Ch. 11 Costal Landscapes
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is swash and backwash?
Waves break when they reach shallow water at the shoreline. The water that moves up the shore is called the swash. The swash carries sediment up the shore. The water that moves back down the shore is called the backwash. The backwash carries sediment back down the shore.
Describe constructive waves and destructive waves.
Constructive waves
Constructive waves have a strong swash and a weaker backwash, deposit sediment on the shore, happen in calm weather and during summer months, when waves have less energy.
Destructive waves
Destructive waves have a weak swash and a stronger backwash, erode sediment from the shore, happen in poor weather and during winter months, when waves have more energy.
Describe the 5 erosion processes.
Hydraulic action is the force of waves hitting the coast, removing rock and sand.
Compressed air occurs when trapped air in rock cracks is compressed by waves, causing pressure that eventually breaks the rock.
Abrasion occurs when waves smash pebbles, stones, and rocks against the coast, breaking off pieces of rock.
Attrition happens when pebbles and stones rub against each other, becoming rounded and worn down into fine sand.
Solution occurs when seawater gradually dissolves rock on the coastline due to its salt content.
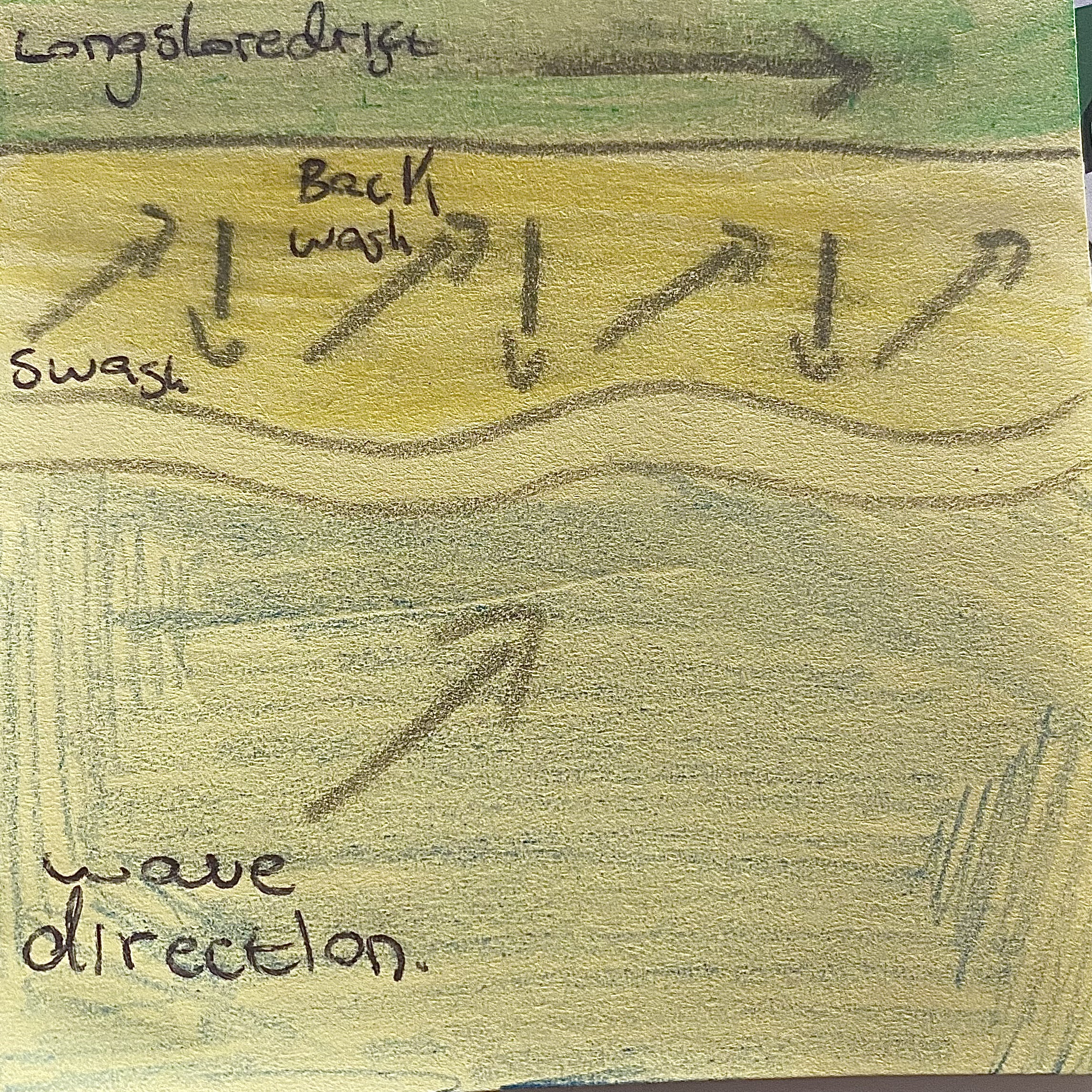
Describe the porches of longshore drift with a labelled diagram.
