OTA 102 MODULE 1
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:11 AM on 2/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
1
New cards
What is a 5150?
A three day or 72 hour hold
2
New cards
What is a 5250?
A hold up to 14 days
3
New cards
What is Sublimation?
The channeling of unacceptable desires into becoming socially acceptable activities
4
New cards
What is Displacement?
Redirecting feelings towards an object to another
5
New cards
Where did OT originate from?
The Moral Treatment Era & Arts and Crafts Movement
6
New cards
What is Mental Health?
A conditional well-being of an individual’s capability to know their potential, cope with normal life stressors, productively work and gain fruit from it, and contribute to their community.
7
New cards
What is Mental Illness?
An affliction known by the significant clincal disturbance within a person’s emotional regulation, cognition, or behavior that reflection dysfunction in developmental, psychological, or biological underlying mental functioning.
8
New cards
OT was shaped on the principles of moral treatment by?
To do no harm, giving a humane and comfortable environment to do a regular daily routine, the development of the idea of “self-restraint” with a reward system to increase confidence and self-esteem, respect of the person, and providing the oppurtnity to productively contribute to ones own care and community welfare by occupational involvement.
9
New cards
How did the Americans with Disabilities Act affect OT?
Allowed for new oppurtunities such as community mobility, mental health occupational therapy, supported housing, and working with consumers trying to gain access to employment. As well as qualified individuals would not be excluded from seeking work and employment due to their disability impairments.
10
New cards
What is the Community Mental Health Act of 1963?
The reinstitutionalization of patients with mental disorders from psych hospitals to community mental health centers. Resulted in deinstitutionalization and trans-institutionalization. Started with the use of tranquilizers that helped OT in treating people with mental illness.
11
New cards
What is the Mental Health Systems Act of 1980?
Legislation that gave support and funding for programs in community mental health to involve social support services, mental health care, and general health care. Later repealed in 1981 by the Regan Administration
12
New cards
What is the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990?
Mandate that says that people with a physical disablity or mental impairment who would be qualified to work not be excluded from employment.
13
New cards
Who is Mary Reilly?
Creator of the occupational behavior theory in the 60s, she believed that occupation is valuable in restoring health. And that by our psychological desire to occupation and balance play, work, and rest that there can be psychological growth based on experience, societal norms, and cultural beliefs.
14
New cards
Who were Gail and Jay Fidler?
Involved OT with Psychoanalytic theory and object relation theory when OT was criticized for not having a scientific backing in the scientific movement.
15
New cards
Who was Jean Ayres?
Founder of sensory integration theory
16
New cards
Who was Claudia Allen?
Founder of the theory of cognitive disabilities
17
New cards
Who was Gary Kielhofner?
Creator of MOHO or Model of Human Occupation
18
New cards
What is an EEG or Electroencephalography?
The use of electrodes placed on the scalp to measure and record the brain’s electrical activity.
19
New cards
What is a PET or Positron emission tomography?
The mapping of the brain’s functional processes by using trace amounts of short-lived radioactive material as it decays and releases a measurable proton
20
New cards
What is CT or Computed Tomography?
X-rays that reveal through scans the gross features of the brain.
21
New cards
What is fMRI or Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging?
Report of neural activity interacting with blood flow and oxygenation.
22
New cards
How did the Introduction of Psychopharamcology affect OT?
Tranquilizers, Direct Advertising to Consumers, Community Mental Health Act, Transintitutionalized Patients, SSDI & SSI concerns
23
New cards
Explain the Consumer Movement of 1979
The political effort of concerned professionals, consumers, and families to advocate for housing, supported employment, community care, reduced stigma, and mental health parity (equal treatment for physical and mental health) advocacy.
24
New cards
How did the Scientific Movement affect OT?
Needing to back the vaildity of OT, the profession developed concepts, terminology, and techniques related to psychoanalysis and patient’s unconscious needs. Regarding occupational studies later, the data of occupational nature is being researched and will further vaildate OT effectiveness.
25
New cards
What are the expected trends of OT practice in Mental Health?
