anatomy of the brain
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
cerebrum
bulk of brain, intellect
cerebral nuclei
deep regions of gray matter
fissures
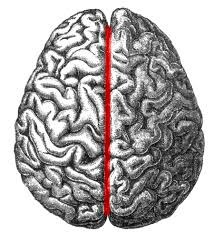
longitudinal fissure
separates hemispheres of brain
cerebral hemispheres
separate, except at a few locations when bundles of axons connect them; similar gyri and sulci but different functions
corpus callosum
largest tract connecting hemispheres
corpus callosum
hemispherice/cerebral lateralization
left brain controls right body functions (vice versa); some functions found only on 1 hemisphere
lobes
each hemisphere has 5
central sulcus
intermediate to parietal and frontal lobes
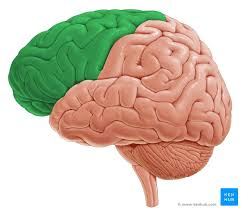
frontal lobe
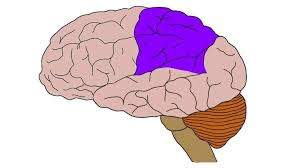
parietal lobe
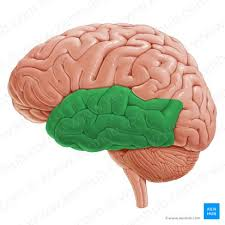
temporal lobe
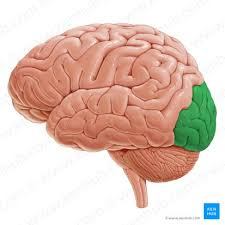
occipital lobe
insula
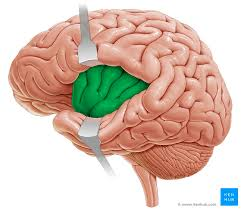
central sulcus
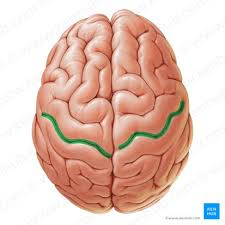
parieto-occipital culcus
intermediate to parietal and occipital lobes
lateral sulcus
superior to temporal lobe
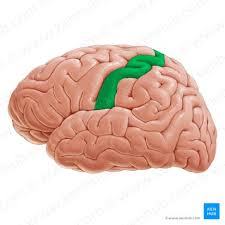
precentral gyrus
anterior to central sulcus; part of frontal lobe
postcentral gyrus
posterior to central sulcus; part of parietal lobe
parieto-occipital sulcus
red line
lateral sulcus
precentral gyrus
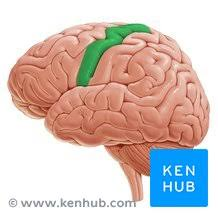
postcentral gyrus
cerebrum functional areas
motor areas, sensory areas, association areas
motor areas
control voluntary motor functions
sensory areas
provide conscious awareness
association areas
allow motor and sensory to communicate
hummonculus
displays region and proportion of cortex that communicates
motor speech area
controls muscular movements necessary for vocalization
primary motor cortex
located in precentral gyrus
primary somatosensory cortex
located in postcentral gyrus; controls sensations
primary visual cortex
processes visual information; located in occipital lobe
primary auditory cortex
processes auditory information; located in temporal lobe
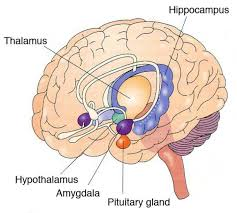
diencephalon
relay station for most sensory and motor pathways, controls visceral activities
diencephalon structures
epithalamus, thalamus, hypothalamus
epithalamus
partially forms roof of diencephalon; covers 3rd ventricle
epithalamus
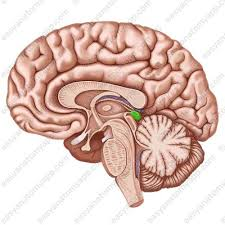
epithalamus components
pineal gland; habenular nuclei
habenular nuclei
relays signals from limbic system to midbrain; involved in visceral and emotional responses to odor
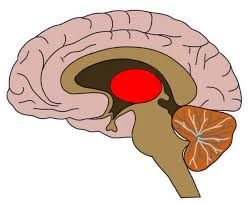
thalamus
2 halves; sensory impulses from all conscious senses converge on thalamus and synapse and one of its nuclei; made up of about a dozen nuclei