Longshore drift is the process where waves move sediment along the coast. Waves approach at an angle, and the swash carries sediment up the beach, while the backwash moves it back down at a right angle. This zigzag motion gradually transports sand, pebbles, and other materials along the shore, reshaping the coastline and forming features like spits and sandbars.
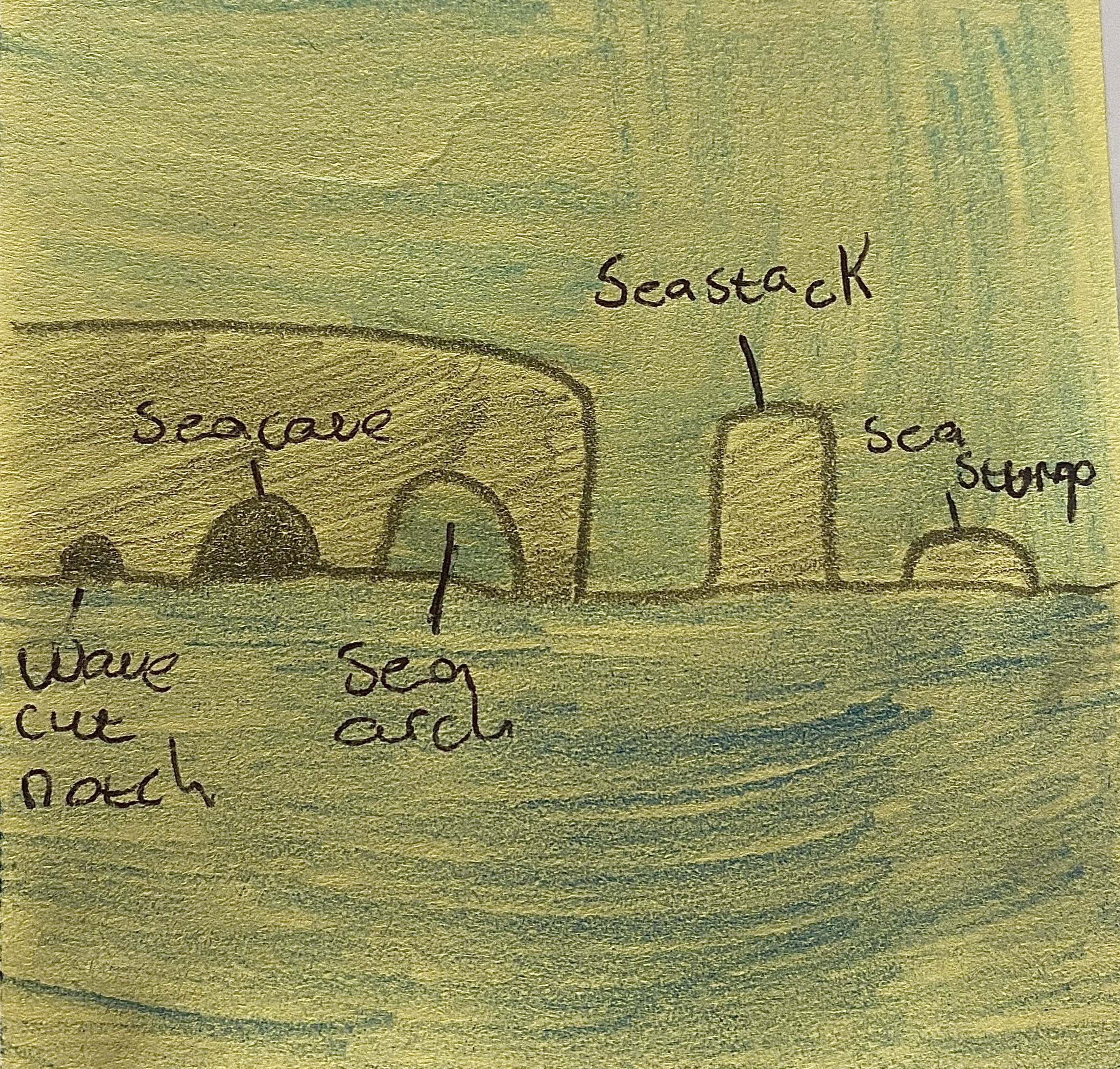
Describe how sea caves, sea arches, sea stacks and sea stumps form with a labelled diagram.
Sea caves, arches, stacks, and stumps are found on rocky coastlines and form due to prolonged erosion of headlands. A sea cave begins as a wave-cut notch eroded at the base of a cliff, eventually expanding into a cave. If erosion continues, it can form a sea arch, and when the arch collapses, a sea stack is created. Over time, the sea stack erodes into a sea stump. An example is the Great Pollet sea arch in Co. Donegal.

