EXPH 3200- EKG Rhythms
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
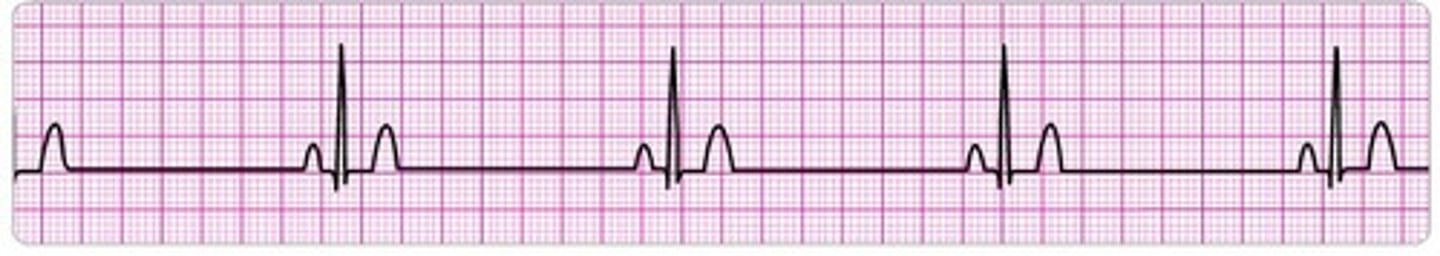
normal sinus rhythm
HR = 60-100 bpm
Rhythm is regular
sinus bradycardia
HR < 60 bpm
Rhythm is regular, but slow
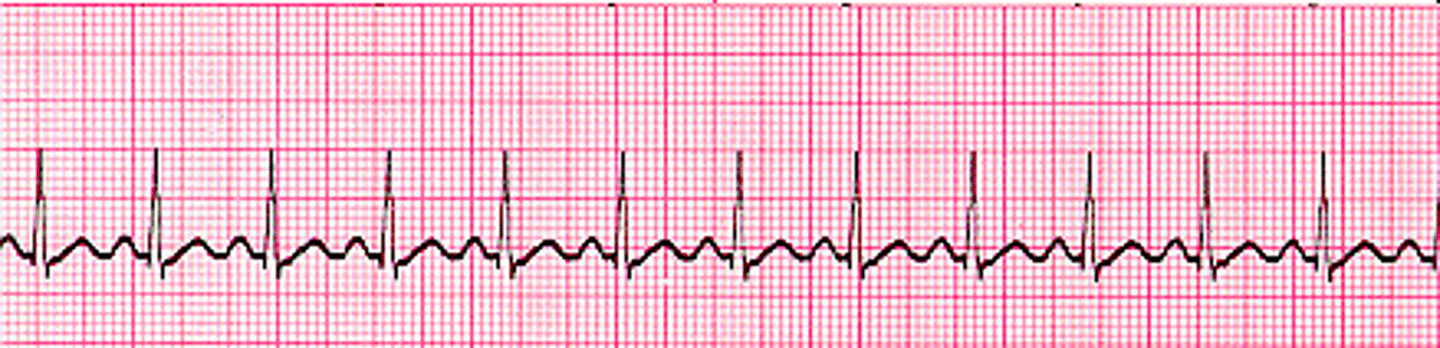
sinus tachycardia
HR > 100 bpm
Rhythm is regular, but fast
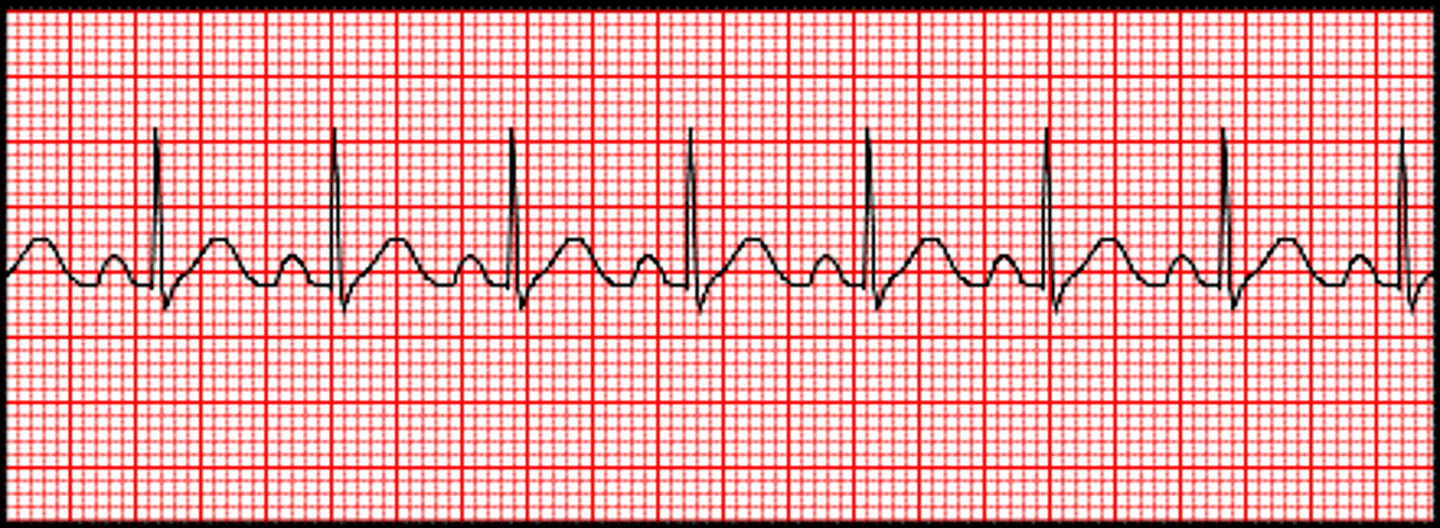
sinus arrhythmia
Rhythm is slightly irregular with areas that are faster or slower
Healthiest of all sinus arrhythmias

