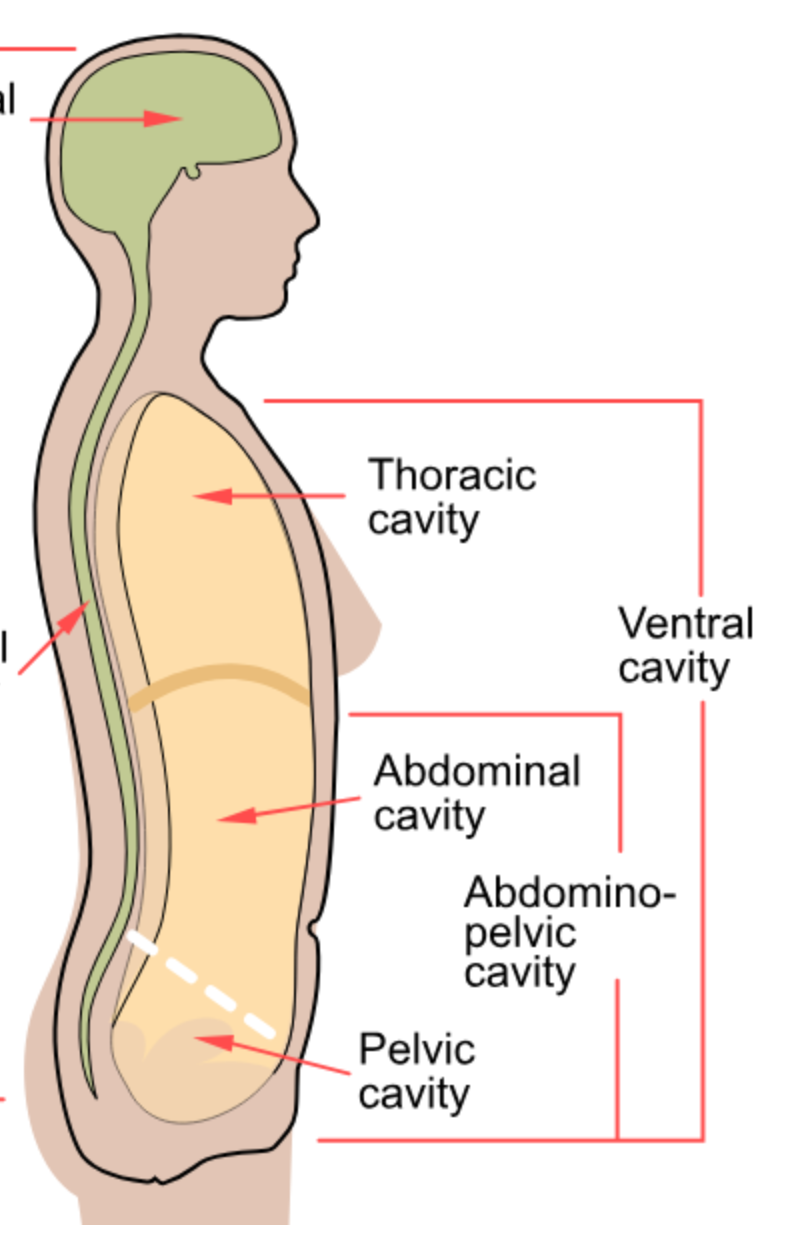
Thoracic Cavity
Contains the heart and lungs.
