DSA23 - Physiology of Pregnancy + Prenatal Care
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
-Sperm sends 10 hrs to get from vagina to ampulla of fallopian tube to fertilize
-300 million enter vagina, but 3 million get to uterus --> Less than 500 encounter ovulated egg
-Only 1 Sperm needs to bind to protein receptors in zona pellicuda ==> Penetration takes 20 mins
How does a sperm eventually fertilize an egg?
Once the egg is fertilized, the membrane rapidly changes electrical charge (effectively demagnetizing) so that all other competing sperm drop off --> 5 mins later, more permanent chemical blocking occurs
How does a fertilized egg stop other sperm from fertilizing it?
1
Fertilization can occur within () day(s) of ovulation
6
Implantation occurs at least () days after fertilization
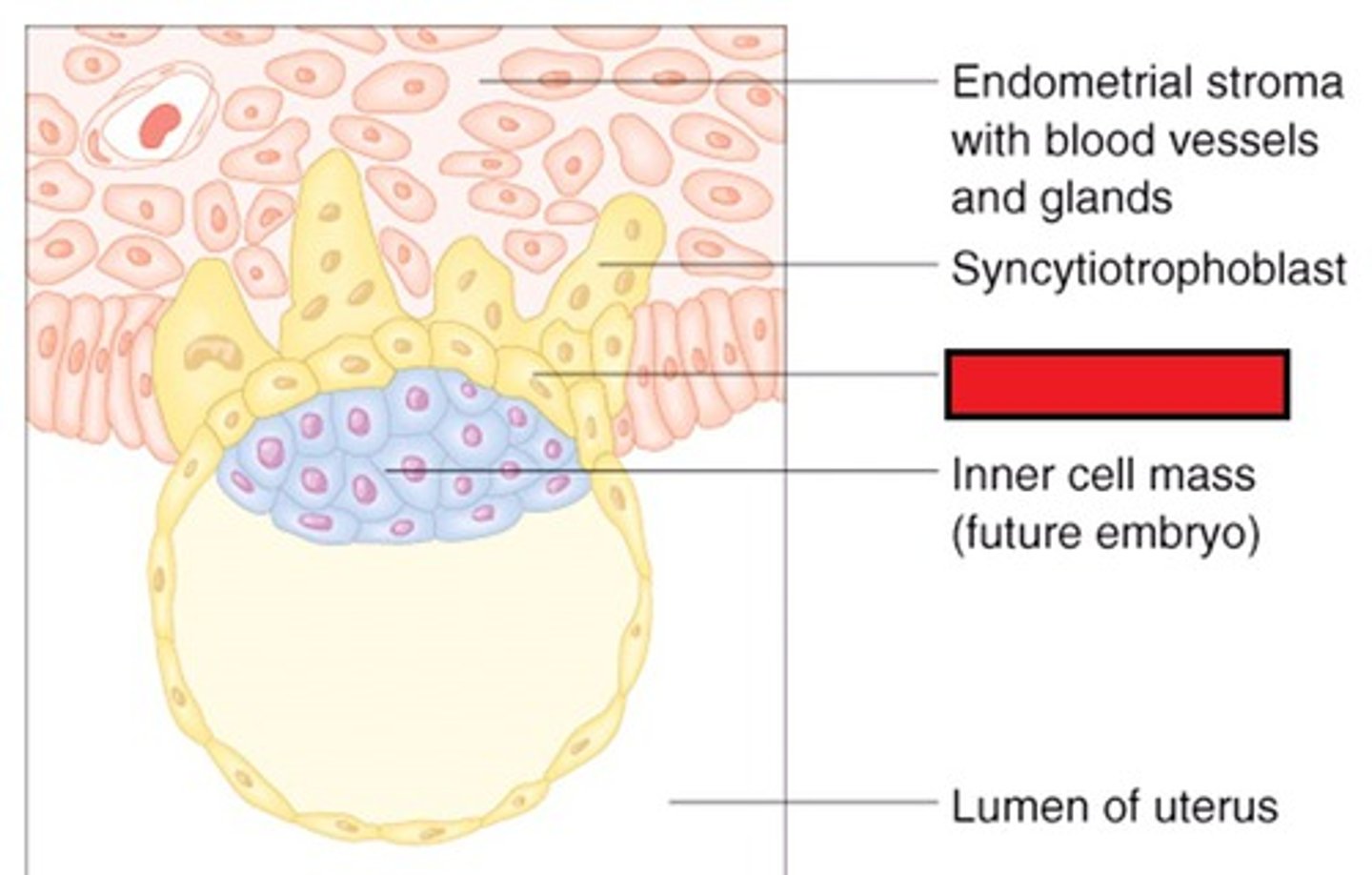
Syncytiotrophoblasts; 1; 2
() begin hCG secretion, causing it to be detectable in serum () week(s) after conception then detectable in urine () week(s)
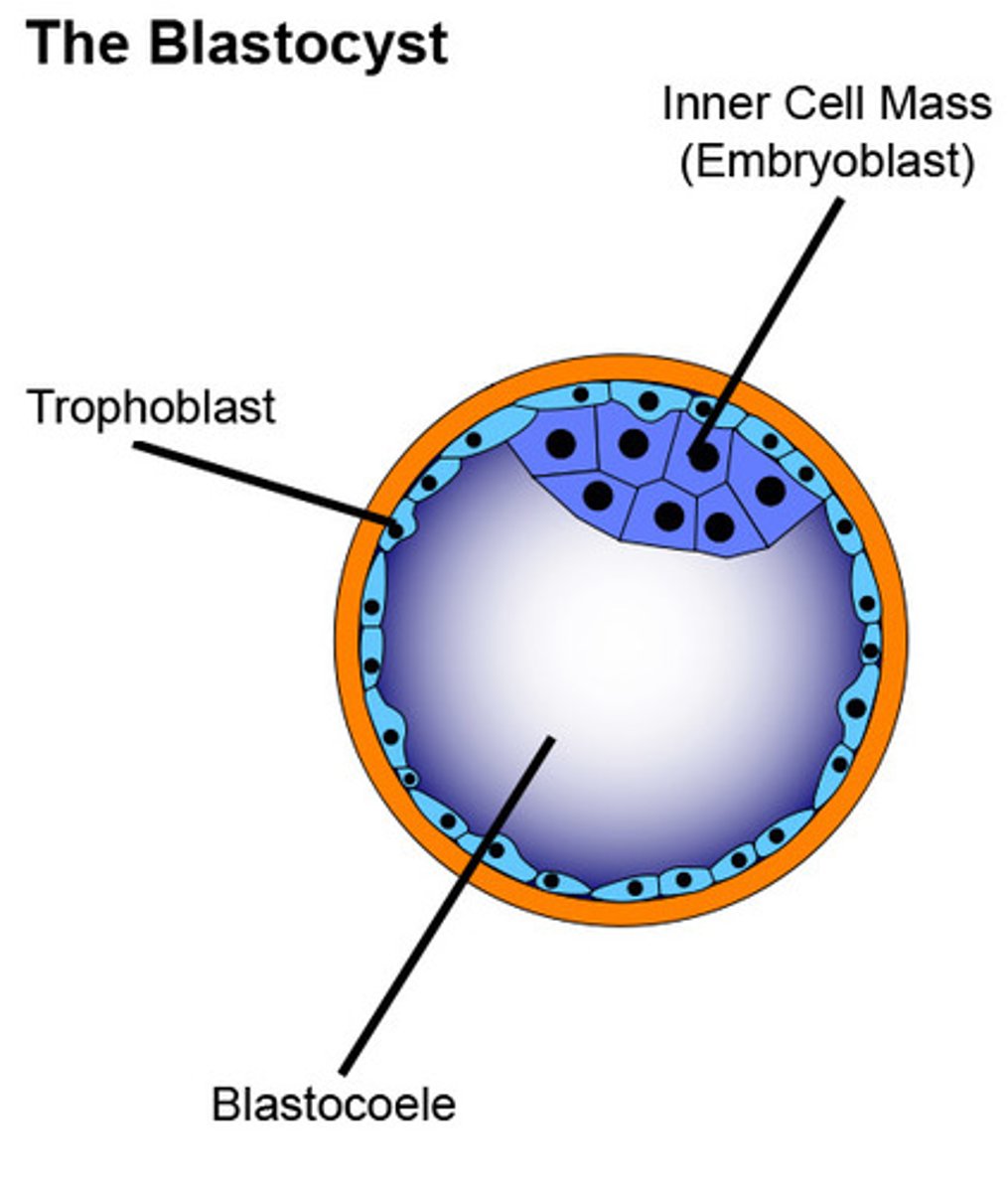
-Blastocyst implants
-hCG secretion starts
By week 1 (since fertilization), what occurs in early fetal development?
•Maintains corpus luteum (and thus progesterone) for first 8-10wks of pregnancy by acting like LH (otherwise no luteal cell stimulation --> abortion)
•α subunit is identical to that of LH, FSH, and TSH (high hCG can cause hypERthyroidism)
What is the function of the human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)?
Placenta makes its own estriol & progesterone --> corpus luteum degenerates
If hCG maintains corpus luteum for the first 8-10 wks of pregnancy, what happens after this?
-Multiple gestations
-Molar pregnancy
-Choriocarcinoma
-Down syndrome
HIGH hCG may indicate what?
-Ectopic/Failing pregnancy
-Edwards syndrome (Tr 18)
-Patau syndrome (Tr 13)
LOW hCG may indicate what?
8-10; delivery
hCG peaks at () weeks, while human placental lactogen, prolactin, progesterone and estrogen peak at ()
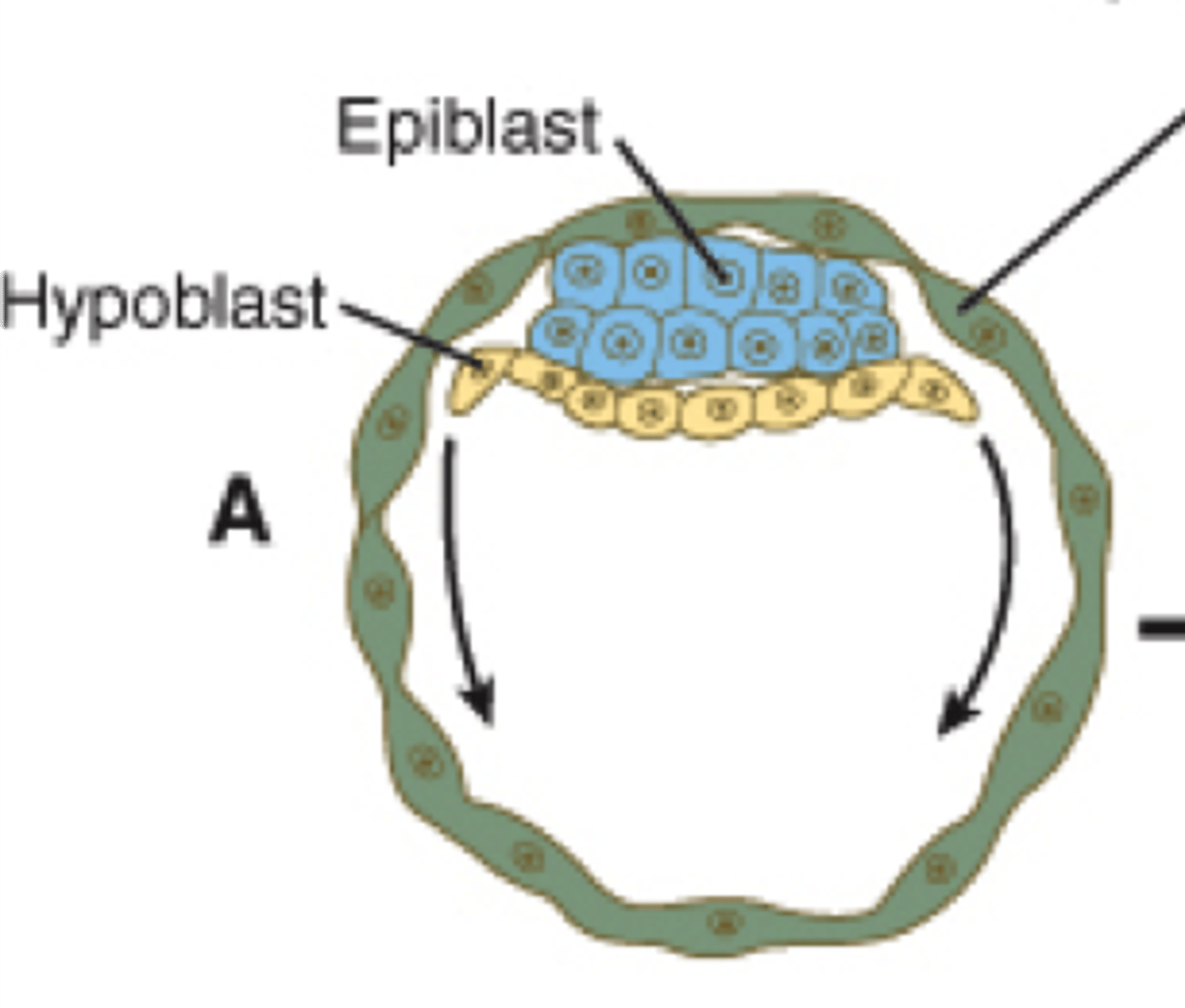
2 layers form: bilaminar disc = epiblast, hypoblast
By week 2 (since fertilization), what occurs in early fetal development?
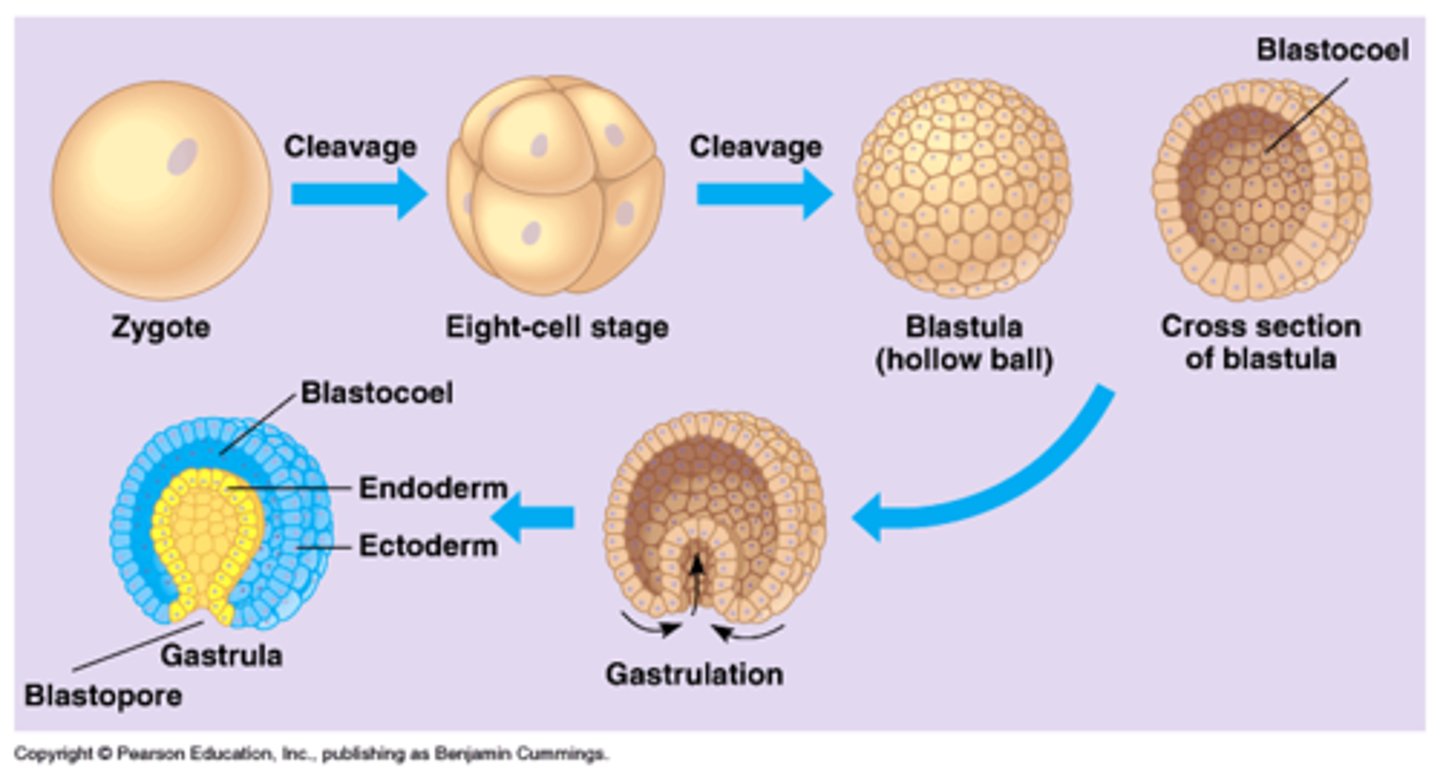
3 layers formed by gastrulation (endo, meso, ecto) + Notochord & Neural plate formed
By week 3 (since fertilization), what occurs in early fetal development?
