Personality, Arousal, Anxiety and Attitudes only
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What is personality
personality is the sum total of an individuals characteristics which make them unique it is stable, enduring and unique to each individual
How can personality be used
Determine the way an individual responds to an environment
Involves: character, temperament etc.
How many theories are there
3
What is theory 1 => the trait perspective
trait = personality you’ve had from birth
traits are stable, enduring and consistent in all situations
Eysenck identified 4 primary personality traits and types. Introvert, extravert, stable and neurotic
What are the limitations of the trait theory
See traits as more fixed and long lasting than they really are
Have not been very useful in consistently predicting behaviour => can be unreliable
Fail to take into account the situation of an individual's behaviour or attitudes
Does not account for the fact that people adapt their behaviour in response to a particular environmental situation
The influence that the environment and other people have on the shaping of personality is not considered
What is theory 2 => the social learning theory
It proposes that all behaviour = learned through experiences and the opinions of other people
=> means that is is the function of an environment
Behaviour is learned when it is reinforced => learnt from significant others
What is theory 3 the interactionist theory
proposed by Hollander
there are 3 levels that interact to form the personality concentric ring
Role related behaviour = surface personality => in certain situations we may behave quite differently. E.g. as a player we may argue with the referee even if we have committed a foul, but as a student if you broke the rules would never argue with a teacher
Typical response = your usual response in most situations => the way in which we usually respond in certain environmental situations. Usually indicates your psychological core e.g. Stopping play when we hear the referee's whistle
Psychological core = The 'real you' => inner most point and is the beliefs and values that remain fairly permanent e.g. the value of fair play in sport
what is level 1 of the interactionist theory/role related behaviour
Role related behaviour = surface personality => in certain situations we may behave quite differently. E.g. as a player we may argue with the referee even if we have committed a foul, but as a student if you broke the rules would never argue with a teacher
What is level 2 of the interactionist theory/ typical response
Typical response = your usual response in most situations => the way in which we usually respond in certain environmental situations. Usually indicates your psychological core e.g. Stopping play when we hear the referee's whistle
What is level 3 of the interactionist theory/ Psychological core
Psychological core = The 'real you' => inner most point and is the beliefs and values that remain fairly permanent e.g. the value of fair play in sport
What is the interactionist view
combines the trait and social learning perspectives. It proposes that personality is modified and behaviour is formed when genetically- inherited traits are triggered by an environmental circumstance
What is behaviour and give an example
Function of personality X environment
E.g. A football player may be an introvert after the game but reveals extrovert qualities during the game
What is arousal
an energised state and a readiness to perform it is a state of activation experience by sports performer before and during activity/competition.
What are the benefits of drive
More drive you have the more chance of an increased performance due to increased effort
What does the drive theory suggest
Drive theory suggests that as arousal increases so does performance
The theory suggest that as arousal increases so does performance
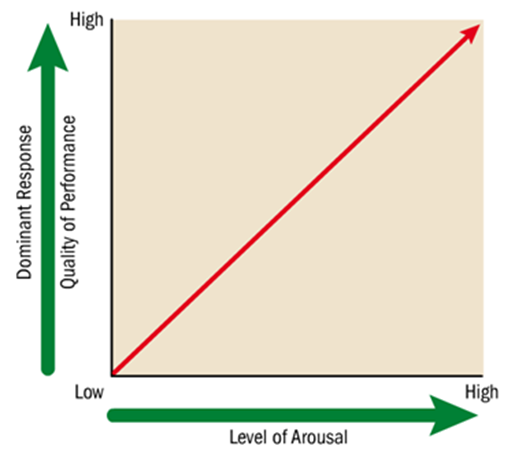
