unit 3.1.1: communicable & infectious diseases
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:00 AM on 3/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
**Communicable** diseases
* **contagious** disease
* transmitted **from one person to another** through a variety of ways that include**:**
* contact with blood and bodily fluids
* breathing in an airborne virus
* or by being bitten by an insect (vector)
* transmitted **from one person to another** through a variety of ways that include**:**
* contact with blood and bodily fluids
* breathing in an airborne virus
* or by being bitten by an insect (vector)
2
New cards
**Infectious** Diseases
* caused by a **pathogen**
* disorders caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi that can be spread directly or indirectly (vector-borne) from one individual to another
* disorders caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi that can be spread directly or indirectly (vector-borne) from one individual to another
3
New cards
pathogen
any microorganism that causes a disease
4
New cards
COVID-19
**Infectious** **Diseases:**
* viral disease
* SARS-CoV-2
* viral disease
* SARS-CoV-2
5
New cards
Malaria
**Infectious** **Diseases:**
* *Plasmodium spp.*
* parasitic disease
* *Plasmodium spp.*
* parasitic disease
6
New cards
Tuberculosis
**Infectious** **Diseases:**
* lung infection
* *Mycobacterium tuberculosis*
* lung infection
* *Mycobacterium tuberculosis*
7
New cards
Athlete’s Foot
**Infectious** **Diseases:**
* caused by fungi
* caused by fungi
8
New cards
No
Are all infectious diseases communicable?
9
New cards
Tetanus
**Are all infectious diseases communicable?**
* bacterial infection caused by *Clostridium tetani*
* it cannot be transmitted easily to another person
* bacterial infection caused by *Clostridium tetani*
* it cannot be transmitted easily to another person
10
New cards
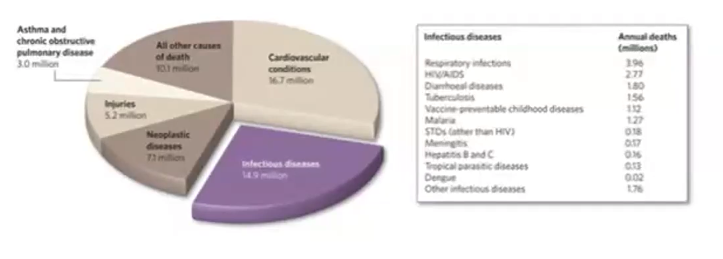
15 million
___ of 57 million annual deaths worldwide are the result of infectious disease
11
New cards
Infectiology
* study of infectious diseases
* **medical specialty** dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of complex infections
* **medical specialty** dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of complex infections
12
New cards
infectious disease specialist's practice
consists of managing **nosocomial** (__healthcare-acquired__) infections or **community-acquired** infections and is historically associated with **travel medicine and tropical medicine.**
13
New cards
**community-acquired** infections
**infectious disease specialist's practice:**
while living in a **community**, you got the infection
while living in a **community**, you got the infection
14
New cards
**nosocomial** infections
* preventable
* preventable
**infectious disease specialist's practice:**
infections acquired in a **healthcare facility**
* acquired by a **patient**
infections acquired in a **healthcare facility**
* acquired by a **patient**
15
New cards
**laboratory** infections
**infectious disease specialist's practice:**
infections acquired in a **laboratory**
* acquired by a **worker** - part of __occupational health__
infections acquired in a **laboratory**
* acquired by a **worker** - part of __occupational health__
16
New cards
Tropical medicine
interdisciplinary branch of medicine that deals with health issues that occur uniquely, are more widespread, or are more difficult to control in **tropical and subtropical regions**
17
New cards
endemic
**Tropical medicine:**
Most infections they deal with are ___ to the tropics
Most infections they deal with are ___ to the tropics
18
New cards
**18 lesser known neglected tropical diseases**
* Chagas
* Rabies
* Dengue
* Chagas
* Rabies
* Dengue