EMBRYONIC PERIOD
-Neural tube formed by neuroectoderm (closes by week 4)
-Organogenesis
-Embryo EXTREMELY SUSCEPTIBLE TO TERATOGENS
Between weeks 3 thru 8 (since fertilization), what is occurring? Why is this important?
Heart beats & Limb buds form
By week 4 (since fertilization), what occurs in early fetal development?
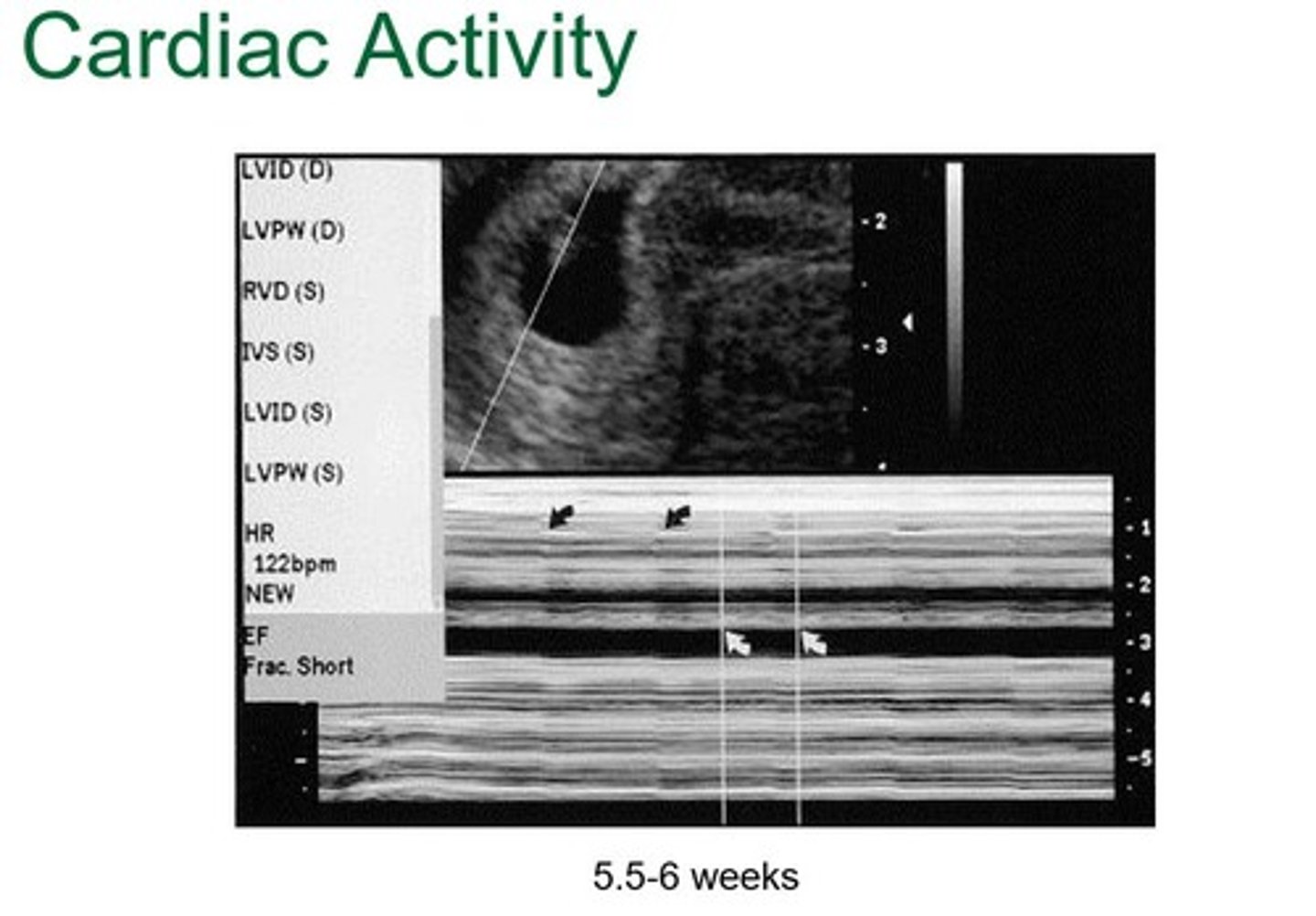
Fetal cardiac activity visible by transvaginal US
By week 6 (since fertilization), what occurs in early fetal development?
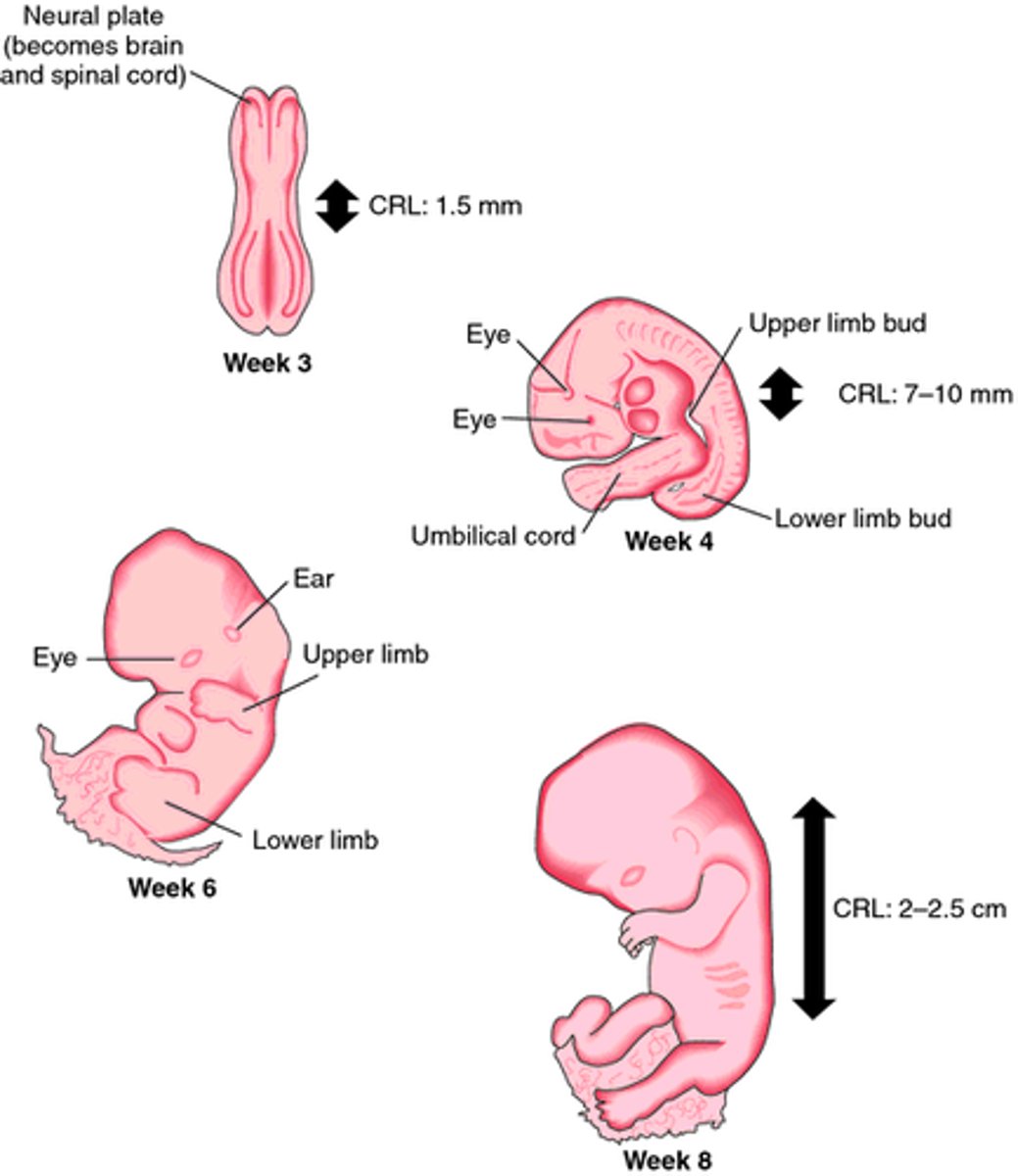
Fetal movements start
By week 8 (since fertilization), what occurs in early fetal development?
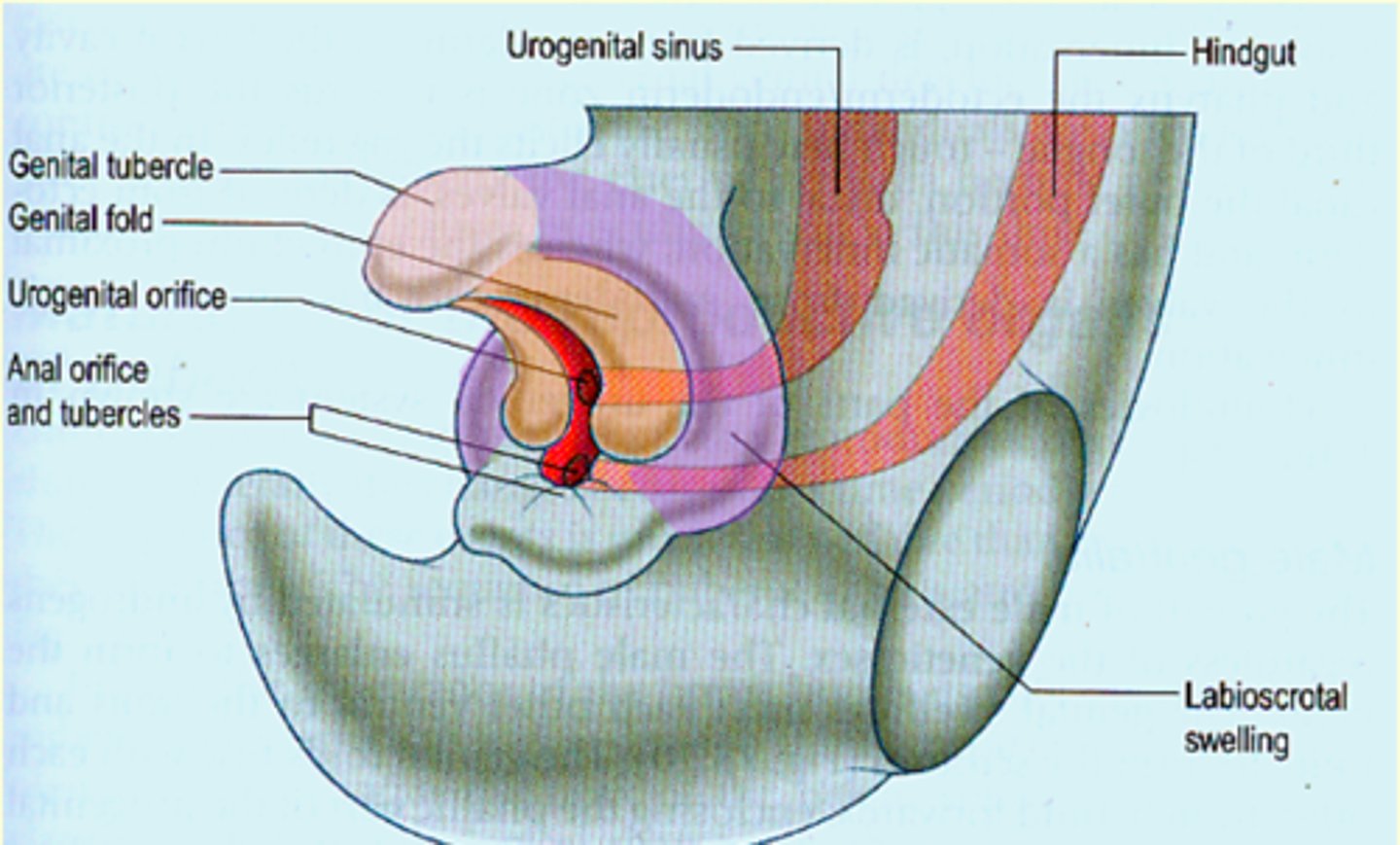
Genetalia may have male/female characteristics
By week 10 (since fertilization), what occurs in early fetal development?
Cytotrophoblasts
What is the cell layer of the fetal side of the placenta that:
> Is closest to the fetus
> Makes up the INNER layer of chorionic villi
> Makes cells?
Syncytiotrophoblasts
What is the cell layer of the fetal side of the placenta that:
> Makes up the OUTER layer of chorionic villi
> Makes hCG
> Lacks MHC-I (less chance of maternal attack)?
