Physics IGCSE - Motion, Forces and Energy
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Force
a push or pull that changes the size, shape and motion of an object
How an objects sinks or floats via density
less density than fluid → float
more density than fluid → sinks
Newton's 1st law
object remains at rest or continue to move at a constant speed unless there is a resultant force on it
Resultant of 2 or more forces acting on same straight line
Add their sizes together
Friction
the force between 2 surfaces that may impede relative motion and make heat
Friction through liquid
drags an object through liquids (e.g. water resistance)
Friction through gas
drags an object moving through gases (e.g. air resistance)
Newton's 2nd law
An object will accelerate in response to a resultant force
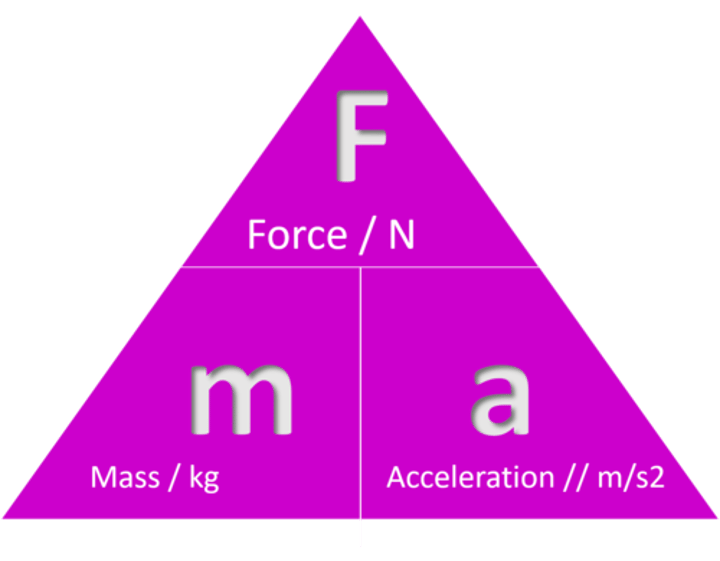
Resultant force equation
F (N) =ma
Direction of resultant force and acceleration
the same direction
Elastic
When objects are stretched and they return to their original shape
Tensile
to stretch
Compressive
to squeeze
Hooke's Law
force applied to a spring will cause it to extend by an amount proportional to the force
Load - extension graph
Straight line: extension of spring is proportional to load applied.
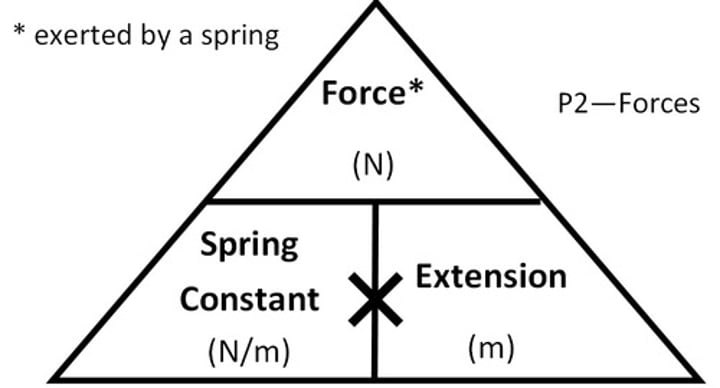
Spring constant
Force per unit extension
Spring constant equation
k (extension) = (force) F/x (extension)
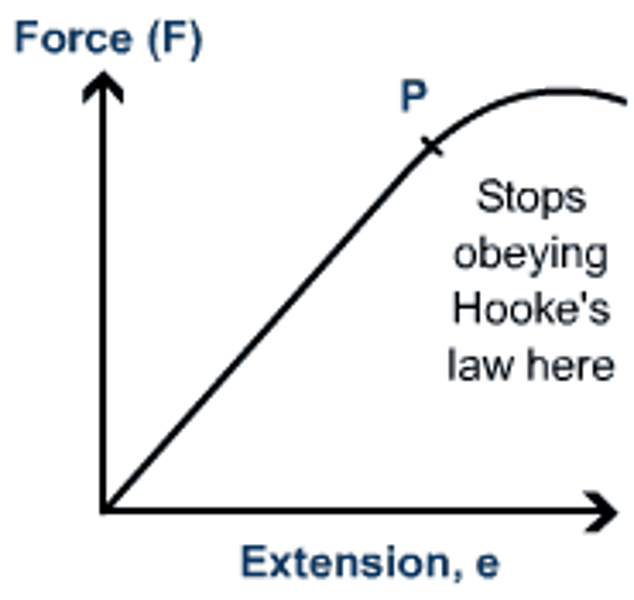
Limit of proportionality
force is no longer proportional to the extension of the object.
Newton's 3rd law
When 2 objects interact, every action has an equal and opposite reaction
Pivot
the central point on which a mechanism turns or oscillates
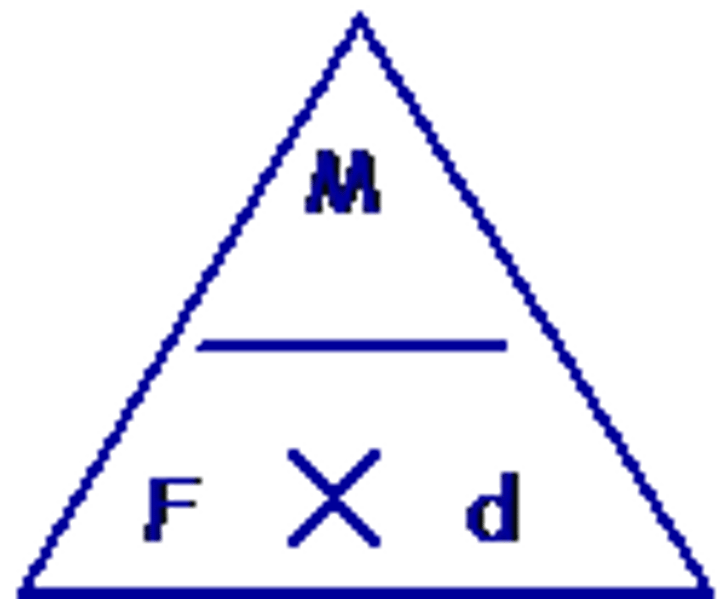
Moment
the measure of a its turning effect (described having clockwise or anticlockwise direction)
Everyday examples
- opening doors
- seesaws
- scissors
Moment equation
Moment (Nm) = Force (N) x perpendicular distance from pivot (m)
Principle of moment
sum of clockwise moments = sum of anticlockwise moments
M = Nm
No resultant force
No resultant force + no resultant movement = object in equilibrium
Centre of gravity
average location of weight of object as centre of gravity (centre of mass)
Regularly shaped objects centre of gravity
perfectly centre (labelled 'g')
Experiment for finding centre of gravity for irregularly shaped object
hang object from several points and using a ruler to mark vertical line, intersection of 2 or more lines show centre of of gravity.
Effects of position of centre of gravity on the stability of simple objects
Higher centre of gravity → easier to topple
Lower centre of gravity → more stable