sinus arrest/pause
Normal sinus rhythm with "dropped beats"
An entire PQRST is missing (period of asystole)
Scariest of all sinus arrhythmias
supraventricualr arrhythmias overview
Originate in atria = P wave
P waves often look abnormal or absent within a single lead
types of supraventricular arrhythmias
premature atrial contraction (isolate and couplet)
supraventricular tachycardia
atrial flutter
atrial fibrillation
premature atrial contraction (PAC)
Beat is early, P wave is absent or changes, QRS is normal
A slight pause follows the PAC (compensatory pause for absolute refractory)
isolated (1 PAC) or couplet (every other PAC)
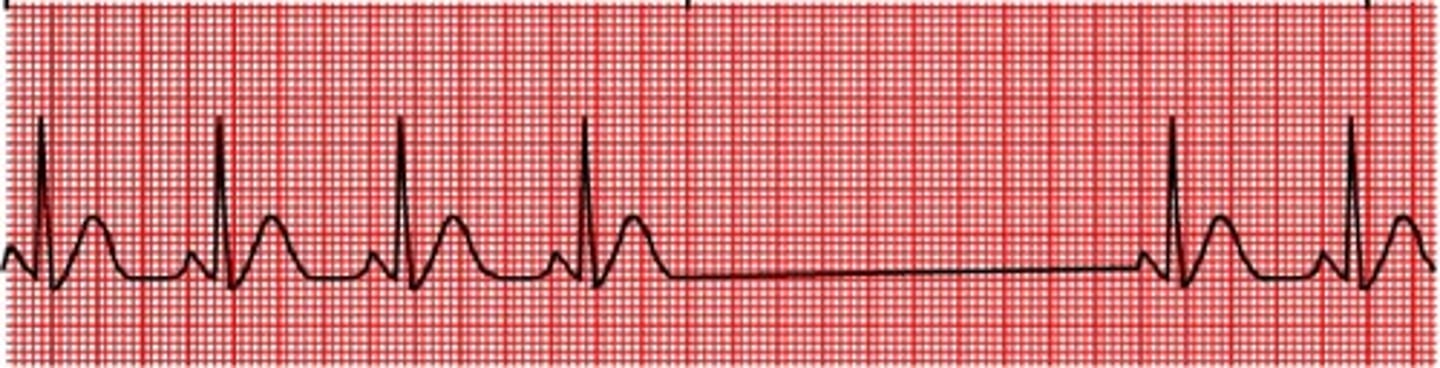
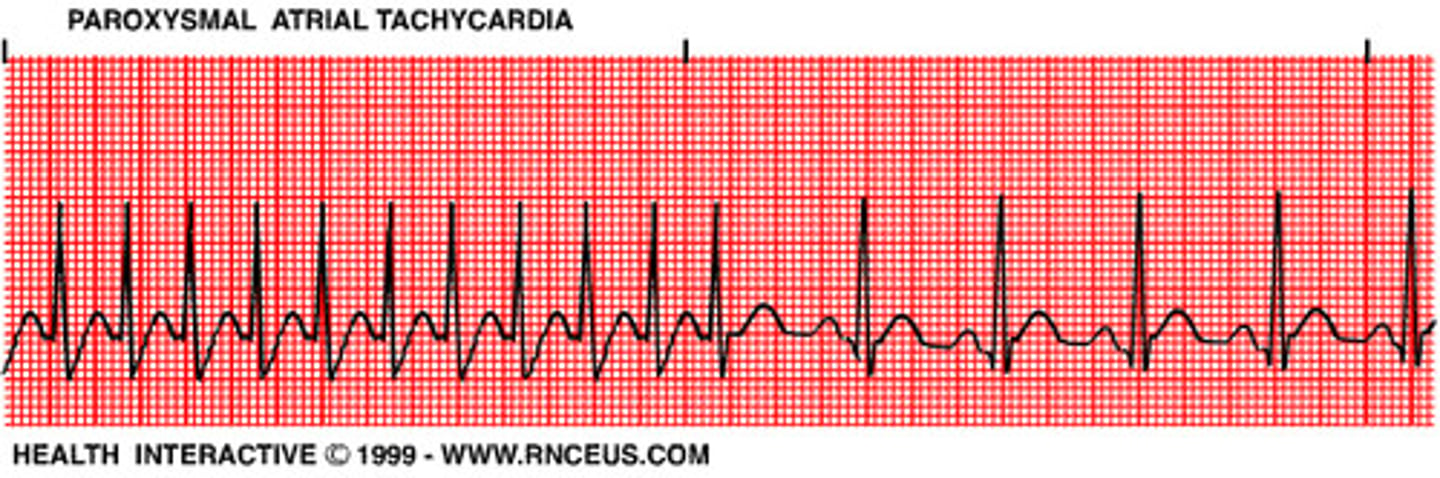
supraventricular tachycardia
Multiple PACs in a row
Onset and termination are sudden and abrupt
HR = 150-250 bpm
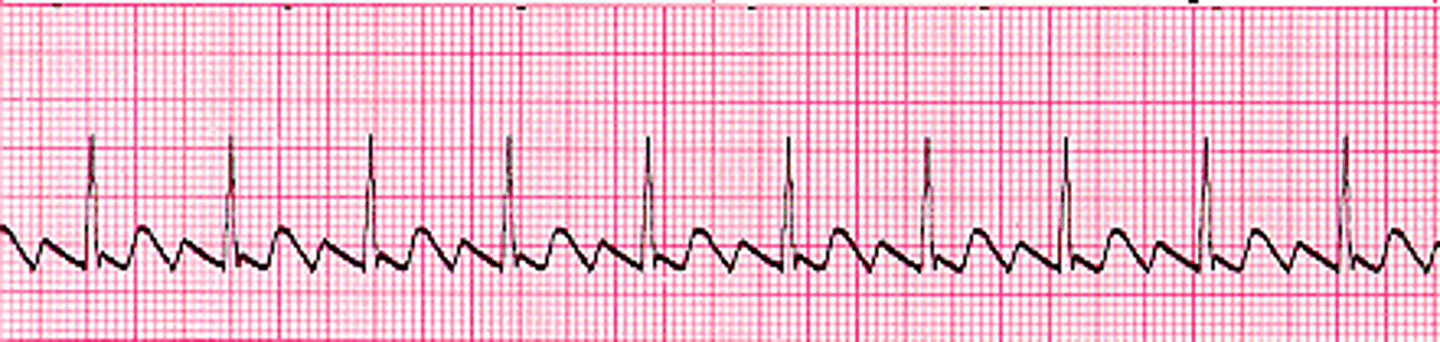
atrial flutter
Atrium fires repetitively at a fast rate with some of the impulses blocked from ventricles
P and T wave can combine after QRS
