Stereoisomers
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Stereoisomers
These isomers differ only in the way atoms are oriented in space.
Constitutional Isomers
These isomers differ in the way the atoms are connected to each other.
Chiral
A molecule that is not superimposable on its mirror image.
Achiral
A molecule that is superimposable on its mirror image.
different, the same
Isomers are ________ compound(s) with ________ molecular formula(s).
A, B
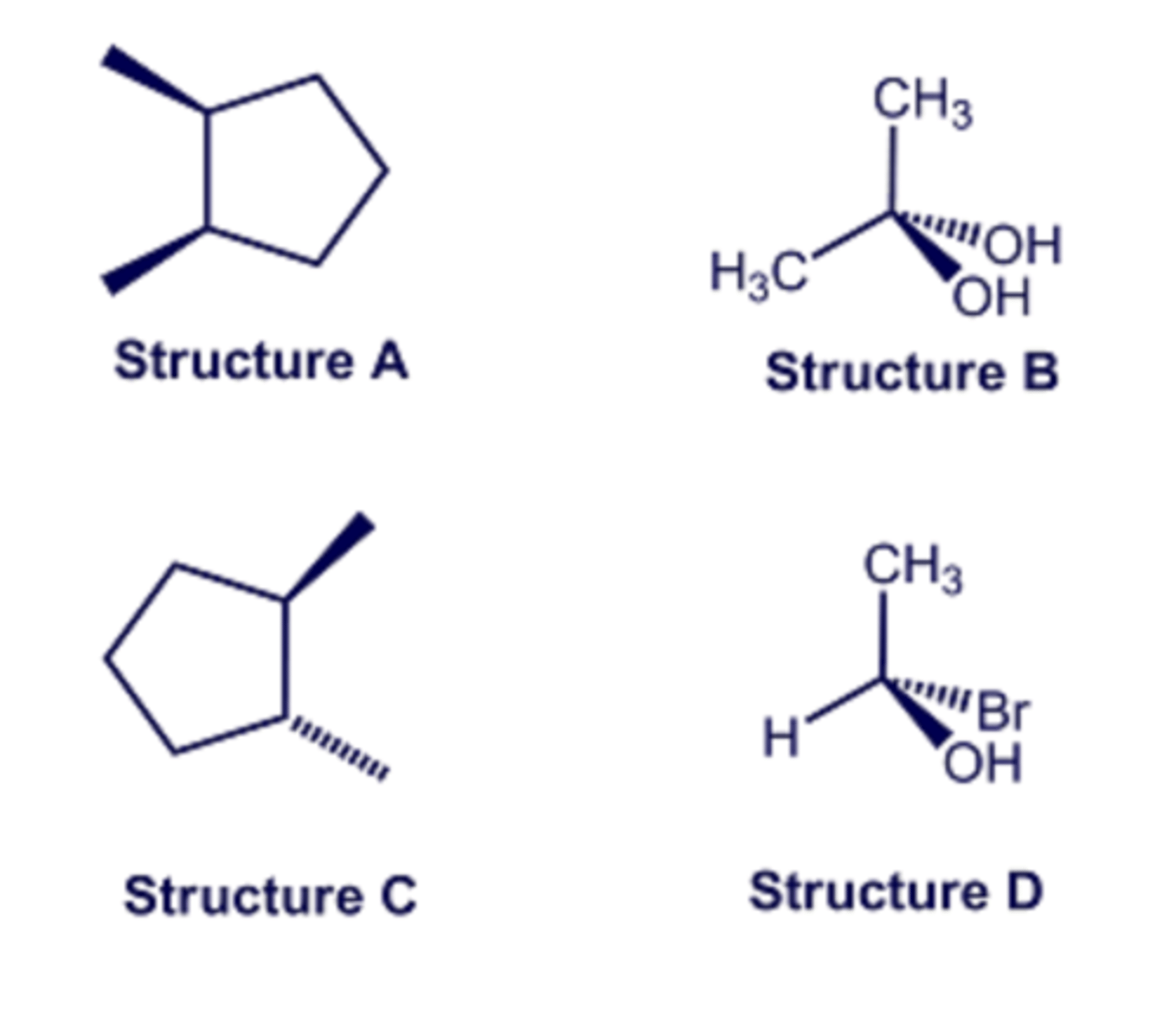
Select all of the structures that are achiral.
True
(T/F) Constitutional isomers give different products in chemical reactions.
3
To test for chirality, you must first draw the molecule in (2/3) dimensions or build a model.
enantiomers
Stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other and are not superimposable are called _________.
4, stereogenic
A carbon atom bonded to ________ different groups is a tetrahedral ________ center.
B, E
Select all of the structures that are chiral.
True
(T/F) Enantiomers are mirror image molecules that are not superimposable.
tetrahedral stereogenic
A ____________ center is a carbon atom bonded to four different atoms or groups.
True
(T/F) A chiral molecule and a stereogenic carbon are not the same thing.
False (May or may not be)
(T/F) Two or more stereogenic centers are usually chiral.
B, C
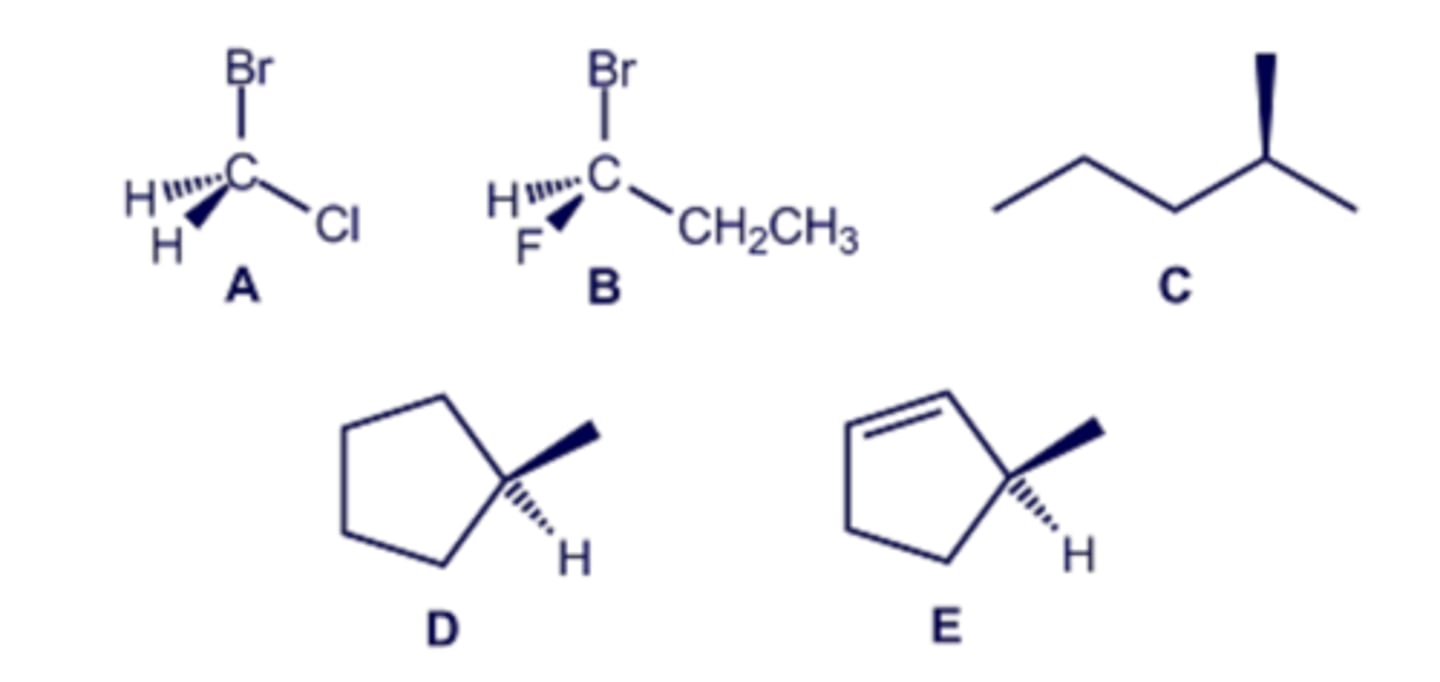
Which of the marked atoms in the structure shown are tetrahedral stereogenic centers?