**Tropical medicine:**
Physicians in this field must be knowledgeable in the ___
Physicians in this field must be knowledgeable in the ___
19
New cards
Ignaz Semmelweis
**Historical Landmarks:**
* father of hand washing
* childbed fever
* suffered from depression and brought to an asylum
* father of hand washing
* childbed fever
* suffered from depression and brought to an asylum
20
New cards
Higher - **Physicians & Medical Students**
**Historical Landmarks:** *Ignaz Semmelweis -* __*Maternal Mortality Rate*__
First clinic
First clinic
21
New cards
Lower - **Midwives**
**Historical Landmarks:** *Ignaz Semmelweis -* __*Maternal Mortality Rate*__
Second clinic
Second clinic
22
New cards
Edward Jenner
**Historical Landmarks:**
* **vaccinations**
* used __cowpox__ to create a **vaccine for** __**smallpox**__
* milkmaids were less likely to get the virus
* **vaccinations**
* used __cowpox__ to create a **vaccine for** __**smallpox**__
* milkmaids were less likely to get the virus
23
New cards
Dr. Henderson
**Historical Landmarks:**
* led the **eradication program against smallpox**
* last disease was detected in Africa in 1978
* formally declared eradicated in 1981
* led the **eradication program against smallpox**
* last disease was detected in Africa in 1978
* formally declared eradicated in 1981
24
New cards
John Snow
**Historical Landmarks:**
* cholera & tracing source of infection
* spot maps
* first to use epidemological tools for the control of a disease
* **father of epidemology**
* cholera & tracing source of infection
* spot maps
* first to use epidemological tools for the control of a disease
* **father of epidemology**
25
New cards
Robert Koch
**Historical Landmarks:**
* first to isolate bacteria
* Postulates
* first to isolate bacteria
* Postulates
26
New cards
organisms suffering from disease
**Historical Landmarks:** *Robert Koch*
1. Microorganism must be found in ___
1. Microorganism must be found in ___
27
New cards
pure culture
**Historical Landmarks:** *Robert Koch*
2. Collected microorganism must be isolated in ___
2. Collected microorganism must be isolated in ___
28
New cards
healthy organism
**Historical Landmarks:** *Robert Koch*
3. Cultured microorganism should be given to a ___
3. Cultured microorganism should be given to a ___
29
New cards
identical
**Historical Landmarks:** *Robert Koch*
4. Microorganism must be reisolated from inoculated experimental host and should be ___ to original agent
4. Microorganism must be reisolated from inoculated experimental host and should be ___ to original agent
30
New cards
Germ theory of disease
**Historical Landmarks:** *Robert Koch*
diseases are caused by a single bacterium
diseases are caused by a single bacterium
31
New cards
Agent
**The Epidemiologic Triad:**
* referred to an **infectious microorganism** or pathogen: a virus, bacterium, parasite, or other microbe
* not necessarily infectious
* concept of necessary and sufficient causes
* referred to an **infectious microorganism** or pathogen: a virus, bacterium, parasite, or other microbe
* not necessarily infectious
* concept of necessary and sufficient causes
32
New cards
Host
**The Epidemiologic Triad:**
* refers to the **human** who can get the disease
* refers to the **human** who can get the disease
33
New cards
Risk factors
**The Epidemiologic Triad:** *Host*
* A variety of factors **intrinsic** to the host can influence an individual’s exposure, susceptibility, or response to a causative agent
* A variety of factors **intrinsic** to the host can influence an individual’s exposure, susceptibility, or response to a causative agent
34
New cards
behaviors and physiologic susceptibility
**The Epidemiologic Triad:** *Host*
* Opportunities for exposure are often influenced by ___