Being able to respond to changes to reinmbursements and legislation for services, the aging population, the moment of services from hospitals to community based treatment, the movement of a disease to a health orientated mindset, and working on new oppurtinites in different populations.
26
New cards
What are the principles of Occupational Behavior from Moral Treatment?
Development of “self-restraint” by using rewards which increase confidence and self esteem. Eliminating the use of force. And providing a human and comfortable environment for clients.
27
New cards
What are the assumptions of Occupational Behavior from Moral Treatment?
That by creating a balanced daily program that pertained to work, leisure, and rest; patientsz with mental disabilities could be capable of the exercise of choice and autonomy.
28
New cards
What are the central themes of Occupational Behavior?
Prescription of daily routine and by treating the patient as an in with respect in order to develop attention and skills for occupation.
29
New cards
What is the Role of OT?
To remediate dysfunction of occupational role. Identify meaningful activities that are meaningful. Teaching adaptation methods and grading as needed activity demands.
30
New cards
What is service competency?
Performing at the same level or achieving the same results as an OTR in evaluation and in intervention.
31
New cards
What is the Role of the COTA?
Implements assessments and reports results of screening, evaluation, and reevaluation. Collabrates on the creation of intervention plan and performs treatment under supervision of the OTR.
32
New cards
What are the key concepts of Object relations theory?
People are born with drives for conservation, exploration, and pleasure. We form a relation with people and non-human objects that result from our environment which can affect our mental health. These relations are developing early in life and reflect patterns in adulthood. A therapist will analysis these symbols in dreams and their relationships in this theory.
33
New cards
What are the three parts of personality from the object relations theory?
ID, EGO, SUPEREGO
34
New cards
What are the key concepts of Behavior Theory?
Behavior is learned and depending on a consequence’s context will it be repeated. The context is dependent of a person’s perspective or a behavior’s function. When adaptive behavior is not reinforced and maladaptive behavior is reinforce will undesirable behavior will be seen in mental illness. When consequence is changed, so will abnormal behavior.
35
New cards
What is Reaction Formation?
Often excessive and overzealous making of a feeling to become its opposite to an extereme degree.
36
New cards
What is Converison?
Physical symptoms that are a result of real world conflicts
37
New cards
What is Intellectualization?
The control of thoughts that makes generalizations or uses abstract thinking excessively
38
New cards
What are the steps to implement a behavioral approach according to behavior theory?
First, one must identify the unwanted behavior. Next, determine how often or what circumstances the behavior occurs by establishing a baseline. Then by determining a method can the behavior be measured and recorded. By then selecting a reinforcement can you determine the reinforcement schedule to finally implement the program.
39
New cards
What are the methods in performing Behavior theory?
Chaining and Shaping
40
New cards
What are the key concepts of Client-centered/Humanistic therapy?
Humanity has the potention to guide their own growth and development, but due to lack of awareness of choices and feelings mental health problems occur. So mental health can be improved by the therapeutic relationship.
41
New cards
What is shaping?
Working on the end desired behavior between approximation or successive steps.
42
New cards
What is chaining?
One step at a time teaching of an activity with many steps. Can start with the first or last step.
43
New cards
What are treatment techniques regarding Client-centered/Humanistic therapy?
By having an open invitation to talk, one starts with asking open-ended questions and asking for clarity, responding very minimally that shows intrigue and encourages more dialogue, placing emotional content of the clients words, paraphrasing to understand and withholding judgement.
44
New cards
What are key concepts of Cognitive-behavior therapy?
Environmental experiences and social role models can shape and impact beliefs and thoughts. Our associated moods and thoughts from our automatic thoughts determine behavior and actions. An event is neutral. By creating our own experience of the world, awareness of thoughts of our experiences can impact mood, physical reactions, and behavior. By having maladaptive thoughts will maladaptive behavior occur.
45
New cards
What are the concepts of Environmental Experiences
How social models & environment shape and impact beliefs and thoughts. In which our automatic thoughts and their tied emotions will determine our behaviors and actions. Therefore creating out world experiences and can change them by awareness.
46
New cards
What are the six areas of adaptive skills?
Sexual identity, self-identity, group interaction, dyadic interaction, cognitive skill, and sensory integration.