True
(T/F) This C is a stereogenic center because the 2 CH2 groups on either side of it are not identical.
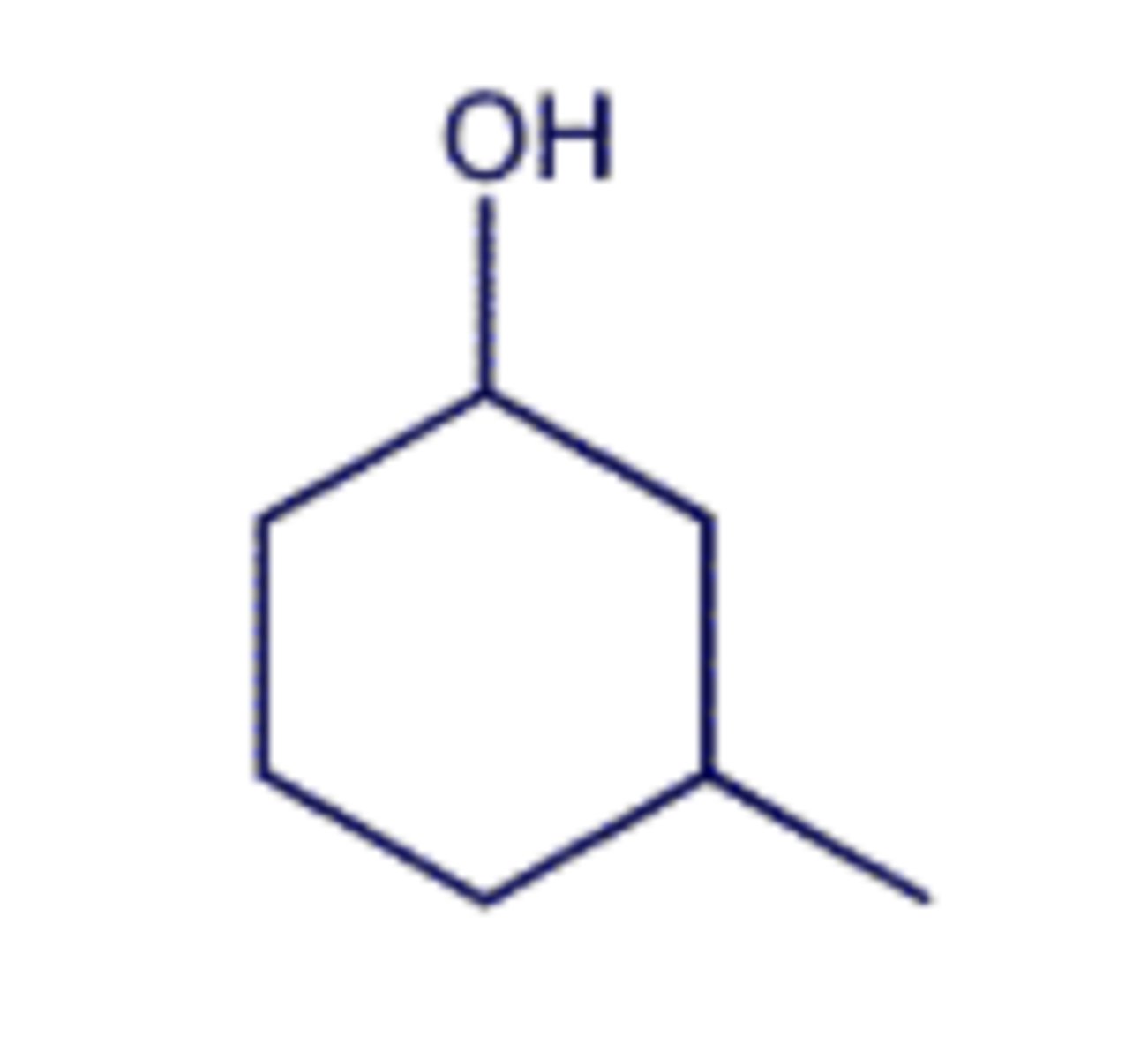
one tetrahedral stereogenic center
A molecule is always chiral if it contains ________.
False
(T/F) If two isotopes are bonded to the stereogenic center, the isotope with the lower mass number has a higher priority.
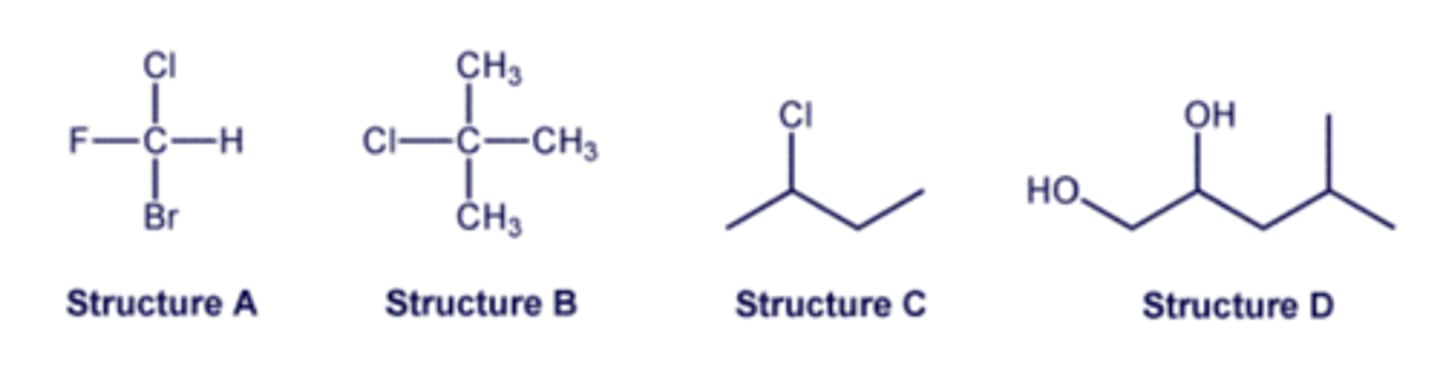
A, C, D
Which of the illustrated molecules contain tetrahedral stereogenic centers?
