AS Chemistry T4 - Inorganic Chemistry
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is the metal Ion Test?
Flame Test
How to conduct a flame test?
Mix a small volume of the unknown compound with a few drop of dilute HCl
Heat Nichrome wire / Platinum wire with Bunsen burner to sterilize it
Dip the wire the sample of the compound / acid mixture over a roaring flame
Observe the color of the flame
Results of the Flame Test
G1 Metals
Lithium - Red
Sodium - Orange / Yellow
Potassium - Lilac
Rubidium - Red
Caesium - Blue
G2 - Metals
Calcium - Brick Red
Strontium - Crimson Red
Barium - Apple Green
How to carry out a Sulphate Ion Test?
Add a few drops of dilute HCl to the unknown compound solution
Then add a few drop of BaCl solution
Note what you observe
Sulphate Ion Test Result
White precipitate of barium sulfate formed means that the sulfate ions are present.
How to Test for Halides?
Add nitric acid to a test tube with unknown compound (Removes ions that may interfere with reaction)
Then add silver nitrate solution (AgNO3(aq))
Reaction:
Ag+(aq) + H-(aq) —> AgH(s)
Result of a Halide Test
Precipitate of Silver Halide Color depends on the Halide
Fluoride Fl-
no precipitate, (AgF) is soluble
Chloride Cl-
white precipitate
> dissolved in dilute ammonia - colorless solution
Bromide Br-
cream precipitate
dissolved in dilute ammonia - ppt unchanged
dissolved in concentrated ammonia - forms colorless solution
Iodide I-
yellow precipitate
Insoluble
Trend in solubility: G7 - Halogens
Solubility decreases down the group
How to test for Carbonate Ions?
(CO32-) and (HCO3-)
Add dilute HCl to the unknown compound
Bubble the solution through lime water
Observe the change in limewater
Result for Carbonate Ions
Lime water turns from colorless to cloudy
How to test for Ammonium Ions
Ammonium gas is alkaline
Add sodium hydroxide to the solution
Gently heat the mixture and hold damp litmus paper above it
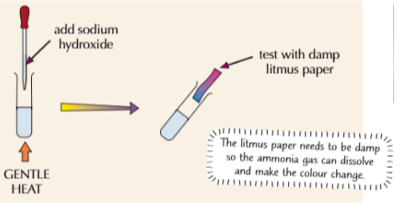
Why does litmus paper in ammonium test have to be damp?
Litmus paper must be damp so that the ammonium gas can dissolve and make the color change
Why in the Halide test do we use nitric acid to remove impurities instead of Hydrochloric Acid (HCl)
Hydrochloric acid contains Chloride ions so it would give a positive result in the Halide test.
How to test for Hydroxide Ions? (OH-)
Dip litmus paper into the solution
Results for Hydroxide Test?
If Hydroxide Ions are present red litmus paper turns blue
indicating a basic alkaline solution
Reactivity of Group 2 Metals..
Increases down the group
Reason for Trend in Reactivity (Group 2) as you go down the group?
As you go down the Group 2
Increased shielding - shield valance electrons from attraction of the nucleus
Increased atomic radius - valance electrons are further → reduces electrostatic attraction between valance electrons & nucleus
→ Easier to lose 2 valance electrons to form 2+ ions
Trend in Ionisation Energy Down Group 2
Ionisation Energy Decreases
Explanation for Trend in Ionisation Energy Down Group 2
Increased shielding - shields attraction of nucleus
Increases Atomic Radius - Valance electron experience less of an electrostatic attraction from nucleus
Making it easier to lose 2 Valance electrons
→ Ionisation energy decreases bc less energy is required to remove valance electrons as you go down Group 2
Group 2 Metal + Water
G2 Metal + Water → Hydroxide + Hydrogen
Metal hydroxides are alkaline solutions
Types of Inorganic Reaction: Reaction of acids
dilute Hydrochloric Acid - Strong Acid
Sodium Hydroxide - Strong base
Acids do not simply mix with water, when they dissolve in it
They react with water to form aqueous hydrogen Ions
e.g. HCl(aq) —> H+(aq) + Cl- (aq)
All dilute acids produce H+(aq) - all dilute acids react similarly
Acid + Metal
Acid + Metal —> Hydrogen Gas + Ionic Metal compounds (Salts)
Types of Inorganic Reaction: Acid + Metal Oxide
Alkalis - dissolve in water to form aqueous solutions
Neutralization Reaction (Acids)
Acid + Metal Hydroxide / Metal Oxide → Salt + Water
Why do Acids & Alkalis Neutralise eachother?
Hydrogen ions react with the Hydroxide ions to form water
H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
Solubility of Acids: Which acid is Soluble & Which is Insoluble in water
Soluble in water…
All common acids
Insoluble in water…
XXX
Solubility of Salts: Which salt is Soluble & Which is Insoluble in water
Soluble in water…
All nitrates
All chlorides…
All sulfates…
→ Calcium & Silver sulfate are slightly soluble
All sodium, potassium & ammonium salts
Insoluble in water…
silver chloride & Lead Chloride
Barium sulfate & Lead Sulfate
G2: Reaction with Oxygen (General)
2M(s) + O2 (g) —> 2MO(s)
Magnesium + Oxygen
2Mg(s) + O2 (g) —> 2MgO(s)
Mg burns with a bright white flame
Calcium + Oxygen
2Ca(s) + O2 (g) —> 2CaO(s)
Ca burns with a red flame
Strontium + Oxygen
2Sr(s) + O2 (g) —> 2SrO(s)
Sr burns with red flame
OR Sr(s) + O2 (g) —> SrO2(s)
forms SrO2 peroxide
Barium + Oxygen
2Ba(s) + O2 (g) —> 2BaO(s)
Ba burns with apple green flame
OR Ba(s) + O2 (g) —> BaO2(s)
Ba forms BaO2 peroxide
G2 Metals Reaction with Water (General) Equation
M(s) + 2H2O(l) → M(OH)(s) + H2(g)
Beryllium + Water
Be doesn’t react with water
No reaction
Magnesium + Water
Magnesium doesn’t react with water
Magnesium reacts vigorously with steam
Mg(s) + H2O(l) → MgO(s) + H2
Magnesium + water → magnesium oxide + hydrogen gas
Calcium + Water
Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) → Ca(OH)(s) + H2(g)
Reacts moderately with cold water
Forms strontium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas
Strontium + Water
Sr(s) + 2H2O(l) → Sr(OH)(s) + H2(g)
Reacts rapidly with cold water
Forms strontium hydroxide + Hydrogen gas