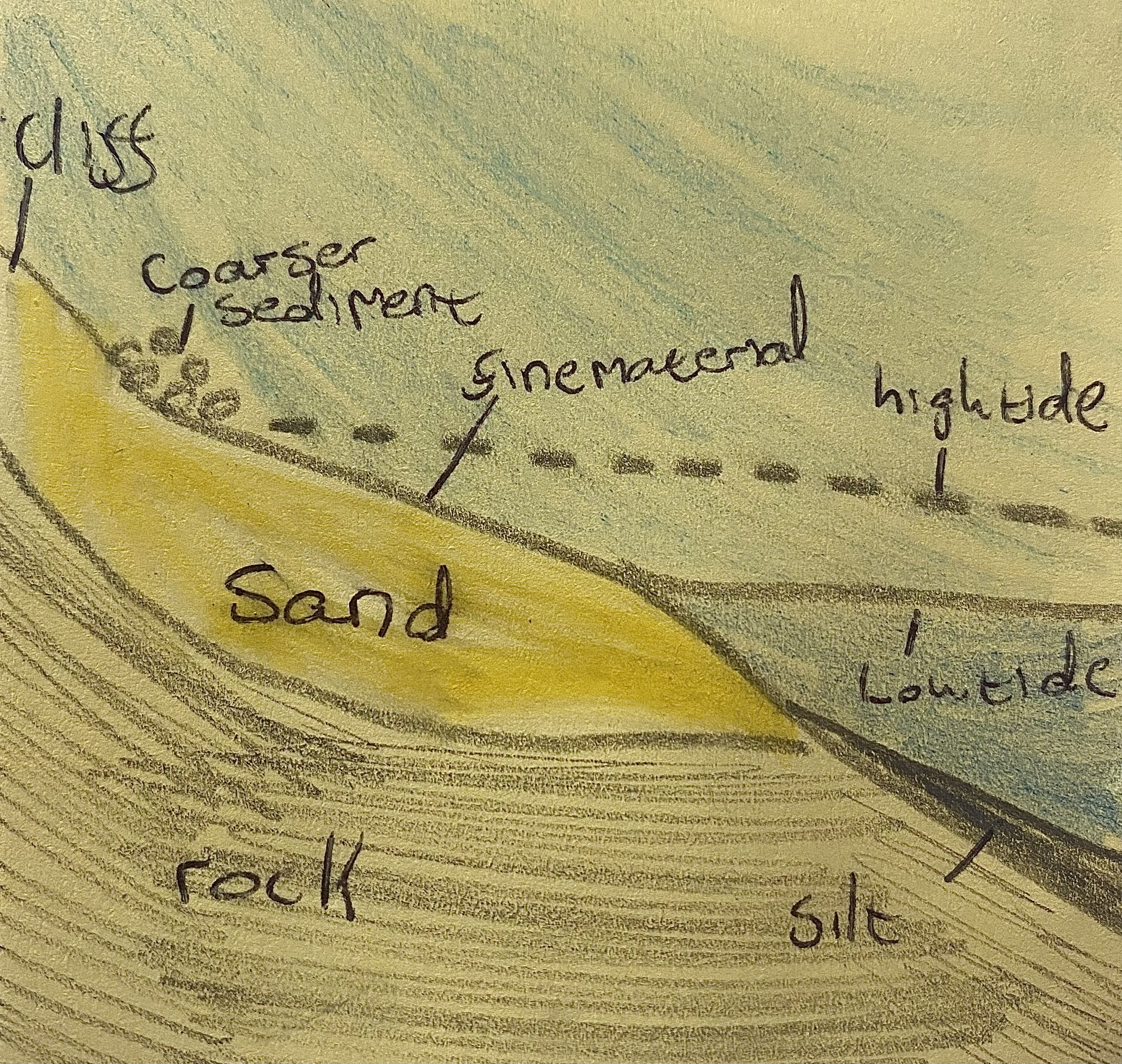
Describe how a beach is formed with a labelled diagram.
A beach is a gently sloping area of sand and shingle found between high and low tide marks, formed by deposition. The swash carries and deposits material on the shore, while the weaker backwash moves only finer particles back. Coarser material gathers at the backshore, and finer material at the foreshore. During storms, strong waves can form storm beaches by throwing large rocks above the high tide line. An example is the sandy beach at Ballybunion, Co. Kerry.
Describe 4 ways people use the sea.
For food ( fishing), energy ( oil, gas, wind farms), transport (boats), and tourism and recreation ( water sports, fishing and sailing.)
Describe 3 environmental impacts of recreation on coastal areas.
Sand dunes are damaged by people walking on marram grass, so fences have been built at Curracloe Beach to protect them.
Untreated sewage from homes and businesses can harm marine life when released into the sea.
Littering increases during the summer months, making it hard for councils to keep beaches clean.
Describe the purpose and what are Groynes.
Groynes are human-made concrete or wooden walls built at right angles to the sea to reduce the effects of longshore drift. They trap sediment, which helps to build up beaches along the coast. However, groynes can lead to coastal erosion further along the shore because they prevent sand from being carried to those areas. An example of this can be seen in Rosslare, Co. Wexford.
Describe the purpose and what is Rock armour.
Rock armour involves placing large boulders at the base of cliffs or sand dunes to absorb the energy of waves and reduce erosion. This method helps protect coastlines made of sand and clay. An example is found in Rosslare, Co. Wexford.
Give 2 examples of coastal defences.
Groynes and rock armour.