47
New cards
What are the guiding principles of adaptive skills?
Making an environment that gives the ability to grow. The mastery of sub-skills is in developmental order. If normally acquired at the same age, sub-skills from another area simultaneously are worked on. The individual engages by having intrinsic motivation.
48
New cards
What are the techniques in role acquisition?
Patient participates in identifying problems and setting goals. They client’s roles, interests, and cultural values should be reflected in the goal. Just right challenge to facilitate optimal performance. As patient progresses, increase the challenge. Skills should be presented in natural developmental sequence. Orient patient each task including reason for task and expectations for completing task. Give feedback to evaluate performance. These skills should be generalized, practiced, and repeated. Present activites in context when possible and show parts of an activity that relate to whole activity. Good role model.
49
New cards
What are the four groups of social skills?
Comms, Assertive, Others-enhancing, & self-expressive skills
50
New cards
What are the phases of social skills training?
Motivation (Awareness and understanding why they are important), Demonstration, Practice, & Feedback
51
New cards
What is psychoeducation?
Skill acquistion taught in educational type setting with training and skill development in mental health
52
New cards
What is Sensory Intergration?
The collabration of all senses to give data for accurate perception and motor action
53
New cards
What are the senses identified in sensory intergration?
Taste, Touch, Smell, Proprioception, Vestibular, Vision, Hearing
54
New cards
Describe the posture of a schizophrenic
Lordosis in spinal S-Curve, Difficulty raising arms above heavy, shuffling gait, inflexibility of shoulders and neck to extend back or rotate, changes in hand, and poor resting posture.
55
New cards
What is spontaneity of movement regarding sensory integration?
Move without having to plan the action of movement. Focus on outcome instead of movement.
56
New cards
What is the three stage process of Psychosocial Rehab?
Diagnosis, planning, & intervention
57
New cards
What is Sensory Modulation Disorder?
The capability to regulate and self-organize responses to senory inputs.
58
New cards
What is dyspraxia?
Difficulty in performance of movements that are cooridinated.
59
New cards
What is MOHO?
The parts of occupational behavior that allow occupations to perform and to perform well.
60
New cards
What are assumptions of MOHO?
Complex is human occupation, with component parts that interact. Humans are born to explore and master their environment. Thus by continually acting and getting new data, actions can change and adapt to surroundings.
61
New cards
What are the subsystems of MOHO?
Volition, Habituation, Performance Capacity
62
New cards
What is Habituation in MOHO?
The habits and roles of an individuals that are rountine and stable.
63
New cards
What is performance in MOHO?
The personal narrative of the experiences we have lived and the capabilities of physical and mental of an individual.
64
New cards
What is underweight according to BMI?
less than 18.5 kg/m^2
65
New cards
What is the average weight according to BMI?
18\.5-24.9 kg/m^2
66
New cards
What is overweight according to BMI?
25\.0-29.9 kg/m^2
67
New cards
What is Obesity class I according to BMI?
30\.0-34.9 kg/m^2
68
New cards
What is Obesity Class II according to BMI?
35\.0-39.9 kg/m^2
69
New cards
What is Obesity Class III according to BMI?
more than 40 kg/m^2
70
New cards
What is the average waist size for women?
88 cm
71
New cards
What is the average waist size for men?
102 cm
72
New cards
What is the environmental aspect of MOHO?
That depending on one’s surroundings; that being demands and oppurtunites taken and presented can influence occupational performance.
73
New cards
What are the levels of cognition?
Automatic Actions, Postural Actions, Manual Actions, Goal directed Actions, Exploratory Actions, and Planned Actions
74
New cards
What is Level 1: Automatic Actions?
All basic needs must be met by a caregiver.
75
New cards
What is Level 2: Postural Actions?
The requirement of 24-hour supervision; as the patient is dependent on care provides due to significant disability of all cognitive skills.
76
New cards
What is Level 3: Manual Actions?
The requirement of 24-hour supervision. Daily care with full assistance with cognitive skills, social skills, and language and memory impairment.
77
New cards
What is Level 4: Goal directed actions?
