Anatomy Axial Skeleton
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Axial skeleton
Divided into 3 parts: skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage
Skull
Composed of the cranium and facial bones
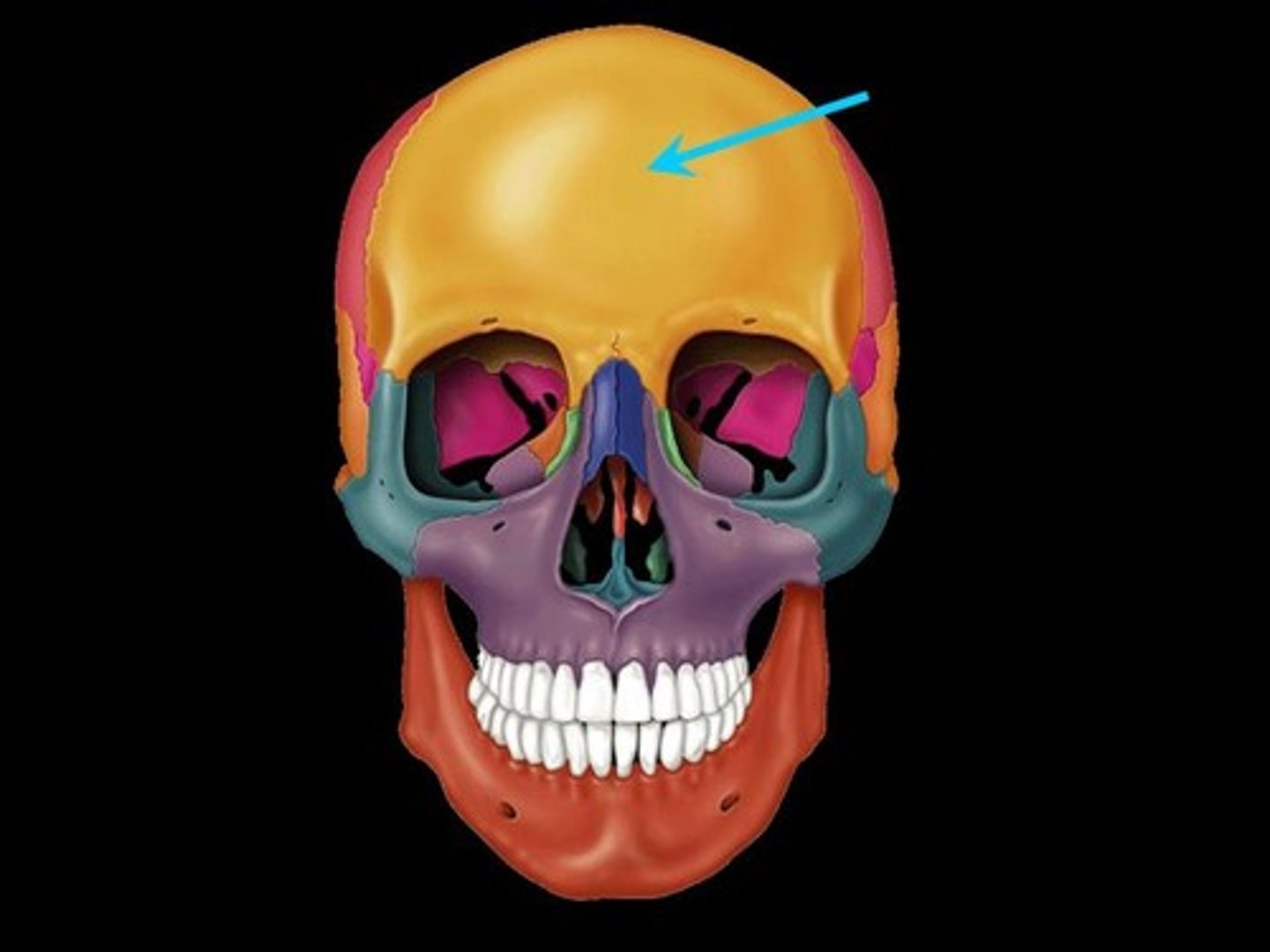
Frontal bone
Anterior portion of cranium; forms the forehead, superior part of the orbit, and floor of anterior cranial fossa
Parietal bone
Posterolateral to the frontal bone, forming sides of cranium
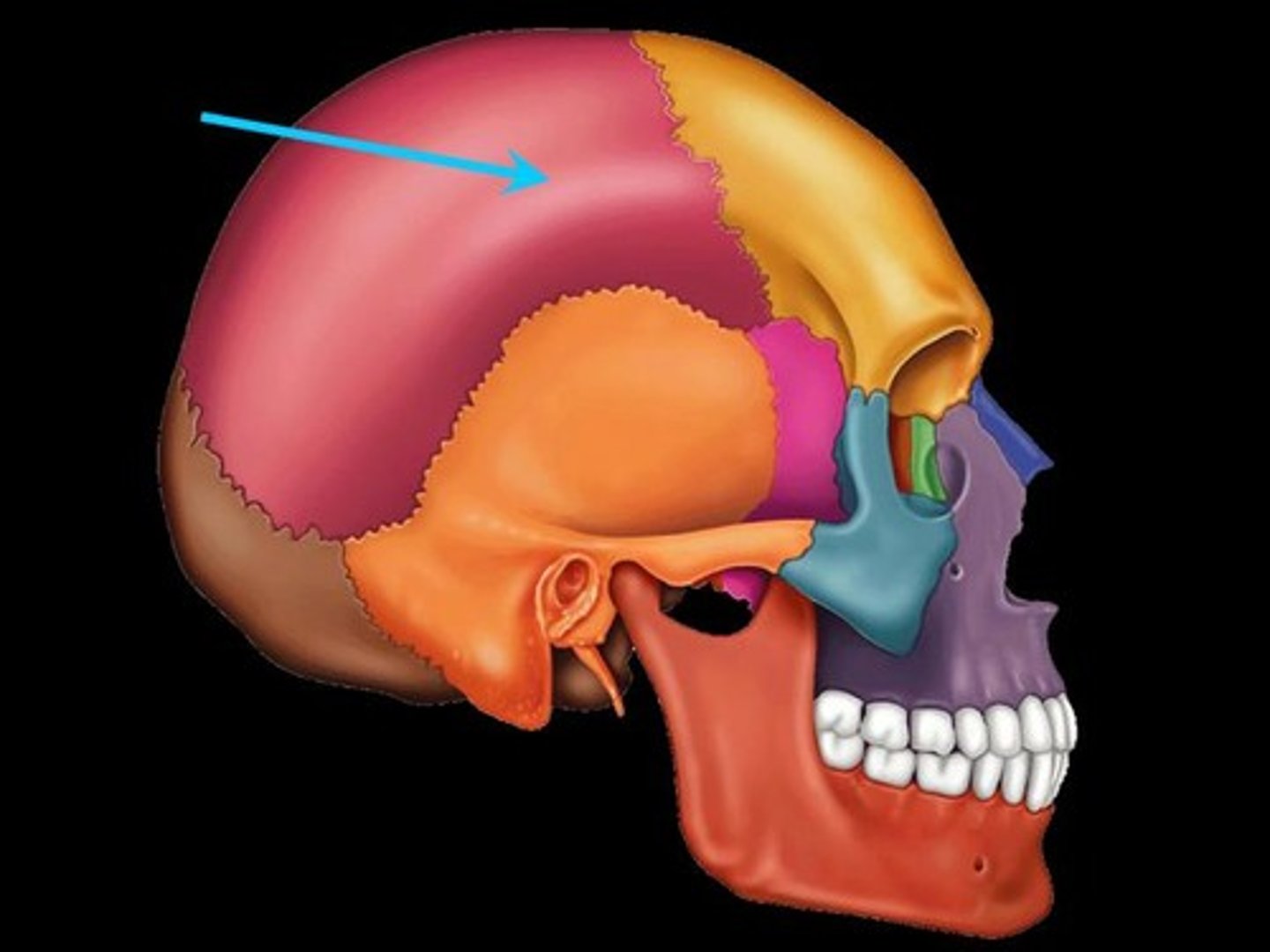
Temporal bone