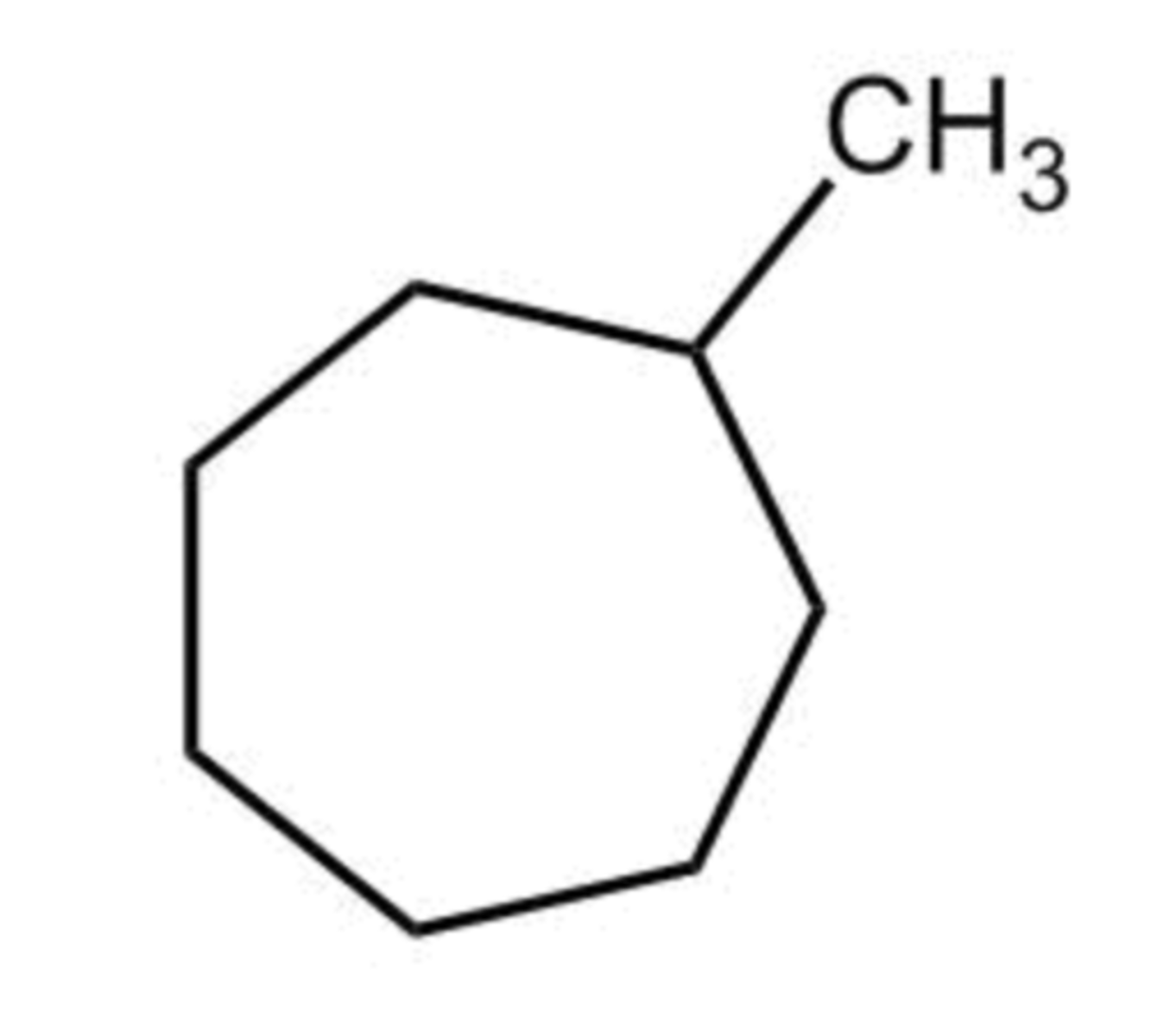
C1 is bonded to identical alkyl groups that happen to be part of a ring.
What best explains why C1 of methylcycloheptane (shown) is not a stereogenic center?
the same, different, different
Two compounds that are enantiomers have ________ molecular formula(s), ________ structure(s), and therefore ________ prefixes are used in their names.
higher, 2
When assigning priorities to groups, a C=O group is assigned a ________ priority than a CH2OH group because the C=O C is treated as if it is bonded to ________ O atom(s).
False
(T/F) When assigning priorities, a CΞC group would be assigned a higher priority than a C=O group because 3 C atoms have a higher combined atomic number than 2 O atoms.
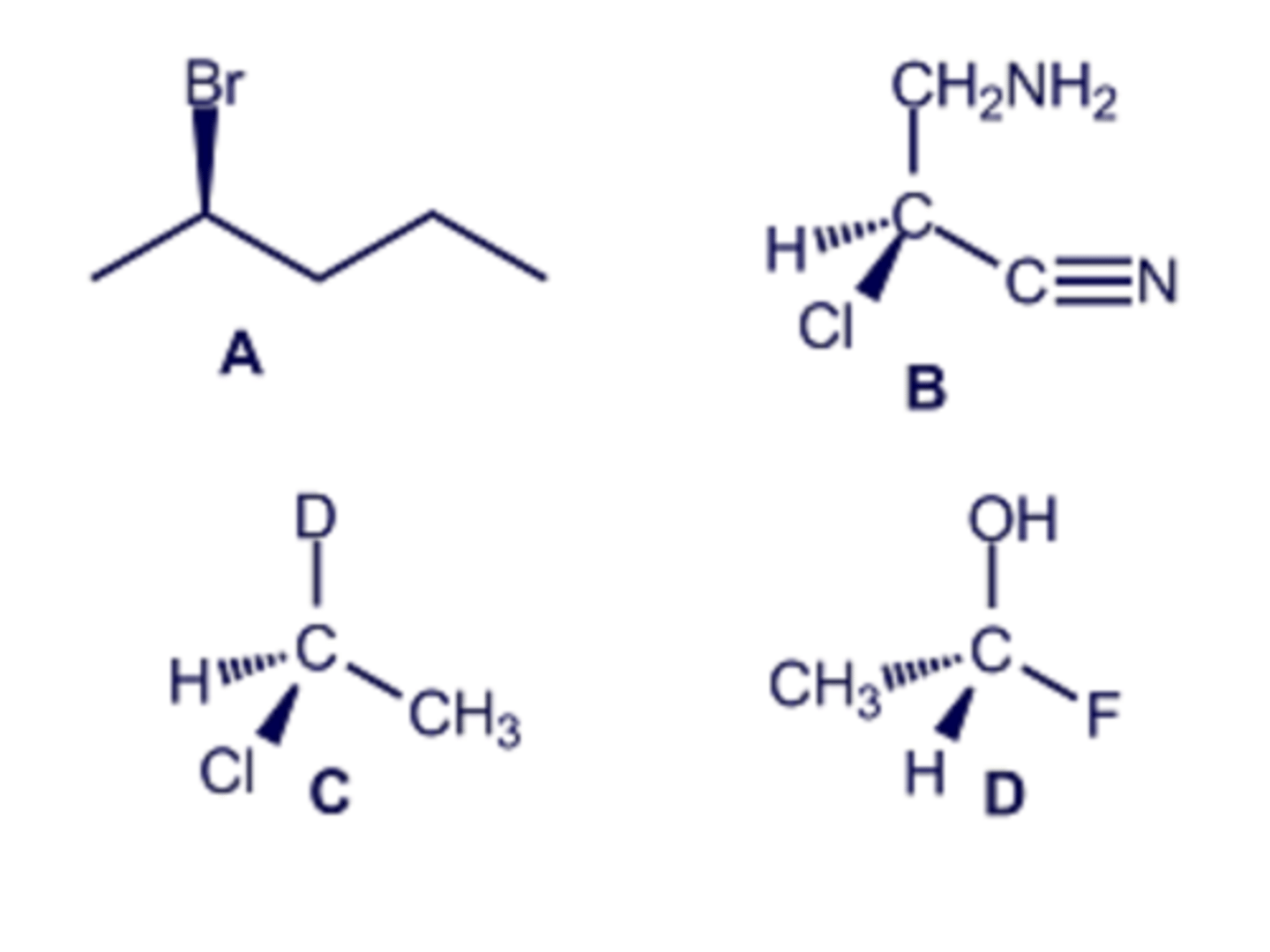
A, D
Consider the structures shown in the diagram. Which of these molecules contain a stereogenic center with the R configuration?