* Opportunities for exposure are often influenced by ___
35
New cards
Environment
**The Epidemiologic Triad:**
* refers to **extrinsic** factors that affect the agent and the opportunity for exposure
* physical factors, biologic factors, and socioeconomic factors
* refers to **extrinsic** factors that affect the agent and the opportunity for exposure
* physical factors, biologic factors, and socioeconomic factors
36
New cards
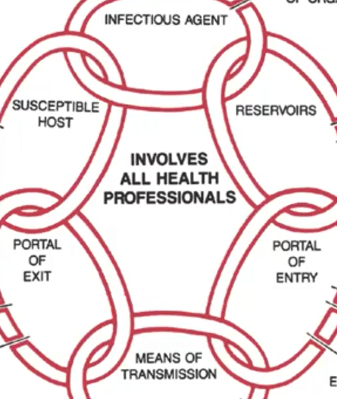
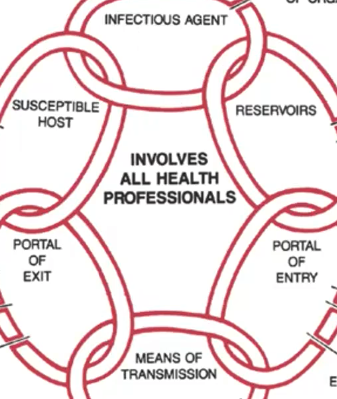
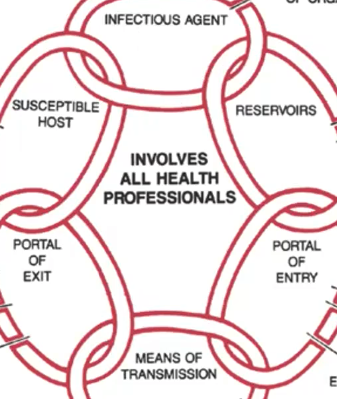
Chain of Infection
* refers to the **spread of infection** (or agent) from a source to a susceptible host
* useful **framework** in the design of __prevention and control measures__
* specific strategies can be aimed at various points along the chain of infection
* useful **framework** in the design of __prevention and control measures__
* specific strategies can be aimed at various points along the chain of infection
37
New cards
Reservoir
**Chain of Infection:**
where the agent lives prior to transmission
where the agent lives prior to transmission
38
New cards
Mode of Transmission
**Chain of Infection:**
process of how the infection is transmitted
process of how the infection is transmitted
39
New cards
Agent
**Chain of Infection:**
germs
germs
40
New cards
Reservoir
**Chain of Infection:**
where germs live
where germs live
41
New cards
Portal of Exit
**Chain of Infection:**
how germs get out
how germs get out
42
New cards
Mode of Transmission
**Chain of Infection:**
germs get around
germs get around
43
New cards
Portal of Entry
**Chain of Infection:**
how germs get in
how germs get in
44
New cards
Susceptible Host
**Chain of Infection:**
next sick person
next sick person
45
New cards
Prevention
* **Strategies or actions** aimed at __eradicating, eliminating or minimizing the impact of disease__ and disability, or if none of these are feasible , __retarding the progress of disease and disability__
* Reduction in the **risk and severity of a disease** at the **individual** level
* Reduction in the **risk and severity of a disease** at the **individual** level
46
New cards
Control
* **Ongoing operations** at reducing the:
* Incidence of Disease
* Duration of disease
* Effects of the disease
* Burden to community
* Reduction in the **frequency and severity of a disease** at the **community** level
* Incidence of Disease
* Duration of disease
* Effects of the disease
* Burden to community
* Reduction in the **frequency and severity of a disease** at the **community** level
47
New cards
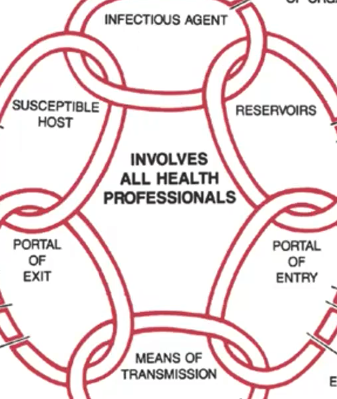
rapid, accurate identification of organisms
**How to Break the Chain of Infection?**
Infectious Agent
Infectious Agent
48
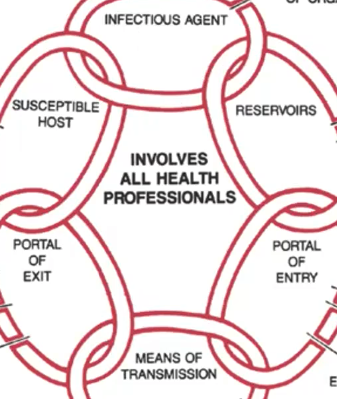
New cards
* environmental sanitation
* employee health
* disinfection sterilization
* employee health
* disinfection sterilization
**How to Break the Chain of Infection?**
Reservoir
Reservoir
49
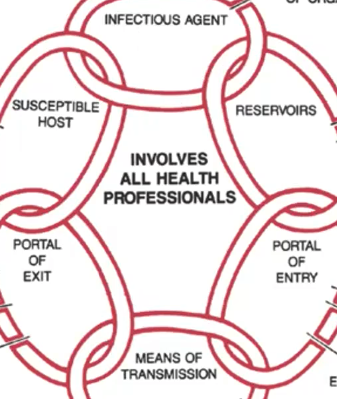
New cards
* PPE
* hand washing
* trash & waste disposal
* control of excretions & secretions
* hand washing
* trash & waste disposal
* control of excretions & secretions
**How to Break the Chain of Infection?**
Portal of Entry
Portal of Entry
50
New cards
* isolation
* food handling
* air flow control
* sterilization
* hand washing
* food handling
* air flow control
* sterilization
* hand washing
**How to Break the Chain of Infection?**
Mode of Transmission
Mode of Transmission
51
New cards
* wound care
* catheter care
* aseptic technique
* catheter care
* aseptic technique
**How to Break the Chain of Infection?**
Portal of Exit
Portal of Exit
52
New cards
* treatment of underlying disease
* recognition of high risk clients