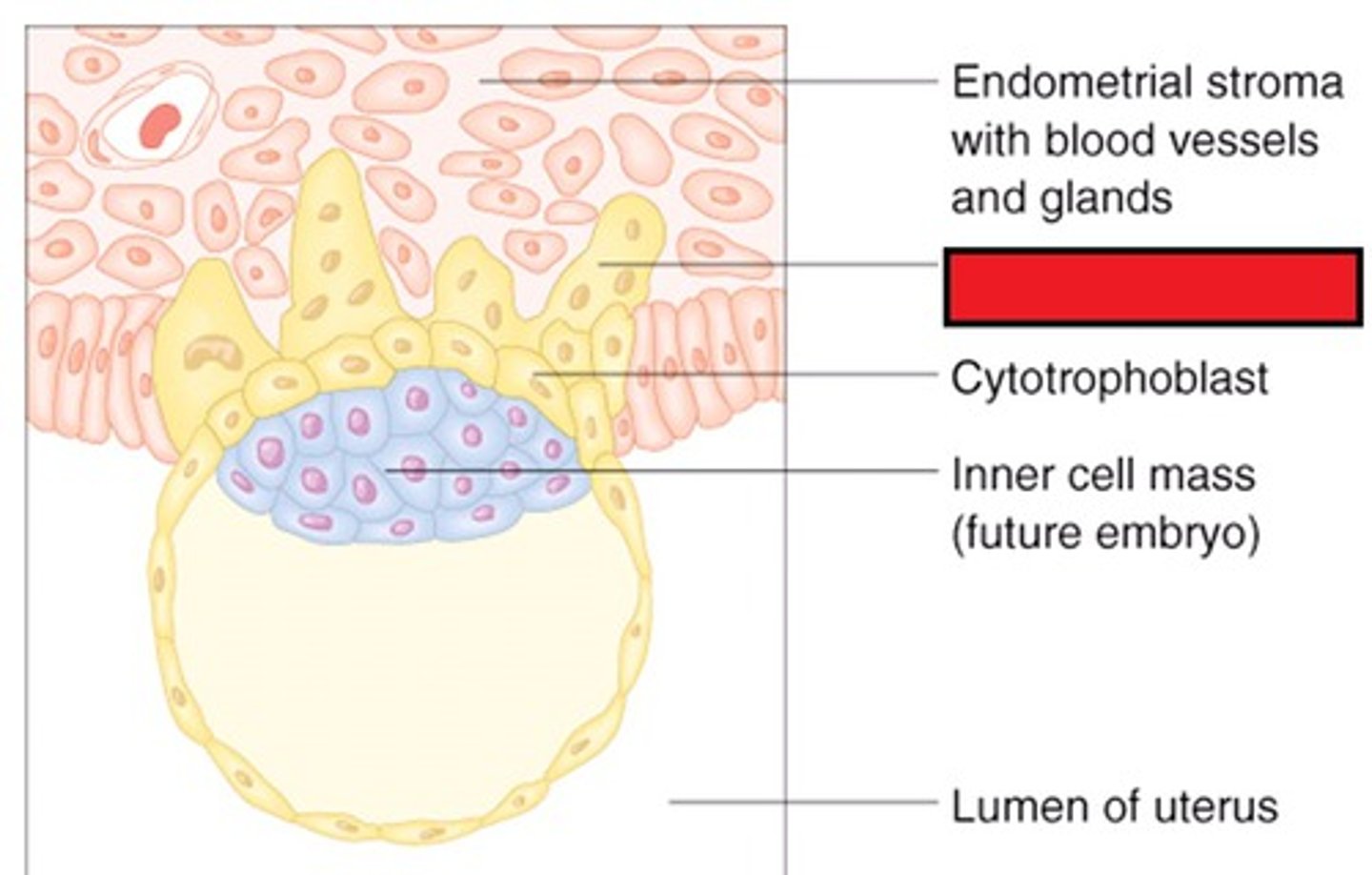
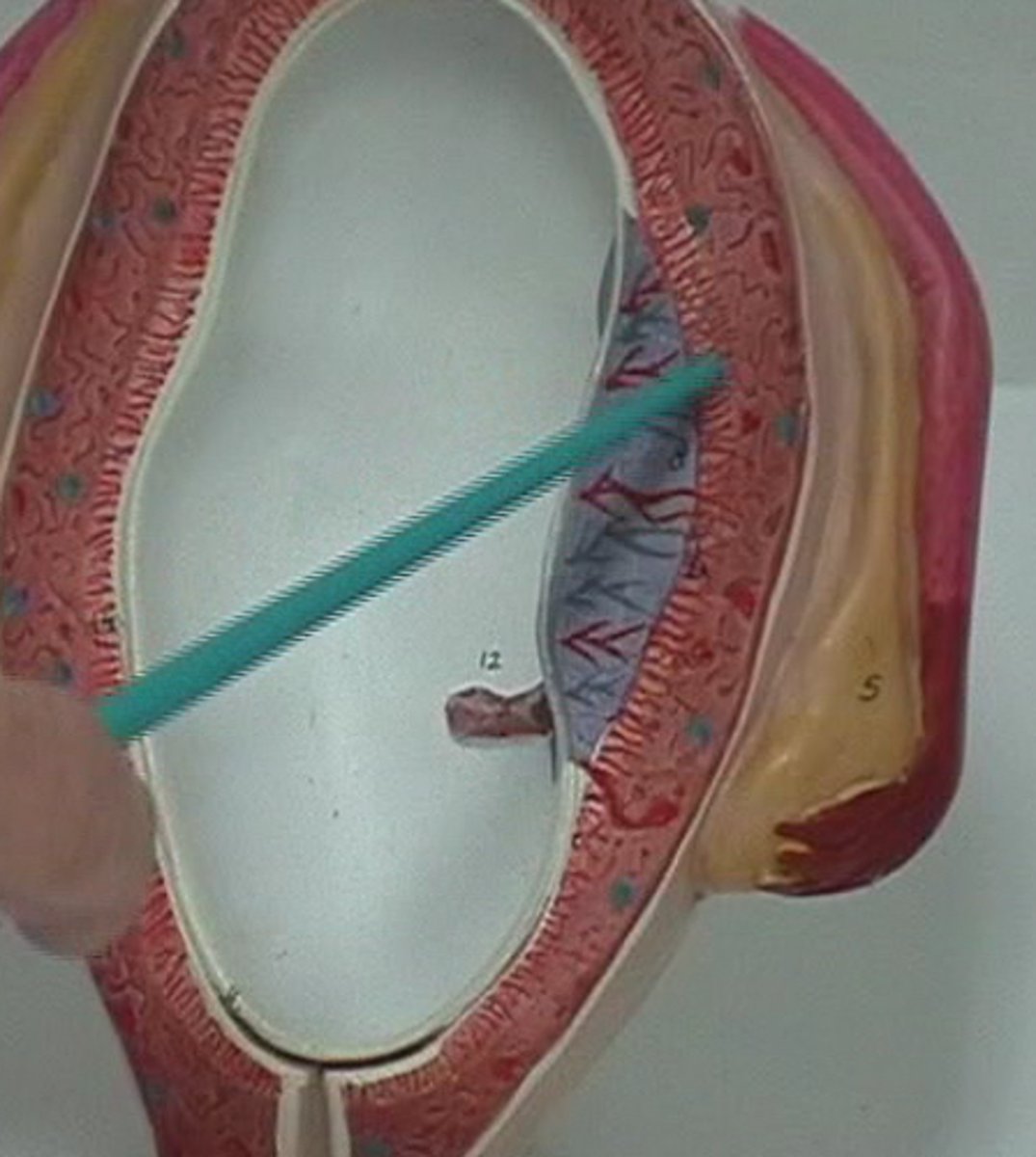
Decidua basalis
What is the cell layer of the MATERNAL side of the placenta that is derived from endometrium?
Delivers oxygen-rich blood from mom to baby (drains into IVC via liver/ductus venosus)
What is the function of the umbilical vein?
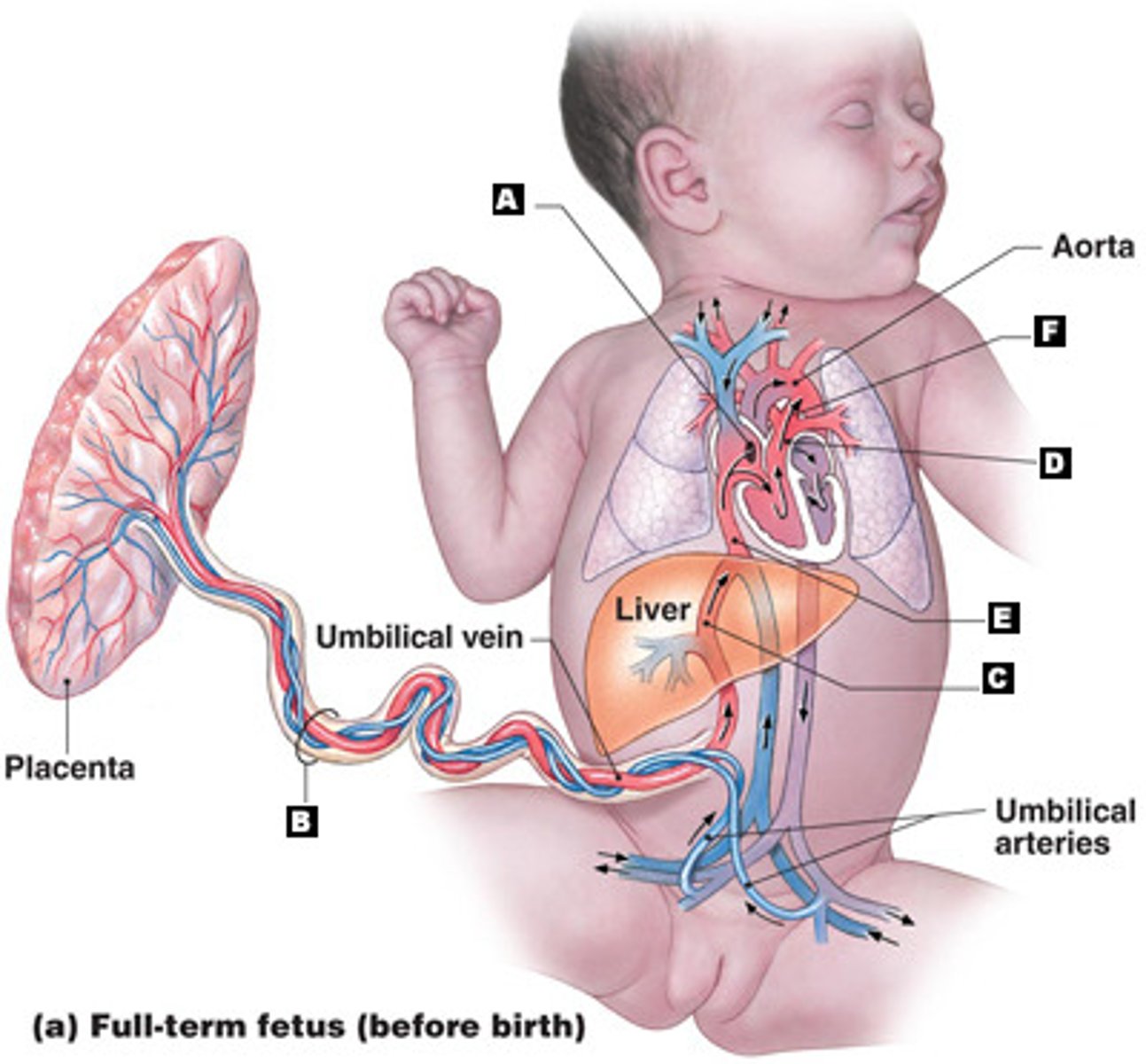
Returns oxygen-poor blood from baby to mom (from fetal internal iliac arteries to placenta)
What is the function of the umbilical artery?
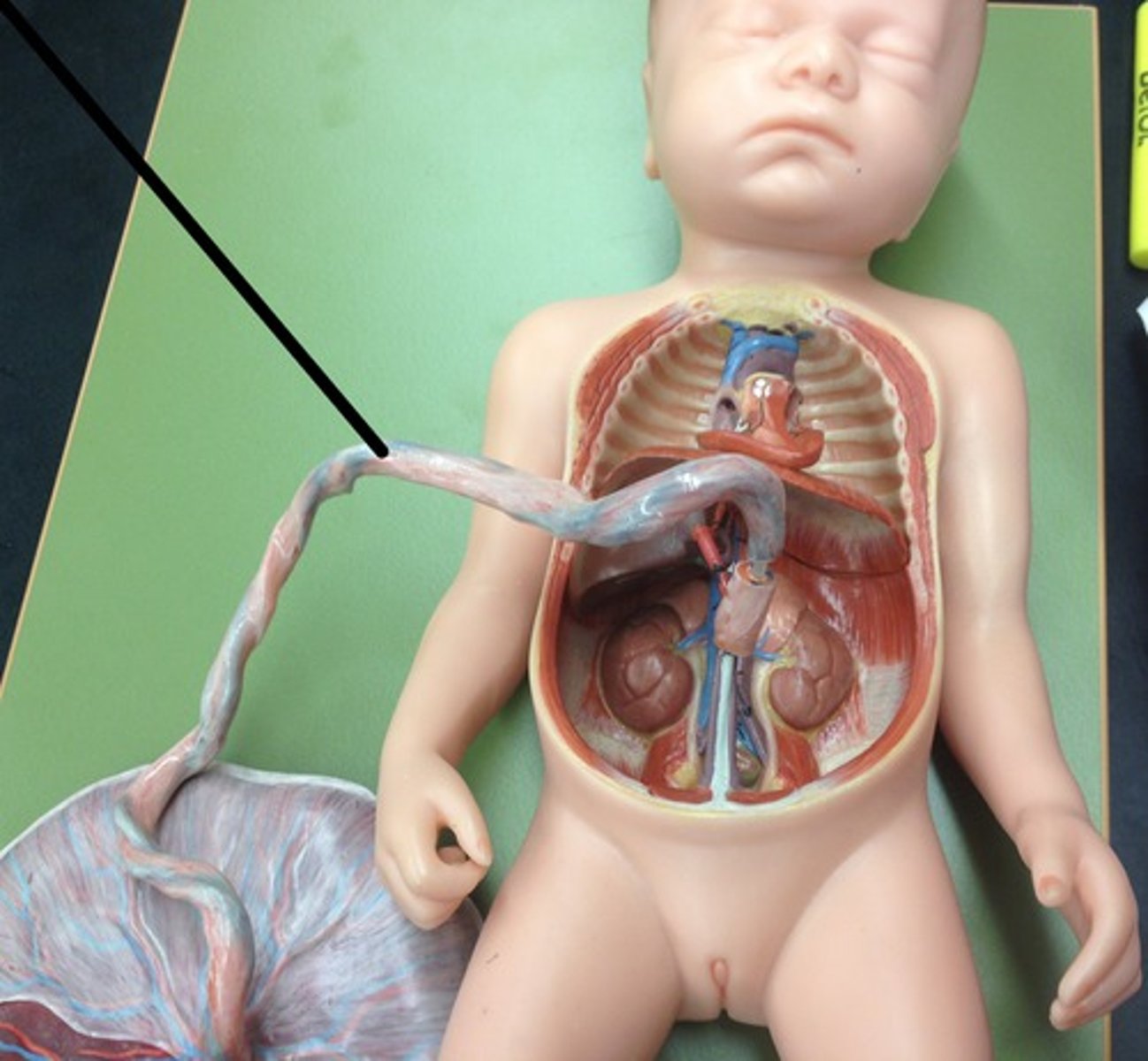
Allantois; Single umbilical artery (2 vessel cord) is a/w congenital and chromosomal abnormalities
From what are umbilical vessels derived? What is the clinical correlate for this?