Daily care is physically indepent but requires assistance to live in community with initiation or monitoring of quality care. Needs assistance with all cognitive skills, memory challenges, precautions on danger and consequences.
78
New cards
What is Level 5: Exploratory Actions?
Independent in daily care, may need help with finances, organization skills, and decision making. Subtle problems with memory and is comfortable learning new data.
79
New cards
What is Level 6: Planned Actions?
Comfortable learning information, is independent in daily care, decision-making skills, and finances.
80
New cards
What are psychosocial treatment settings?
Long-term, prison, partial day programs, acute in-patient hospitals, gero-psych, clubhouse model, partial day programs, home health care, & adult day health care.
81
New cards
What are safety considerations in psych settings?
Awareness of supplies, restricted items, potiental dangers, fire code, escape route, safety equipment, surroundings, food safety, medication side effects, proper body mechanics, assualt, suicide, and electrical technology.
82
New cards
Why are groups used in OT?
Interdependent relationships, sense of belonging, oppurtunities for modelling behavior & social interaction, cost effective, peer support, and feedback.
83
New cards
Types of groups that are used in OT?
Assertiveness, grooming, cognitive, self-esteem, physical, & IADLs
84
New cards
What should we consider when developing a group?
Safety considerations, supplies, location, goals, size, & admission criteria
85
New cards
What are the types of group leadership?
Directive & Facilitative
86
New cards
What are Mosey’s groups
Parallel, project, egocentric cooperative, cooperative, & mature
87
New cards
What is a parallel group?
Indiviuals working solo projects in proximation with each other with limited interaction and leader defining the task and giving the needed help and support.
88
New cards
What is a project group?
Group works together on short term task that is emphasized on the completion accomplishment.
89
New cards
What is an egocentric cooperative group?
Long term group activites that require cooperation, sharing, and increased interaction. Being aware of others and their behavior effecting others begin and assuming responsibility. Having the leader foster cooperation and guidance.
90
New cards
What is a cooperative group?
Organized groups of homogenous goals and interests, to which the members and the interpersonal relationships that they create see the need in having others to support their own needs.
91
New cards
What is a mature group?
Leader is a co-equal member
92
New cards
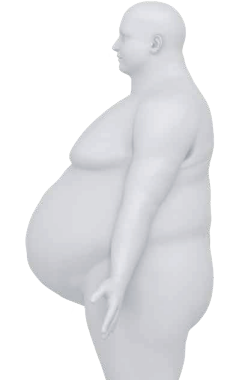
What is the body type of Apple ascites?
Excessive abdominal adipose tissue centered around the abdoment with anterior distention
93
New cards
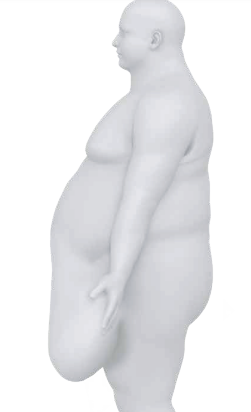
What is the body type of Apple pannus?
Excessive abdominal adipose tissue with drift inferiority to high level
94
New cards
What is the body type of Pear abducted?
Excessive adipose tissue dominates in medial thigh resulting in lower extremity abduction
95
New cards
What is the body type of Pear adducted?
Excessive adipose tissue dominates in lateral thighs and lower extremities allowing LE adduction
96
New cards
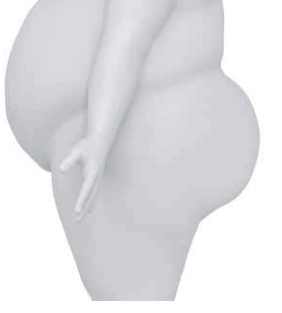
What is the body type of Gluteal shelf?
Excessive adipose tissue protrudes posteriorly at the level of the gluteus
97
New cards
What is the body type of Posterior adipose?
Excessive adipose tissue distrubted on posterior trunk at thoracic to lumbar regions
98
New cards
What are the guiding principles of recovery?
Hope, Person driven, many pathways, hollistic, peer support, relational, culture, addresses trauma, strengths/ responsiblities, and respect