Inferior to parietal bone of lateral skull. Can be divided into three major parts: squamous part (borders the parietals) the tympanic part (surrounds the external ear opening) and the petrous part (forms the lateral portion of the skull base and contains the mastoid process
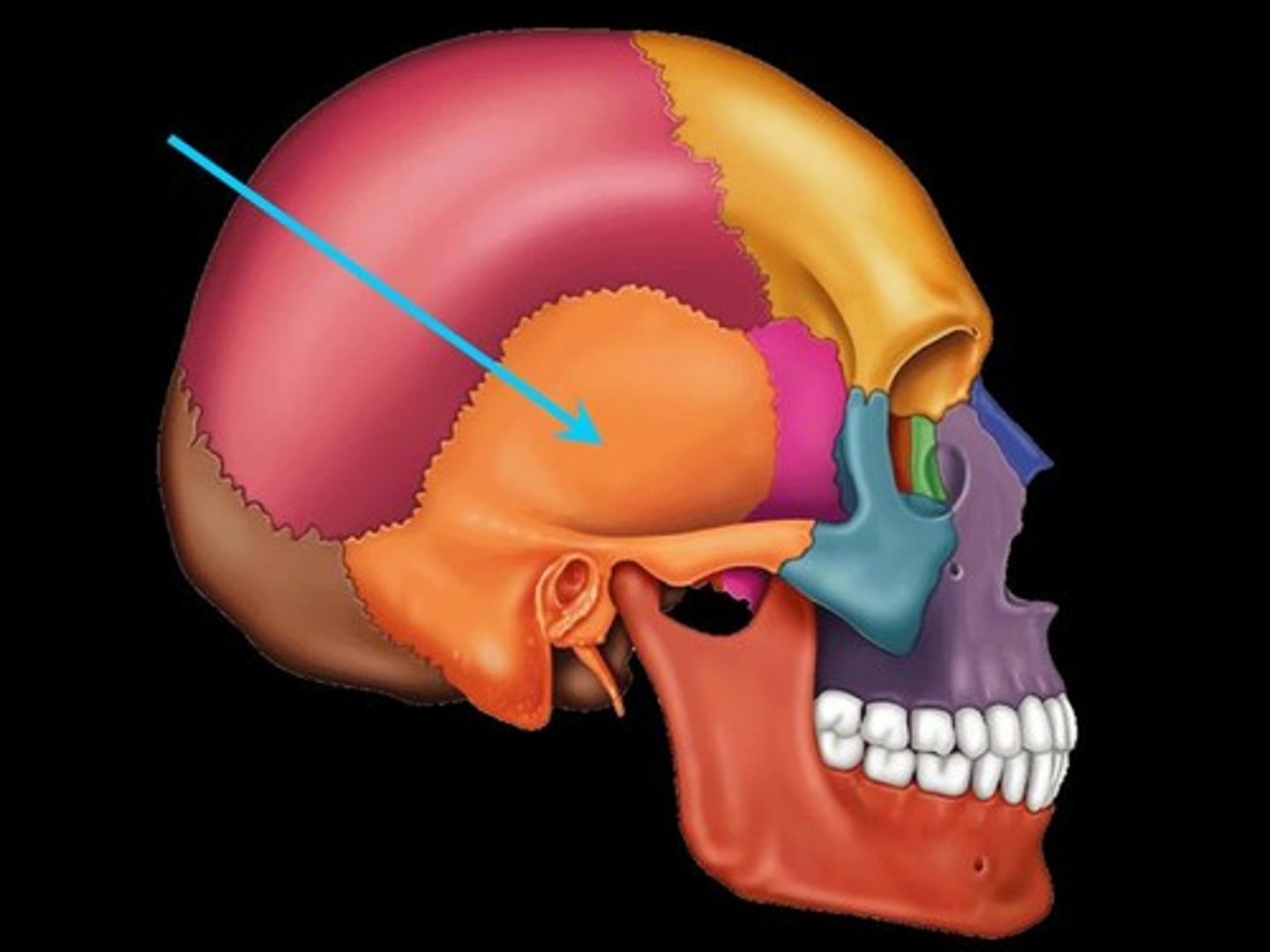
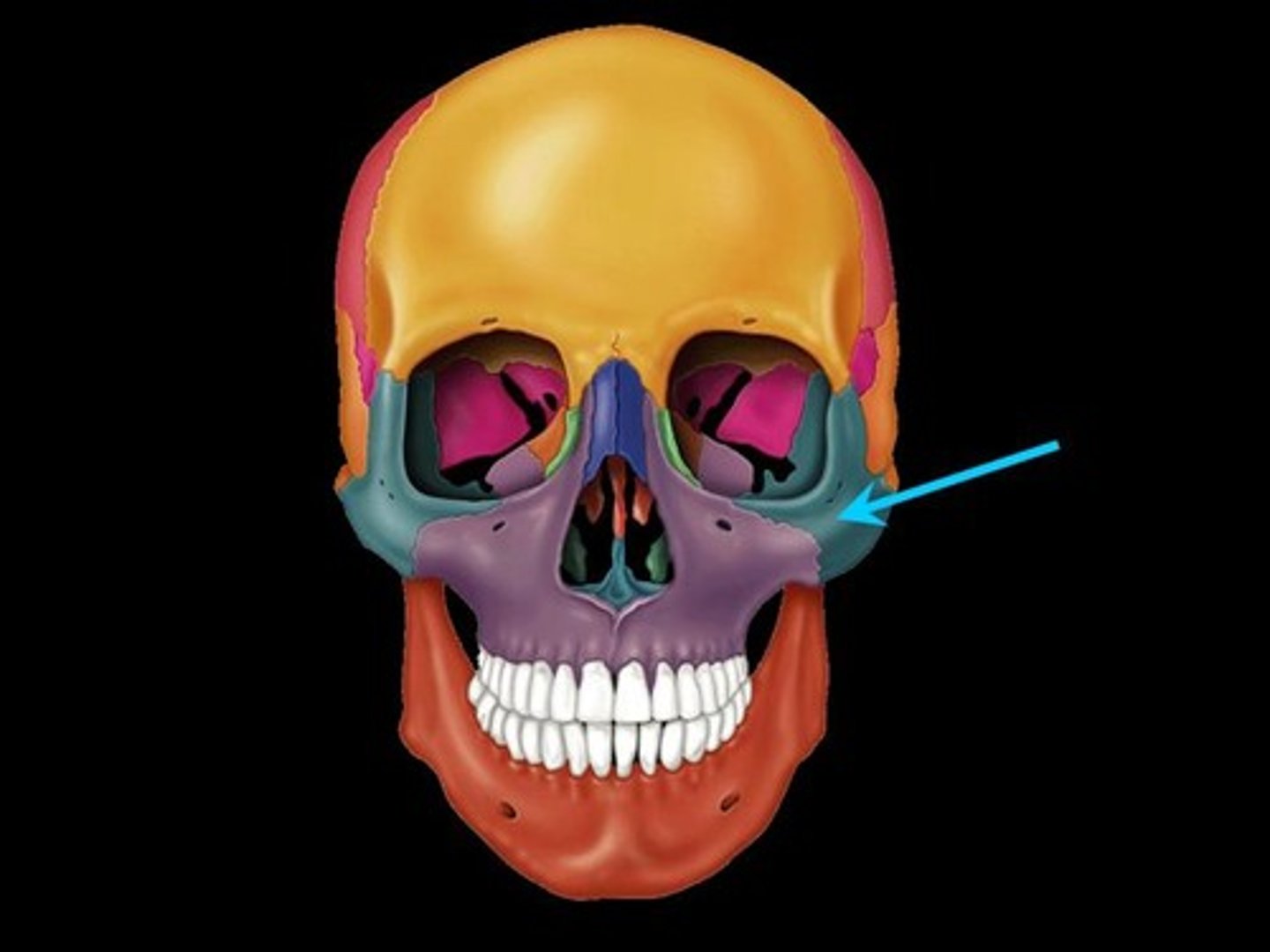
Zygomatic process
A bridge-like projection joining the zygomatic bone (cheekbone) anteriorly.
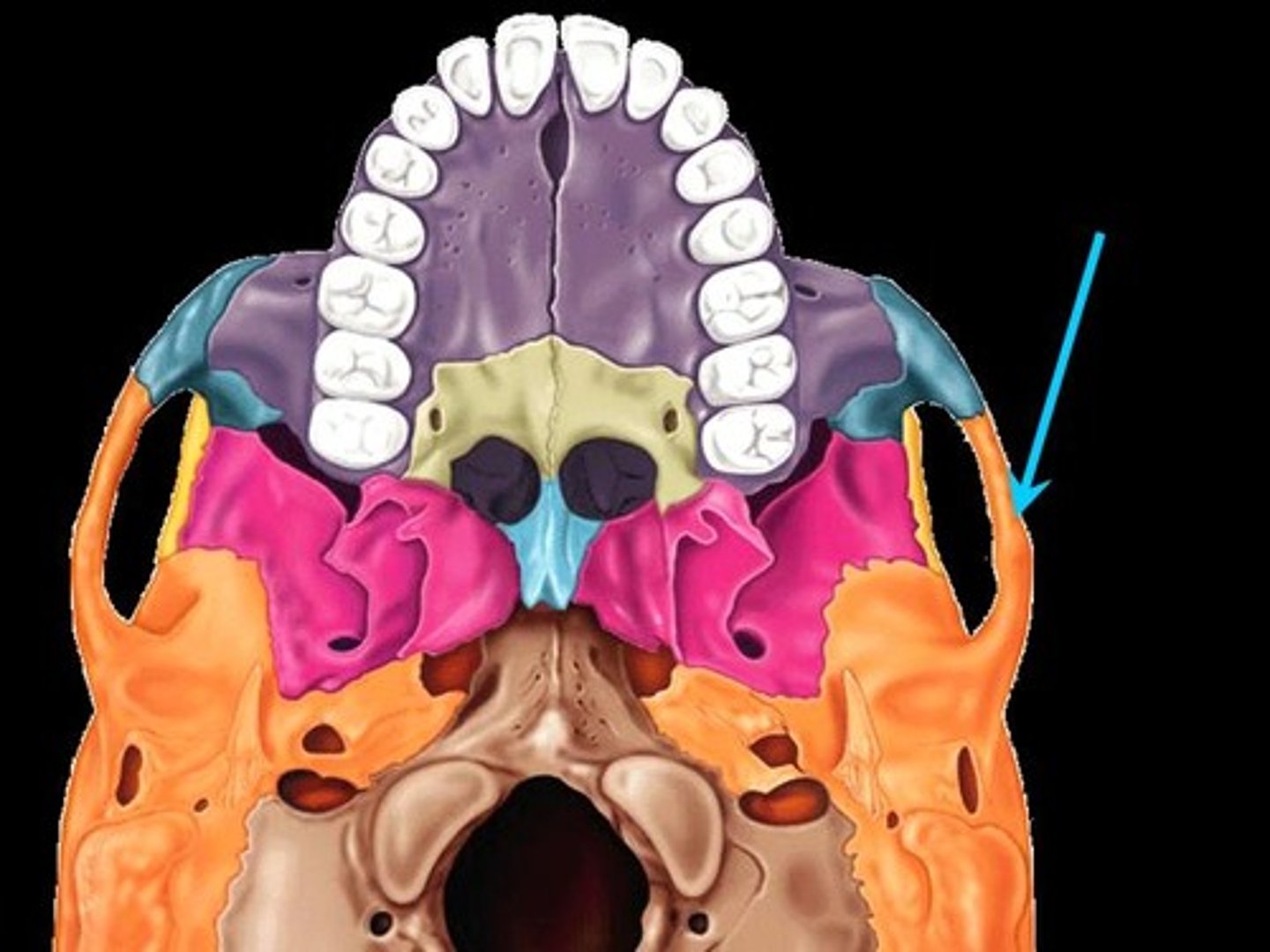
Styloid process
Needle like projection inferior to external acoustic meatus
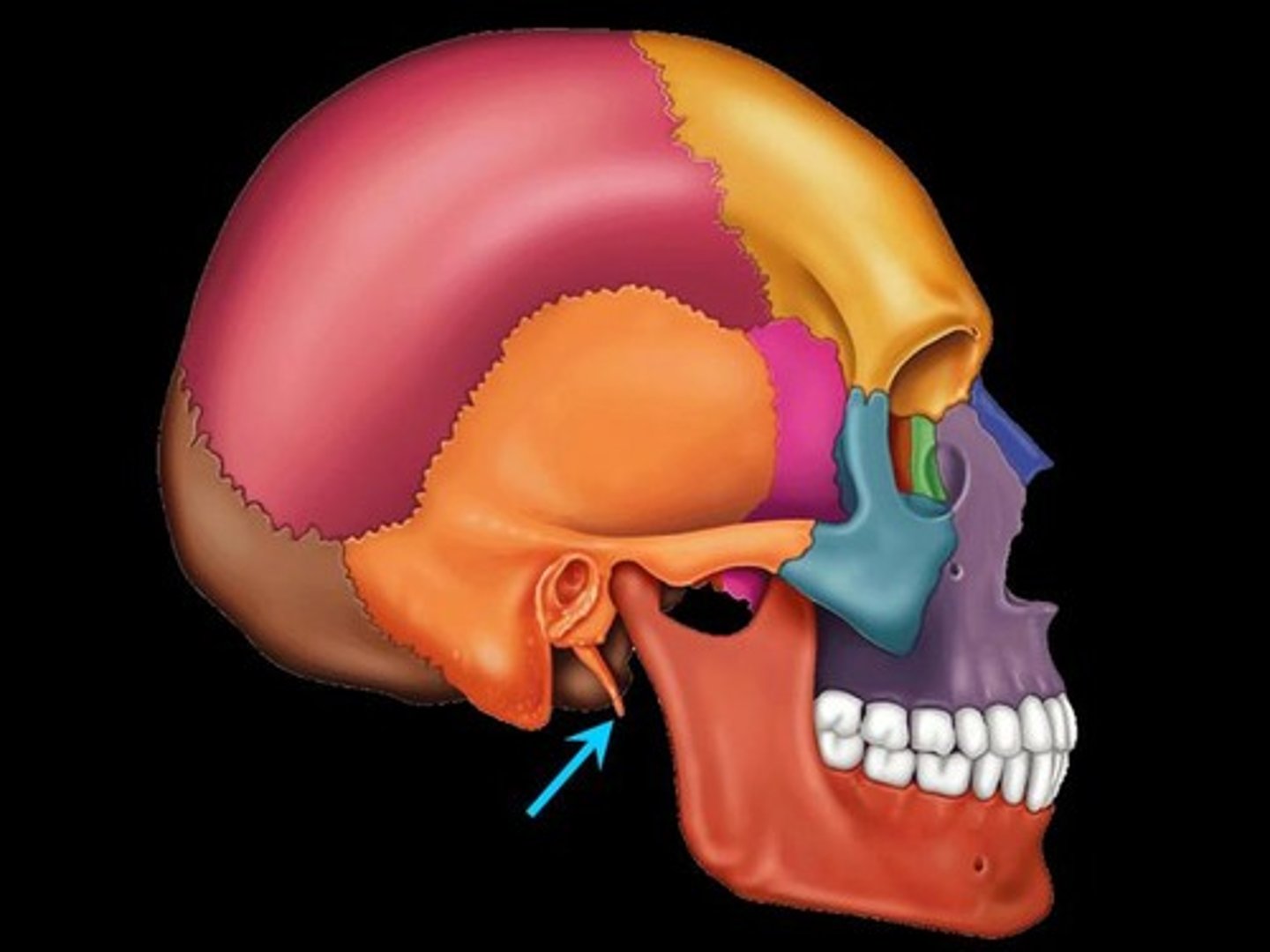