4, R, S
When determining the configuration of a stereogenic center, priorities are assigned to the four attached groups. The group designated priority ________ is placed at the back, and a circle is traced through the remaining groups, from 1 → 2 → 3. If this circle is clockwise the configuration is ________; if counterclockwise, the configuration is ________.
True
(T/F) A meso compound contains two or more stereogenic centers.
False
(T/F) A meso compound is chiral.
achiral, two or more
A meso compound is a(n) _________ compound containing _________ stereogenic centers.
S and R, R and S
An unknown compound X has two stereogenic centers that each have the R configuration. The diastereomer(s) of X will have the ________ configurations at the stereogenic centers. Select all that apply.
Enantiomers
What is the stereochemical relationship between the two compounds shown?
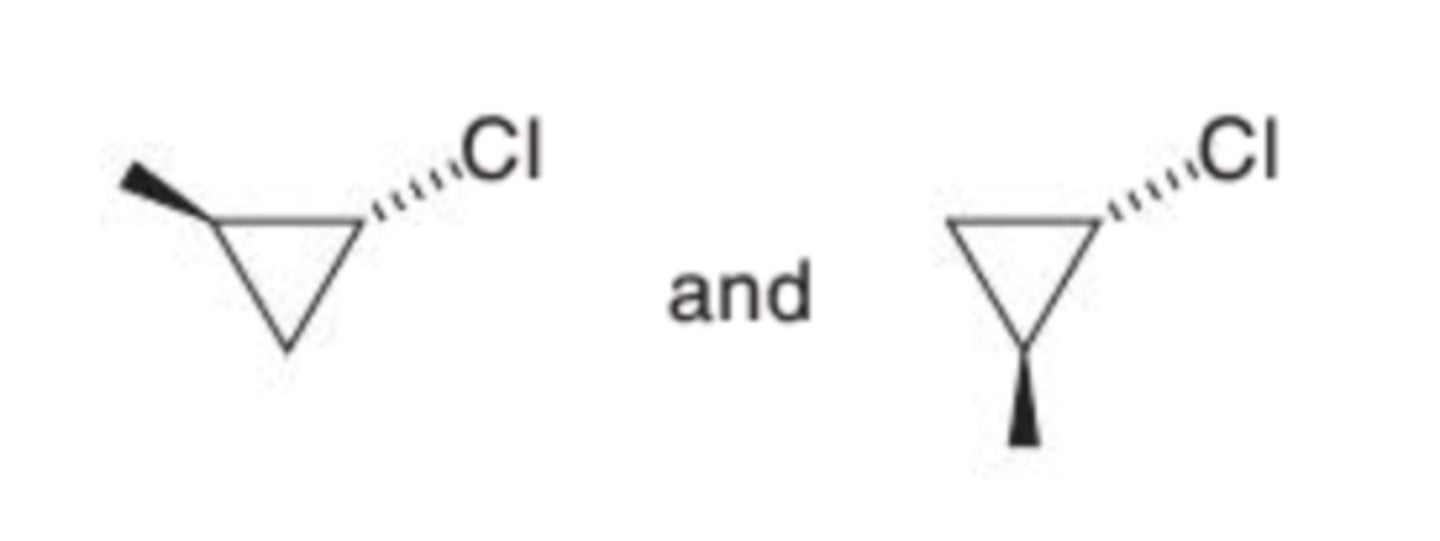
A, C, D
Consider the molecules drawn in the diagram below. Select all of the structures that are meso compounds.
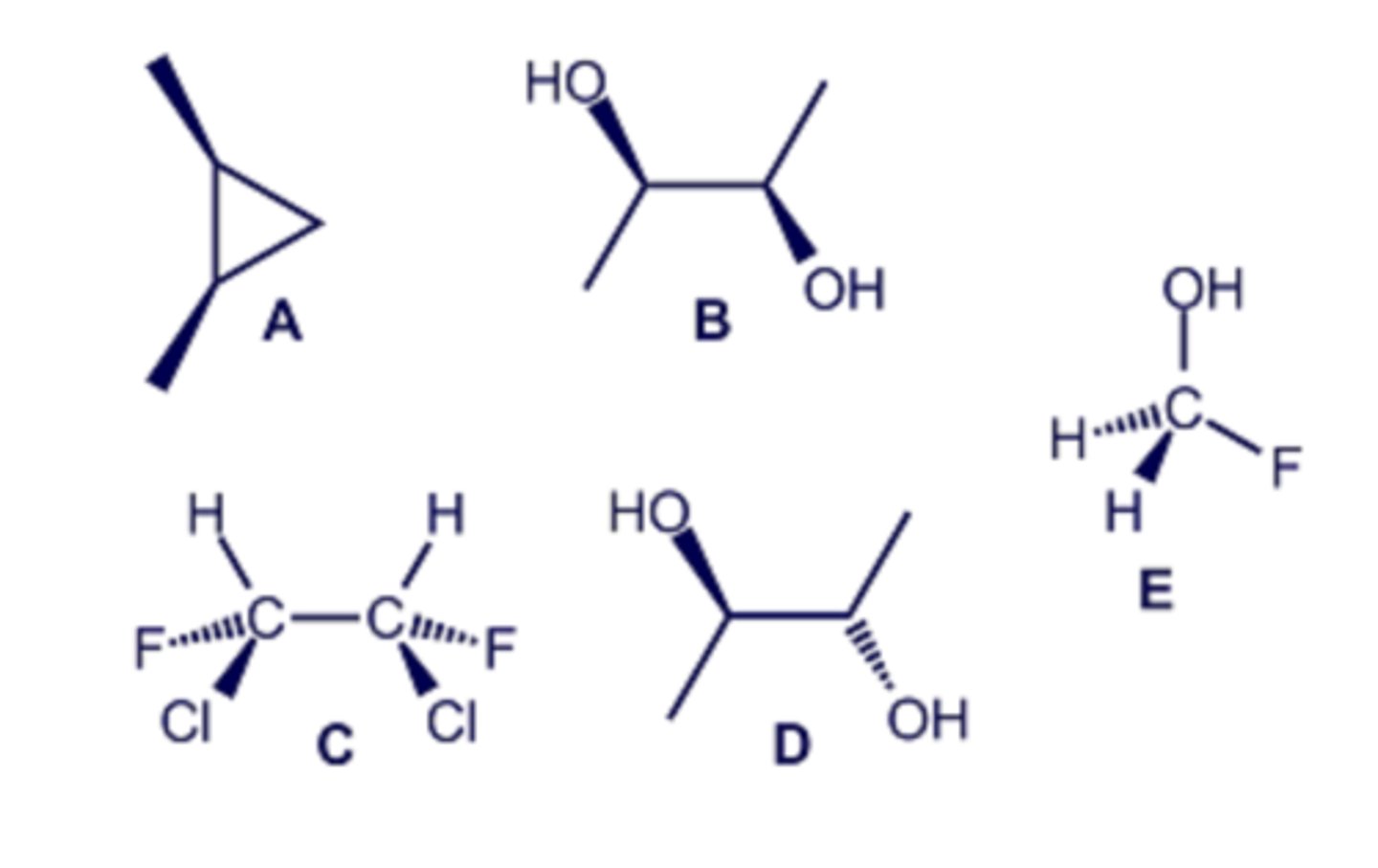
A, C
Which of the structures A-D are diastereomers of compound X? (Select all that apply.)