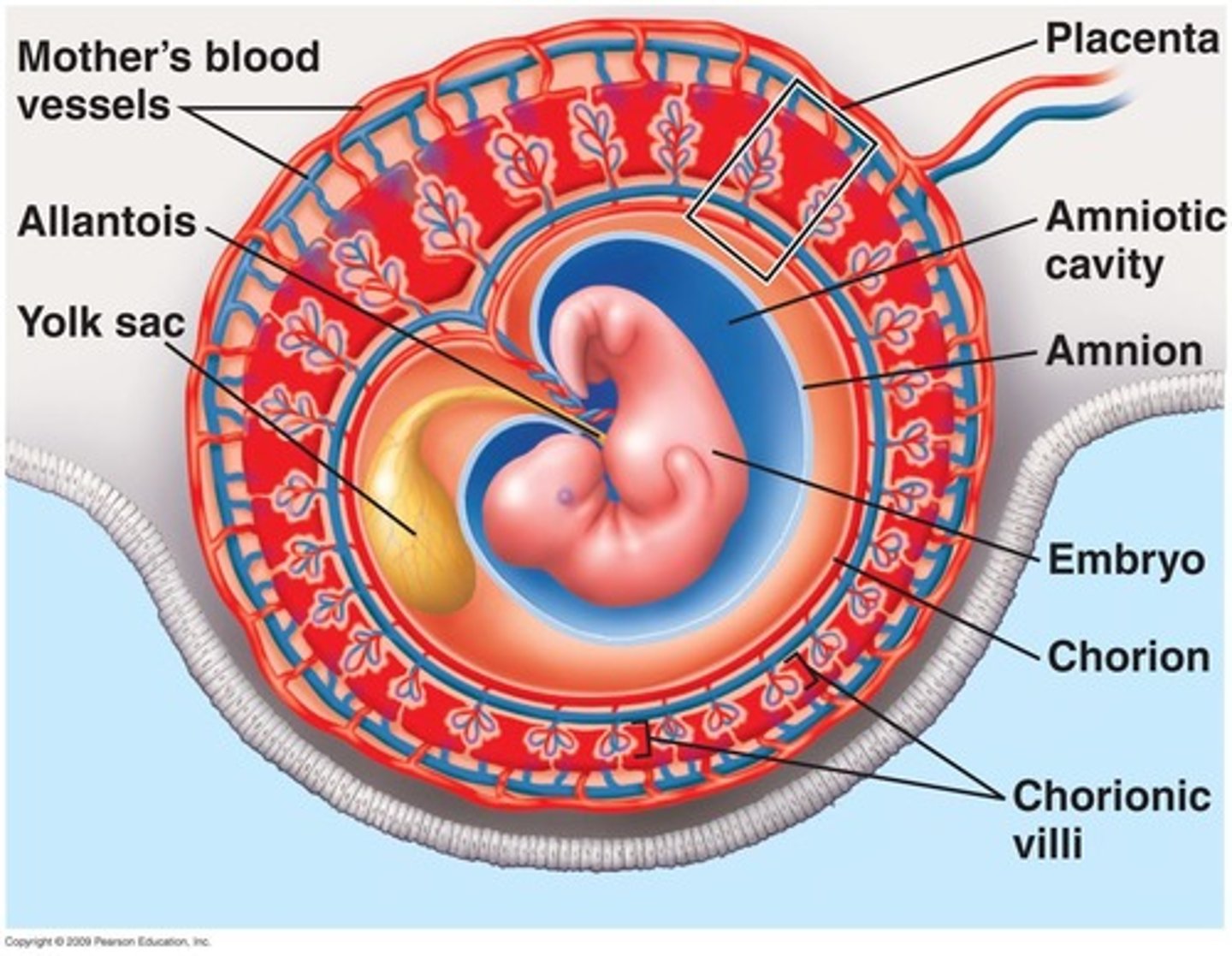
-Increased GFR
-Increased Cardiac Output (More Preload, Less Afterload, Increased HR --> to perfuse uterus/placenta)
-Physiologic Anemia (More plasma than RBCs)
-Hypercoagulability (to decrease blood loss at delivery)
-Hyperventilation (eliminate fetal CO2)
-More lipolysis and fat utilization (maternal HypOglycemia + insulin resistance --> glucose & AAs preserved for fetus)
-Suppress maternal immune system (prevent attack on fetus)
What are physiologic changes that occur during pregnancy?
Perinatal morbidity & mortality increase substantially due to earlier delivery
What is a risk of multiple gestations?
Zygosity (MONOzygotic more complicated)
Prognosis & Expected Morbidity of twins is strongly dependent on what?
•2 eggs fertilized by 2 different sperm
•Will have 2 zygotes, 2 amniotic sacs, 2 separate placentas (chorions)
•STRONGLY INFLUENCED by FHX & ETHNICITY!!
•"Siblings in utero simultaneously"
Define Dizygotic gestation (80% of twin pregnancy)
Discordant fetal gender & lambda sign
What are the US signs for Dizygosity/Dichorionic (2 placentas)?
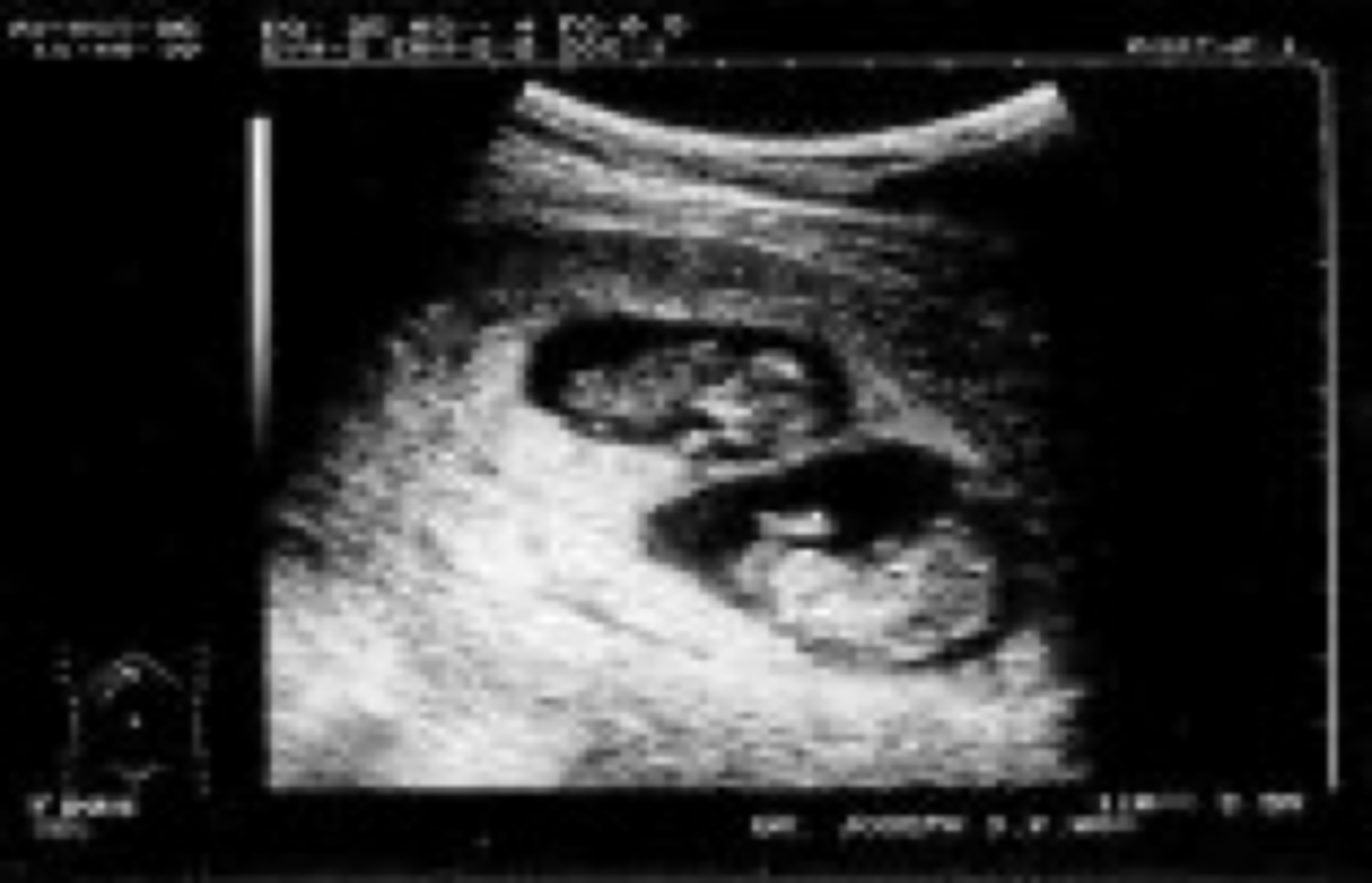
•1 egg fertilized by 1 sperm followed by cleavage of embryo into 2 zygotes
•Arrangement of fetal membranes/placentas depends on timing of split
Define Monozygotic gestation (20% of twin pregnancy)
Dichorionic-Diamniotic (Thick, 4-layered intervening membrane)
If the split in Monozygotic gestation occurs between Days 0-4/FIRST 72 HRS (25%), what type of arrangement of the fetal membranes/placenta occurs?
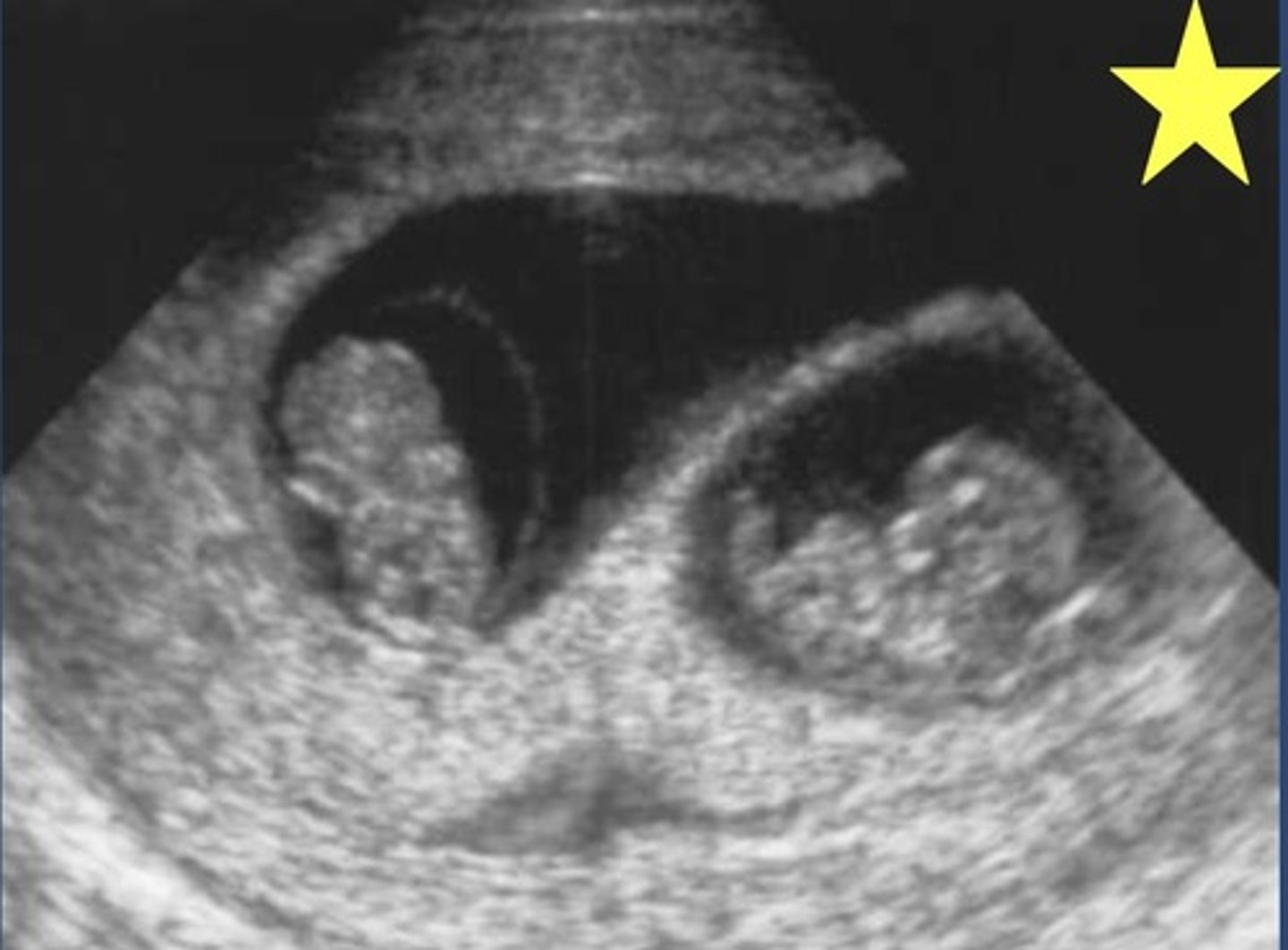
T Sign
What are the US signs for Monochorionic (aka one placenta)?
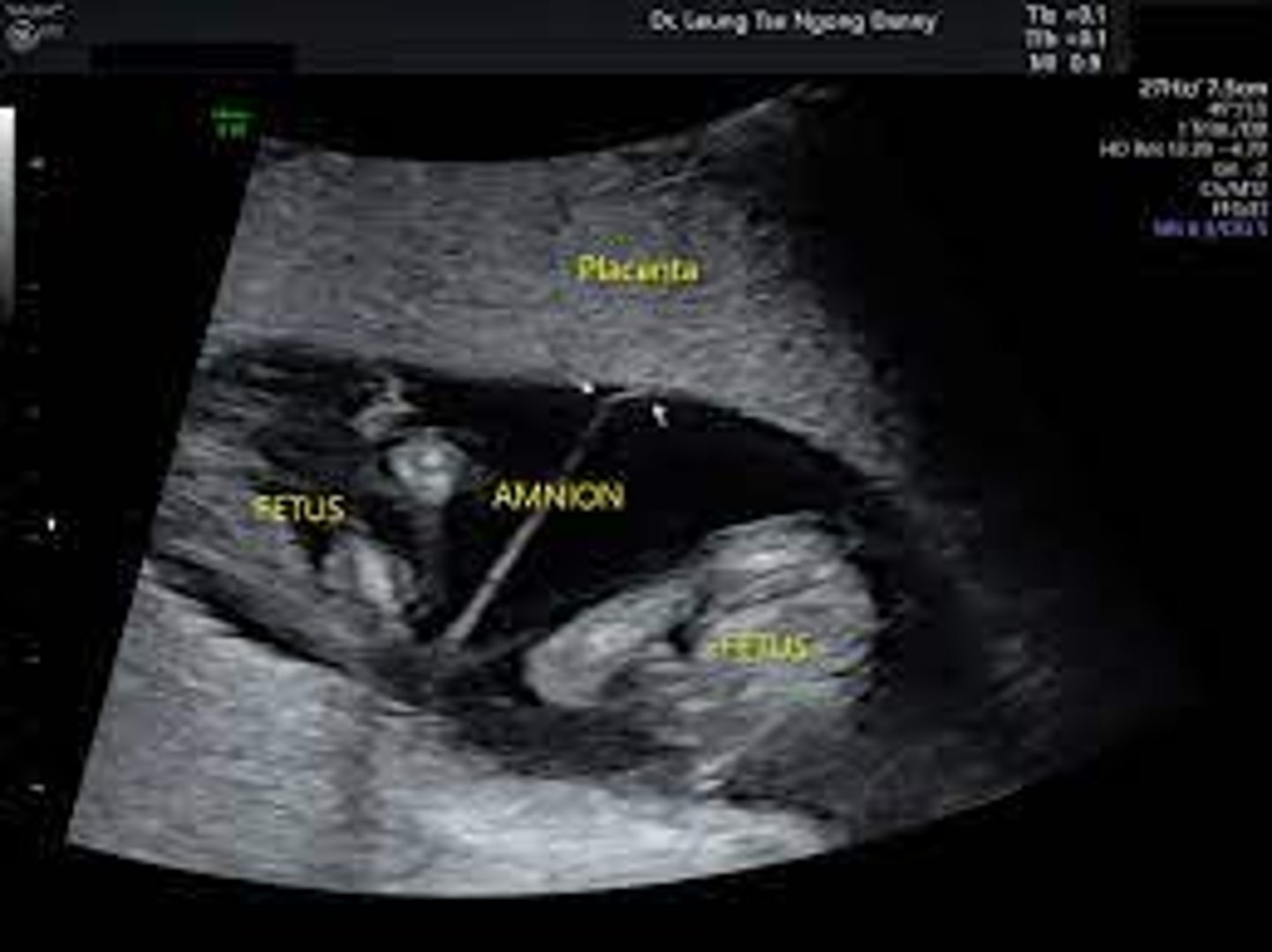
Monochorionic-Diamniotic (Chorion already formed + thin, 2-layer septum)
If the split in Monozygotic gestation occurs between Days 4-8 (75%), what type of arrangement of the fetal membranes/placenta occurs?