* recognition of high risk clients
**How to Break the Chain of Infection?**
Susceptible Host
Susceptible Host
53
New cards
SARS-COVID 2
**Chain of Infection:** *COVID-19*
Agent
Agent
54
New cards
Bats, Infected individuals
**Chain of Infection:** *COVID-19*
Reservoir
Reservoir
55
New cards
Mucus, biological fluids
**Chain of Infection:** *COVID-19*
Portal of Exit
Portal of Exit
56
New cards
Airborne, direct contact
**Chain of Infection:** *COVID-19*
Mode of Transmission
Mode of Transmission
57
New cards
Inhalation of contaminated air
**Chain of Infection:** *COVID-19*
Portal of Entry
Portal of Entry
58
New cards
Comorbidities, elders, children
**Chain of Infection:** *COVID-19*
Susceptible host
Susceptible host
59
New cards
Virus
**Chain of Infection:** *Rabies*
Agent
Agent
60
New cards
Domesticated or wild animals
**Chain of Infection:** *Rabies*
Reservoir
Reservoir
61
New cards
Saliva
**Chain of Infection:** *Rabies*
Portal of Exit
Portal of Exit
62
New cards
Licking
**Chain of Infection:** *Rabies*
Mode of Transmission
Mode of Transmission
63
New cards
Puncture or open wound
**Chain of Infection:** *Rabies*
Portal of Entry
Portal of Entry
64
New cards
Non-vaccinated people
* usually children
* usually children
**Chain of Infection:** *Rabies*
Susceptible host
Susceptible host
65
New cards
96%
**Species Affected by Rabies:**
positives from canines
positives from canines
66
New cards
72%
**Species Affected by Rabies:**
rabies cases were owned pets
rabies cases were owned pets
67
New cards
88%
**Species Affected by Rabies:**
rabies cases were free roaming
rabies cases were free roaming
68
New cards
smallpox, measles and polio
**Chain of Infection:**
have no non-human reservoir
have no non-human reservoir
69
New cards
smallpox
**Chain of Infection:** *Smallpox, Measles, & Polio*
concept of vaccination originated with ___
concept of vaccination originated with ___
70
New cards
**molecular sequence** of the virus is publicly known
**Chain of Infection:** *Smallpox Eradication*
One concern is that the ___, meaning that someone could synthesize it in a laboratory and loose it on the world
One concern is that the ___, meaning that someone could synthesize it in a laboratory and loose it on the world
71
New cards
Dr. Henderson
**Chain of Infection:** *Smallpox Eradication*
*“Let’s destroy the virus and be done with it... We would be better off spending our money in better ways.”*
*“Let’s destroy the virus and be done with it... We would be better off spending our money in better ways.”*
72
New cards
Polio
**Chain of Infection:**
contagious viral illness in its most severe form that causes **paralysis, difficulty breathing, and death**
contagious viral illness in its most severe form that causes **paralysis, difficulty breathing, and death**
73
New cards
2000
* it was not met
* it was not met
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
In 1988, at a time when **350,000 children were being paralyzed** each year, WHO set a goal of eradicating polio by the year ___
In 1988, at a time when **350,000 children were being paralyzed** each year, WHO set a goal of eradicating polio by the year ___
74
New cards
99% worldwide
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
by 1999, annual polio cases were reduced by
by 1999, annual polio cases were reduced by
75
New cards
Nigeria, Pakistan, and Afghanistan
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
Only three countries continue to have endemic polio
Only three countries continue to have endemic polio
76
New cards
In humans, found in feces
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
Agent
Agent
77
New cards
patient treatment
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
Agent: How to break the chain?