Atrial rate = 250-350 bpm
P waves = classic "saw tooth pattern"
P:QRS = more P waves than QRS (3:1)
NOT IN NORMAL HEARTS
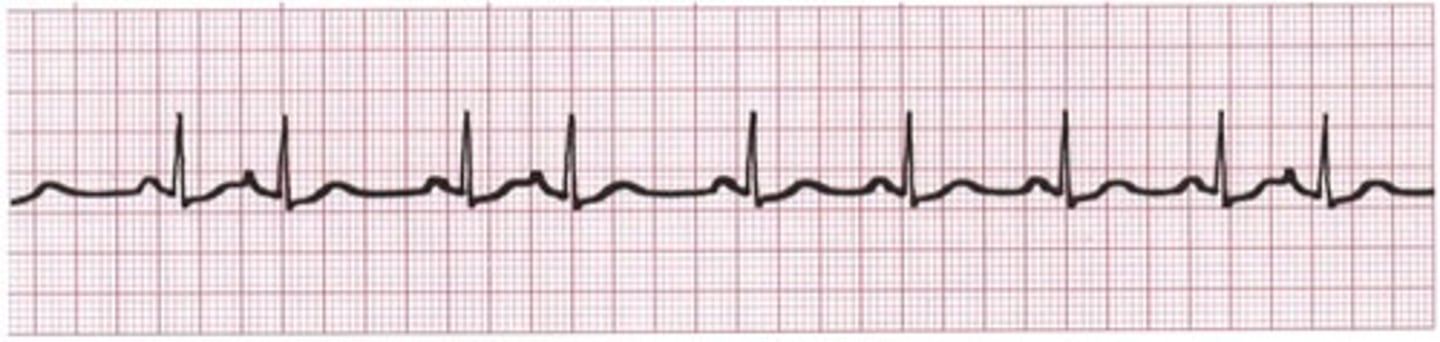
atrial fibrillation (a-fib)
Atria are so irritable that a multitude of foci initiate impulse causing atrium to "quiver"
Atrial rate = 350-600 bpm (chaos)
P:QRS = irregular
NOT IN NORMAL HEARTS
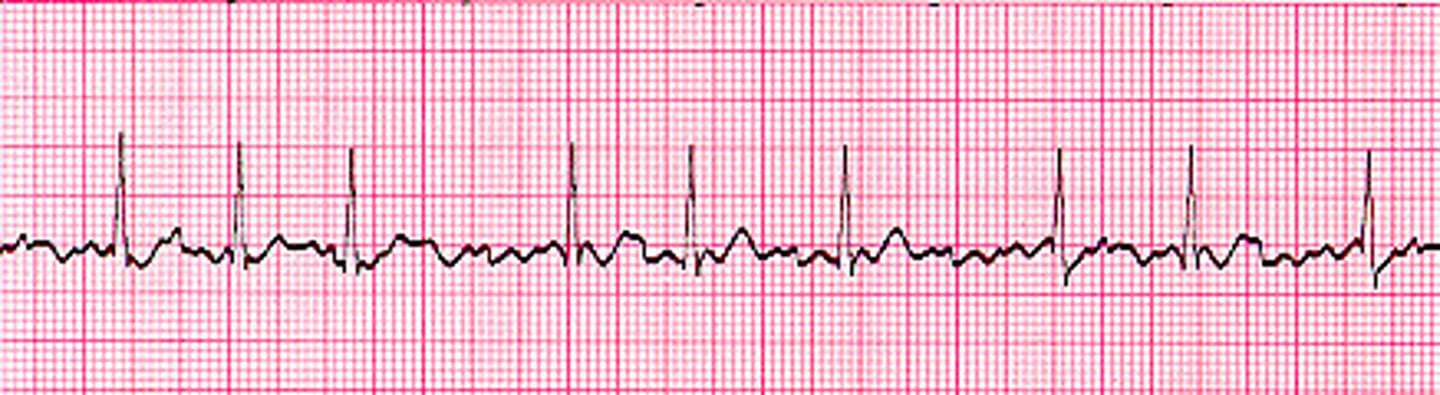
junctional rhythms overview
originate in the AV node
abnormal P waves (inverted) or no P waves are possible