Mastoid process
Rough projection inferior and posterior to external acoustic meatus; attachment site for muscles
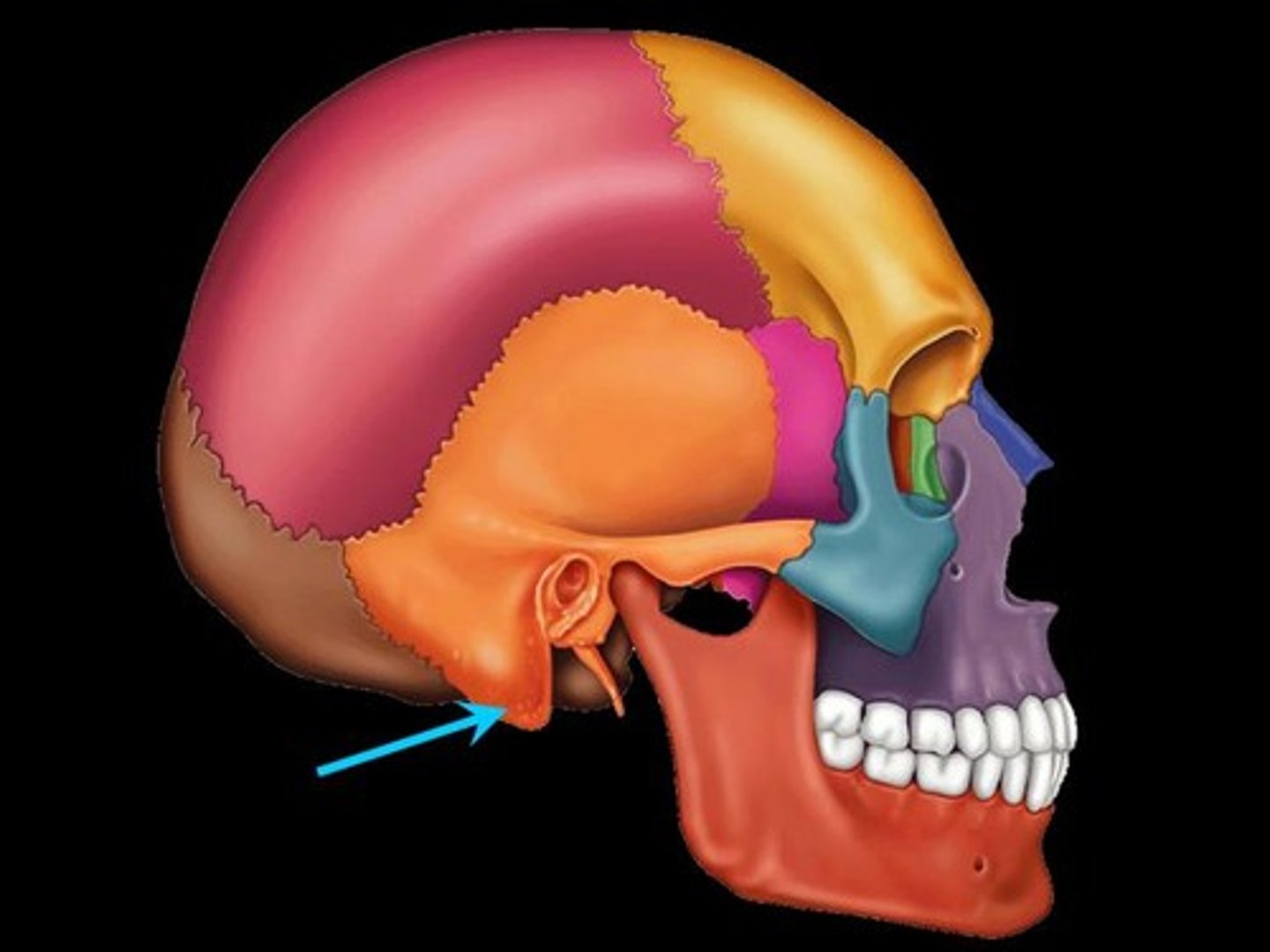
Occipital bone
Most posterior bone of cranium- forms floor and back wall
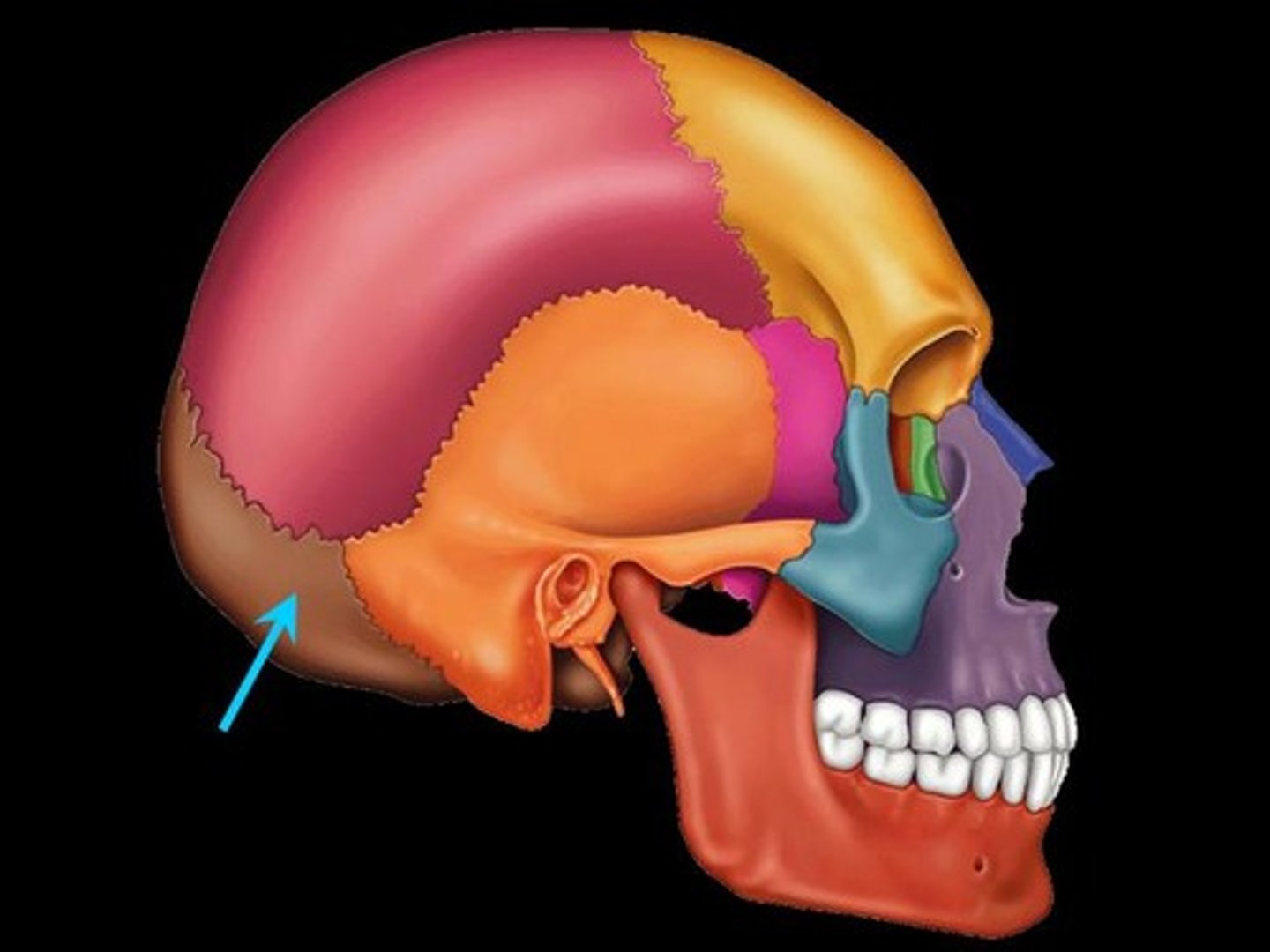
sphenoid bone
Bat-shaped bone forming the anterior plateau of the middle cranial fossa across the width of the skull. Keystone of the cranium because it articulates with all other cranial bones
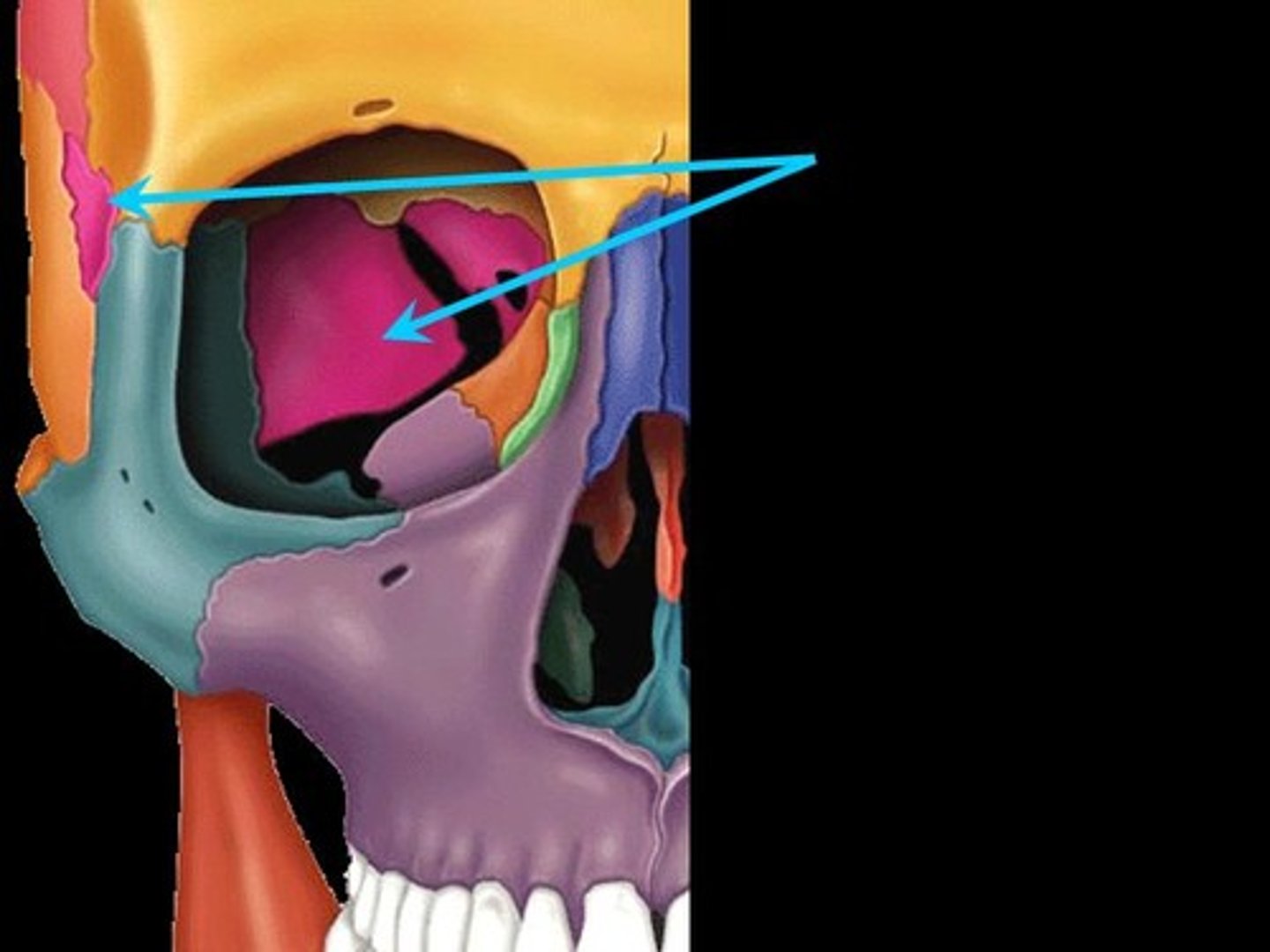
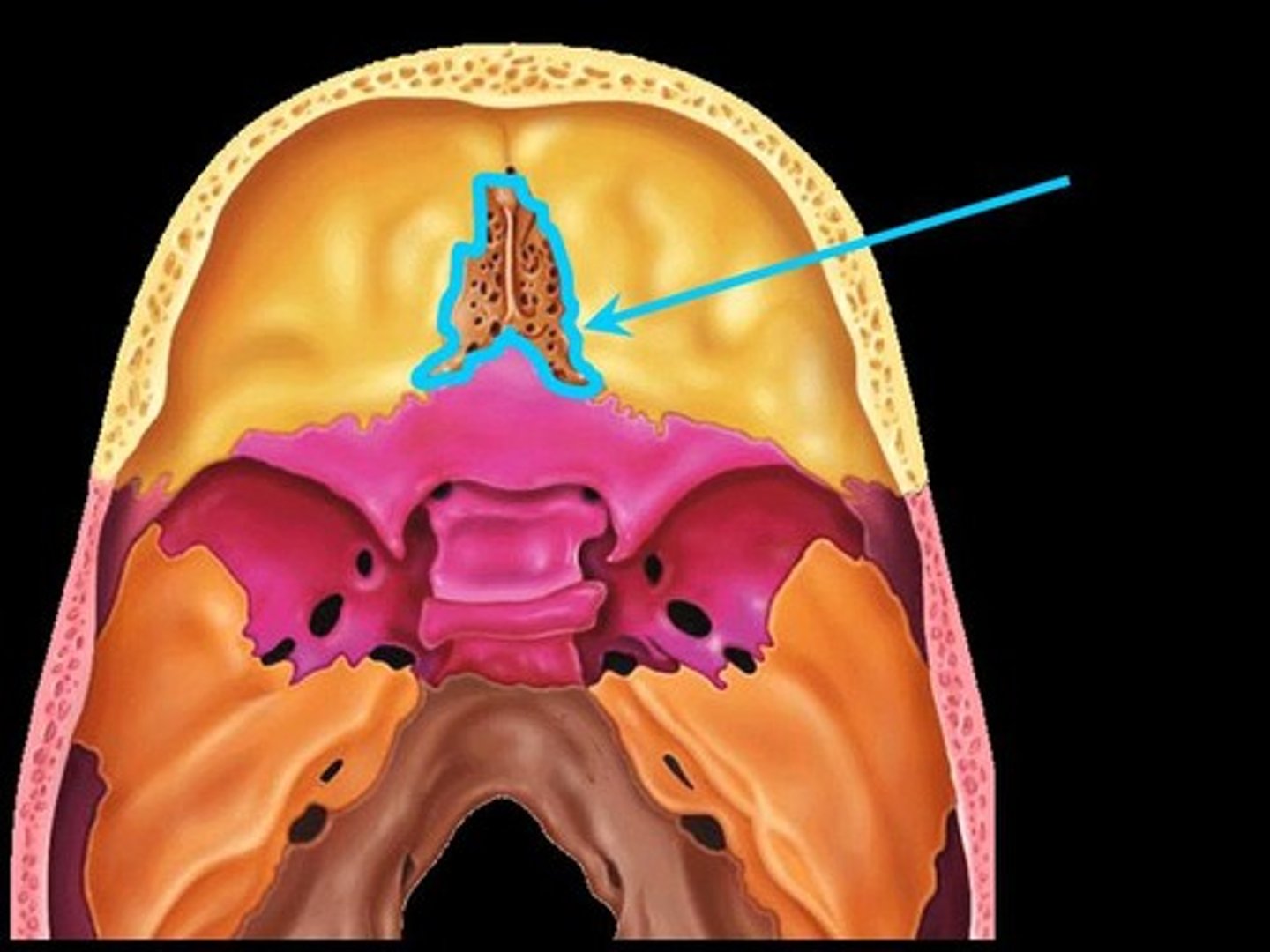
Ethmoid bone