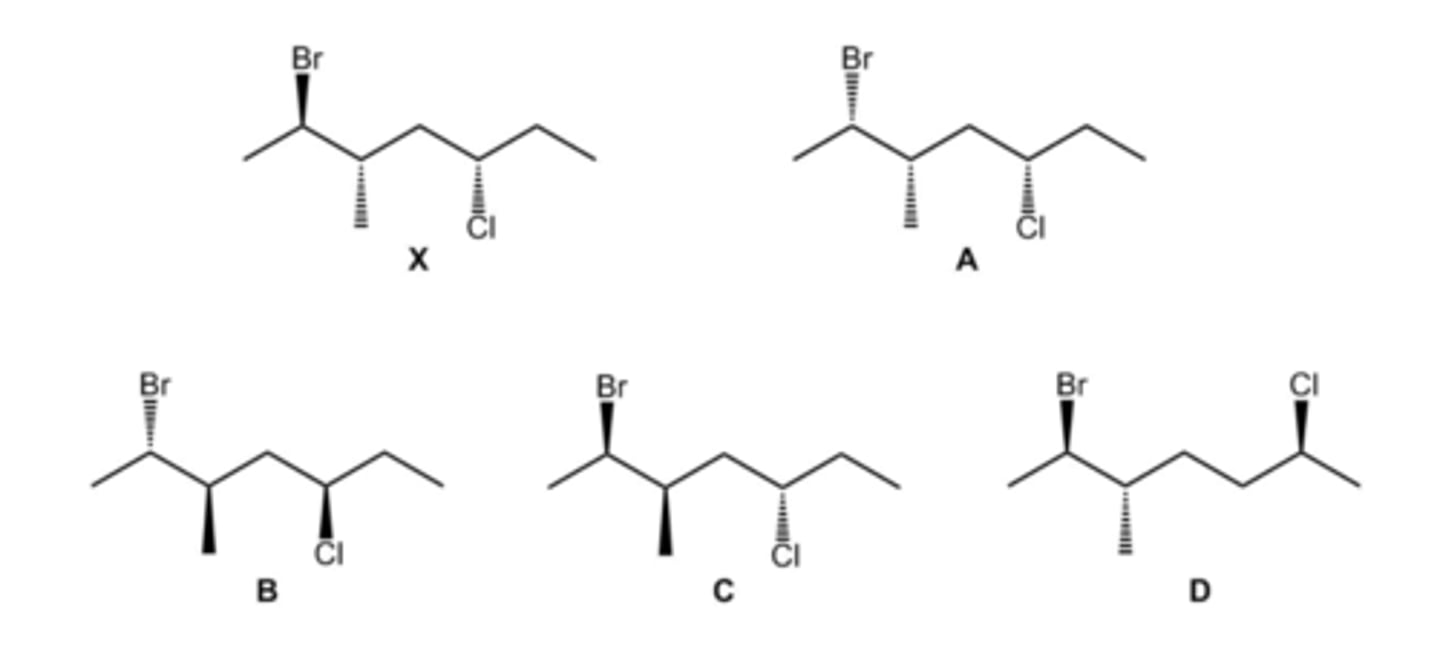
different, identical
Structural isomers can have _______ chemical and physical properties, whereas enantiomers have _______ chemical and physical properties except their interaction with chiral substances.
chiral, plane-polarized
The observed rotation is the angle (α) by which a ________ compound rotates ________ light in a polarimeter.
True
(T/F) Chiral compounds rotate plane-polarized light while achiral compounds do not.
False
(T/F) Enantiomers interact identically with plane-polarized light.
enantiomers, different
Two ________ always rotate plane-polarized light to an equal extent but in ________ direction(s).
observed
The amount by which an optically active compound rotates the plane of polarized light is measured as an angle. This angle is given the symbol α and is called the ________ rotation.
active, inactive
Chiral compounds are optically ________, while achiral are ________.
Racemic mixture
A mixture that contains equal amounts of the (+) and (-) enantiomers and thus are not optically active.
clockwise, +, -
If a compound rotates plane-polarized light in a ________ direction, the compound is called dextrorotatory, and is labeled d or ____. Rotation for a levorotatory compound is labeled l or _____.
specific, observed
The ________ rotation denoted by [α], is a physical constant that is calculated by measuring the ________ rotation of a sample in a tube with a defined length at a specific temperature, concentration, and wavelength.
True
(T/F) There is no relationship between configuration and optical rotation.
False
(T/F) All dextrorotatory compounds have the S configuration.
False
(T/F) All levorotatory compounds have the R configuration.
False
(T/F) The observed rotation is the angle (α) by which an achiral compound rotates plane-polarized light in a polarimeter.
True
(T/F) The observed rotation is the angle (α) by which a chiral compound rotates plane-polarized light in a polarimeter.
Enantomeric excess (ee)
Measurement of how much one enantiomer is present in excess of the racemic mixture
concentration in g/mL
In the equation for specific rotation, [a] = a/lc, c stands for ________.
optical purity
Another term for enantiomeric excess is ________.
not, chemical
Diastereomers are ________ mirror images of each other and therefore their ________ properties are different.
racemic mixture, enantiomers
Many chiral drugs are sold as a ________. It is difficult and costly to separate the two ________, since they have the same physical properties.
Molecular shape
_________ is an important property for determining the odor of a molecule.
chiral
The chemical properties of enantiomers are identical except for their reaction with ________, non-racemic reagents.
True
(T/F) Smaller doses can be used if chiral drugs are sold as a single enantiomer.
