year 11 psychology exam
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
what is psychology
•the systematic study of human behaviour and mental processes.

Behaviour
Any kind of response that can be observed & measured.
Behaviour is driven by thoughts & feelings.
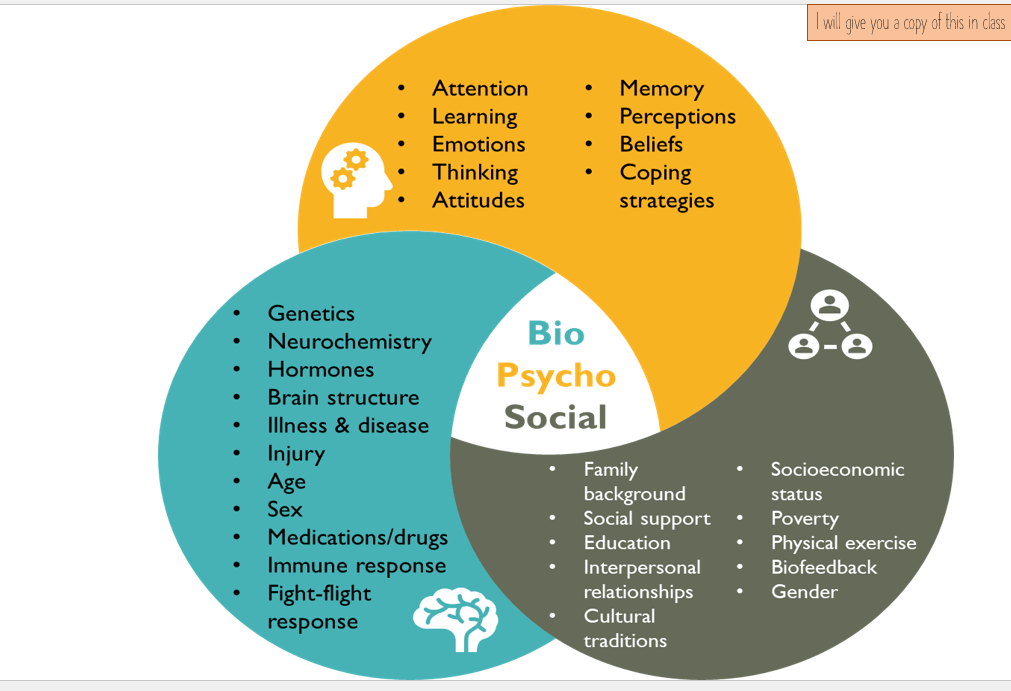
BioPsychoSocial Model
bio - physical
social - support group
psychology- mind
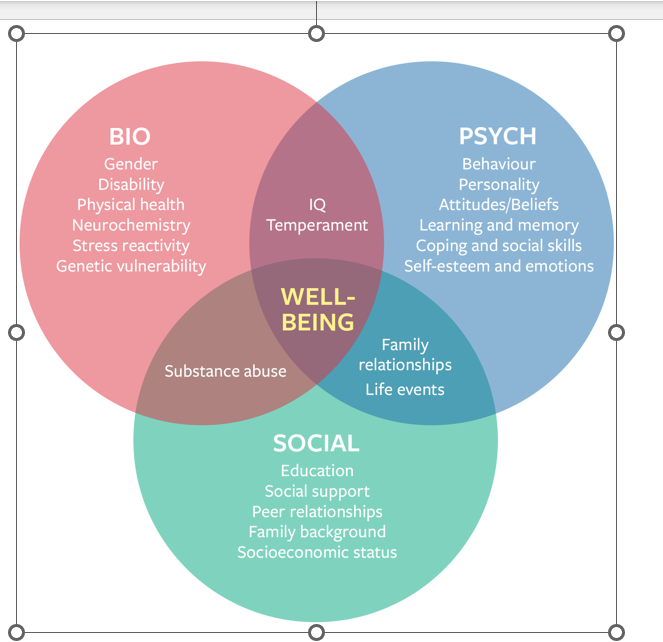
Biopsychosocial Model

•The biopsychosocial model states that psychological health, illness, treatments and factors are affected and/or caused by the interaction between biological, psychological and social factors.

Biological

Biological factors influence behaviour through chemicals (like hormones and neurotransmitters), bodily functions (e.g. heart rate, breathing), and brain structures like the amygdala, which affects emotion, memory, and decision-making.
Psychological