Irregular shaped bone anterior to the sphenoid. forms the roof of the nasal cavity, upper nasal septum, and part of the medial orbit walls
Mandible
The lower jawbone, which articulates with the temporal bones in the only freely movable joints of the skull
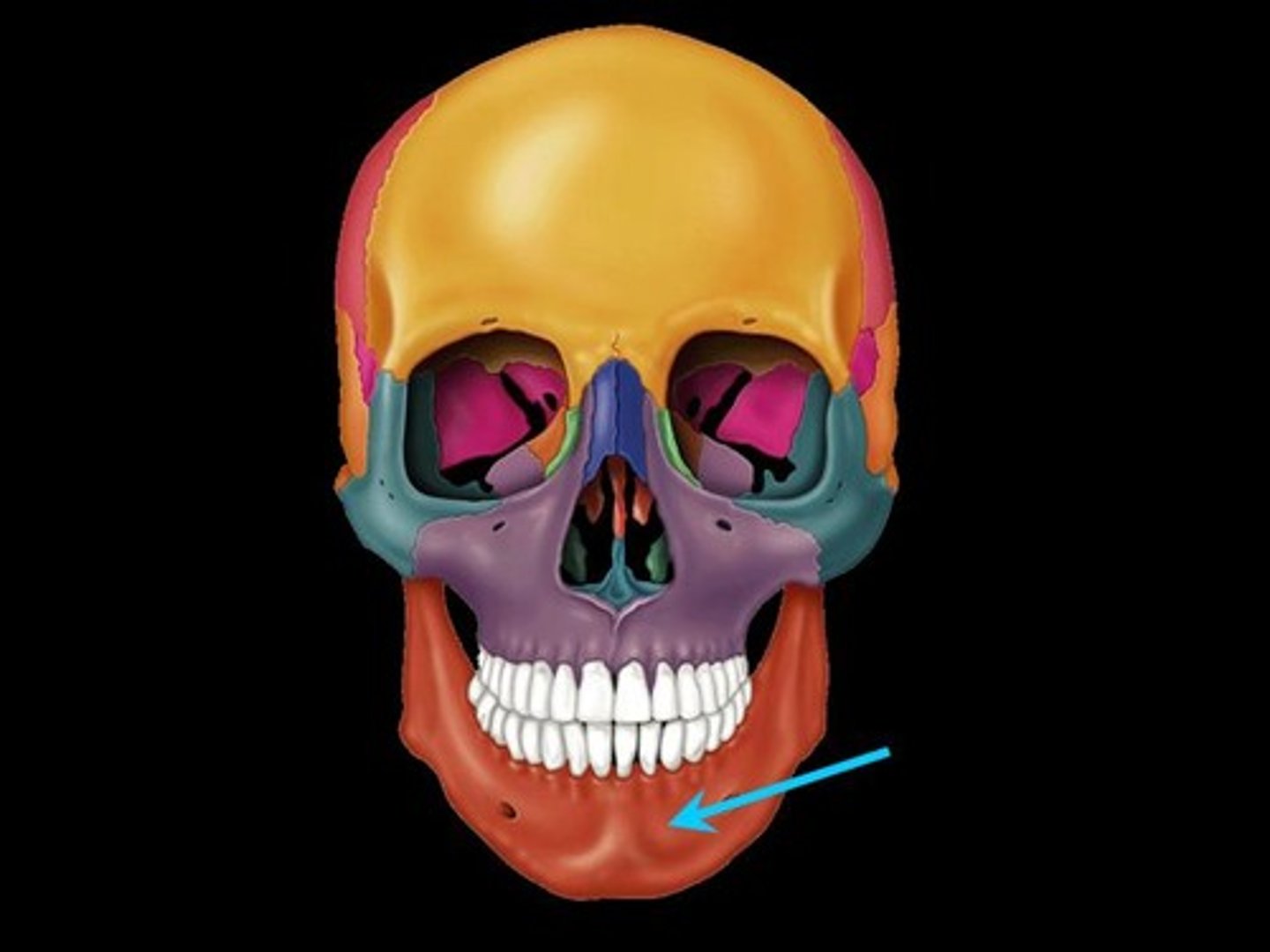
Maxillae
Two bones fused in a median suture; form the upper jawbone and part of the orbits. All facial bones, except the mandible, join the maxillae. Thus they are the main, or keystone, bones of the face.
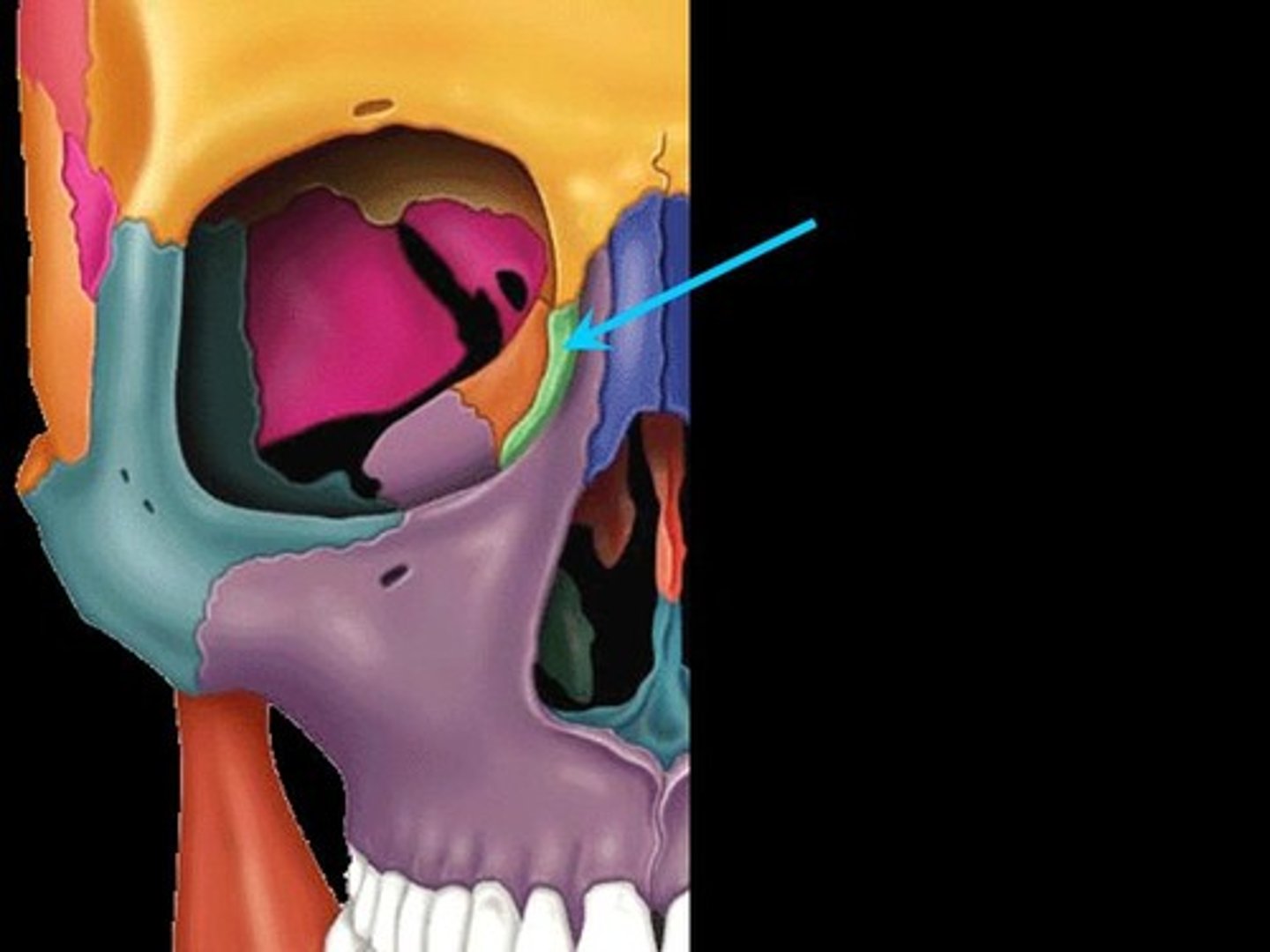
Lacrimal bone