Agent: How to break the chain?
78
New cards
Areas that have **poor sanitation**
* Fecal-oral route
* Fecal-oral route
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
Reservoir
Reservoir
79
New cards
* improved public sanitation
* vaccines
* personal hygiene
* vaccines
* personal hygiene
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
Reservoir: How to break the chain?
Reservoir: How to break the chain?
80
New cards
* Pregnant women
* Children
* Weak immune systems
* Children
* Weak immune systems
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
Susceptible Hosts
Susceptible Hosts
81
New cards
* respiratory secretions
* ingestion
* bathroom
* ingestion
* bathroom
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
Portal of Exit
Portal of Exit
82
New cards
* hand washing
* keep area clean & disinfected
* keep area clean & disinfected
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
Portal of Exit: How to break the chain?
Portal of Exit: How to break the chain?
83
New cards
* contaminated water
* direct contact with infected person
* direct contact with infected person
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
Mode of transmission
Mode of transmission
84
New cards
check if food is contaminated
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
Mode of transmission: How to break the chain?
Mode of transmission: How to break the chain?
85
New cards
* eyes
* mouth
* nose
* mouth
* nose
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
Portal of Entry
Portal of Entry
86
New cards
Research
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
* 2%
* to **facilitate eradication**
* 2%
* to **facilitate eradication**
87
New cards
Vaccines
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
3%
3%
88
New cards
Surveillance
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
* 11%
* disease detection
* 11%
* disease detection
89
New cards
Social Mobilization
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
* 19%
* raise **awareness** of vaccination campaigns & benefits of immunization
* 19%
* raise **awareness** of vaccination campaigns & benefits of immunization
90
New cards
Technical Assistance
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
* 20%
* **salaries** for health professionals
* 20%
* **salaries** for health professionals
91
New cards
Operational Support
**Chain of Infection:** *Polio*
* 45%
* **stipends for community based vaccinators** that administer house-to-house visits
* 45%
* **stipends for community based vaccinators** that administer house-to-house visits
92
New cards
* **400 to 500 deaths** a year in the United States
* 4000 cases of **chronic disability** from measles encephalitis
* 4000 cases of **chronic disability** from measles encephalitis
**Chain of Infection:** *Measles*
Before a vaccine was available, almost all children contracted measles, causing ___
Before a vaccine was available, almost all children contracted measles, causing ___
93
New cards
1963
**Chain of Infection:** *Measles*
vaccine became available in ___
vaccine became available in ___
94
New cards
vaccinated as babies
**Chain of Infection:** *Measles*
outbreaks of measles began to occur among high school and college students who had been ___
outbreaks of measles began to occur among high school and college students who had been ___
95
New cards
Rubeola virus
**Chain of Infection:** *Measles*
Agent
Agent
96
New cards
* respiratory tract
* nasal passages
* throats
* nasal passages
* throats
**Chain of Infection:** *Measles*
Reservoir
Reservoir
97
New cards
* **air currents**: airborne droplets
* direct secretion
* direct secretion
**Chain of Infection:** *Measles*
Mode of Transmission
Mode of Transmission
98
New cards
inhalation
**Chain of Infection:** *Measles*
Portal of Entry
Portal of Entry
99
New cards
secretion
**Chain of Infection:** *Measles*
Portal of Exit
Portal of Exit
100
New cards
* non-vaccinated
* close proximity to infected
* close proximity to infected
**Chain of Infection:** *Measles*
Susceptible Host
Susceptible Host