ECON- 2003 McLean exam 1
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Scarcity
wants and needs > resources
opportunity cost
the value of the next-best forgone alternative; the value of the opportunity that you gave up when you chose one activity, or opportunity, instead of another
assumptions for decision making
1. self-interest
2. marginal decision making
3. optimization
marginal benefit (MB)=
chance in Total Benefit (TB)/ Change in quantity (Q)
Marginal Cost (MC)=
change in total cost (TC)/ Change in quantity (Q)
MB> MC
DO IT
MB< MC
DON'T DO IT
With increased activity...
-MB tends to fall.
-DIMINISHING marginal benefits
-MC tends to rise.
- INCREASING marginal cost
Michelle wants to purchase a new pone. Michelle will purchase the phone if:
the marginal benefit of the phone is greater than its marginal cost
PFF assumptions
- full employment of our factors of production
-use the best available technology
- freeze everything in time
a production possibilities frontier (PPF) illustrates?
-attainable production combinations
-unattainable production combinations
-opportunity cost.
comparable advantage
the ability to produce a good or service at a lower relative opportunity cost than another producer
the law of increasing opportunity cost
A principle in economics which holds that since some resources are better suited to producing one good or service than another, as the production of a good or service increases, the opportunity cost of each additional unit rises.
circular flow model
a model that concisely describes how goods, services, resources, and money flow back and fort in an economy
circular flow model
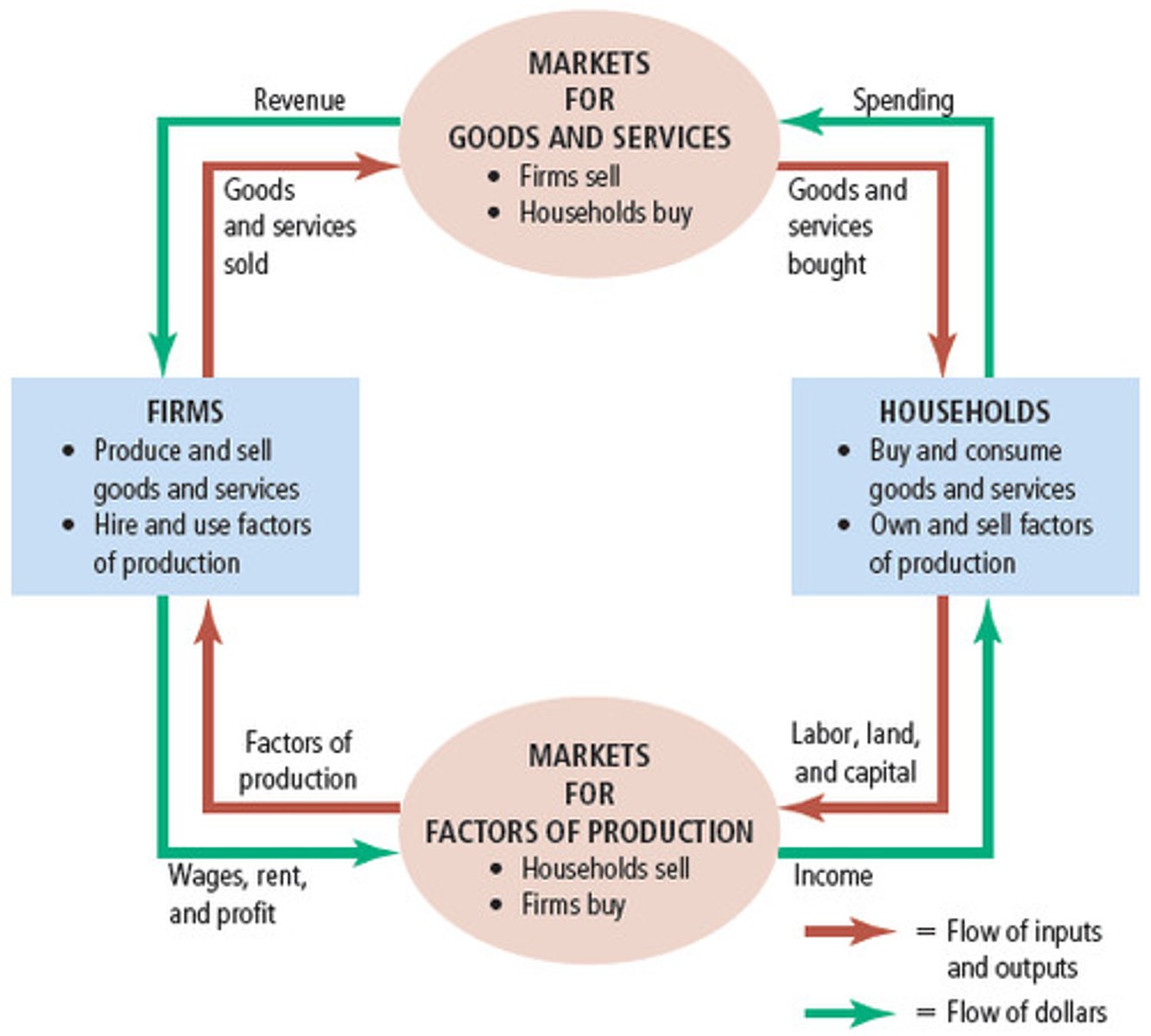
market
any place where, or mechanism by which, buyers and sellers interact to trade goods, services or resources
Law of demand
a price goes down quantity goes up
vise versa
demand curve
Demand curves are
Downward- sloping
three reasons demand slopes down
- income effect
-diminishing marginal utility
- substitution effect
income effect
the effect that a change in the price of a good, service, or recource has on the purchasing power of income
diminishing marginal utility
as people consume more of a good during a fixed time period, the satisfaction received from each additional unit falls