Fingernail-sized bones forming a part of the medial orbit walls between the maxilla and the ethmoid. Each lacrimal bone is pierced by an opening, the lacrimal fossa, which serves as a passageway for tears (lacrima=tear)
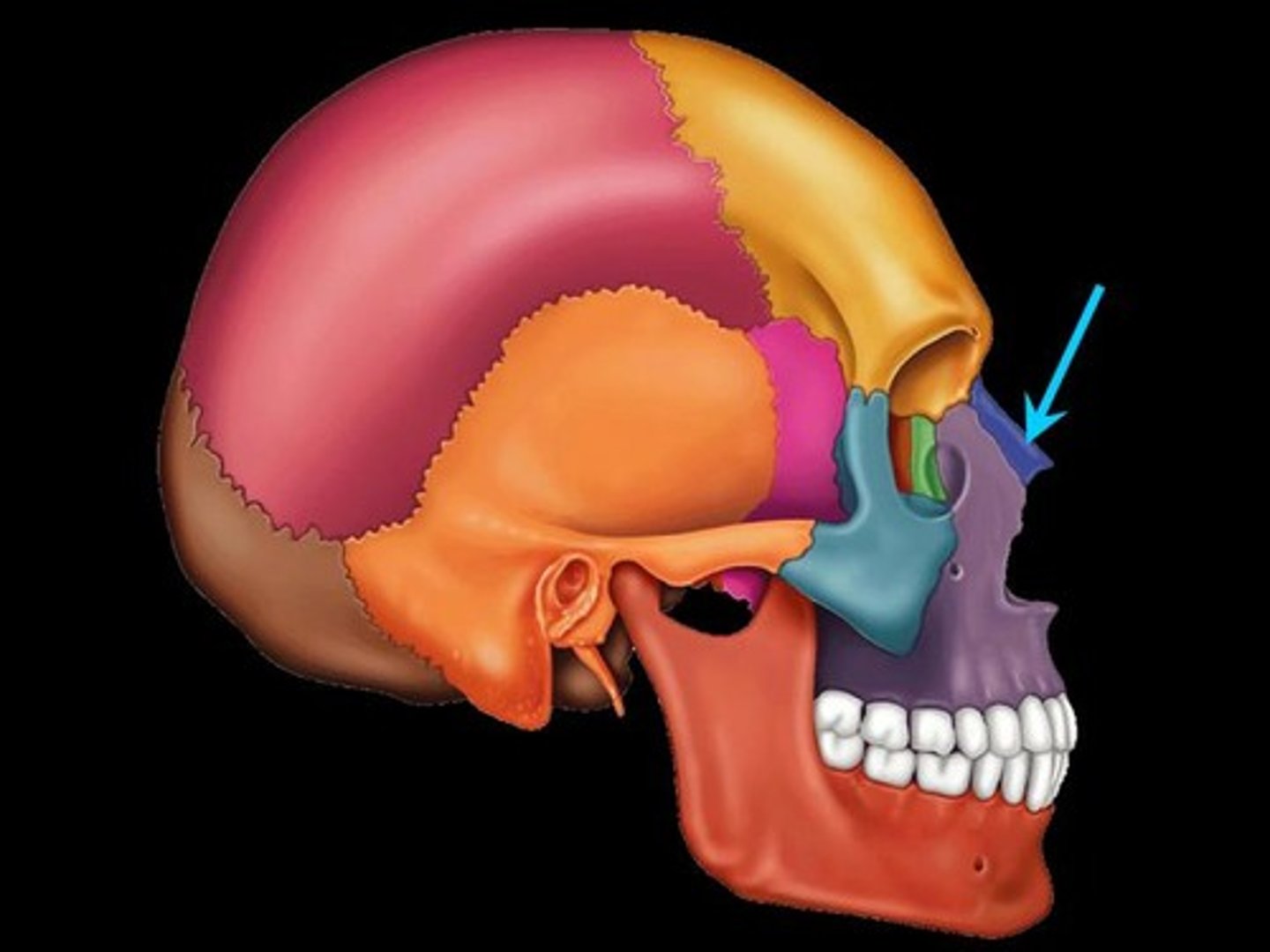
Nasal bone
Small rectangular bones forming the bridge of the nose
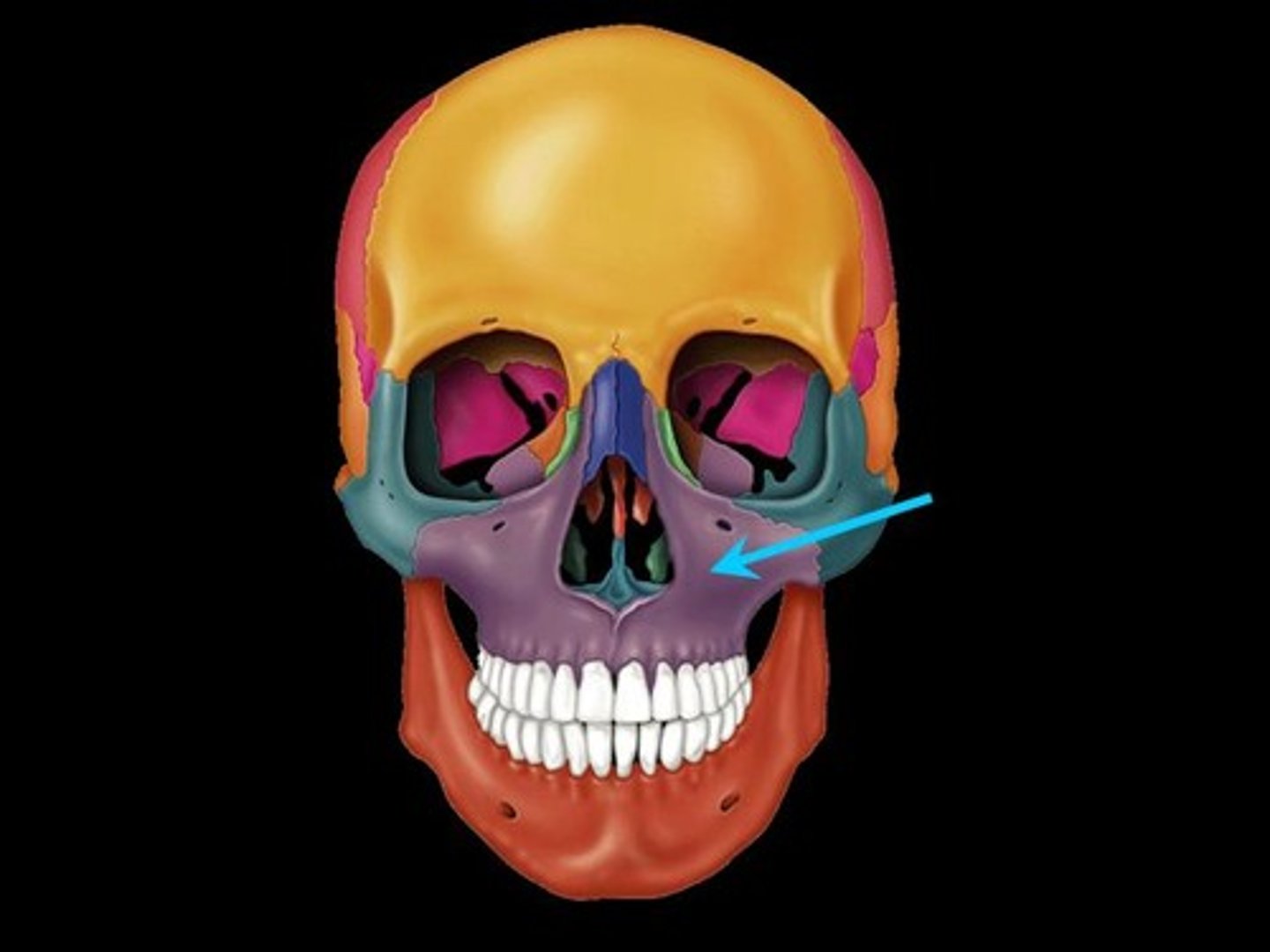
Zygomatic bone
Lateral to the maxilla; forms the portion of the face commonly called the cheekbone; and forms part of the lateral orbit. Its three process are named for the bones with which they articulate.