S, S, S
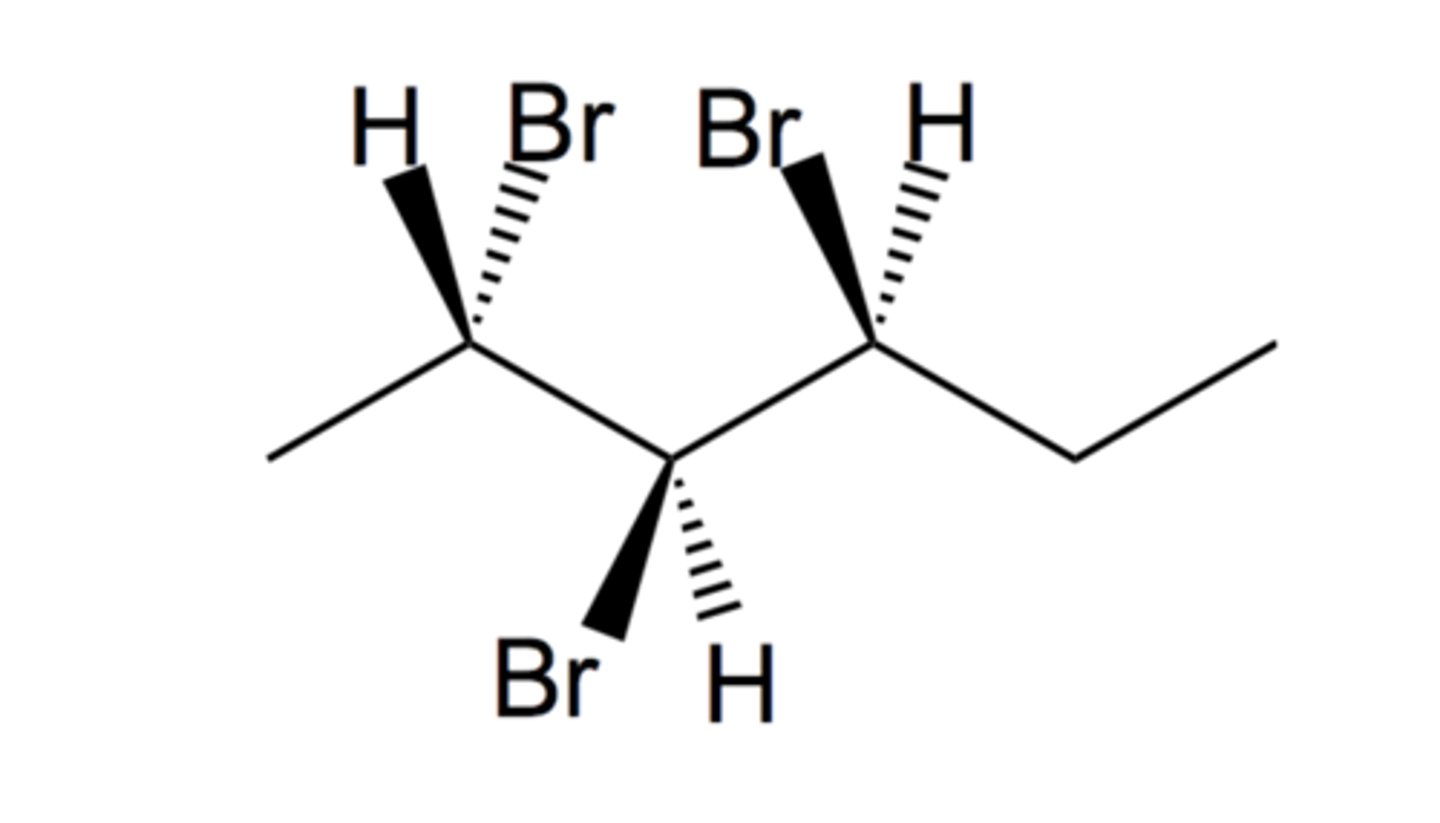
This compound is (2__, 3__, 4__)-2,3,4-tribromohexane
Enantiomers
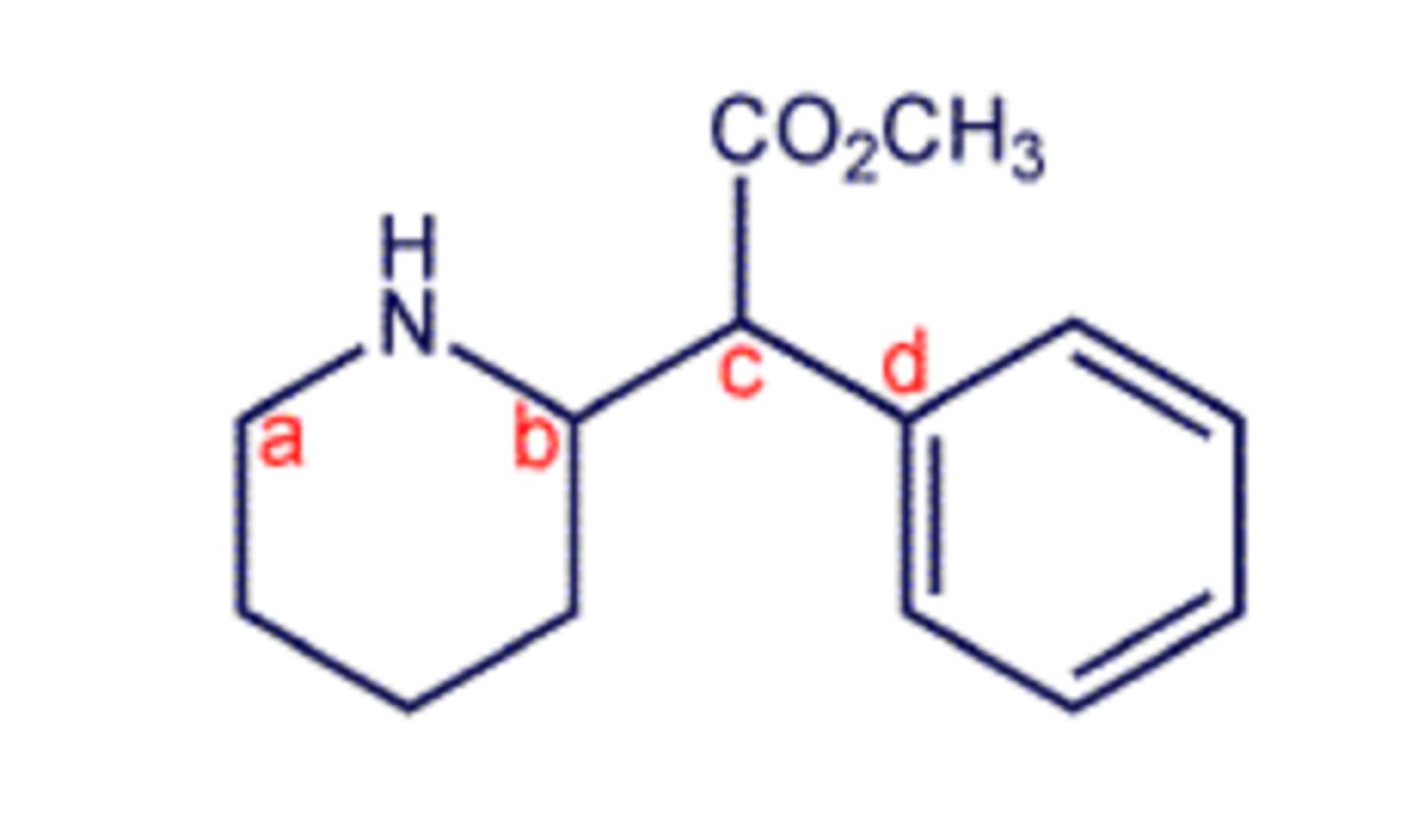
How are the following compounds related?