What is the limitation of the drive theory
However increased drive does not always improve performance
Our dominant response = the action we are most likely to produce, or habit
A novice learner = is more likely to make more errors as their arousal increases as their dominant response is not likely to the correct action
An expert stage learners dominant response is more likely to be the correct one => more likely to see improved performance as arousal increases
What is performance
a function of drive multiplied by habit
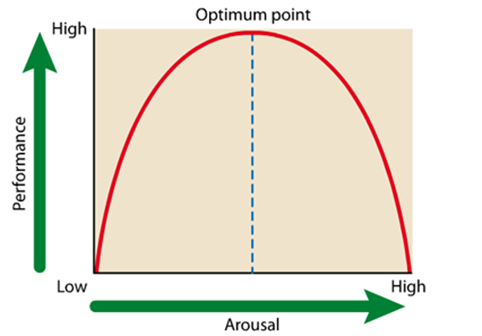
What is the inverted U theory and what does it suggest
This theory suggests that as arousal increases, so does performance => only to an optimal point
Any further increases in arousal can cause performance to deteriorate
Under-arousal and over-arousal can be equally bad for performance
the optimum level can vary depending on experience, personality and the task
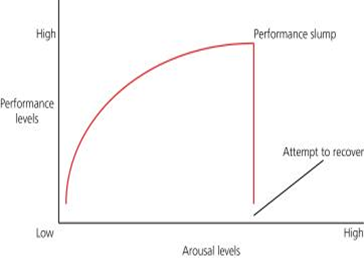
What is the catastrophe theory and what does it suggest
As arousal increases, so does performance until there is a sudden dramatic reduction in performance
This slump in performance is a combination or high levels of both somatic (physiological) and cognitive (psychological) anxieties
Somatic anxiety includes muscular tension and increased heart rate
Includes the loss of concentration and worrying about performance
The player can regain control by reducing anxieties which will help arousal and performance gradually return to the optimum
This is possible if the cause of the anxiety is mild and the performer has time to recover
What is the zone of optimal functioning
suggested by Hanin in 1986 that people respond differently to arousal
Some performers succeeded when arousal was high and some when it was low
Each athlete has their own preferred level of arousal
The athlete doesn't psych up to or over exceed the optimum threshold, they simply within or outside of the zone that is their individual preference
Athletes perform best when they are in the…..
ZONE
Performer is confident
Performer is calm
They feel in control of their actions
They are full focused

What is the peak flow experience
When the athlete experiences greatest happiness and self-fulfilment
Peak flow is an intrinsic experience felt when an athlete has a positive attitude, feels confident and is focused and efficient
What can the peak flow experience be disrupted by
Poor mental prep
Failure to reach optimum arousal
Pressure from the crowd
Frustration caused by ref. decision
Injury
Fatigue
What is anxiety
state of nervousness and worry
What are the 4 types of anxiety in sport
Trait = personality => genetic and stable
State = situation dependent
Cognitive = psychological => the irrational thinking or worries about performance => the performer may believe they do not have the ability to perform the task and therefore experience nervousness which can lead to a loss in concentration
Somatic = physiological => it is the response of the body. Symptoms include inc. HR, sweating, muscular tension and sickness
What is competitive trait anxiety
a personality trait when a player feels nervous in most sporting situations --> genetic and stable
what is competitive state anxiety
a response to a particular sporting situation a temporary rush of anxiety caused by a threatening circumstance e.g. taking a penalty
give an example of competitive state anxiety
An individual with a high trait anxiety is more likely to experience high state anxiety when faced with stressful situation, especially if others are watching or evaluating their performance.
what is cognitive anxiety
psychological => it is the irrational thinking or worries about performance. The performer may believe they do not have the ability to perform the task and therefore experience nervousness which can lead to loss in concentration
what is somatic anxiety
physiological = has an identical effect on performance as arousal does in the inverted-U theory.