Psychological factors include emotions, moods, thoughts, and memory. Common emotions like sadness, joy, and fear, along with cognition, learning, and past experiences, all significantly shape behaviour.
Social
Social factors like culture, religion, socioeconomic status, peer influence, and upbringing shape behaviour. Social support, family background, gender roles, relationships, and social media also play key roles, and cultural values can impact mental health.
Bio =
psychology
society
what is going on in the body to influence behavior
what is going on in the brain to influence behaviour
what are the external factors that are influencing this persons behaviour?
Research Methods
Step 1: Identify the research problem
↓
Step 2 : Review the Literature
↓
Step 3: Formulate a hypothesis
↓
Step 4: Design the method
↓
Step 5: Collect the data
↓
Step 6: Analyse the data
↓
Step 7: Interpret the data
↓
Step 8: Report the findings
•Experimental design
designed to test hypotheses or questions about the relationship between variables. Focus is on determining cause/ effect relationship
pro
objective, cause and effect , control over variables
cons
time and cost,ethical limitation
•Observational design
involve watching and recording behaviour, focusing on pre-existing groups to find patterns or correlations.
pro
naturalistic setting , real time data ,ethical consideration
con
lack of control, observerr bias, ethical challenges
•Qualitative design
Designs use focus groups and the Delphi technique to collect verbal data, which researchers interpret descriptively rather than numerically.
. Experimental research
Etests cause-and-effect by manipulating the independent variable (IV) and measuring its effect on the dependent variable (DV) under controlled conditions (controlled group )
pro
control over variables
relicatbility
causal inferences , rigorous desing
con
artificality
, ethical constraints , time and resource intensive
Sample
a group that is a subset or part of a larger group chosen to be studied for research purpose
•Population:
the larger group from which a sample is selected and to which the researcher will generalise the results.
Observational Investigations
watch behaviour without changing/manipulating the IV, observing its natural effect on the DV
Correlation
is a relationship between two or more variables (etc studying and grade)
Causation
that variable causes another to change. To show this, researchers need to control the experiment and change one variable on purpose to see the effect
Illusory Correlation
Illusory Correlation
or false correlations, occur when people believe that relationships exist between two things when no such relationship exists.
qualitative investigations
study feelings and experiences using words, not numbers, through interviews or observations
indepth understanding, flexiability , participant perpectives,
con
limted generlizatiaility
, subjectivity, time and resource intensive , bias
Objective Quantitative Data
numerical information that is measured without personal bias and can be verified. It’s based on facts and numbers, like test scores or heart rates.
Standardised tests
•Tests that have been designed to be used exactly in the same way each time
Subjective Quantitative Data
Numerical measurement that is based on an opinion or personal input
Rating scales
a type of closed-ended questionnaire where respondents choose from set options, often numbered, to show how much they agree or feel about something.
Qualitative Data
Non numerical data usually obtained verbally, in writing or via images
.g. focus group records, Delphi technique records, interviews, responses to open-ended questions
Open ended items
•Type of questionnaire allowing participants to respond in any way they wish
Internal validity
External validity
The study’s accuracy in proving cause and effect.
The extent to which results apply beyond the study to other people or settings.
Reliability
how consistent and dependable a measurement or test is. If repeated under the same conditions, it should give the same results each time.
Standard Deviation
shows how spread out the data is from the mean (average).
Low standard deviation = data is close to the mean
High standard deviation = data is spread out from the mean
PSEUDOSCIENCES
come from unreliable conclusions because they do not follow scientific method
•empirical evidence
Data from observation or experiments, based on the scientific method and real evidence.
What are Ethics
•Ethics are moral principles and codes of thinking and behaviour.
Ethical Considerations
informed consent
confidentiality
voluntary participation
withdrawal rights
deception in research
emotion
•: A personal experience that involves a mixture of physiological responses, subjective feelings and expressive behaviour.
•EXTERNAL FACTORS: A comment made by a person, something you observed.
•
•INTERNAL FACTORS: Needs and thoughts (missing someone, loving someone)



SUBJECTIVE FEELINGS
Feelings experienced by an individual that are based upon their opinion.
Cannot be directly observed.
The inner, personal experience and emotion
EXPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR
Observable actions, often through facial expressions, that can be intentional or unintentional.
EXPRESSING BEHAVIOUR THROUGH VOICE
Emotions can be interpreted through vocal qualities such as speed, pitch and volume.
When a person is happy they tend to speak more quickly with a higher pitch and volume.
Paul Ekman
theorised that there are 6 key emotions that can be determined based upon facial expressions: Happiness, Sadness, Fear, Disgust, Surprise and Anger.

PHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSE
refer to the changes in our bodies that occur when we experience an emotion. etc
Not all strong emotions
when someone is walking behind you and ur hear started to beat fast
GALVANIC SKIN RESPONSE
•is used to refer to the electrical conductivity of the skin
role of the autonomic nervous system
•Autonomic NS regulates body organs automatically.
THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM

Prepares the body for fight or flight.
Reacts very quickly to prepare the body for action in an emergency.
Coordinates all of the physiological changes associated with stress.
THE PARASYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM