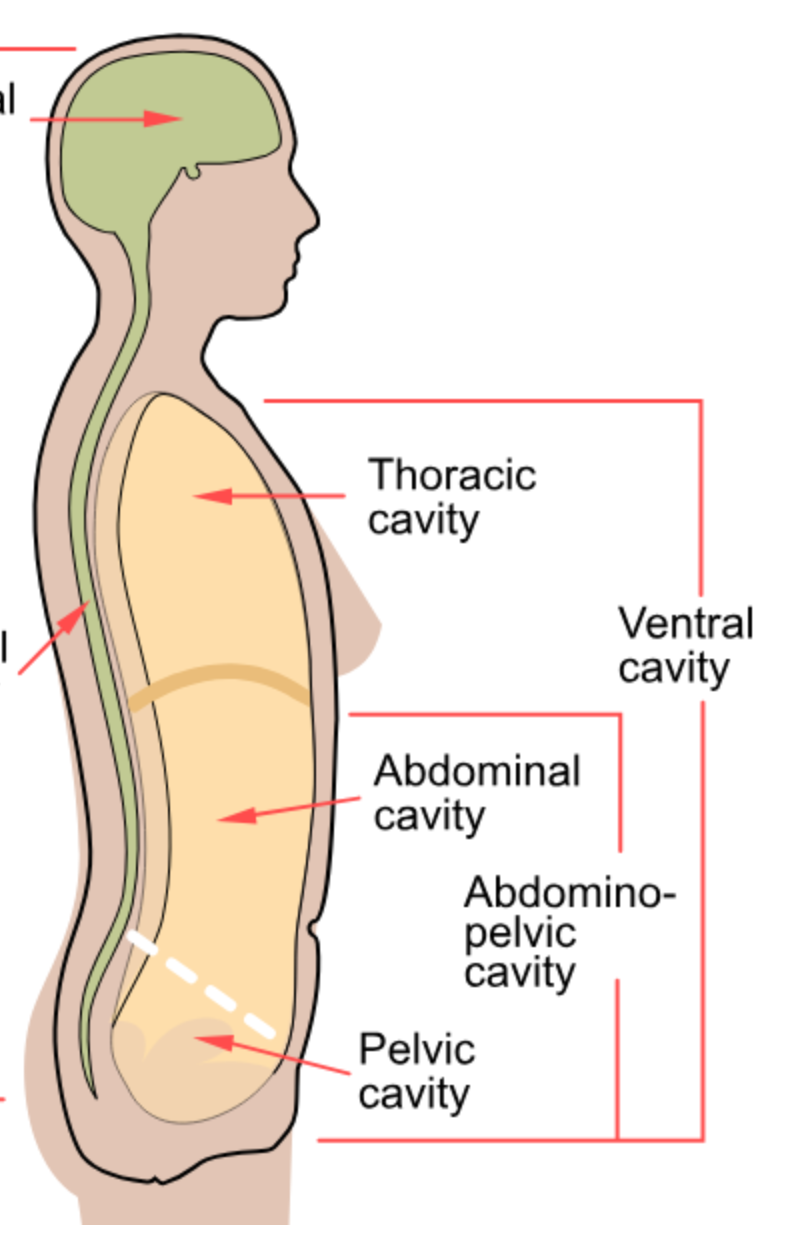
Abdominopelvic Cavity
Contains organs such as the liver, stomach, and intestines.
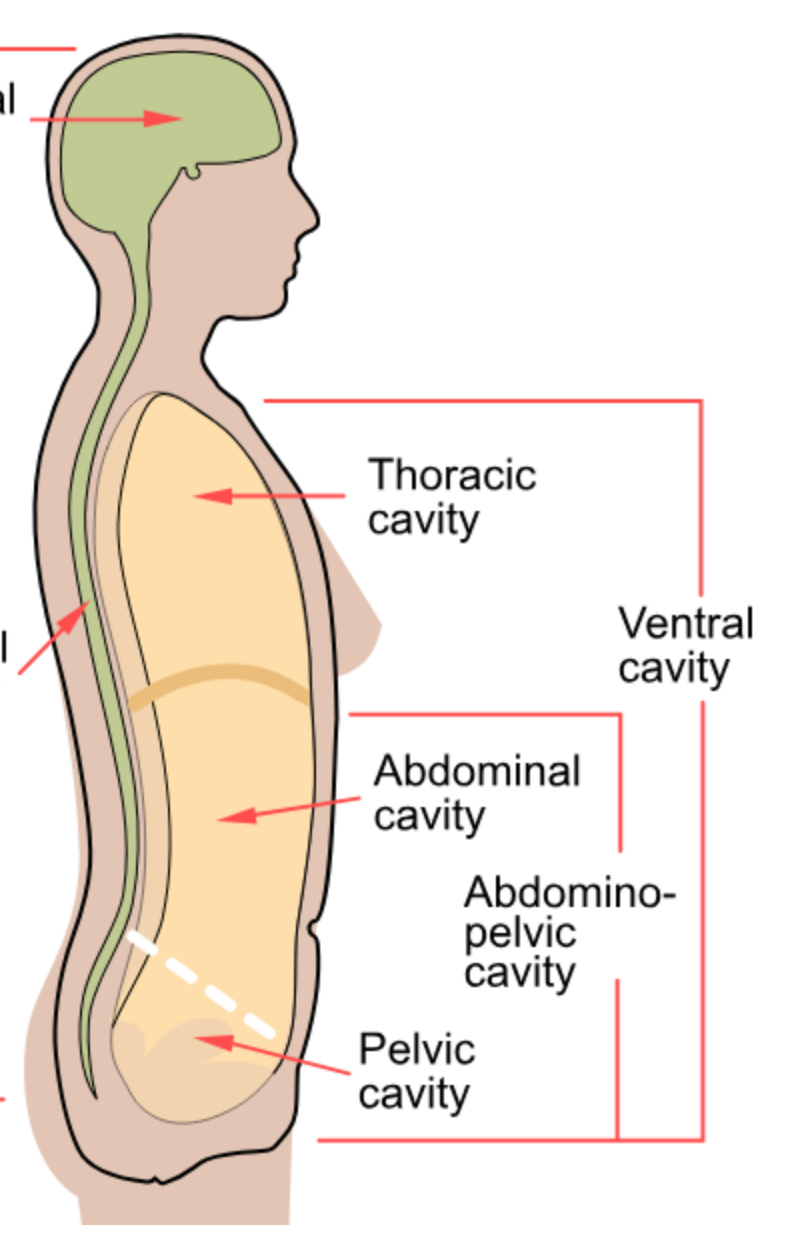
Pelvic Cavity
Contains the bladder, rectum, and reproductive organs.
Serous Membranes
Double-layered membranes lining body cavities to reduce friction.
