Metallic Bonding, Giant Covalent Bonding/Structure, Stoichiometry
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
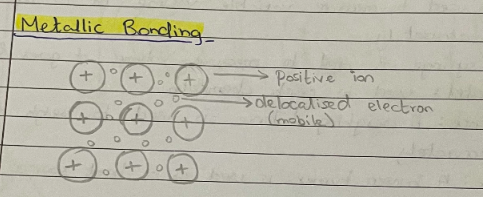
Metallic Bonding -
Electrostatic attraction between the positive ions in a giant metallic lattice and a ‘sea’ of delocalised electrons. Structure of metal made up of positive ions surrounded by electrons that move freely between ions.
Properties of metals
Malleable and ductile - Layers of metal ions can slide over each other
2. Good conductors of heat and electricity - electrons in ‘sea’ of electrons are free to move
How is diamond structure and silica similar
1. Show similar physical properties
2. Very hard, high melting points
3. Tetra hedral-giant covalent structure
Diamond
1. Hardest natural substance because each carbon atoms attached to 4 other carbon atoms
2. Diamond used in cutting tools
3. Does not conduct electricity because there are no free moving electrons
Silicon (IV) Oxide (SiO2)
1. Each Si atoms covalently bonded to 4 oxygen atoms
2. Each oxygen atom is covalently bonded to 2 silicons atoms
3. Tetra hedral-giant covalent structure
Graphite -
1. High melting point
2. Hexagonal arrangement giant covalent structure
3. Strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms
4. Used as lubricant
5. Carbon bonded 3 other carbon, 1 atom free so conducts electricity because free electrons
6. soft because carbon atoms arranged in flat layers of linked hexagons. Weak forces of attraction between layers so able to slide over each other easily
Why is Graphite soft?
Why metals conduct electricity?
Electrostatic attraction produced by negatively charged electrons move freely between positively charged ions
High melting point and Low melting point
HMP strong electrostatic force of attraction between positive ions and negative ions. LMP weak intermolecular force of attraction between molecules.
Relationship between group, charge, valency
Polyatomic Ions
Positive: Ammonium (NH+)
Negative: Hydroxide (OH-)
Nitrate (NO3-)
Sulphate (SO4^2-)
Carbonate (CO3^2-)
Phosphate (PO4^3-)
Cyanide (CN-)
Manganate (MnO4-)
Bicarbonate (HCO-3)
Happy Noodles Swim Calmly, Playing Crazy Monkey Beats.
00423243043