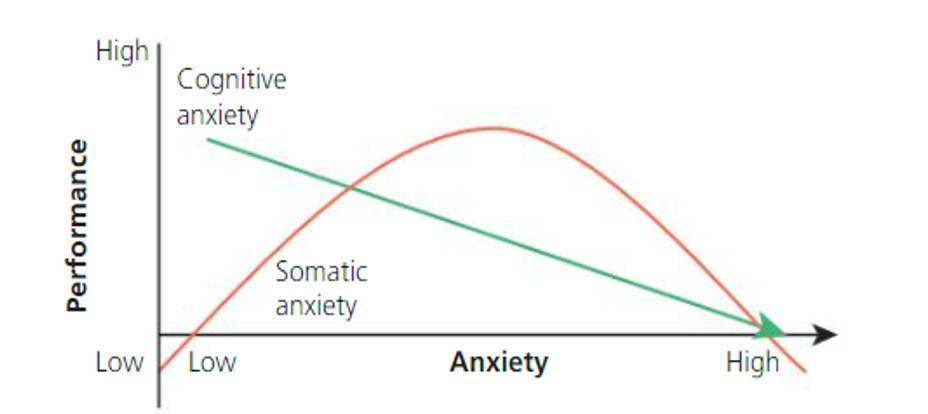
What does this graph show about cognitive and somatic anxiety when it comes to the inverted U theory
Increases in somatic anxiety improves performance up to a point => beyond which performance is impaired => cognitive anxiety has a negative effect on performance as cognitive anxiety increases, performance decreases.
How can you measure anxiety
Self-report questionnaires
Observation
Physiological testing
What are the strengths of questionnaires
Quick
Cheap
Efficient = large numbers that can be assessed quickly
What are the limitations of questionnaires
Players might not answer truthfully
Dependent on mood (answers can be given differently after they win or loose a match)
Time pressure could cause answers to be rushed => leading to incorrect answers
What are strengths of observations
True to life
what are some limitations to observations
Subjective (based on opinions)
Time consuming as prior knowledge of performer required
Performers can change behaviour if they know they are being watched
What are physiological measures
HR, inc. sweating, inc. respiration and hormone levels can be measured to assess anxiety
What are some strengths of physiological measures
Results = factual
Can be measured in both training and competition
Advanced in technology mean that HR can be measured by electronic devices within clothing and relayed immediately back to the coach
What are some limitations of physiological measures
Training is required to use devices
Costs may deter amateur performers
Wearing a device can restrict movement => affecting performance
If a performer is aware they are being measured is can lead to additional stress and false readings
What is attitude
is a mode of behaviour which is thought to be the typical response of an individual
they are associated with personality and are believed to influence a response or behaviour in a given situation
can be positive or negative
can be directed towards an object, person, place or event
A positive or negative attitude towards an object…
influences an individuals behaviour towards it
How are attitudes formed
Formed with experiences and socialisation
=> positive experience = positive attitude
=> negative experience = negative attitude
what is socialisation how is it learnt
when someone associates with others and picks up their opinions and values
Learnt from => friends, parents and role models
Can also stem from culture
What is the triadic model of attitudes
It consists of the cognitive component, the affect component and the behavioural component
What is the cognitive component
what you think -> represents your beliefs e.g. a performers belief in their ability to win a game
What is the affective component
your feelings or emotions e.g. enjoyment or dislike
What is the behavioural component
what you do and actions of the performer
What is the cognitive dissonance theory
Predicts that is a person has 2 different ideas there is emotional conflict or dissonance arises
E.g. if someone has a negative attitude towards exercise or sport, a coach can apply pressure by changing one attitude components to create dissonance or an uneasy feeling
which 3 components of attitude can be altered by coaches
Cognitive = coach gives player some new information
Affective = the coach makes sessions more enjoyable
Behavioural = using rewards and reinforcements for attending training
What is the persuasive communication theory
The individual has to have all of these elements to change someone's attitude

What are some strategies used by coaches to improve a performers attitude
Reward successful elements of a performance
Use positive role models
Give positive reinforcement for correct behaviour/attitude
Negative reinforcement for unacceptable behaviour
Ensure training is enjoyable to maintain enjoyment