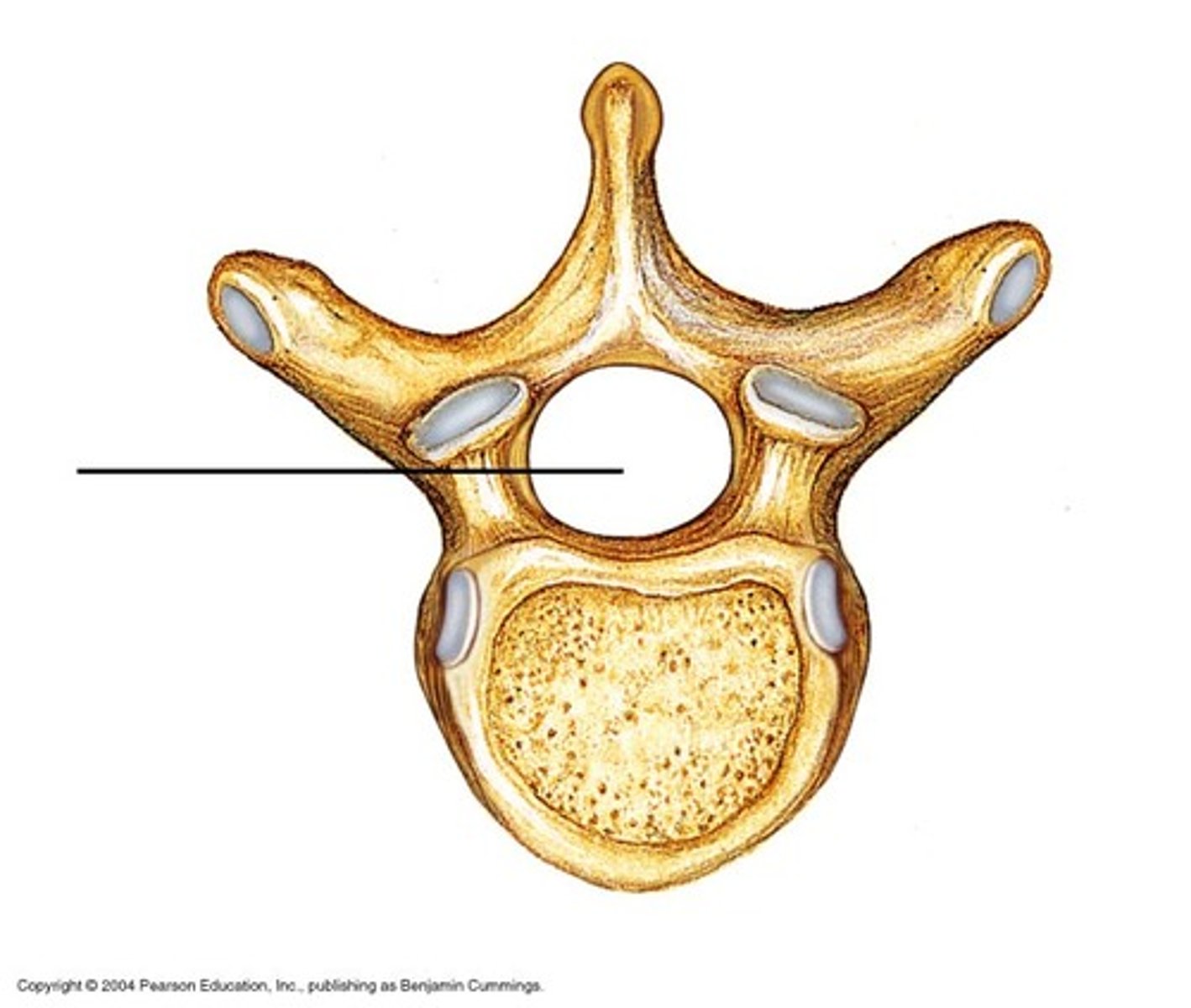
Vertebral arch
Composed of pedicles, laminae, and a spinous process, it represent the junction of all posterior extensions from the vertebral body
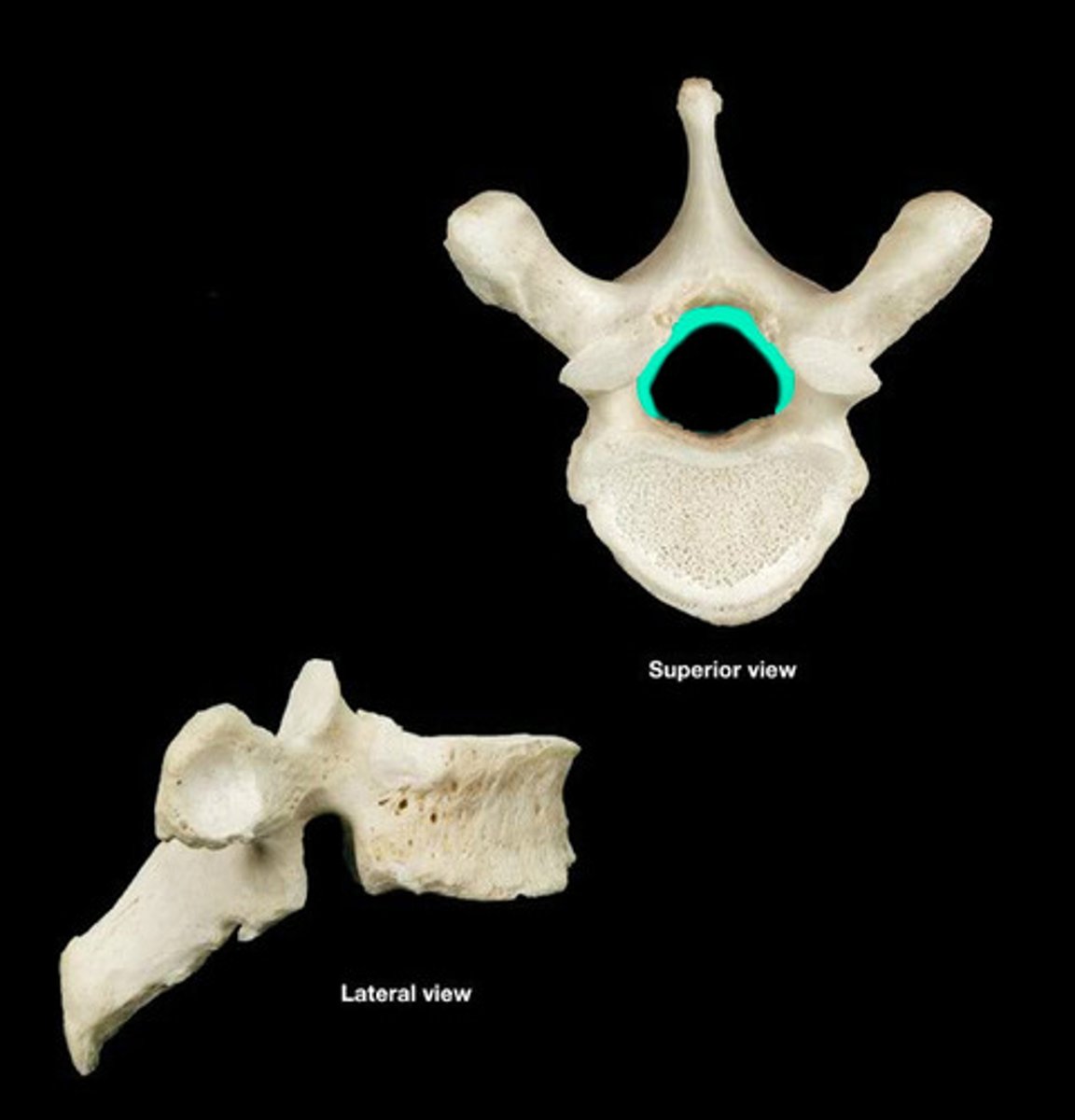
Vertebral foramen
Opening enclosed by the body and vertebral arch; a passageway for the spinal cord
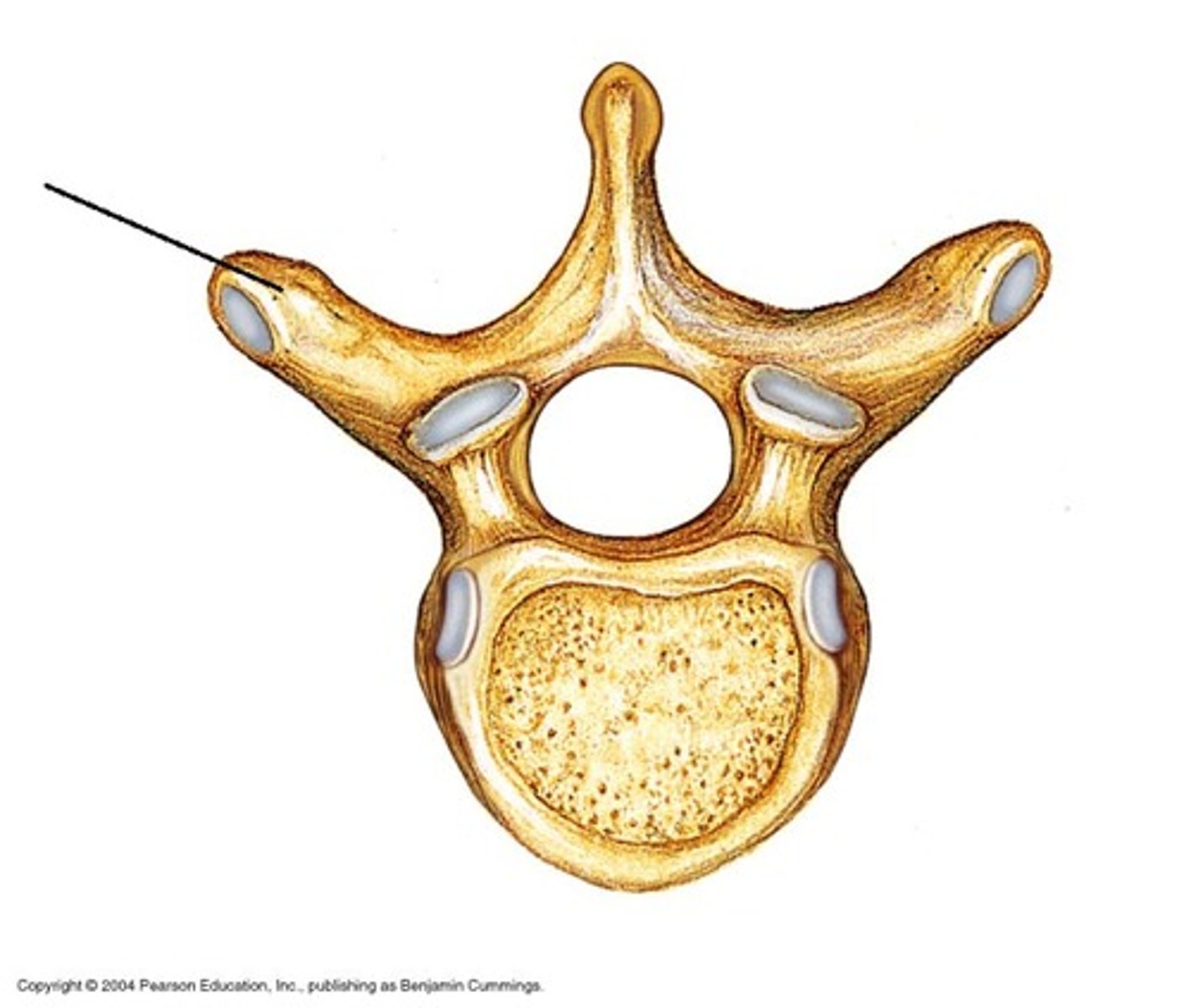
Transverse processes
Two lateral projections from the vertebral arch
Spinous process
Single medial and posterior projection from the vertebral arch
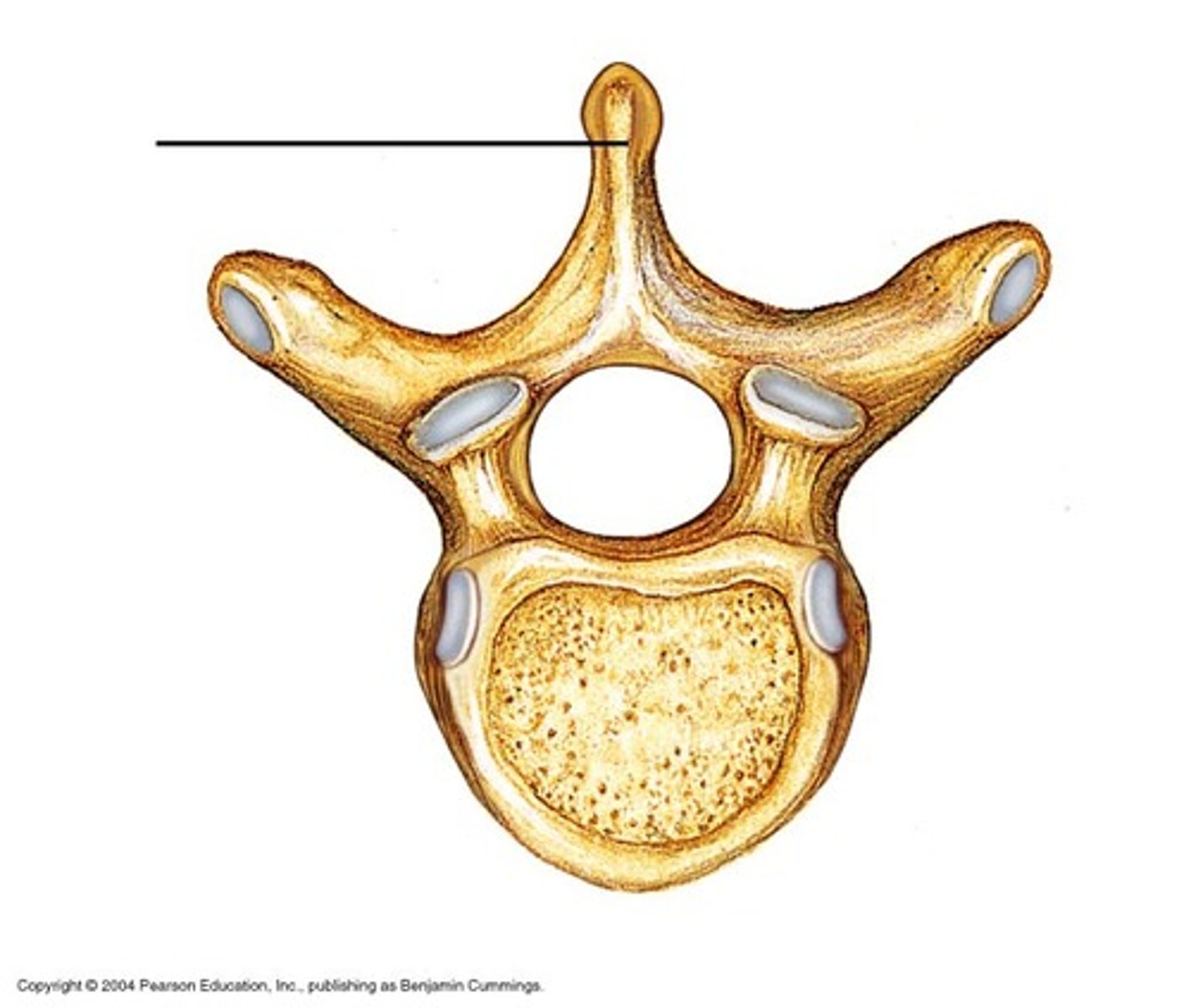