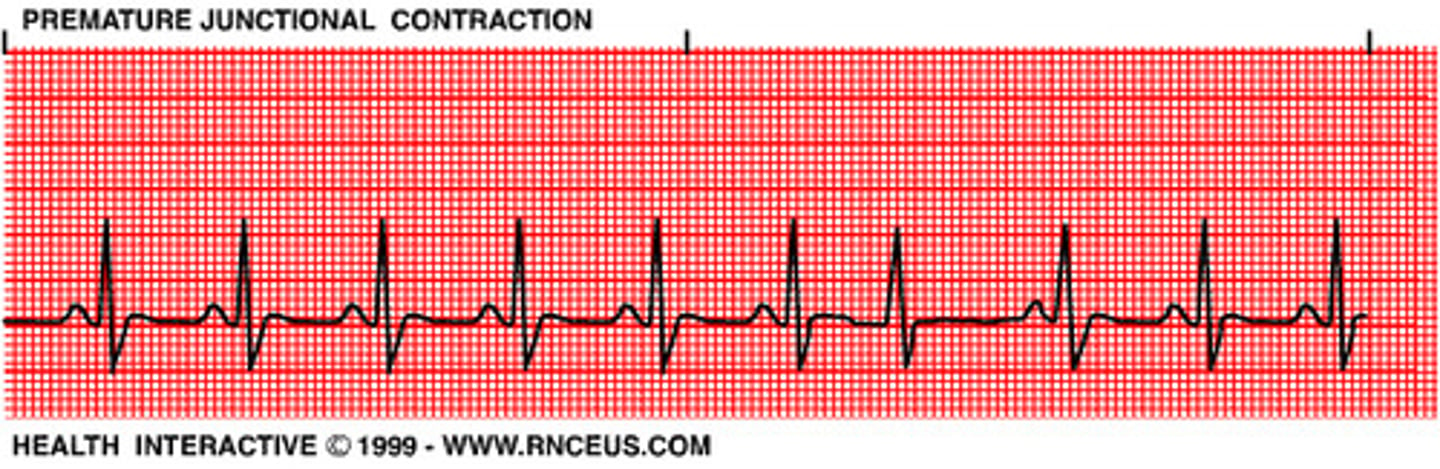
premature junctional contraction (PJC)
Irritable focus produces an early beat
Usually followed by a pause
Similar to PAC
junctional escape beat
Higher pacemaker (SA node) site fails
AV node produces beat (no P wave) to protect against asystole
switch off between SA and AV node producing beat (P and no P)
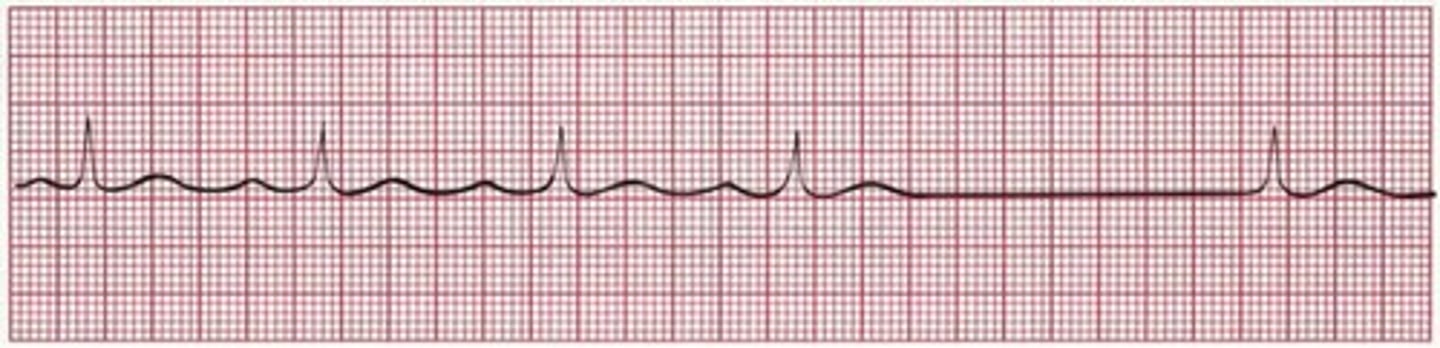
junctional rhythm
Irritable foci speeds up to override the SA node for control (possible SA node failure)