thalamus
hypothalamus functions
control of autonomic nervous system and endocrine system; regulation of body temp; control of emotional behavior; control of food and water intake; regulation of circadian rhythms
infundibulum
connection between hypothalamus and pituitary gland
hypothalamus
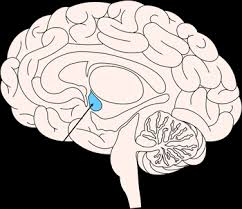
brainstem
passageway for all tracts between cerebrum and spinal cord
3 regions of brainstem
midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
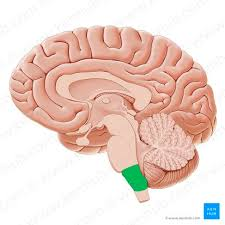
midbrain
green portion
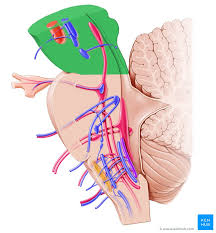
pons
pink portion
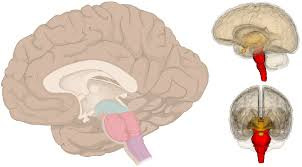
medulla oblongata
medulla oblongata
contains many autonomic nuclei: cardiac center, vasomotor center, medullary respiratory center
cardiac center of medulla oblongata
regulates heart rate, strength of contraction
vasomotor center of medulla oblongata
controls blood pressure by regulating contraction of smooth muscle in walls of arterioles
medullary respiratory center of medulla oblongata
regulates respiratory rate
cerebellum regions
cerebellar cortex, arbor vitae, cerebellar nuclei
cerebellum
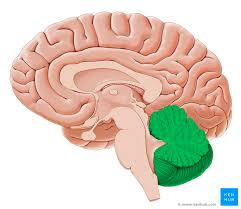
cerebellar cortex
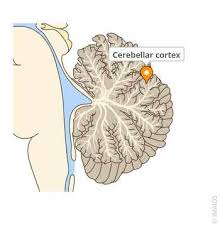
superficial region of gray matter
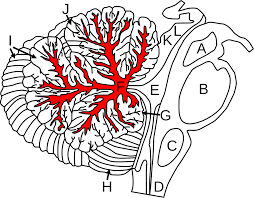
arbor vitae
deep layer of white matter (looks like trees)
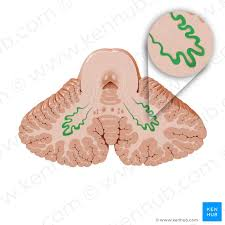
cerebellar nuclei
deep areas of gray matter
cerebellar cortex
arbor vitae
cerebellar nuclei
cerebellum functions
coordinates and fine-tunes movements; stores memories of previously learned movement patterns; adjusts muscle activity to maintain equilibrium and posture; uses proprioceptive information from muscles and joints to regulate the body’s position; monitors position of each body joint and its muscle tone
peduncles
a stalk-like structure composed of tracts connecting 2 regions of the brain
tract
CNS axon bundle in which the axons have a similar function and share a common origin and destination
superior cerebellar peduncle
midbrain to cerebellum
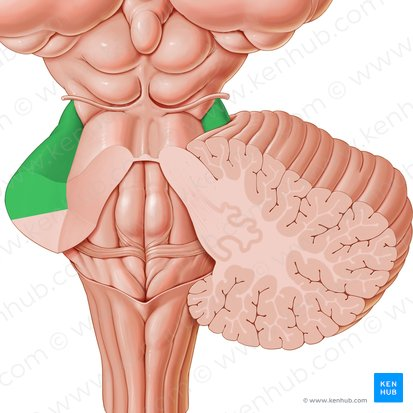
middle cerebellar peduncle
pons to cerebellum
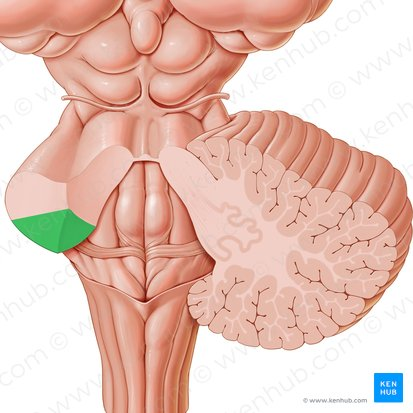
inferior cerebellar peduncle
medulla oblongata to cerebellum
superior cerebellar peduncle
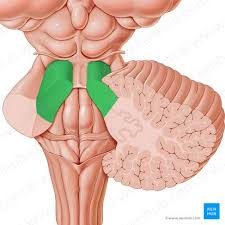
middle cerebellar peduncle
inferior cerebellar peduncle
limbic system
forms a ring around diencephalon
limbic system functions
structures process and experience emotions; affects memory formation through integration of past memories of physical sensations with emotional states
limbic system