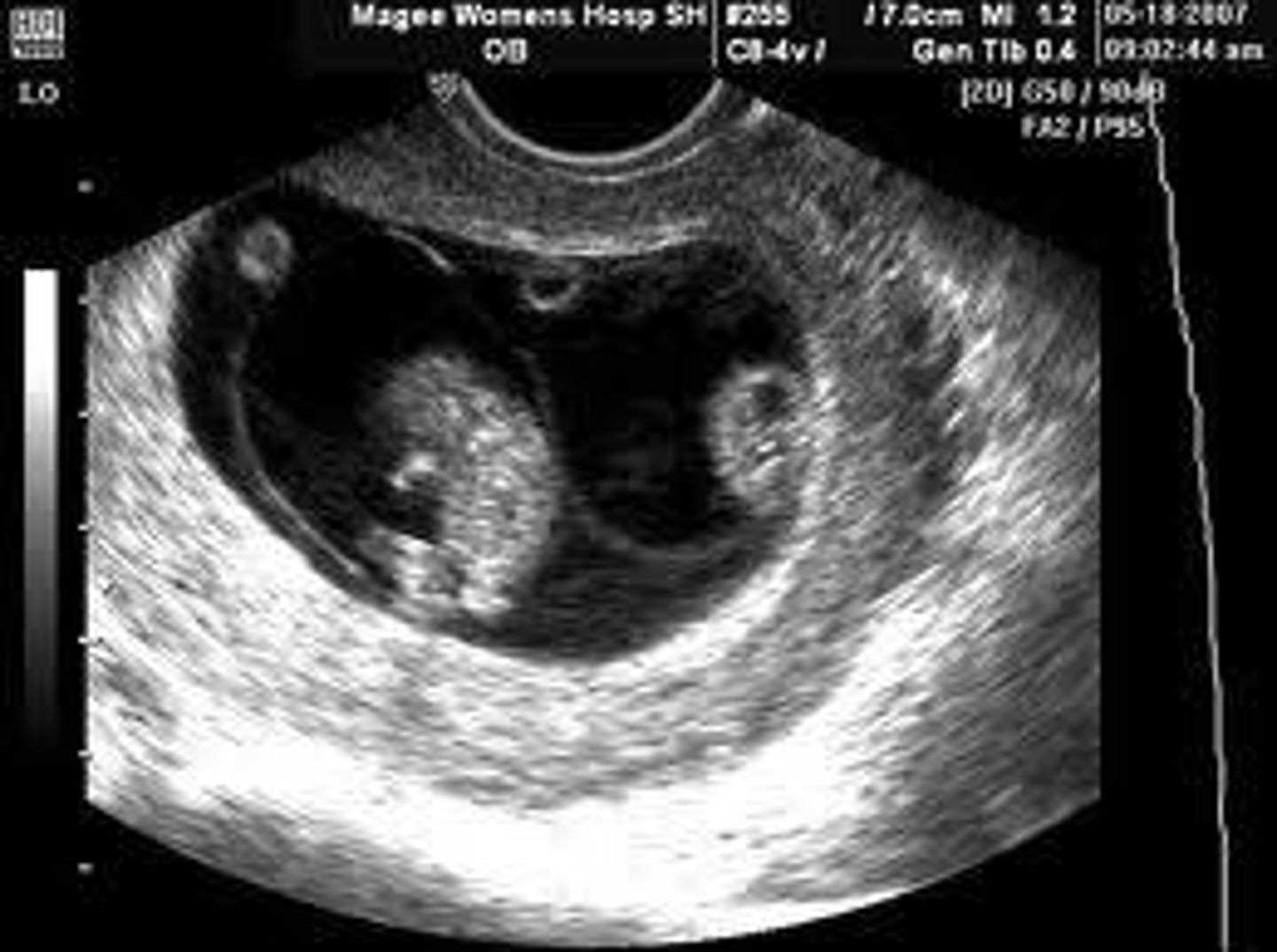
Monochorionic-Monoamniotic (Both Chorion & Amnion already formed = single sac w/ no septum) --> RISK OF CORD ENTANGLEMENT (Mortality = 50%)
If the split in Monozygotic gestation occurs between Days 8-12 (< 1%), what type of arrangement of the fetal membranes/placenta occurs?
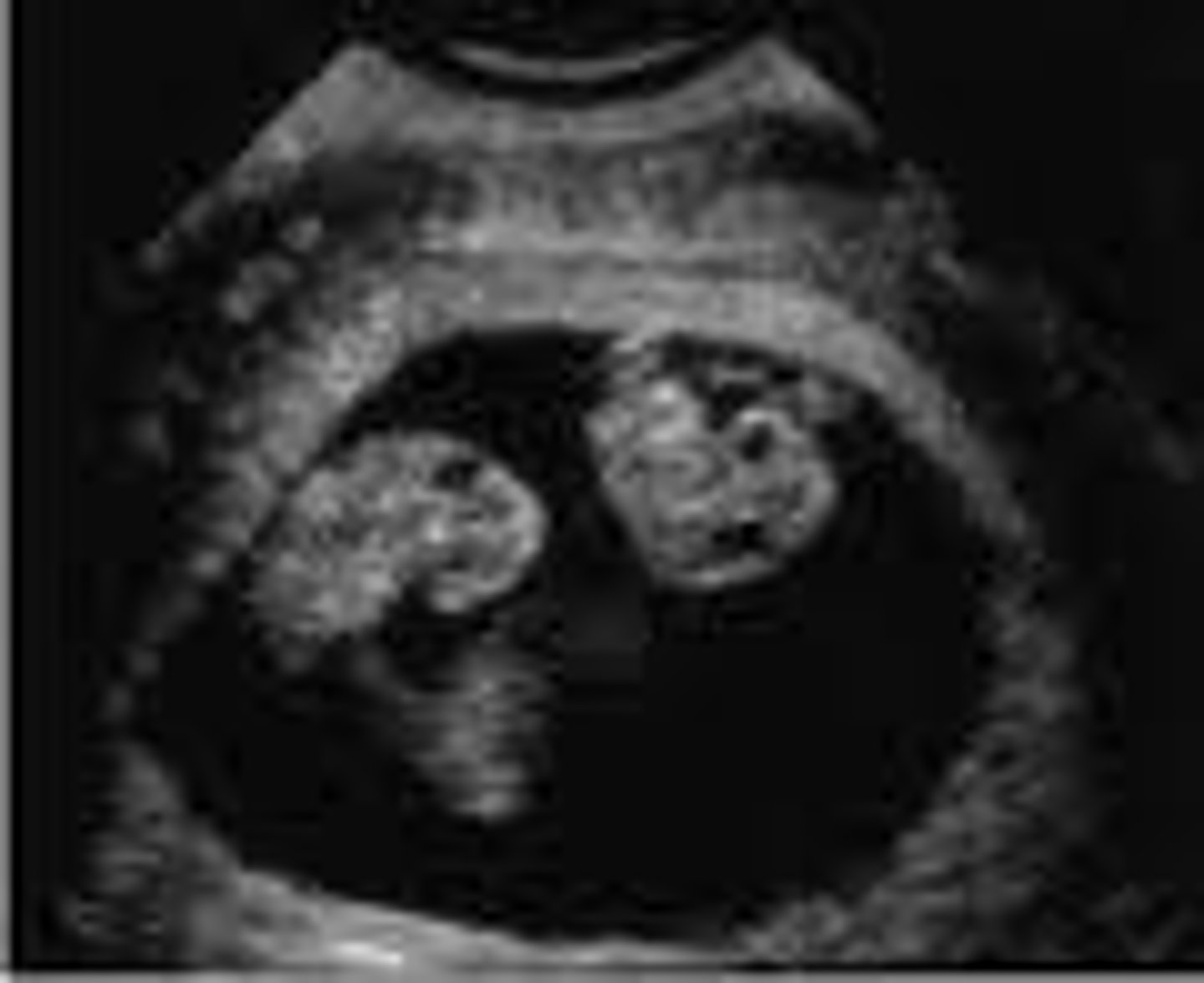
Conjoined Twins
If the split in Monozygotic gestation occurs between Days > 13 (RARE), what type of arrangement of the fetal membranes/placenta occurs?
Once they hit reproductive age (regardless of actively trying or not); may be too late at first prenatal visit to reduce risks of birth defects and maternal obesity
When should female pts receive preconception counseling? Why?
6 to 12 months PRIOR to attempting OR ASAP
When should higher risk patients start health promotion interventions if they are planning to conceive?
-Unprotected intercourse every other day x 3 during fertile window
-Supine x 20 mins
-Avoid heated seats/hot tubs/restrictive male undergarments
What are cycle and fertility principles for conception?
-hCG doubles every 2.2 days
-30-40% implantation bleeding
If a reproductive age female comes in for CC of amenorrhea w/ positive home pregnancy test, what are the clinical signs for a normal pregnancy?
-hCG rises slow/plateau/declines (more likely to abort)
-Bleeding during early pregnancy that is NOT d/t implantation as 10-15% result in abort; >50% of ALL conceptions lost w/n 14 days!
If a reproductive age female comes in for CC of amenorrhea w/ positive home pregnancy test, what are the clinical signs for an ABNORMAL pregnancy?
•Can identify multiple gestations
•Can identify ectopic pregnancies, miscarriages, or molar pregnancies
•Dating accuracy decreases with advancing gestational age
Why is a Transvaginal ultrasound useful in earlier pregnancies?
LMP + 9 mos + 7 days = LMP + 280 days
How can one estimate gestational age/determine Estimated Due Date (EDD) without U/S?
Crown-rump length between 6-11 WGA
How can one estimate gestational age/determine Estimated Due Date (EDD) WITH U/S?
> 1500
What should the hCG level be for to detect early intrauterine pregnancy on TRANSVAGINAL U/S?
5000-6000
What should the hCG level be for to detect early intrauterine pregnancy on TRANSABDOMINAL U/S?
•Sex chromosome aneuploidies (45 XO, 47 XXY)
•Balanced Robertsonian translocations
•Autosomal trisomies (Tr21 > Tr18 > Tr13)
Chromosomal Abns occur in 0.5% of live births & are a/w 50% of spontaneous abortions; what are the most common abns in LIVE BIRTHS?
Increased maternal age (>34 y/o); Increased risk of autosomal trisomies & sex chromosomal abns
What is an important risk factor for Chromosomal Abns in live births and why?
Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)
Define Chromosomal Abnormality:
Most common viable chromosomal disorder & cause of genetic intellectual disability
-Path: 1% Increased risk of subsequent pregnancy being affected
> 95% = Meiotic Nondisjunction (leading to 47 chromosomes/extra copy of chromosome 21)
> 4% = Balanced translocation (rearrangement btwn Chromosomes 14 & 21)
-PE:
> Intellectual disability
> Flat facies
> Single palmar crease
-Dx:
> 1st Trimester US/10-14 WGA
>> Increased nuchal translucency
>> Hypoplastic nasal bone
> Markers
>> (@ 10-14 WGA)
>>> Decreased PAPP-A
>> (@ 16-20 WGA)
>>> Decreased Estriol
>>> Decreased AFP
>>> Increased hCG & Inhibin/HI
-Prog:
> Duodenal atresia
> Hirschsprung dz
> Congenital heart dz
> Increased risk of AML/ALL
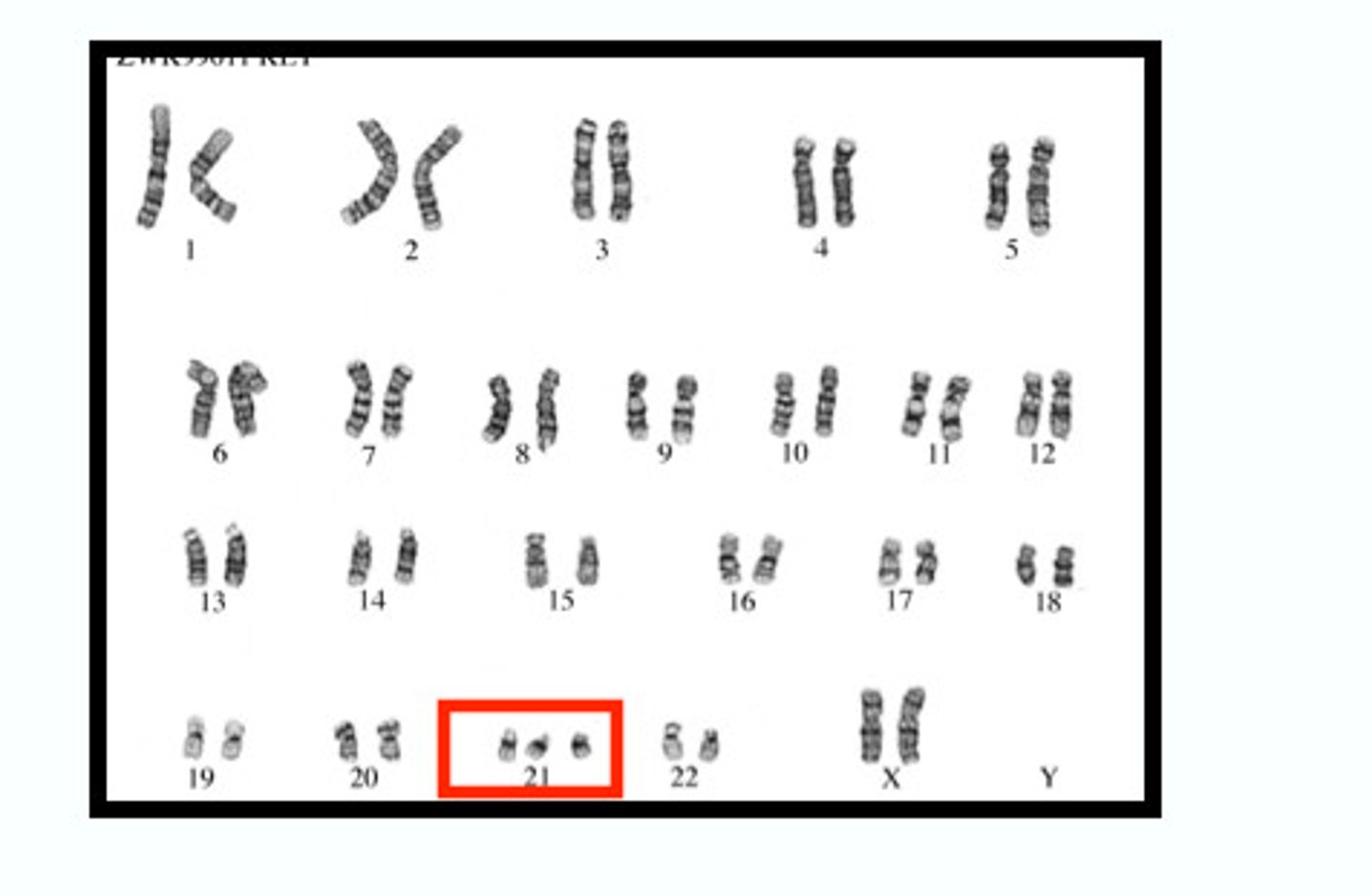
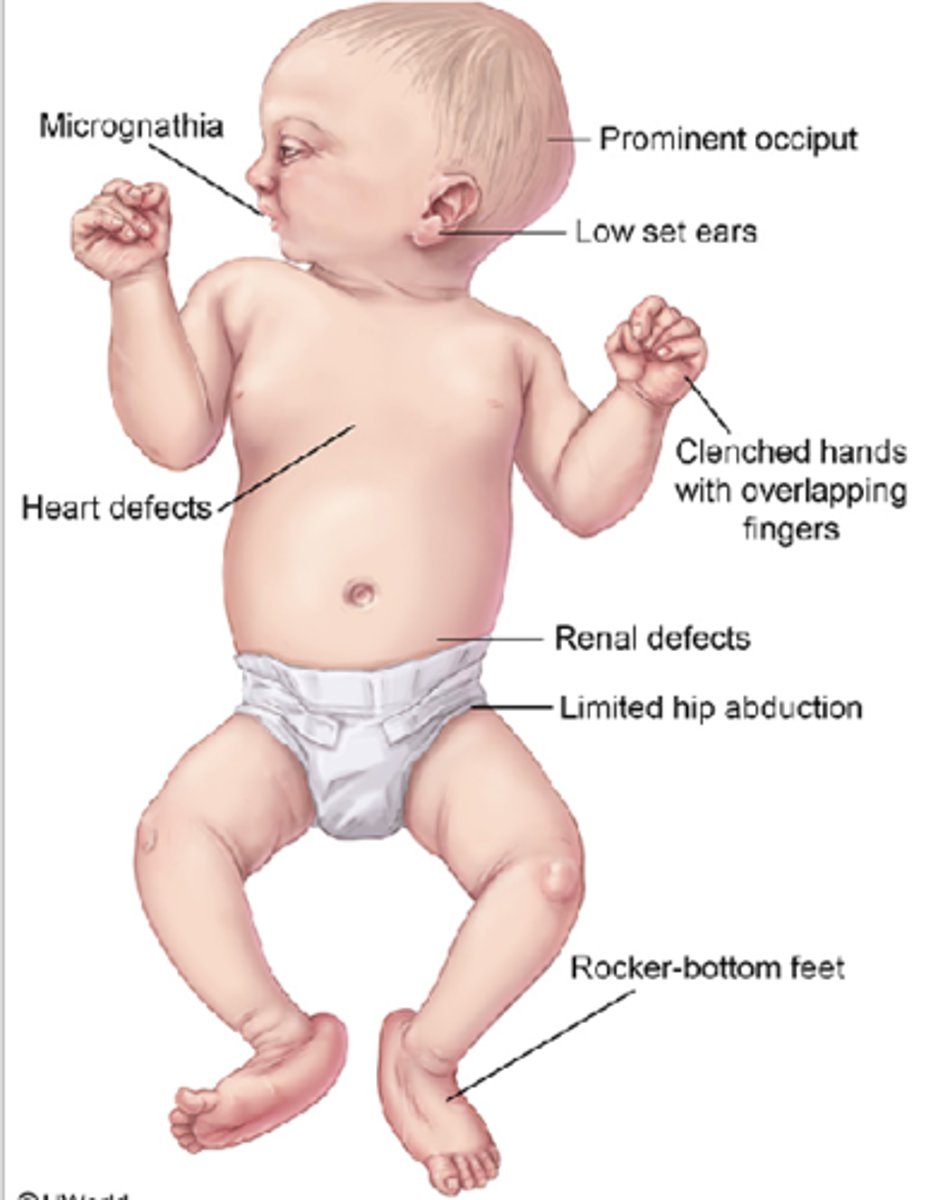
Edwards Syndrome (Trisomy 18)
Define Chromosomal Abnormality:
2nd MC Autosomal Trisomy resulting in live birth
-Path: Meiotic Nondisjunction
-PE: "PRINCE Edward"
> Prominent Occiput
> Rocker bottom feet
> Intellectual disability
> Nondisjunction
> Clenched fist w/ overlapping fingers
> Low-set Ears
> Small Jaw/Congenital Heart Dz/Omphalocele/Myelomeningocele
-Dx: Markers
>> Low hCG
>> Low Inhibin (HI)
>> Low Estriol
>> Low AFP
>> Low PAPP-A (Pregnancy associated plasma protein A)
-Prog: Death by 1 y/o
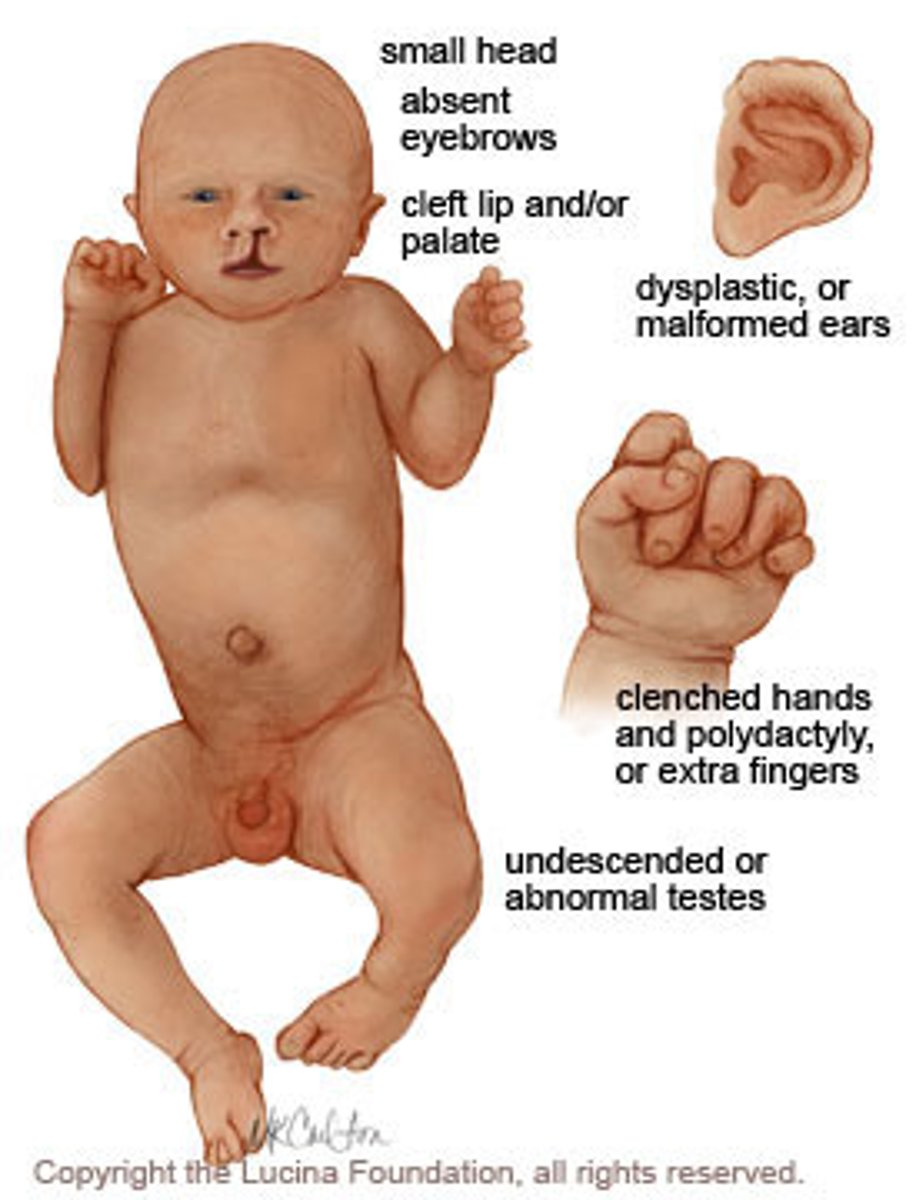
Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13)
Define Chromosomal Abnormality:
Chrosomal Abn that occurs in 1 in 15,000 live births
-Path: Defect in fusion of prechordal mesoderm --> midline defects
-PE:
•Severe intellectual disability
•Rocker-bottom feet
•Microphthalmia & microcephaly
•Cleft lip/palate
•Holoprosencephaly (no forebrain)
•Polydactyly (extra digits)
•Cutis aplasia (no skin on scalp)
•Congenital heart disease
•Polycystic kidney disease
•Omphalocele (intestines in a bag outside of abdomen)
-Dx: Markers
> Low hCG
> Low PAPP-A
-Prog: Death by 1 y/o
> Adult-onset PCKD
> Neurofibromatosis
> Achondroplasia
> Tuberous Sclerosis
> Marfan Syndrome
> Huntington Disease
What are some examples of AD Disorders (Only 1 Abn gene, 50% passage, spontaneous mutation vs inheritance, differing phenotypes)?
•Sickle cell disease: 1/10 African Americans
•Tay-Sachs disease: 1/30 Ashkenazi Jews or French Canadians
•Thalassemia: 1/25 Mediterranean or Southeast Asian descent
•Cystic Fibrosis: 1/25 North American Caucasians
What are some examples of AR Disorders (2 Abn genes, more w/ consanguinous couples, can be Dx prenatally)?
•X-linked dominant = Fragile X syndrome
•X-linked recessive
> Duchenne muscular dystrophy
> Hemophilia A/B
> G6PD deficiency
What are some examples of Sex-Linked Disorders (D/t recessive genes on X chromosome --> affects MALES, but female carriers)?
Fragile X Syndrome
Define X-Linked Dominant Disorder:
2nd most common cause of genetic mental disability after Down syndrome
-Path: Trinucleotide repeat disorder, affects FMR1 gene expression
-PE:
> Enlarged testes
> Long face with large jaw
> Large ears
> Autism

Both genes & environment have causative role
MOST birth defects are actually MULTIFACTORIAL, meaning what?
-Cleft lip and/or palate
-Neural tube defects (spina bifida, anencephaly)
-Congenital heart defects
-Pyloric stenosis
What are common Multifactorial Disorders?
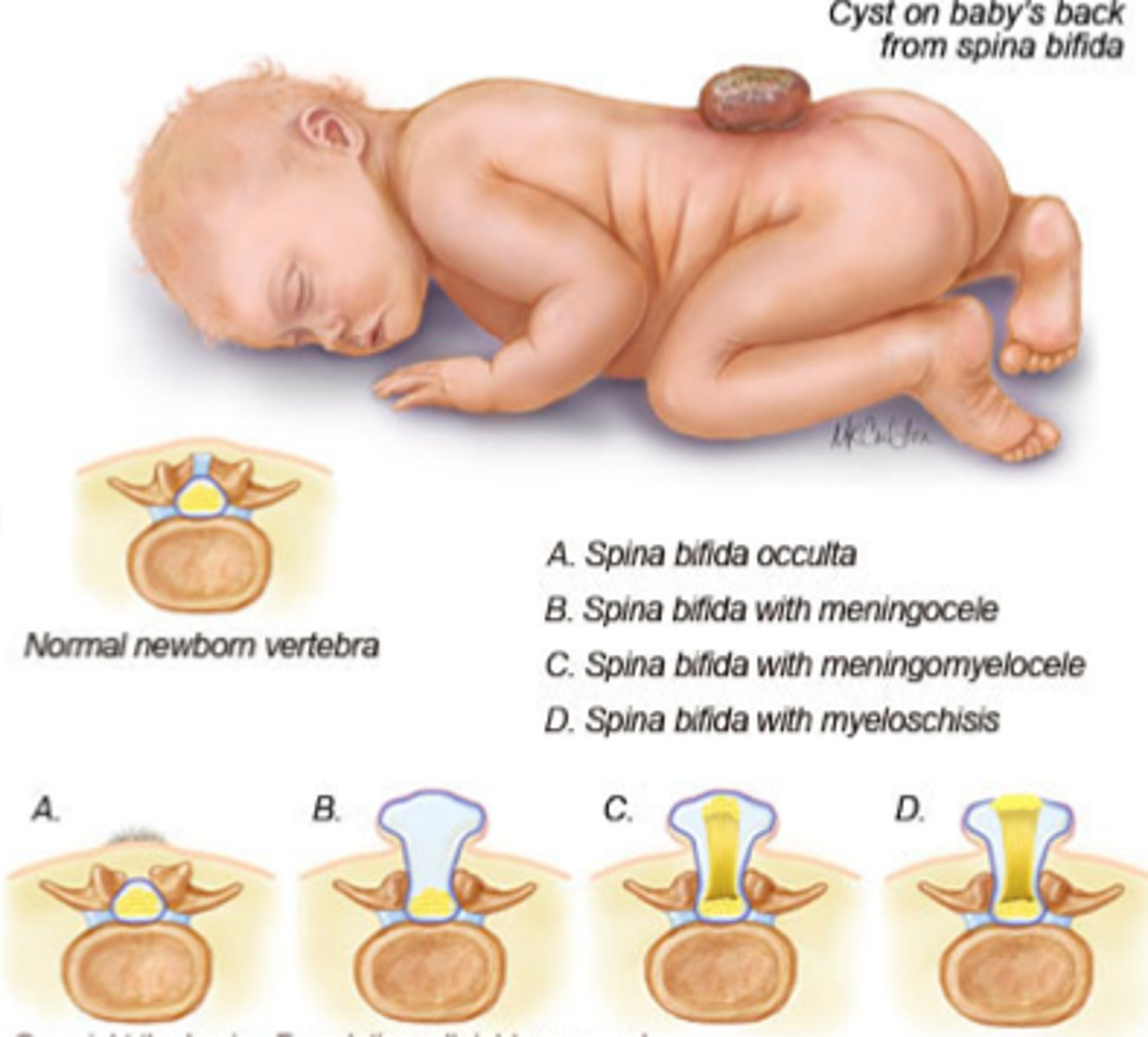
Neural Tube Defects
Define Multifactorial Disorder:
A group of birth defects caused by the failure of the neural tube to close, resulting in an opening in the spinal cord and/or brain
-Hx: Occurs in 4th wk of pregnancy; A/w LOW FOLIC ACID INTAKE
•Folate levels 3 months prior to fetal development most important
•Previous NTD, must take 4mg folic acid prior to conception
•Also associated with maternal diabetes
-Path/PE:
> Anencephaly = intrauterine fetal demise or die w/in few days of birth
> Spina bifida
>> Meningocele = Herniation of Meninges through spinal defect; cord in usual position
>> Myelomeningocele = herniation of meninges AND spinla cord through open defect
-Dx: AMNIO Markers (@ 16-20 WGA) = Elevated AFP
-Prog: 3% recurrence risk
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
What testing is usually done in the first trimester for Chromosomal/Genetic Disorders?