P wave is lost completely
goes directly into QRS complex
atrial rate = ventricular rate
RATE = 40-60 bpm
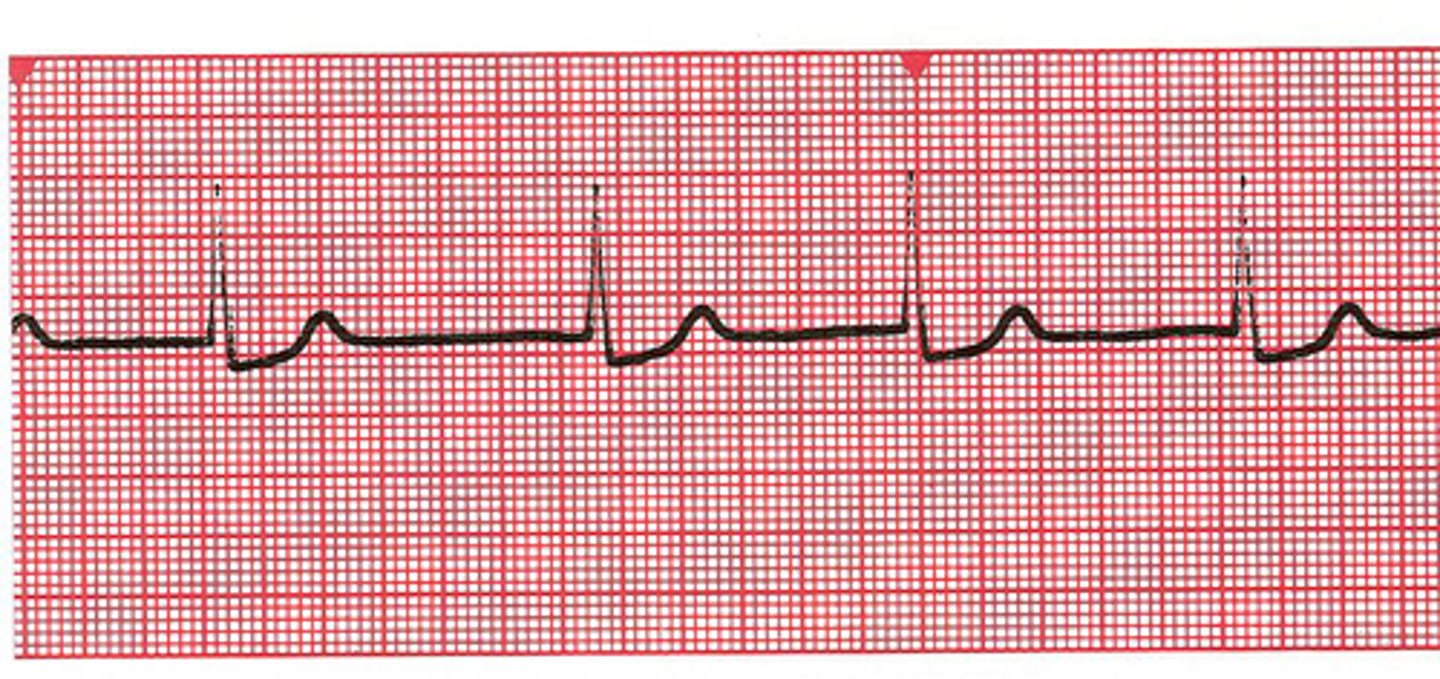
accelerated junctional rhythm
same characteristics as junctional rhythm
RATE = > 60 bpm
ventricular arrhythmias overview
originate in the ventricles
ventricular rate = 20-40 bpm
abnormal/wide QRS complex
types of ventricular arrhythmias
premature ventricular contraction
ventricular escape beat
accelerated ventricular rhythm