Calms the body, reverses stress responses, and works slowly to return it to a "rest and digest" state.
MEASURING PHYSIOLOGICAL AROUSAL
A polygraph tracks heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and skin response. It doesn’t detect lies but measures signs of physiological arousal.
James-lange Theory
Emotions result from physiological reactions in the body.
We feel emotion after the body responds (e.g., trembling → fear).
Cannon-Bard Theory
Emotions and physiological reactions happen at the same time, not one after the other.
Example: You see a snake → you feel fear and your body trembles at the same time.
Schachter-Singer Theory
Emotions happen when a body’s physical reaction is combined with an interpretation of the situation.
Example: Heart beats fast → the person thinks “I’m scared” → fear is felt.
Emotion = body response + thought.
Plutchik’s Theory
are evolutionary tools that help survival. The Wheel of Emotions shows eight primary emotions that combine to create complex feelings.
mental illness
•medically diagnosable illness that results in significant impairment of an individual’s cognitive abilities.
refers to health conditions that affect a person’s thinking, feeling, mood, or behaviour, and may impact daily functioning.
wellbeing
Psychological Wellbeing refers to feelings of happiness and life satisfaction.
PERMA Theory
The PERMA Model represents the five core elements of happiness and well-being.
PERMA stands for:
•Positive Emotion,
•Engagement,
•Relationships,
•Meaning, and
•Accomplishments.
flourishing
thriving with purpose, happiness, and strong social connections.
Resilience

the ability to recover quickly from adversity or stress.
Character strengths
•Creativity
•Curiosity
•Judgment
•Love of Learning
•Perspective
Original Mindfulness
present-moment awareness with nonjudgmental, open attention.
Benefits of
mindfulness
•Reduce stress and anxiety
•Improve mental health
•Better focus and concentration
•Increased self-awareness
•Improved relationships
•Better physical health
Limitations
•It is not a one-size fits all solution
•May not be effective for everyone
•Need to approach with openness and curiosity
•Should always be practiced under the guidance of a professional
Gratitude
Deliberately taking time to appreciate the good things in life, whether it be the people, personal experiences or things that we have.
Application of CBT
advantage
disadvantage
•Therapist and client to work together to identify negative thoughts and beliefs
through techniques
Evidence-based and effective
Works for many mental health issues
Short-term and time-efficient
Collaborative therapist-client approach
Personalized and goal-focused
cons
Requires active client participation; motivation may be low
Challenging to confront negative beliefs
Relies on potentially biased self-reports
Can be costly
Communication Styles
Assertive –
Aggressive –
Passive – .
Passive-aggressive –
Expresses needs clearly and respectfully; confident and direct.
Forceful, disrespectful, and dominating; violates others’ rights.
Avoids expressing needs; often submissive or overly accommodating.
Indirectly expresses anger; avoids confrontation but undermines subtly
•Forensic psychology
involves applying psychology to the field of criminal investigation and the law
common functions
•Competency evaluations
•Sentencing recommendations
•Evaluations of the risk of reoffending
•Testimony as an expert witness
•Child custody evaluations / disputes
Forensic Psychology vs. Criminal Psychology

Forensic psychology applies psychology to legal systems, helping courts, assessing offenders, and working with victims and witnesses. Criminal psychology focuses specifically on understanding criminals’ behavior, motives, and profiling offenders.
stalking
repeatedly following, harassing, or threatening someone in a way that causes them fear or distress.
VIP stalker
someone who obsessively follows or harasses a very important person (like a celebrity, politician, or public figure), often invading their privacy or safety.
The Stalkerazzi – Stalking & the Paparazzi

Aggressive paparazzi invading celebrities’ privacy like stalkers.
The rejected stalker |
The intimacy-seeking stalker |
The predatory stalker |
The incompetent suitor |
The resentful stalker |
Attempts to continue or rekindle a relationship. |
Believes they are in love with the victim. |
Seeks control, often leads to more serious crimes. |
Socially awkward; misreads signals. |
Seeks revenge for a perceived wrong. |
What is criminal profiling?
analyzing a criminal’s behavior to identify them.
Offender signature
is the unique behavior or pattern a criminal repeats during crimes.
Criminal profiling methods: Behavioural Evidence Analysis (BEA)
Collect detailed crime scene evidence.
Analyze victim and crime scene behaviors.
Identify the offender’s actions and motives.
Develop a profile of the offender’s personality.
Use profile to help catch the criminal.
serial murder
when someone kills three or more people over time, with breaks between each crime.
4 types of serial killer
Visionary –
Mission-Oriented
Hedonistic
Power/Control
– Kills because of voices or visions (often psychotic).
– Believes they're removing a specific group (e.g., "undesirables").
– Kills for pleasure, thrill, or satisfaction.
– Enjoys having control or dominance over victims.
Mass Murderer
Spree Killer
is someone who kills four or more victims in one location in one incident and the killings are all part of the same emotional experience.
•) is someone who murders at two or more locations within a very short period of time (almost no time break between murders)
Psychopaths
It is a personality disorder.
lack empathy, fake charm, lie easily, and manipulate others without guilt.
Bowlby’s Theory of Maternal Deprivation
losing a mother’s care early can cause emotional and social problems later in life.
Expressive Behaviour
refers to the observable expressions of behaviour.
Microexpressions
are very brief, involuntary facial expressions that reveal true emotions.
mental health /illness
•Mental health: The state of well-being, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and is able to make a contribution to his or her community.[1]
m is a recognised, medically diagnosable illness that results in significant impairment of an individual’s cognitive abilities.
The good life
finding happiness through engagement and flow (etc being fully active in actives which include your strengths )
looking time while painting or drawing
the meaningful life
receiving happiness through service other(e.g helping other people)
spending time helping other
The pleasant life
involves using positive feeling to achieve happiniess or pleasure
listening to music to lift you mood