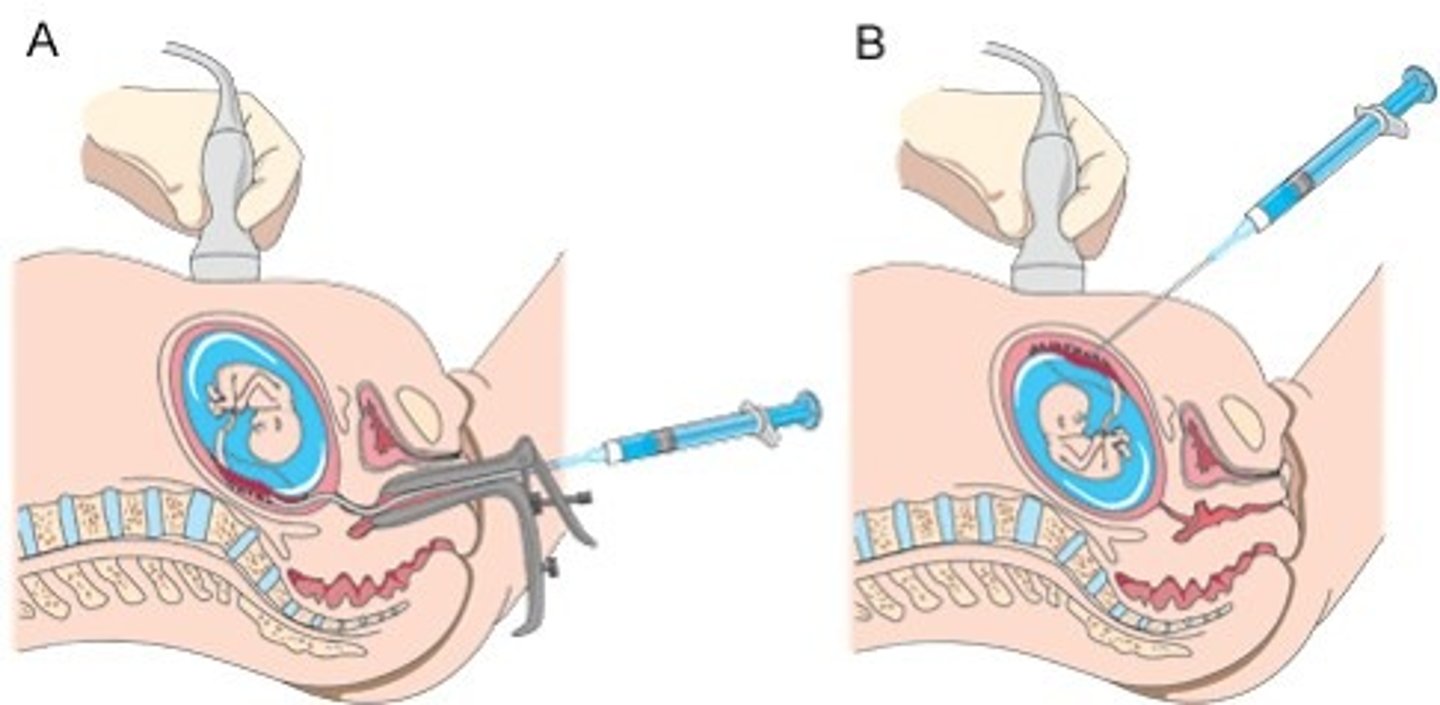
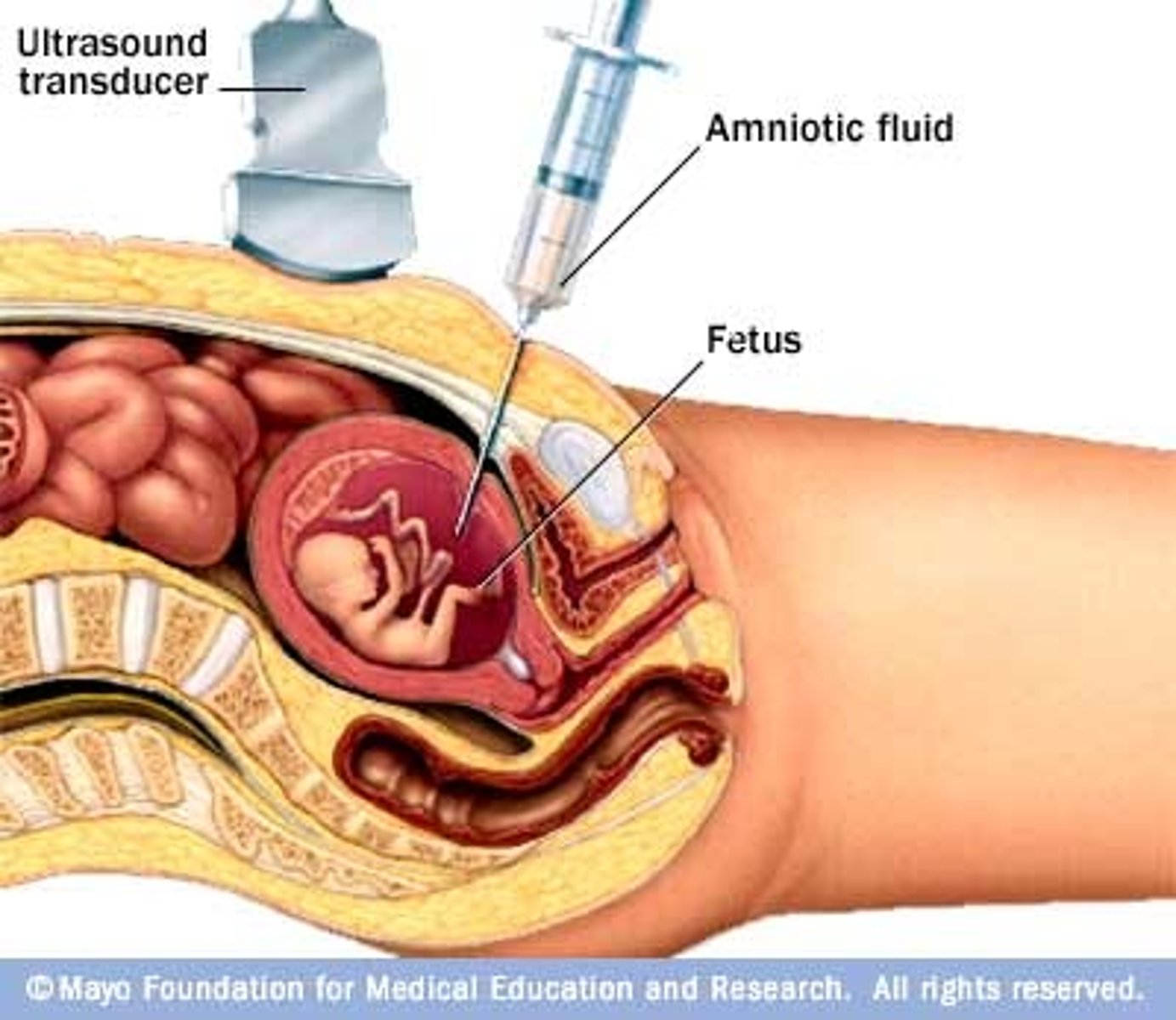
Amniocentesis:
Diagnostic =
•Amniotic cells cultured for 2 wks before final fetal chromosomal analysis
•AFP level: if elevated -->NTD or ventral wall defect
•Performed with direct ultrasound guidance under sterile conditions
•Rhogam for Rh negative mom
Therapeutic = Mgmt of polyhydramnios in twin-twin transfusion syndrome
What testing is usually done in the second trimester (18-20 wks) for Chromosomal/Genetic Disorders?
Rubella Infex (1941)
What was the first known teratogen?
Thalidomide
•Used as a sedative and anxiolytic for pregnancy nausea
•Caused phocomelia and other malformations ("flipper limbs")
What is the best known teratogen?
Renal failure --> oligohydramnios, hypOcalvaria
What is the Teratology of ACE Inhibitors?
Absence of digits, Multiple anomalies
What are the Teratologies of Alkylating Agents?
CN VIII Toxicity (OtOtoxicity)
What is the Teratology of Alkylating Agents?
Facial dysmorphism, developmental delay, neural tube defects, phalanx/fingernail hypoplasia (Carbamazepine, phenytoin, valproate, phenobarbital)
What are the GENERAL Teratologies of Antiepileptic Rxs?
Fetal hydantoin syndrome- craniofacial + limb reduction defects, cardiovascular defects, mental deficiency
What are the Teratologies of the Antiepileptic Rx, Dilantin?
1-2% risk open spina bifida
What is the Teratology of the Antiepileptic Rx, Valproate/Carbamazepine?
Neonatal withdrawal sx, Neonatal Hemorrhage
What are the Teratologies of the Antiepileptic Rx, Phenobarbital?
Vaginal clear cell adenocarcinoma, congenital Mullerian anomalies
What are the Teratologies of the Diethylstilbestrol (DES)?
Cartilage Damage (long bones)
What is the Teratology of the Fluoroquinolones?
NTDs
What are the Teratologies of the Folate Antagonists (Antiepileptics, TMP, Methotrexate)?
Multiple severe birth defects
What are the Teratologies of the Isotretinoin (Accutane)?
Ebstein cardiac anomaly (defective tricuspid valve)
What are the Teratologies of the Lithium?
Aplasia cutis congenita
What are the Teratologies of the Methimazole (aka why PTU is used in 1st Tri)?
Fetal hydantoin syndrome: cleft palate, cardiac defects, phalanx/fingernail hypoplasia
What are the Teratologies of the Phenytoin?
Discolored Teeth, Inhibited Bone Growth
What are the Teratologies of the Tetracyclines?
Bone/cartilage deformities, fetal hemorrhage, abortion, optic nerve atrophy
What are the Teratologies of the Warfarin (aka why Heparin should be used instead b/c it doesn't cross placenta)?
Abnormal fetal growth and fetal addiction; placental abruption (vasoconstriction)
What are the Teratologies of the Cocaine?
Low birth weight, preterm labor, placental problems, IUGR, SIDS, ADHD (vasoconstriction)
What are the Teratologies of the Smoking?
Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
-D/t impaired migration of neuronal and glial cells
-Signs = Craniofacial Abns, Cardiac defects, Mental retardation, Behavioral Issues
What are the Teratologies of the Alcohol?
-Hepatosplenomegaly
-Jaundice
-Thrombocytopenia
-Growth Retardation
What are GENERAL signs of TORCH/Teratogenic Infex?
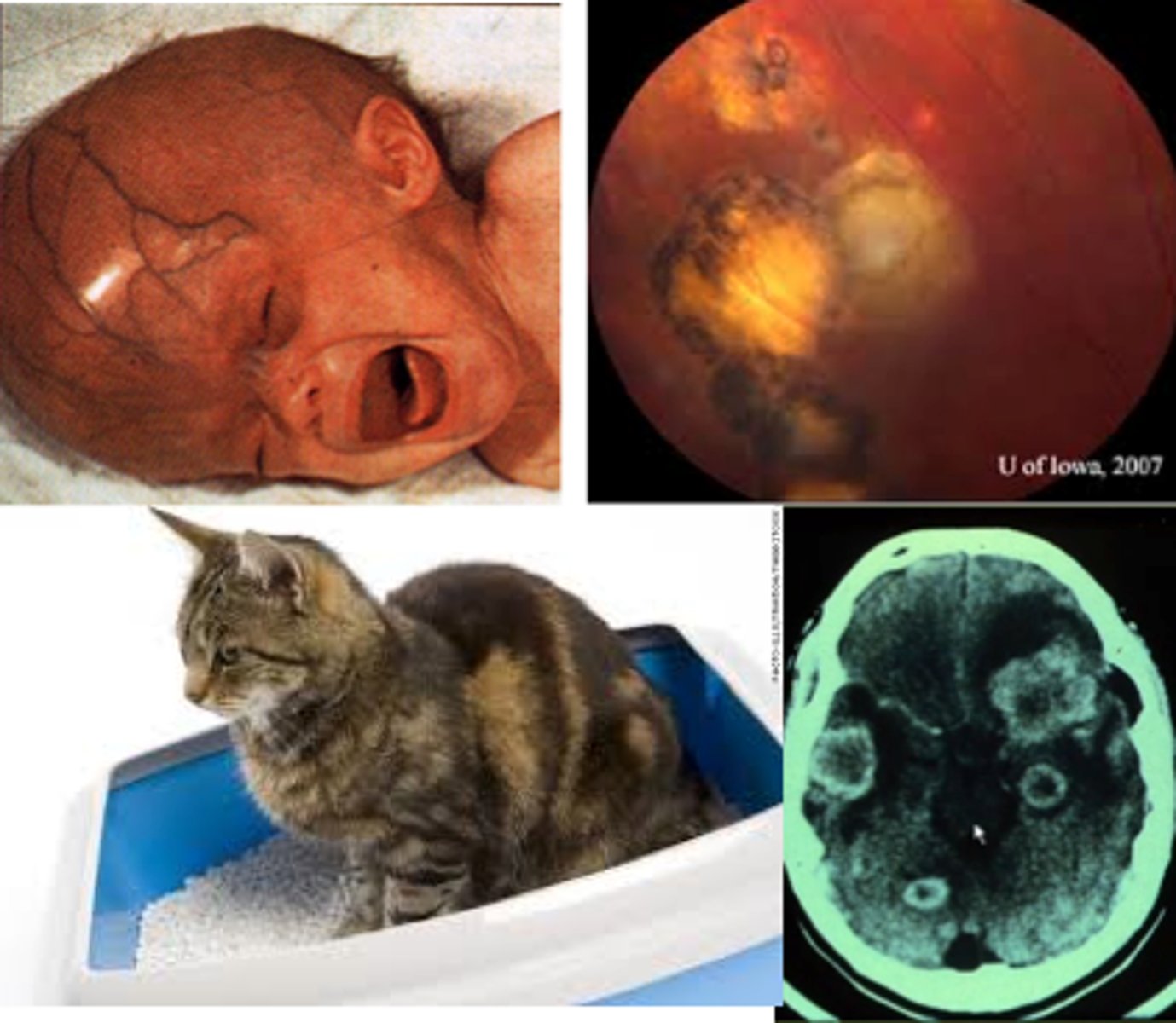
Toxoplasmosis
Define TORCH Infex:
D/t obligate intracellular protozoan
-Hx:
•Uncommon in US
•Household cats bring from soil to litter box
•Undercooked infected beef, lamb, other animals
-Sx: ASX in Mom; if Sx = fever, rash, fatigue, rarely lymphadenopathy
-PE:
> Classic Triad = chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus, and intracranial calcifications, +/- “blueberry muffin rash”
> Congenital = enlarged placenta, fetal hepatomegaly + ascites, fetal microcephaly (5%)
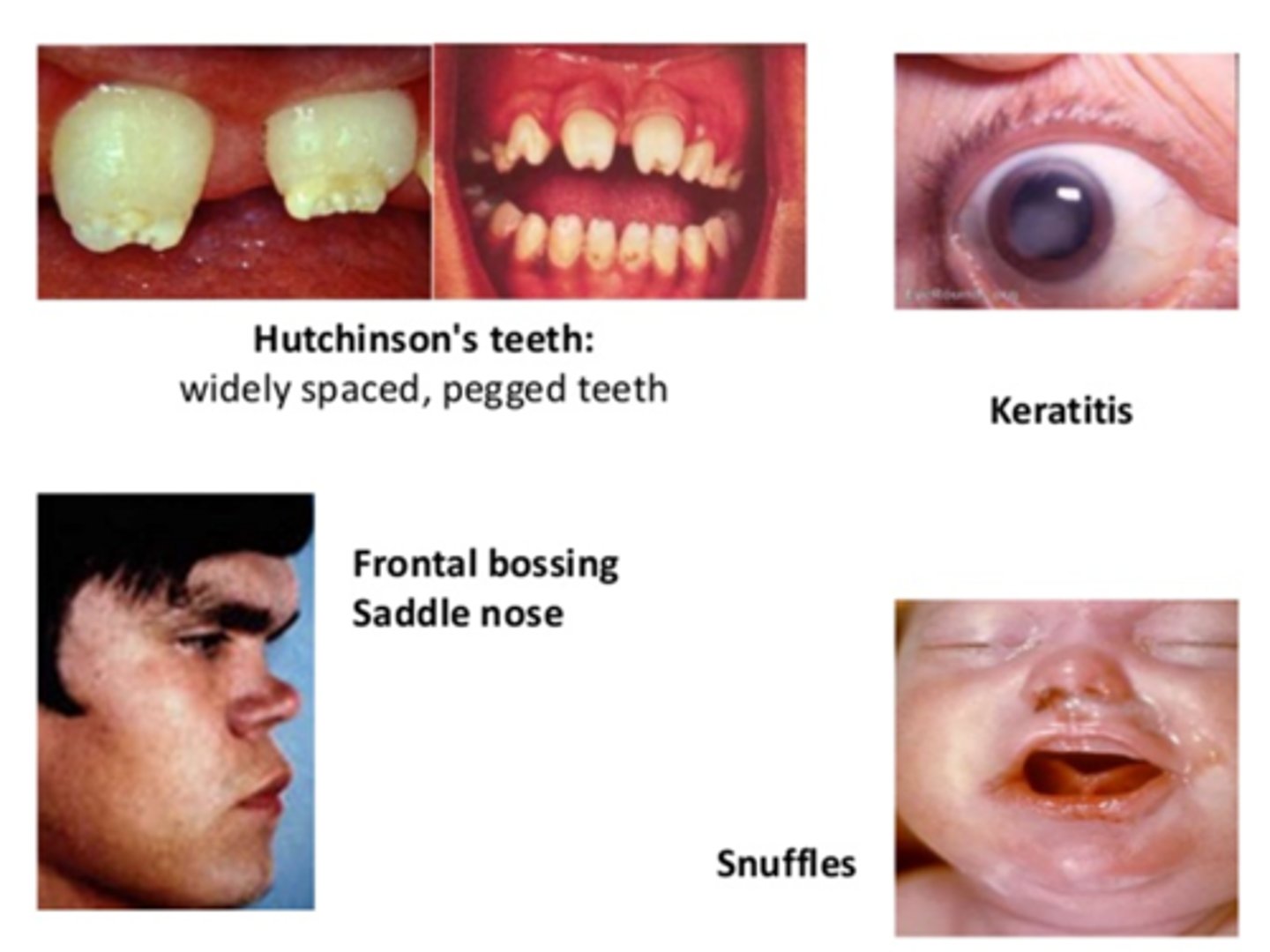
Congenital Syphillis
Define TORCH Infex:
Most severe congenital infex during 1st trimester
-Hx: Vertical transmission
• Primary - 90-100%
• Secondary - 70-90%
-PE:
> Stillbirth
> IUGR (intrauterine growth restriction)
> Nonimmune hydrops
> Rhinitis
> HSM
> "mulberry molars", "saber shins", "saddle nose deformity"
> Interstitial keratitis
-Tx: PENICILLIN
•Variable maternal presentation based on CD4 count
•Baby will have recurrent infections, chronic diarrhea
What are the results of congenital HIV?