ventricular tachycardia
ventricular fibrillation
asystole
premature ventricular contraction (PVC)
Irritable focus in the ventricles fires prematurely to produce a single ectopic beat
QRS findings are wide
couplet (every other) or trigeminy (every third)
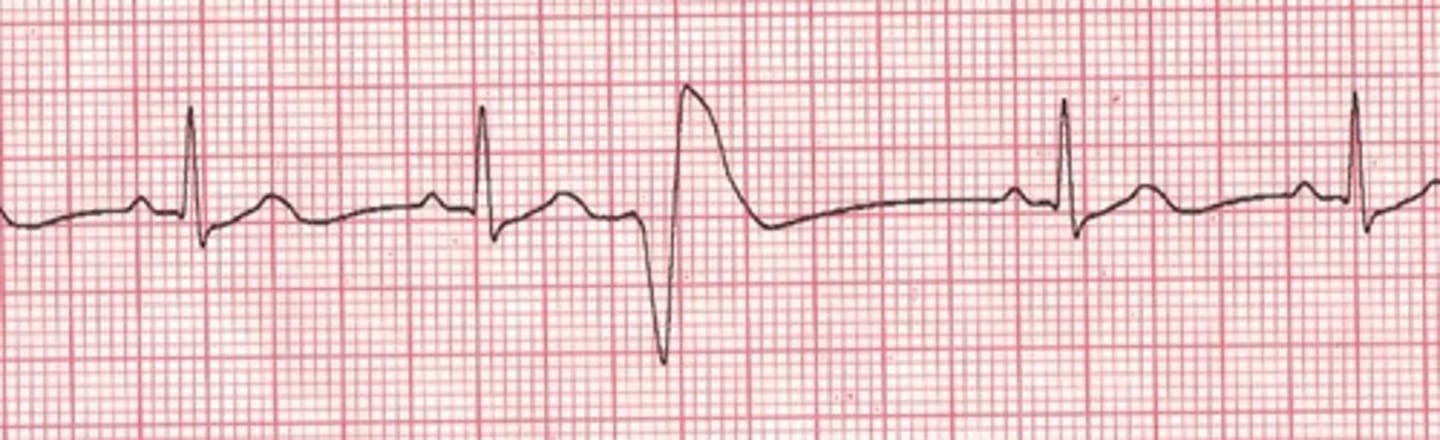
ventricular escape rhythm
SA and AV node fail, so the ventricles produce an impulse to protect from asystole
RATE = 20-40 bpm
no P waves
QRS > 0.12 seconds (VERY wide)
NOT IN CLINICALLY NORMAL HEARTS