Parietal Serosa
Lines the cavity wall.
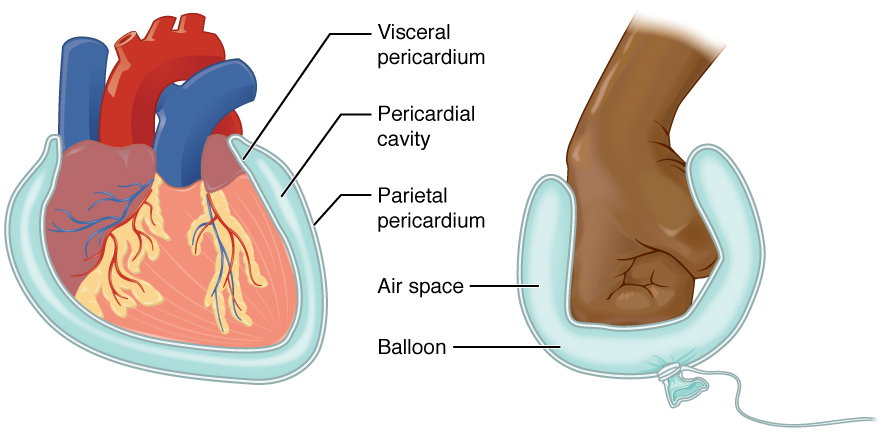
Visceral Serosa
Covers the organs within the cavity.
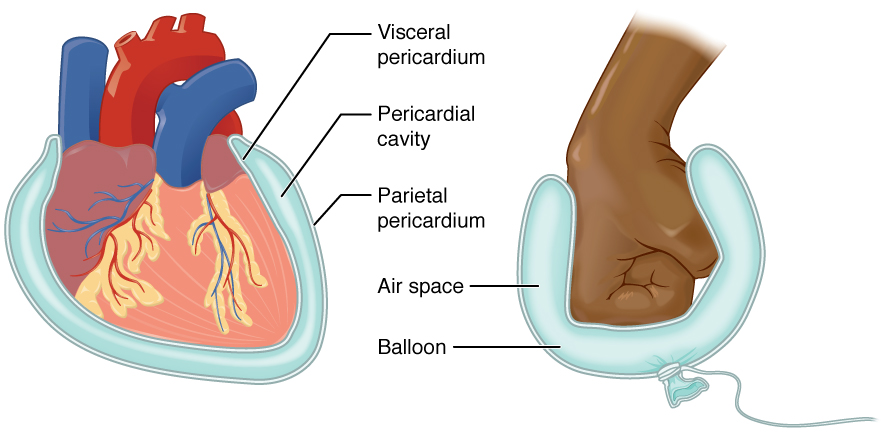
Serous Fluid
Fluid in between the two layers that reduces friction and allows the layers to slide past each other during organ movement.