Superior and inferior articular processes
Paired projections lateral to the vertebral foramen that enable articulation with adjacent vertebrae. The superior articular process typically face toward the spinous process, whereas the inferior articular processes face away from the spinous process
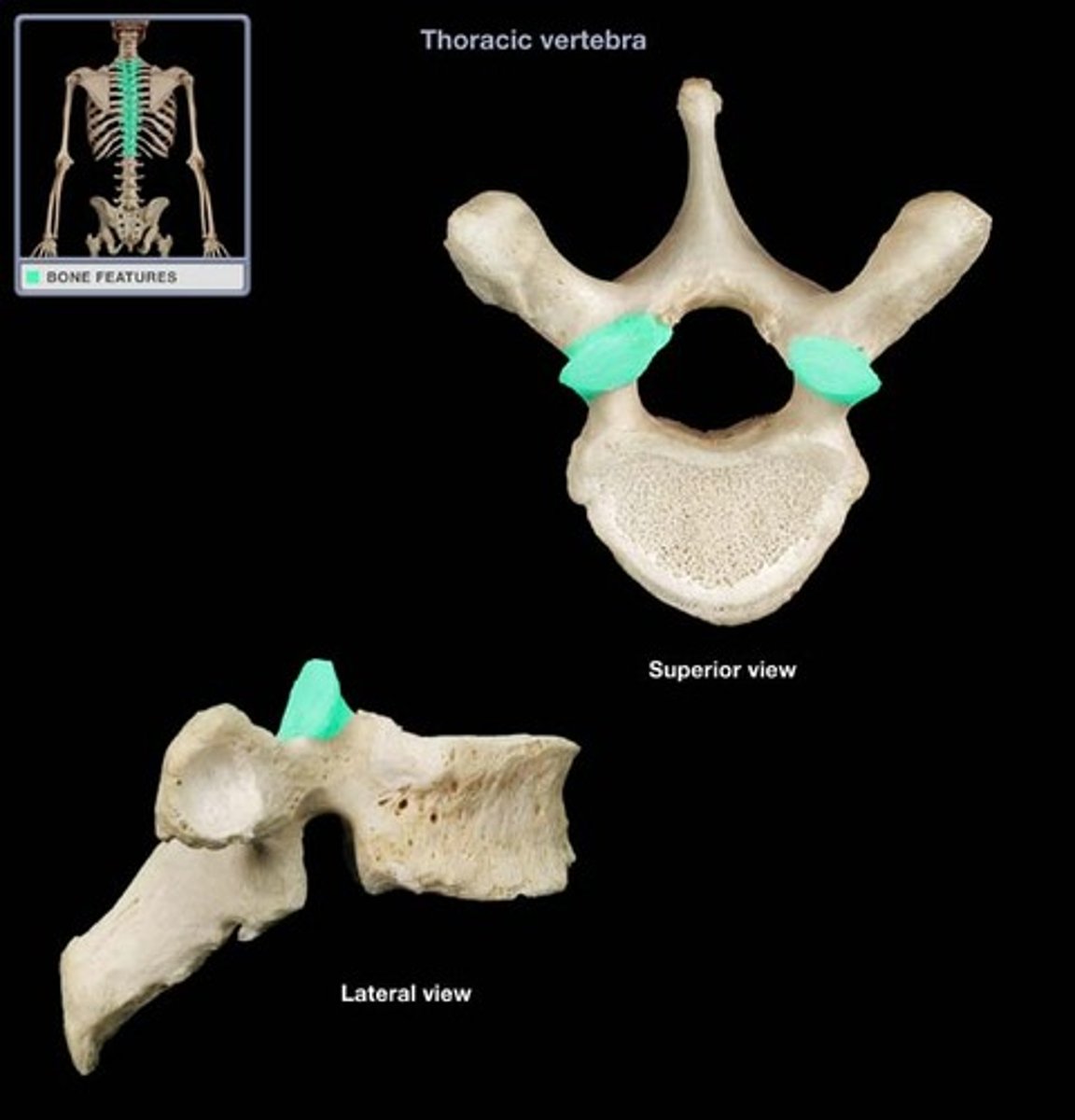
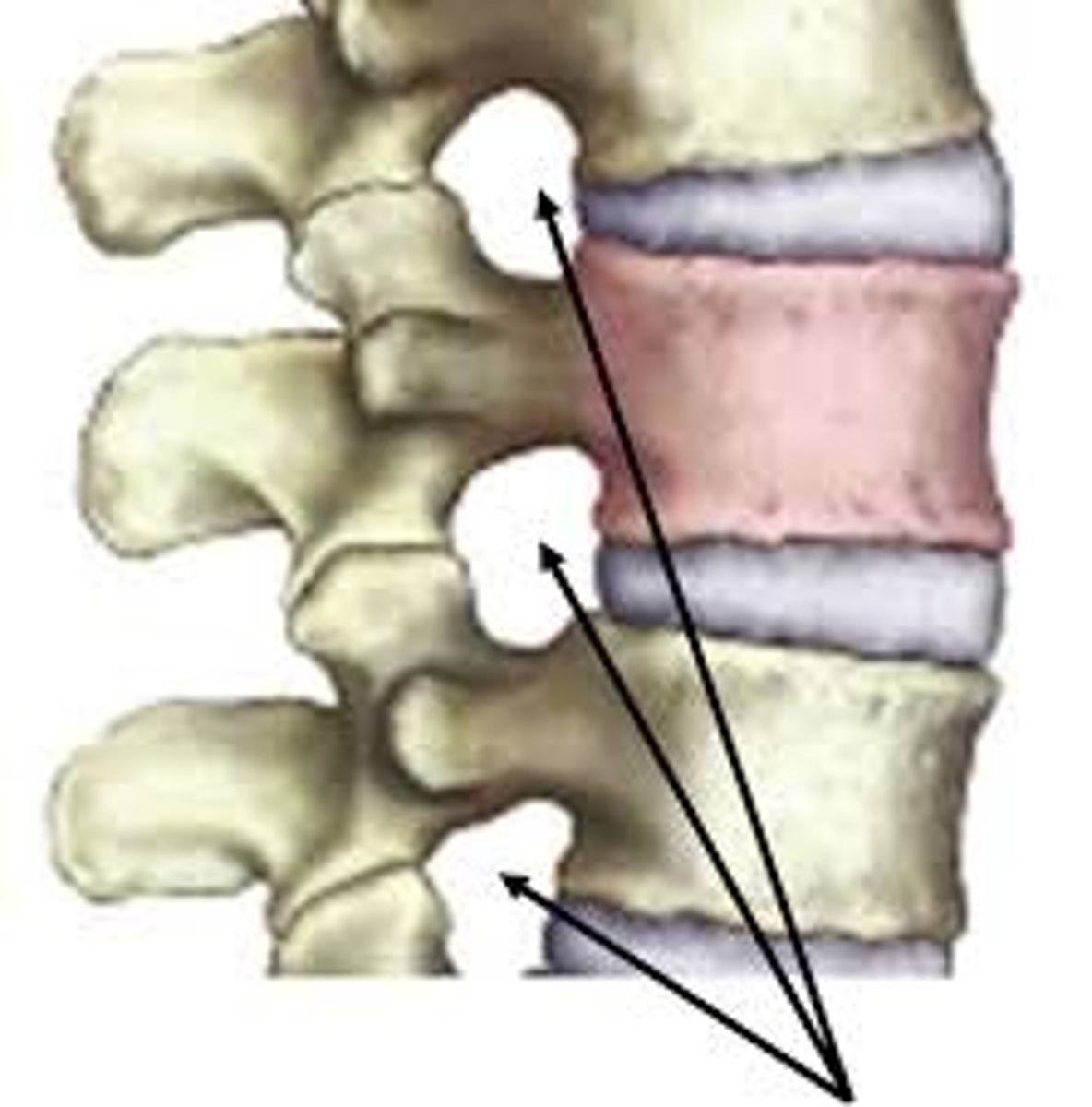
Intervertebral foramina
The right and left pedicles have notches on there inferior and superior surfaces that create openings for spinal nerves to leave the spinal cord between adjacent vertebrae