•Causes erythema infectiosum (fifth disease) = "slapped cheek" fever
•Can cause hydrops fetalis in pregnant women
What are the results of congenital Parvovirus B19?
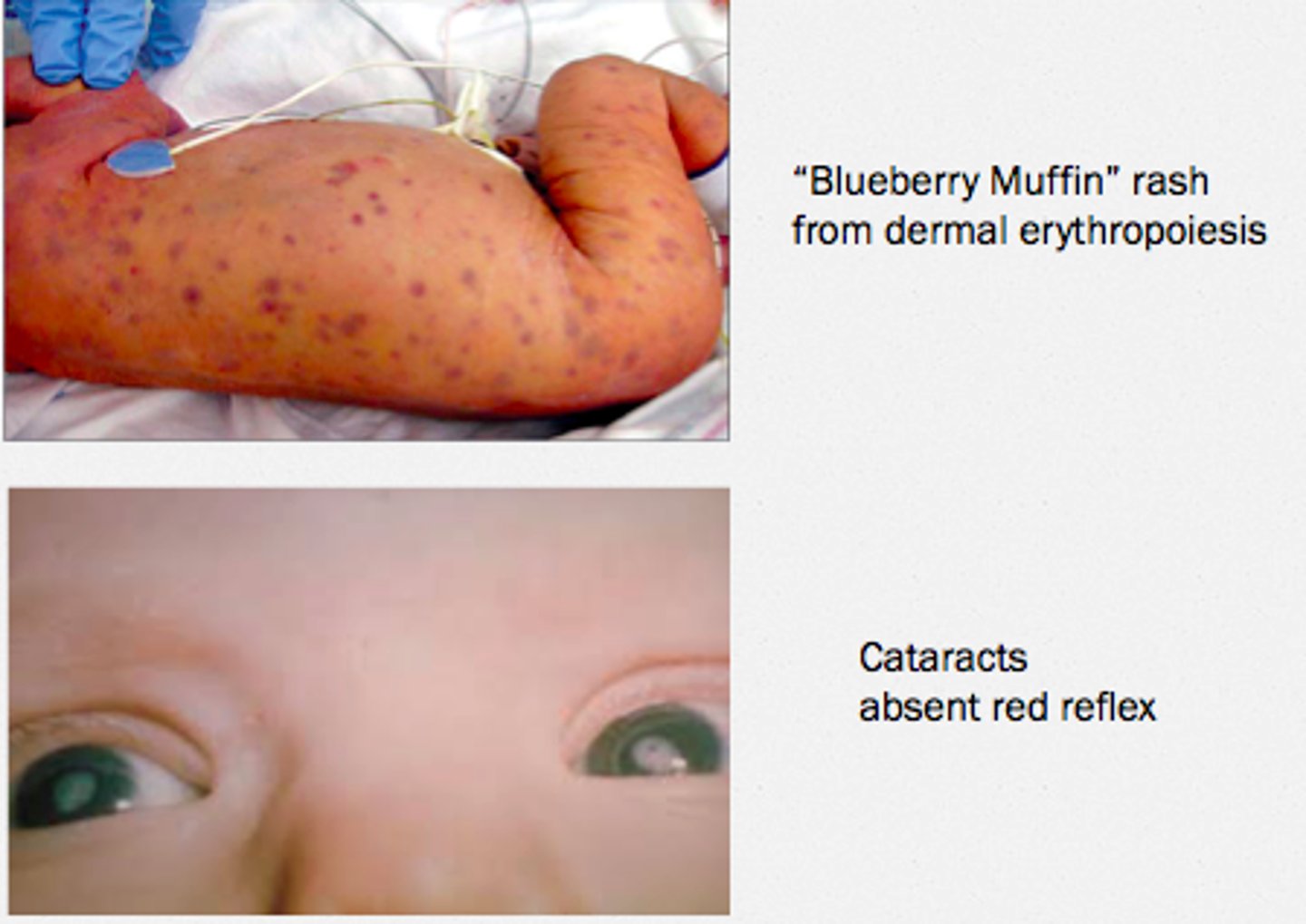
Congenital Rubella
Define TORCH Infex:
RNA virus
-Hx: Most primary infex in unvaccinated children; <0.1% pregnancies (do NOT give MMR vaccine)
-Path: Resp droplet spread; 2-3 wk incubation
-Sx: malaise, myalgia, nonpruritic rash, polyarthritis/arthralgia
-PE:
> Triad = Deafness, Retinopathies + Cardiac anomalies (eyes/ears/heart)
> Congenital = "Blueberry muffin" (dermal extramedullary hematopoiesis)
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Define TORCH Infex:
MC Intrauterine viral infex
-Hx: Most primary infex in unvaccinated children; <0.1% pregnancies (do NOT give MMR vaccine)
-Path: Via urine, blood, saliva, semen, cervical secretions
-Sx: Asx/Mono-like illness
-PE/Dx:
> Jaundice
> Thrombocytopenia
> IUGR
> Microcephaly
> Hearing loss
> Seizures
> Chorioretininits
> Periventricular Calcifications
> Blueberry muffin (petechiae)
-Tx: Ganci/Valacyclovir for NONPREG/NEONATES after birth
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
Define TORCH Infex:
-Path: 20-30% women are IgG + prior to pregnancy
> At risk for viral shedding during pregnancy
-PE:
> Seizures
> Tremors
> Poor Feeding
> Bulging Fontanelles (meningoencephalitis) --> 30% die, 50% neuro damage
-Tx: Antiviral Prophylaxis @ 36 WGA
•Main risk is between 4-8 weeks gestational age
•No effect if less than 5 rads (dx levels - dose dependent)
•Consider if multiple imaging studies done during pregnancy
•PE = Microcephaly, intellectual disability
Describe the Teratology of Radiation
Congenital goiter or hypOthyroidism (cretinism)
Describe the Teratology of Iodine (lack or excess)
Caudal regression syndrome, cardiac defects, NTD, macrosomia, neonatal hypOglycemia (islet cell hypERplasia), polycythemia
Describe the Teratology of Maternal DM
Neurotoxicity
Describe the Teratology of Methylmercury (From Swordfish, Shark, Tilefish, King Mackerel)
Interferes w/ Homebox gene = spontaneous abortion, cleft palate, cardiac defects
Describe the Teratology of Vitamin A
-Best food for newborn
-Accelerates Uterine Involution (more oxytocin --> more uterine contractions)
-Immunologic advantages (maternal IgA, macrophages/lymphocytes = passive immunity, maternal bacteria to infant gut)
What are advantages of breastfeeding?
Colostrum = Protein, fat, minerals, IgA, macrophages, lymphocytes
Around Day 2 after birth, what comes out of nipples (doesn't look like breast milk)?
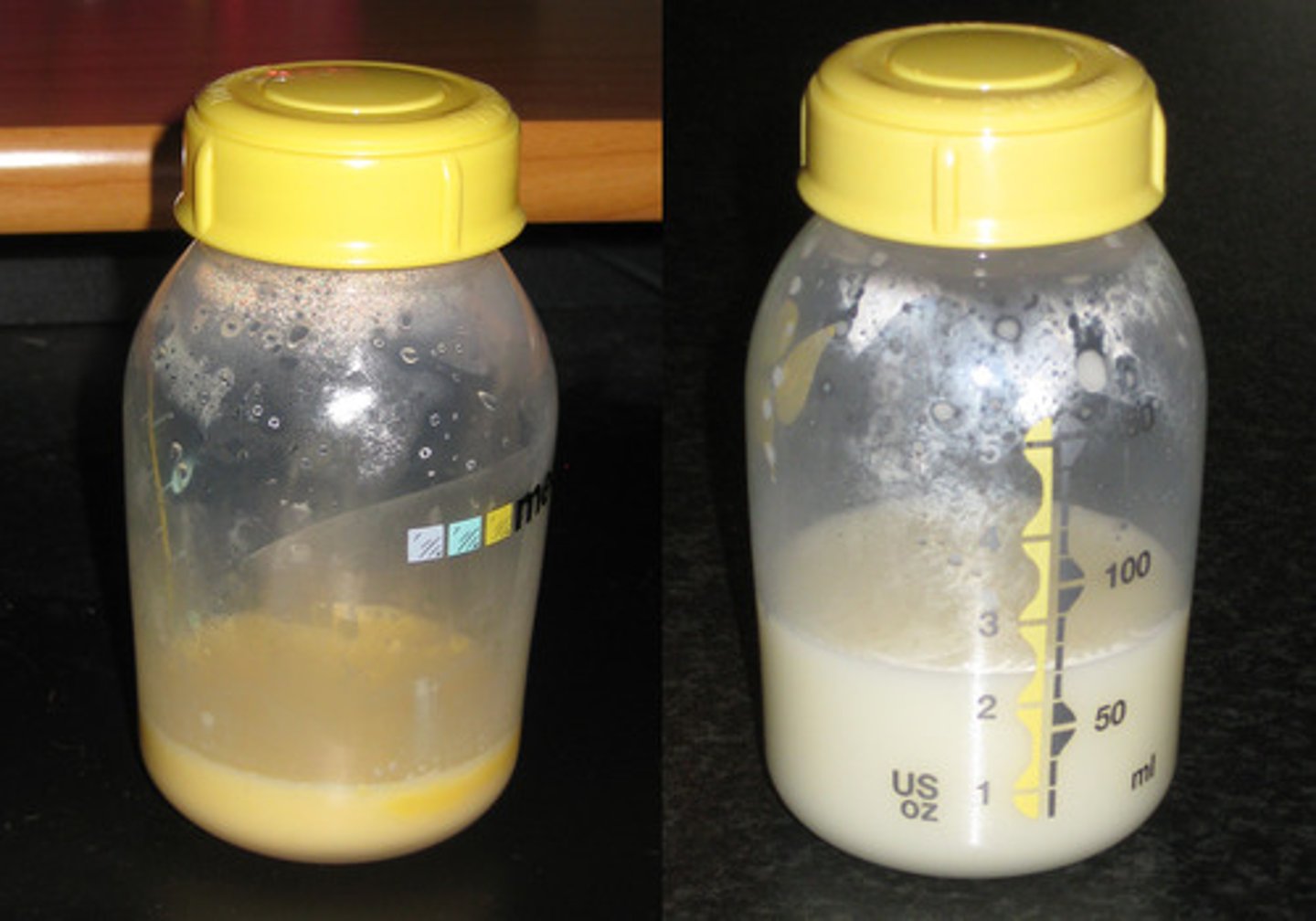

•Proteins, lactose, water, and fat
•Casein, lactalbumin, Beta-lactoglobulin (none are found in cow's milk)
•Omega-3-fatty acids essential for brain development
Around Day 3-6 from birth, what are important nutrients found in mature breast milk?
•Nipple stimulation --> increased oxytocin and prolactin --> milk!
•Prolactin: induces/maintains lactation and decreases reproductive function (lactational amenorrhea)
•Oxytocin: assists in milk letdown and uterine contraction/involution following delivery
Why is suckling required to maintain milk production & ejection?
1. Progesterone drops after delivery
2. Prolactin disinhibited
3. Nipple stimulation/suckling
4. Oxytocin & prolactin increased
5. Colostrum secretion (Day 2)
6. Mature Milk (Day 3-6)
What is the order in which breastfeeding occurs (based on hormones)?