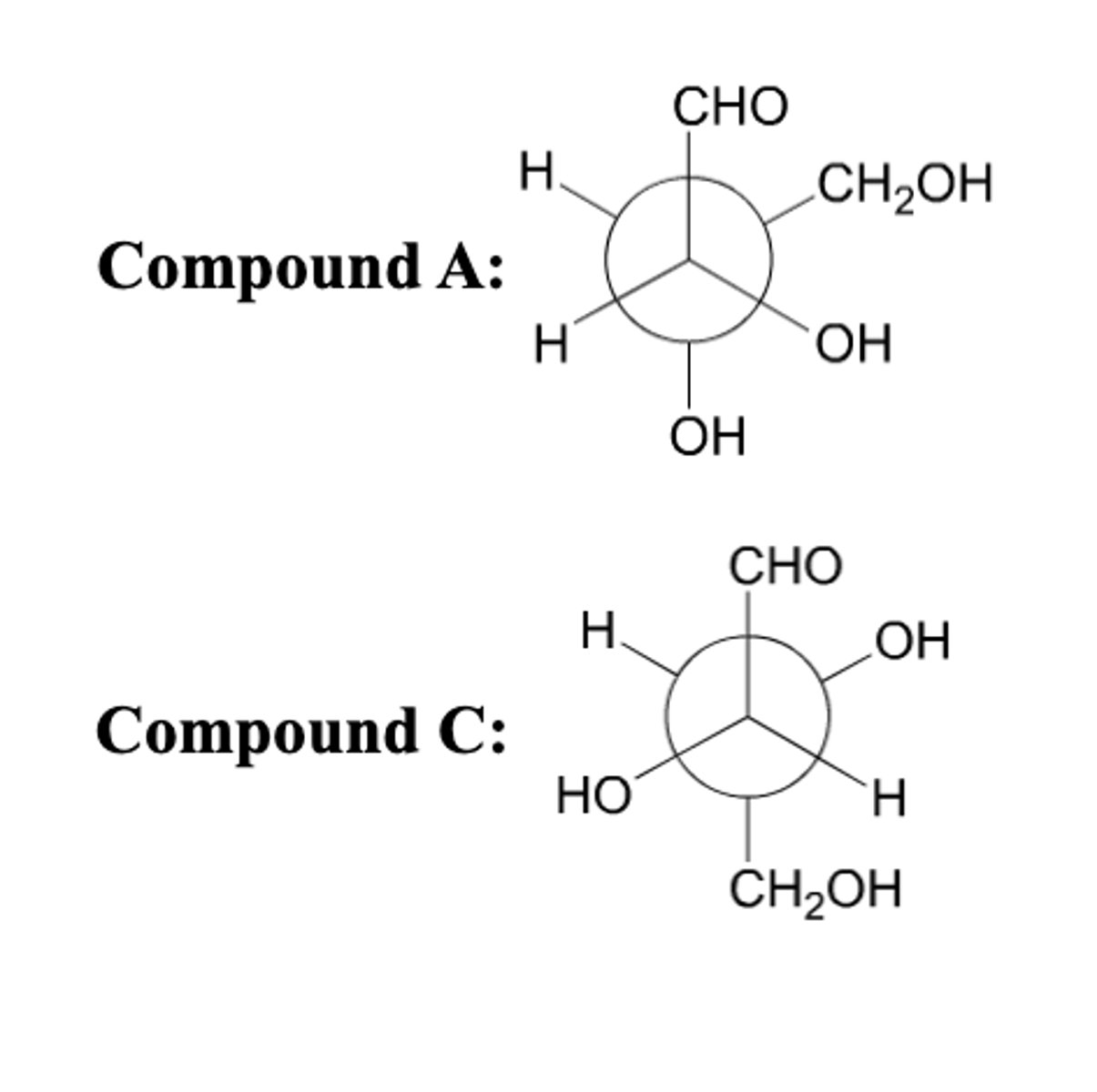
A, D, B, C
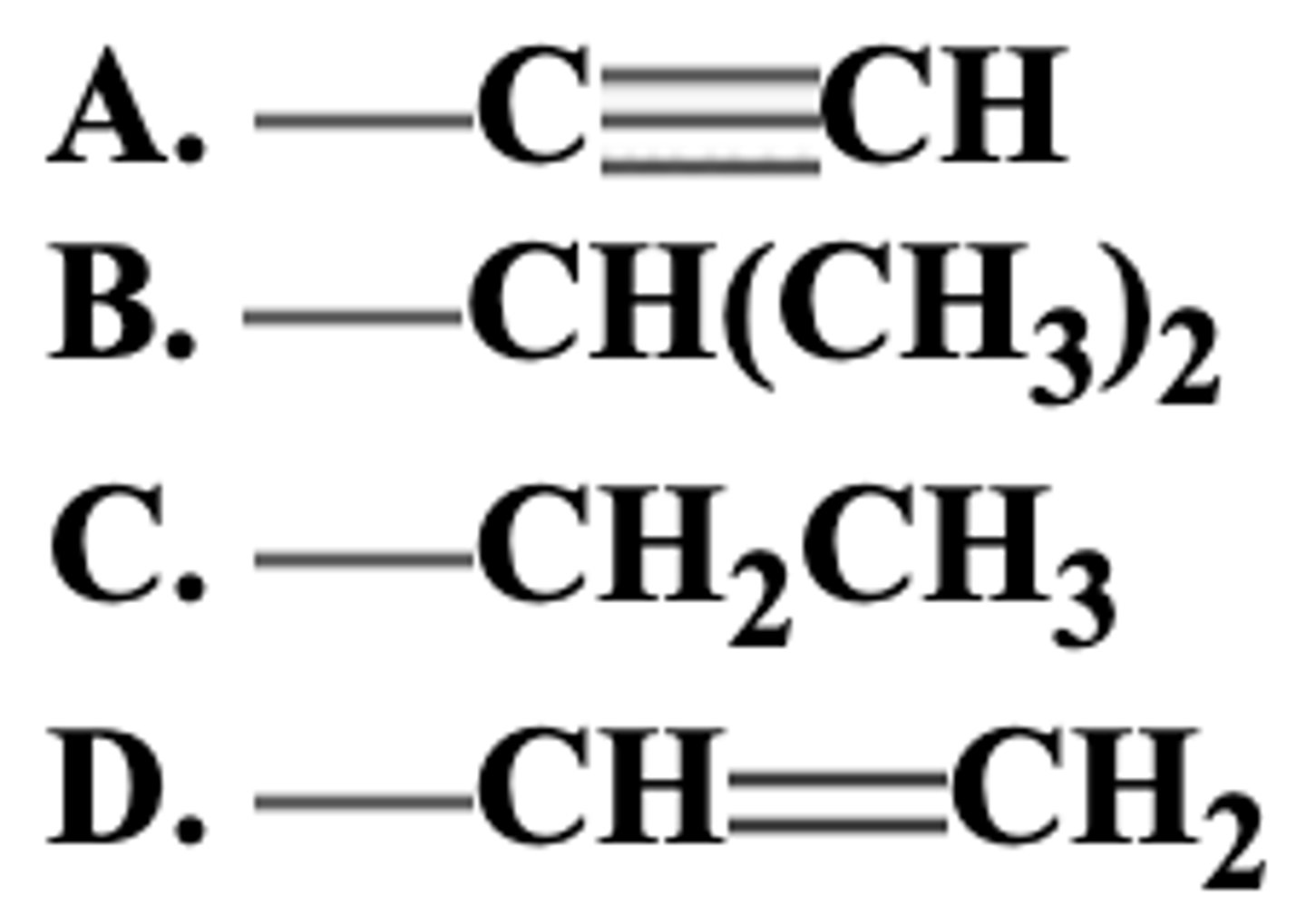
Rank the following groups in order of decreasing priority (highest to lowest).