diminishing marginal utility definition
the negative relationship between the quantity of a good, service, or resource and the marginal utility obtained from each additional unit consumed in a given period of time
substitution effect
the effect that a change in the price of one good, service, or resource has on the demand for another
market demand
the overall or total demand for a good, service, or recource. it represents the summation of indivitual demand curves, whether they represent individuals, communities, states, or nations
increase in demand
demand curve shift to the right
decrease in demand
demand curve shift to the left
determinants of demand
- change in taste or preferance
-change in income
-normal good
- inferior good
-change in the price of related goods
-change in the price of related goods
-change in the price of a compliment
-change in the numbers of buyers
-change in expected future prices
related goods
-substitutes
-complements
substitutes
goods, service, or recourses that are viewed as replacements for one another
complements
goods, services, or resources that are used or consumed with one another
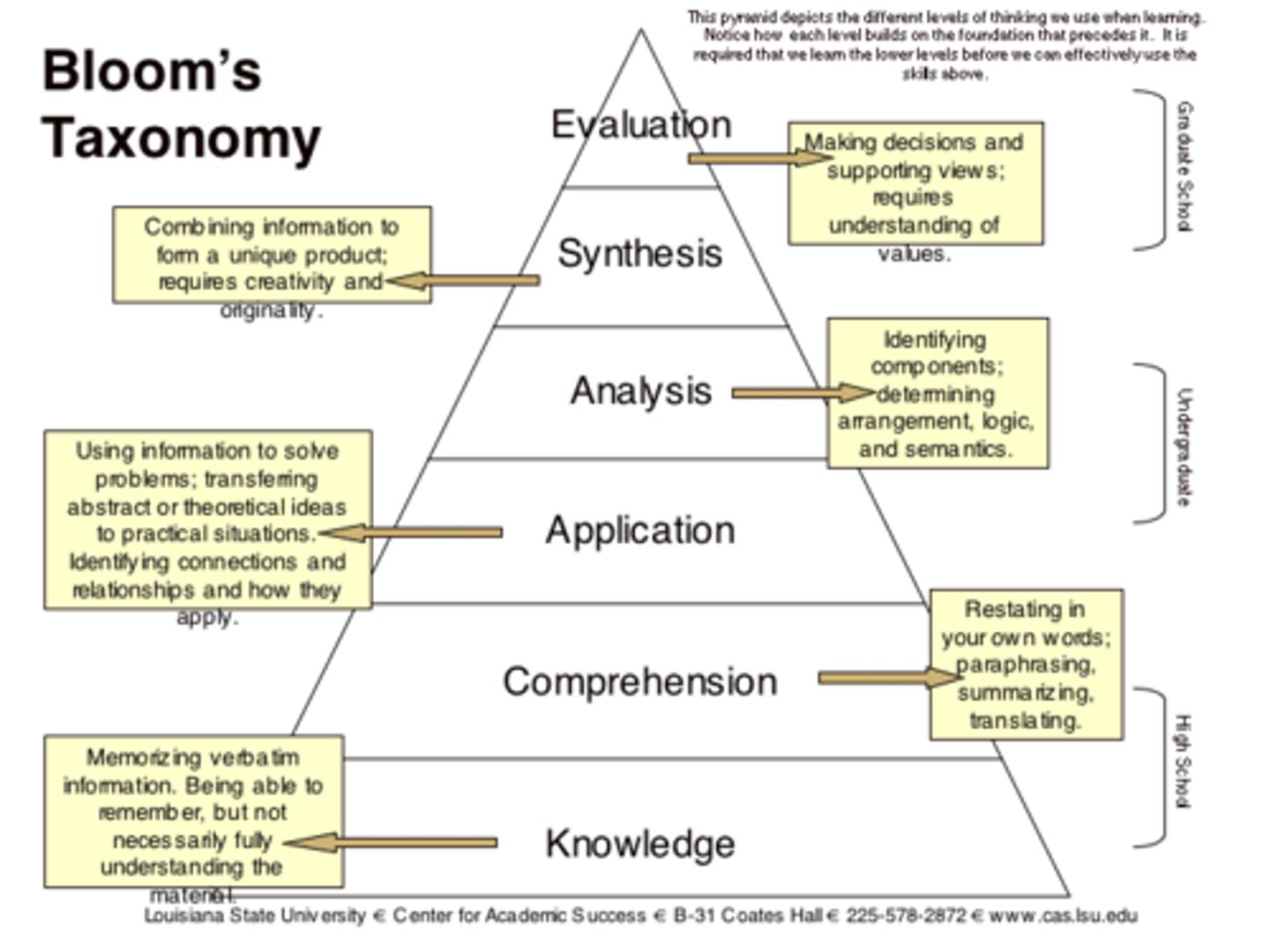
blooms taxonomy
non price determinants of supply
- change in resource costs
-change in use of technology
- change in number of sellers
-change in taxes and change in subsidies
-change in expectations of future prices
where does the market equilibrium occur? and how do we show this graphically?
S=D
(Qs=Qd)
what happens when supply and demand change?
- it will depend on many things
-shapes of the supply and demand curves
-intensity of the change
- direction of the change
price ceiling
a maximum legal price at which a good, service, or resource can be sold
price floor
a minimum legal price at which a good, service, or resource can be sold
tools, machinery, and infrastructure are classified under the resource category of:
physical capital
self interest, marginal decisions, and optimization all form the basis of:
rational decision making
increasing marginal cost describes:
the direct relationship between the marginal cost associated with the use of a good or service and the quantity produced
when the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost, we reach an:
optimal level of output