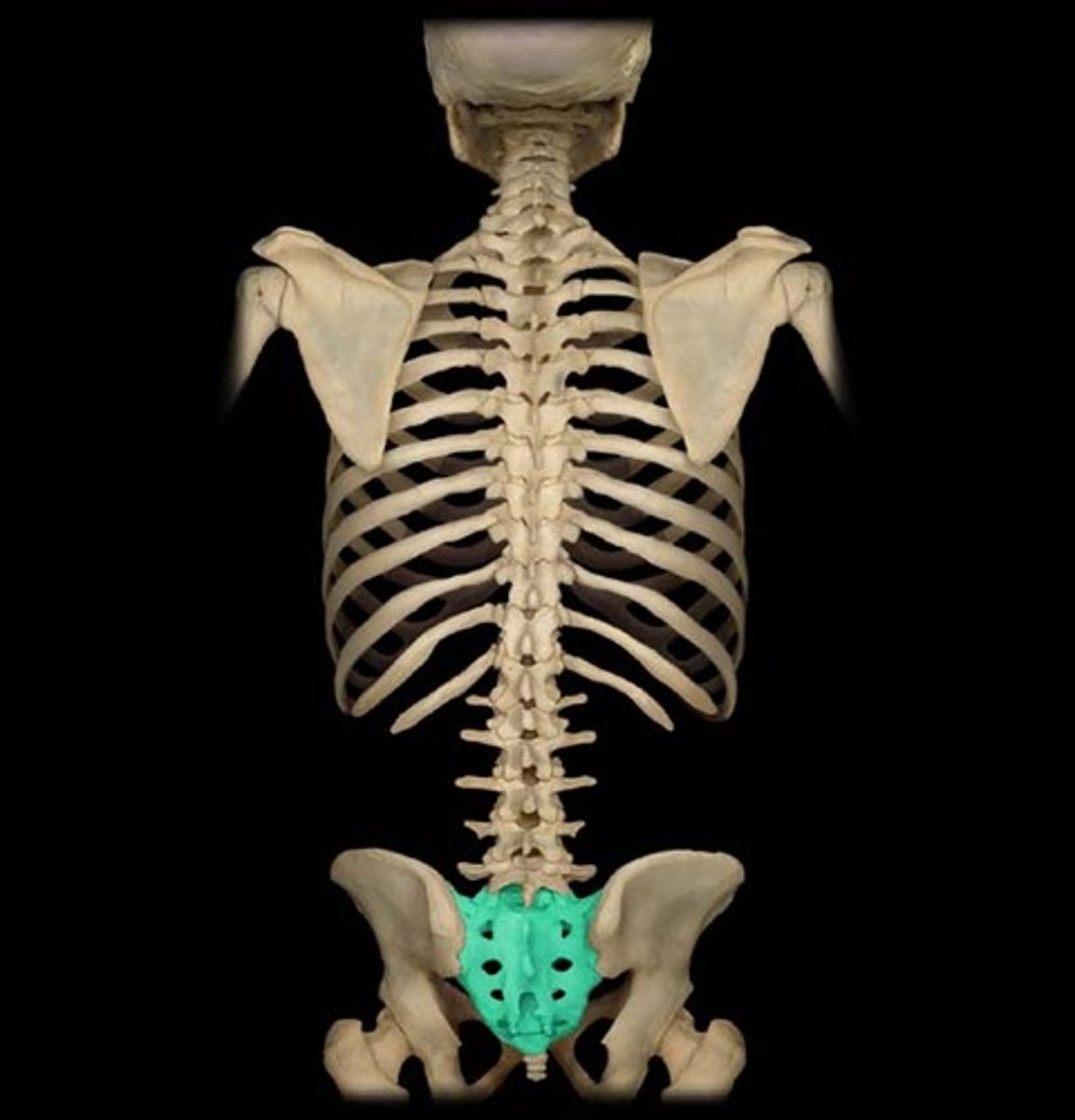
Sacrum
Composite bone formed from the fusion of five vertebrae
Coccyx
Human tailbone
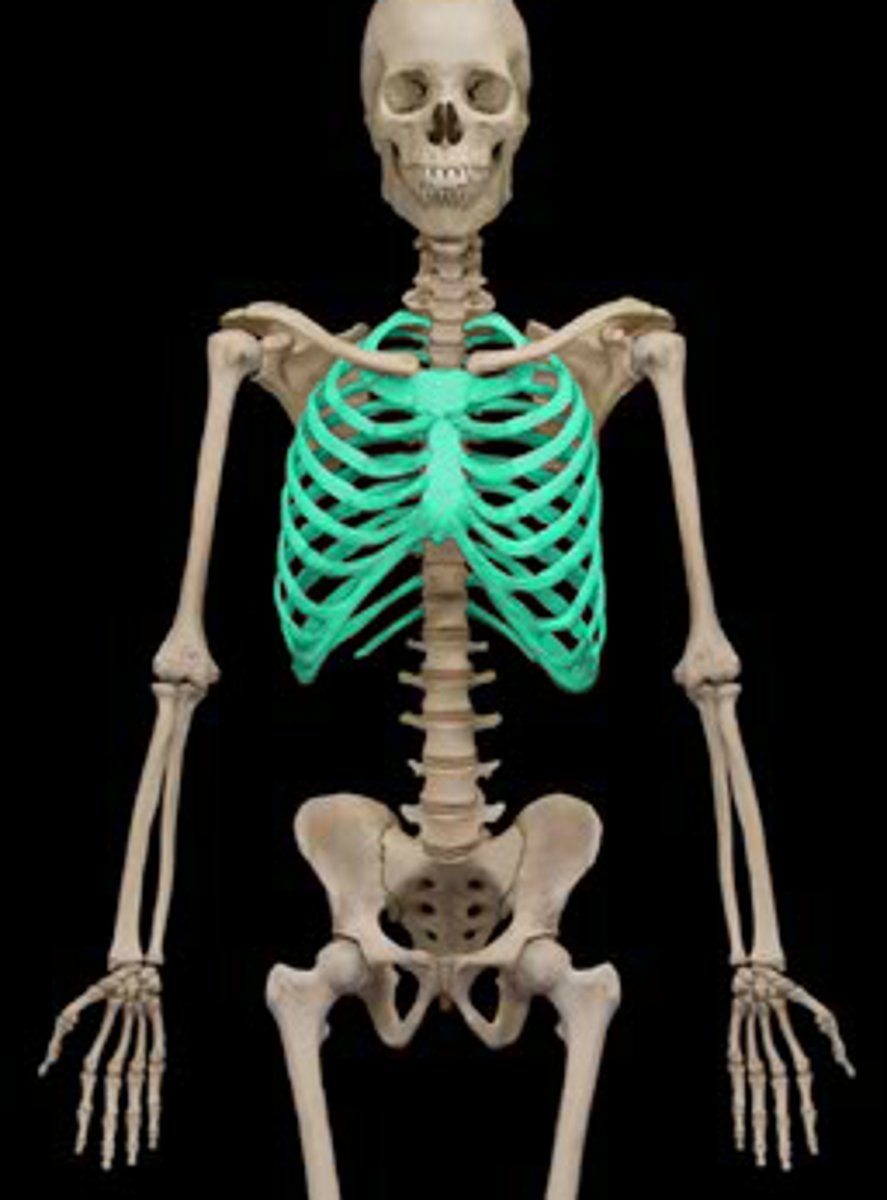
Thoracic cage
Consists of the bony thorax, which is composed of the sternum, ribs, and thoracic vertebrae, plus the costal cartilages
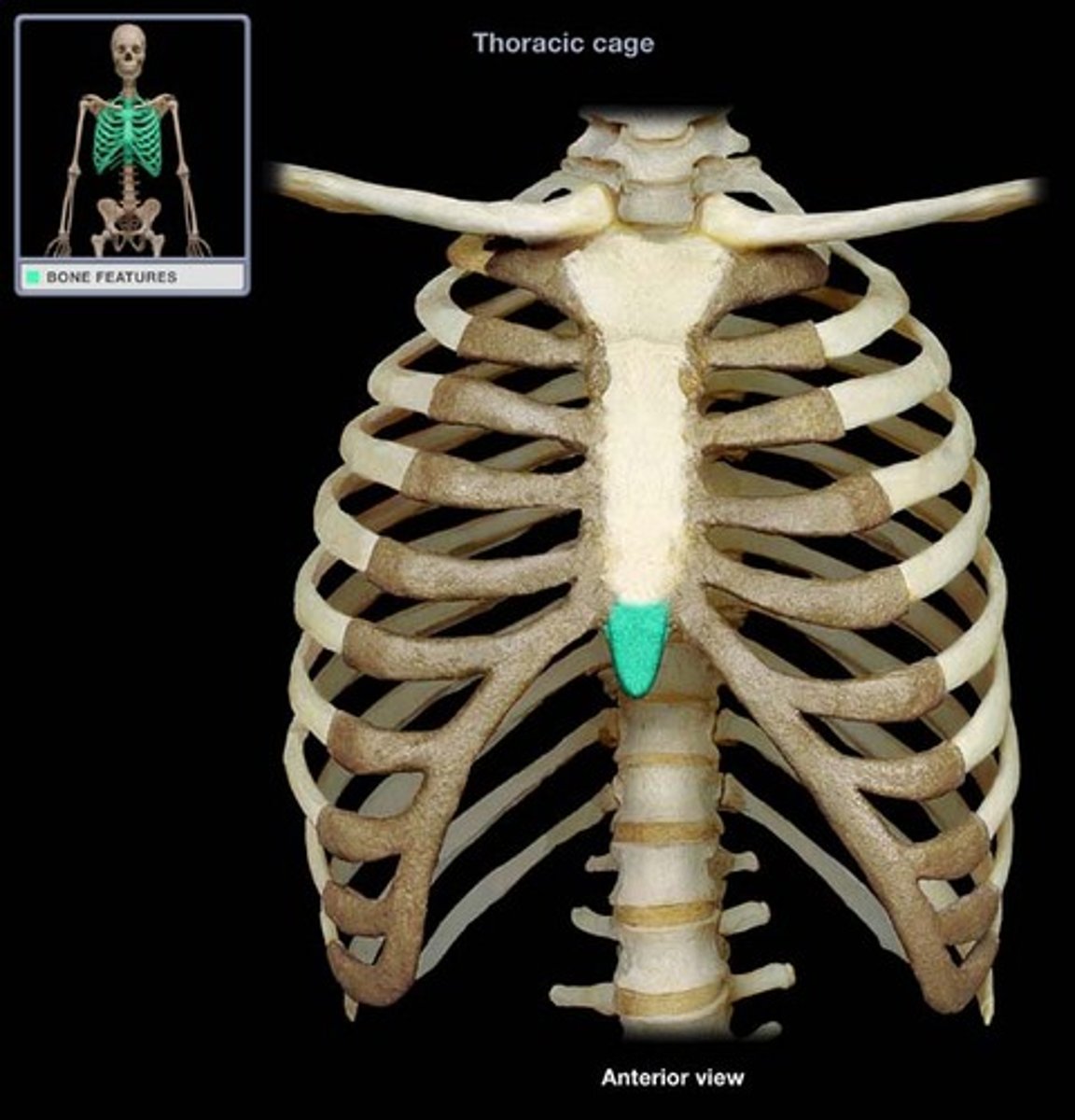
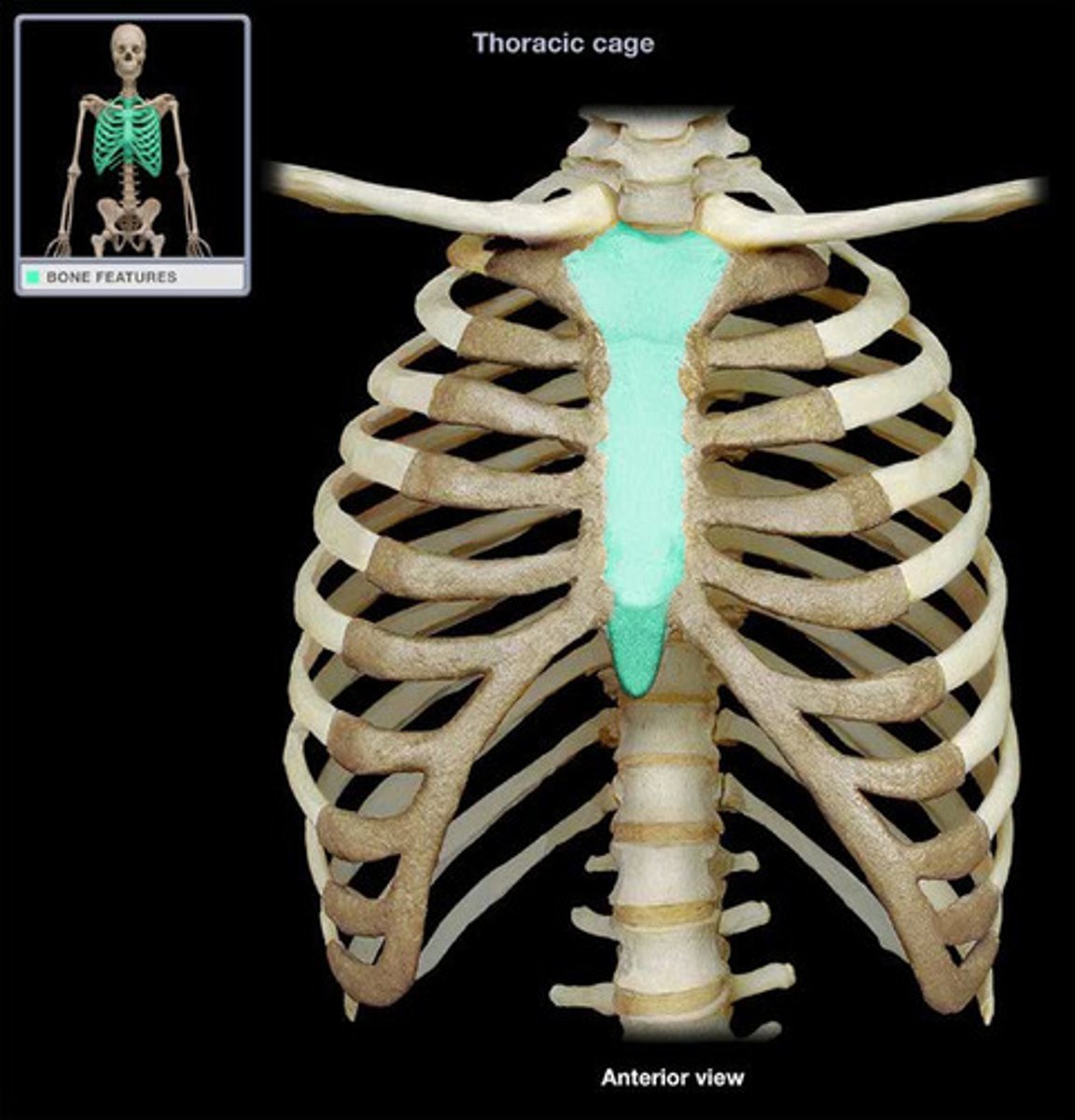
Sternum
Breastbone. Composed of three fused bones- manubrium, the body, and xiphoid process. It is attached to the first 7 pairs of ribs
Xiphoid process
Construct the inferior end of the sternum