S, R, S
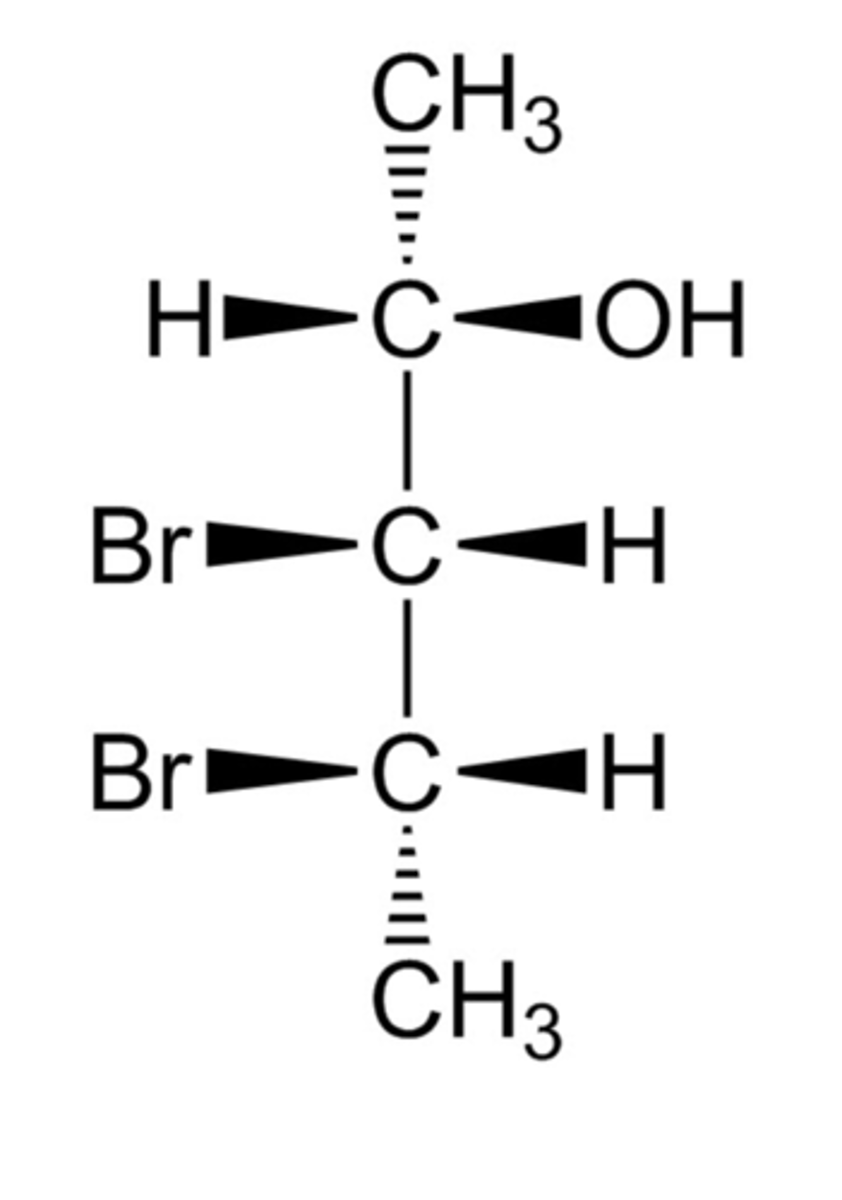
This compound is (2__, 3__, 4__)-3,4-dibromo-2-pentanol.
R, R, S
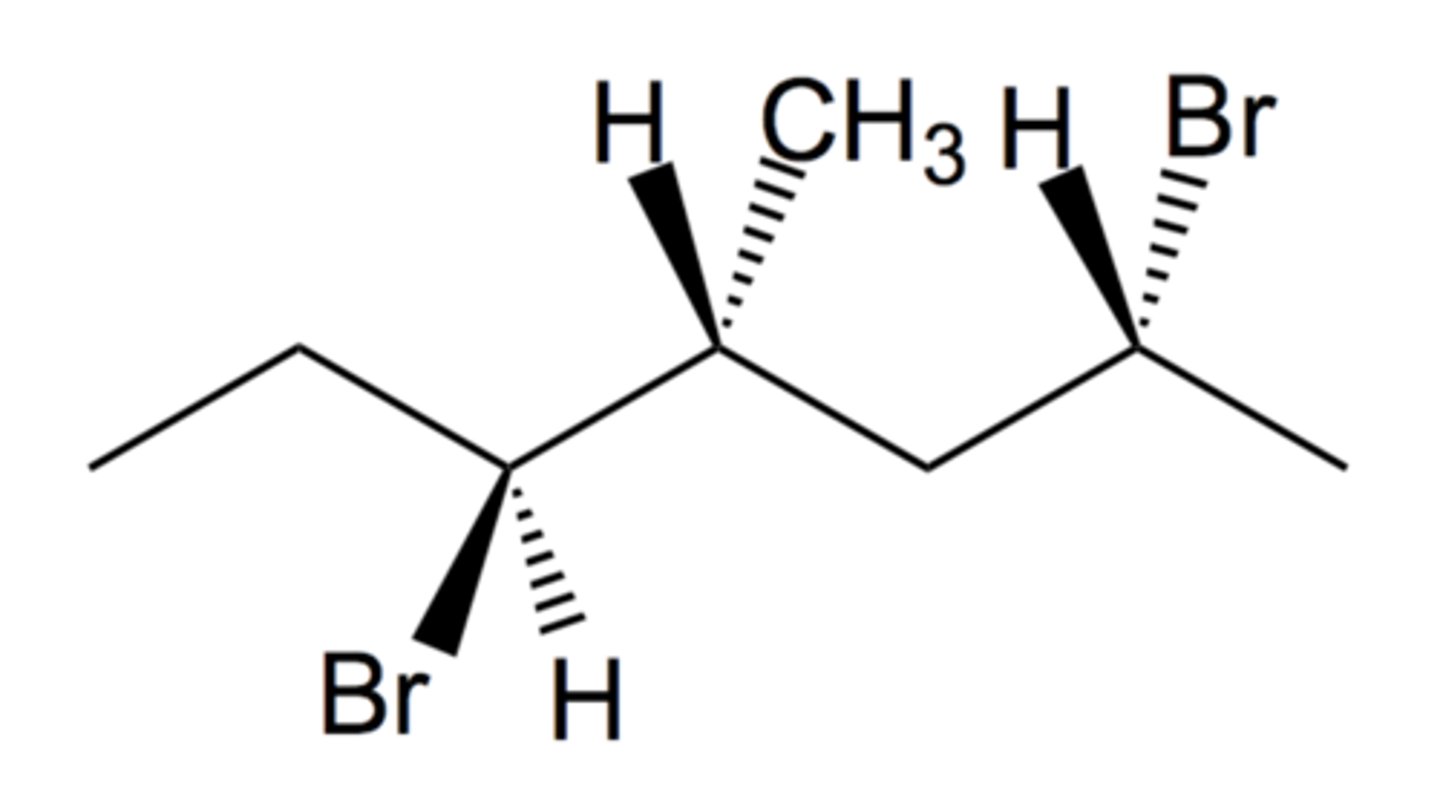
This compound is (2__, 4__, 5__)-2,5-dibromo-4-methylheptane.