ECON 248 8.3 The Market For Loanable Funds
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
A market where all savers go to deposit their savings, and all borrowers got to to receive loans.
Market For Loanable Funds
The total amount of income people have chosen to save and lend out.
Loanable Funds
The () of loanable funds comes from () who have some extra income they want to save and lend out.
Supply, Savers
The () for loanable funds comes from ()(households and firms) who wish to borrow to make ().
Demand, Borrowers, Investment
The supply and demand curve for loanable funds and interest rate has () on the x-axis and () on the y-axis.
Loanable Funds, Interest Rate
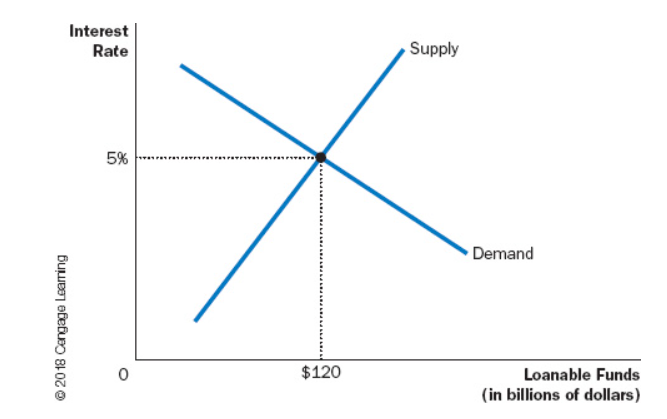
When interest rate (), supply of loanable funds rises while the demand for it decreases and vice-versa.
Increases
A () saving rate leads to a higher () and a better () overall.
Higher, GDP, Standard Of Living
A way to promote saving is to ensure that saved income and interest is not ().
Taxed
Less taxing on saving would increase the quantity of loanable funds () and would cause interest rate to ().
Supplied, Decrease
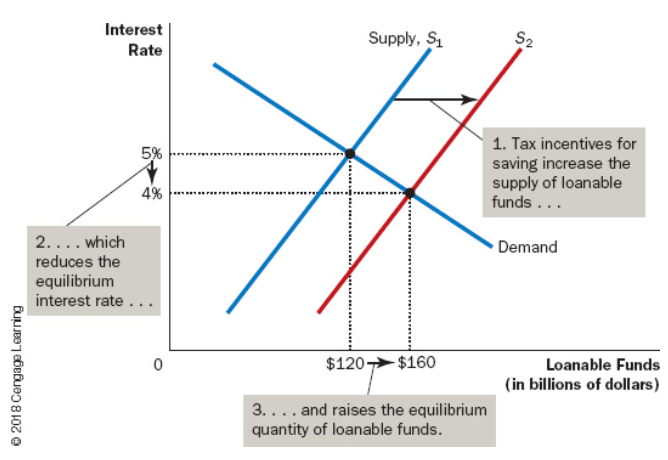
An () gives a tax advantage to any firm building a new factory or buying a new piece of equipment.
Investment Tax Credit
Investment tax credit would cause an increase in loanable funds () and interest rate to ().
Demanded, Increase
When a government spends more than it receives, it’s called a (), with the opposite being called a (). If it spends the exact same amount as revenue earned, that is called a ().
Budget Deficit, Budget Surplus, Balanced Budget
The total past budget deficits minus the total past budget surpluses is called ().
Government Debt
A budget deficit decreases (), and () interest rate, while a budget surplus does the opposite.
Loanable Funds Supplied, Increases
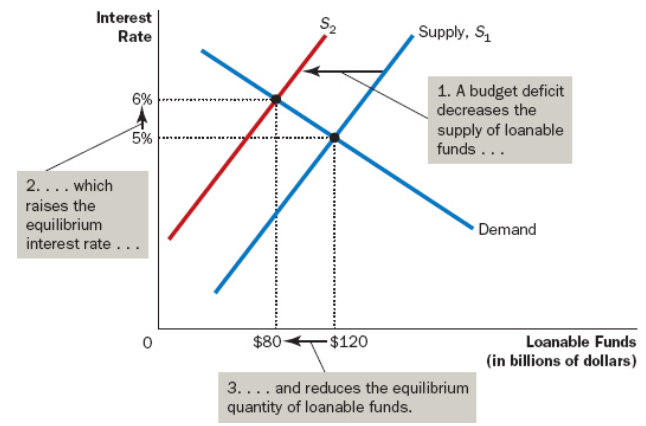
The fall in investment because of government borrowing is called ().
Crowding Out
Increased borrowing from () shifts the demand curve.
Private Investors
Continuous budget deficits can push an economy into a () where they only cause less economic growth, which means even lower saving and more spending.
Vicious Cycle
The difference between the value of financial liabilities and financial assets of a government.
Government Net Debt
A method to gauge government debt is to compare it to () debt.
Other Countries
A way to gauge government debt is to compare () of the government to other Countries.
Default Risk