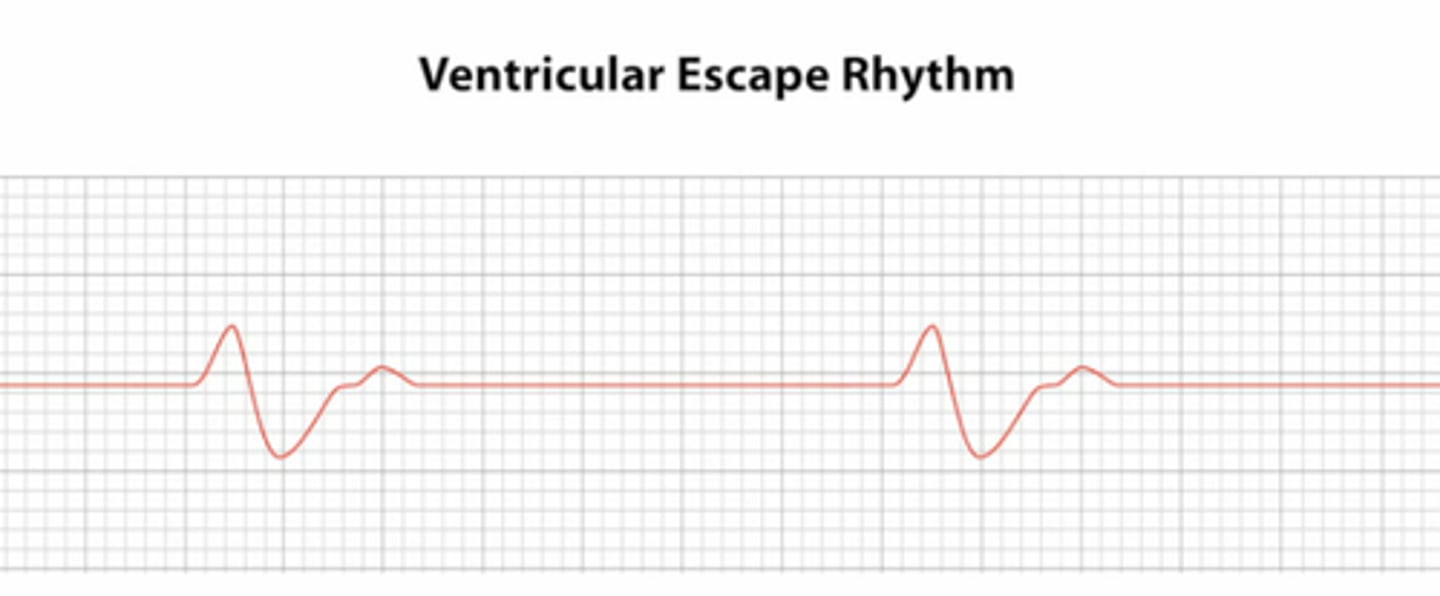
accelerated ventricular escape rhythm
same characteristics as ventricular escape rhythm
RATE = 40-100 bpm
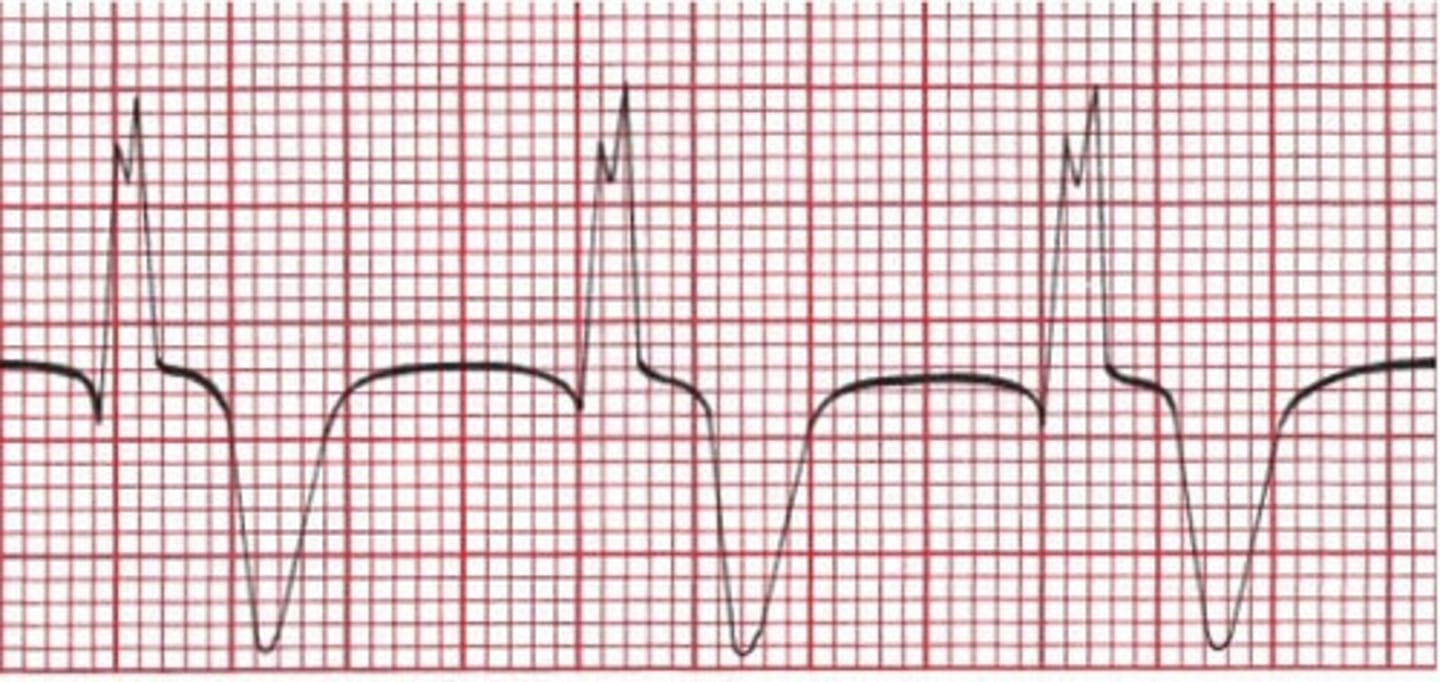
ventricular tachycardia
A run of 3 or more consecutive PVCs
RATE = 100-300 bpm
wide QRS
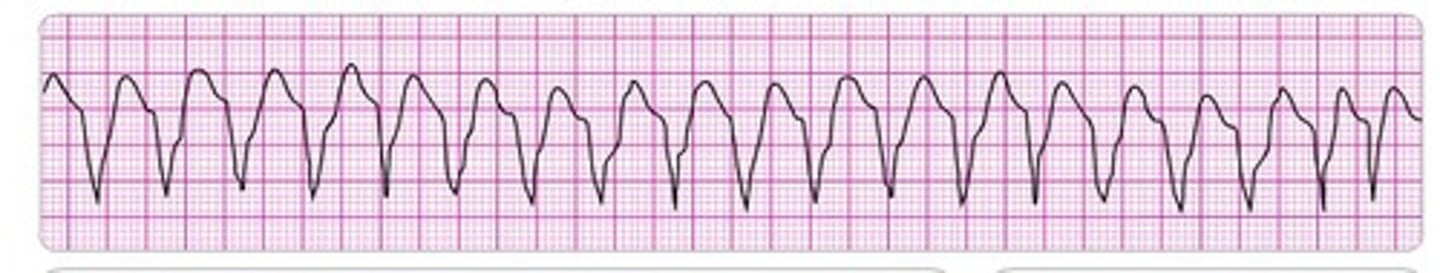
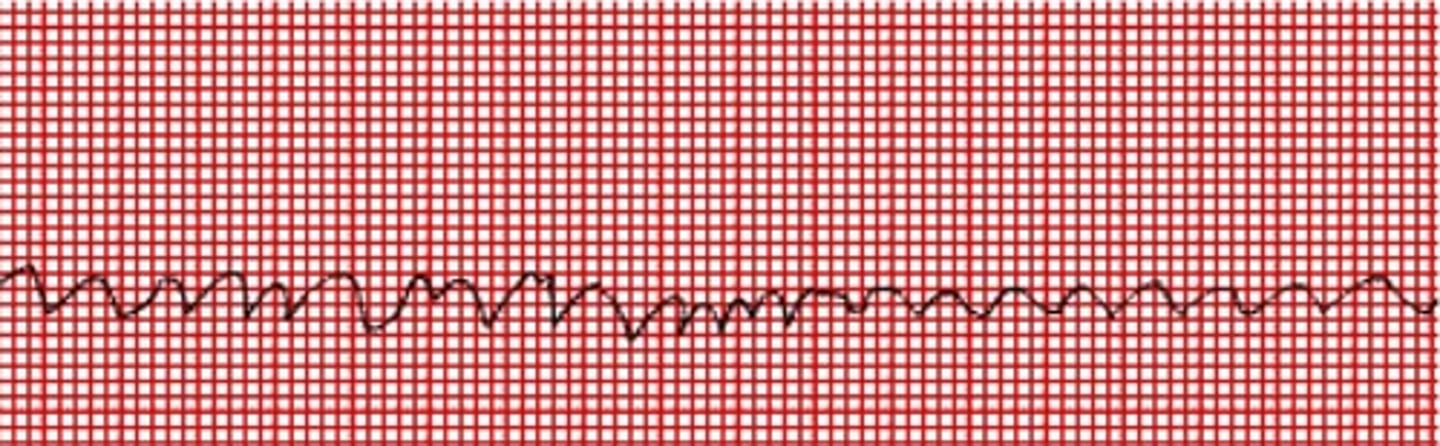
ventricular fibrillation
Multiple foci within the ventricle become irritable and generate uncontrolled, chaotic impulses
quivering baseline
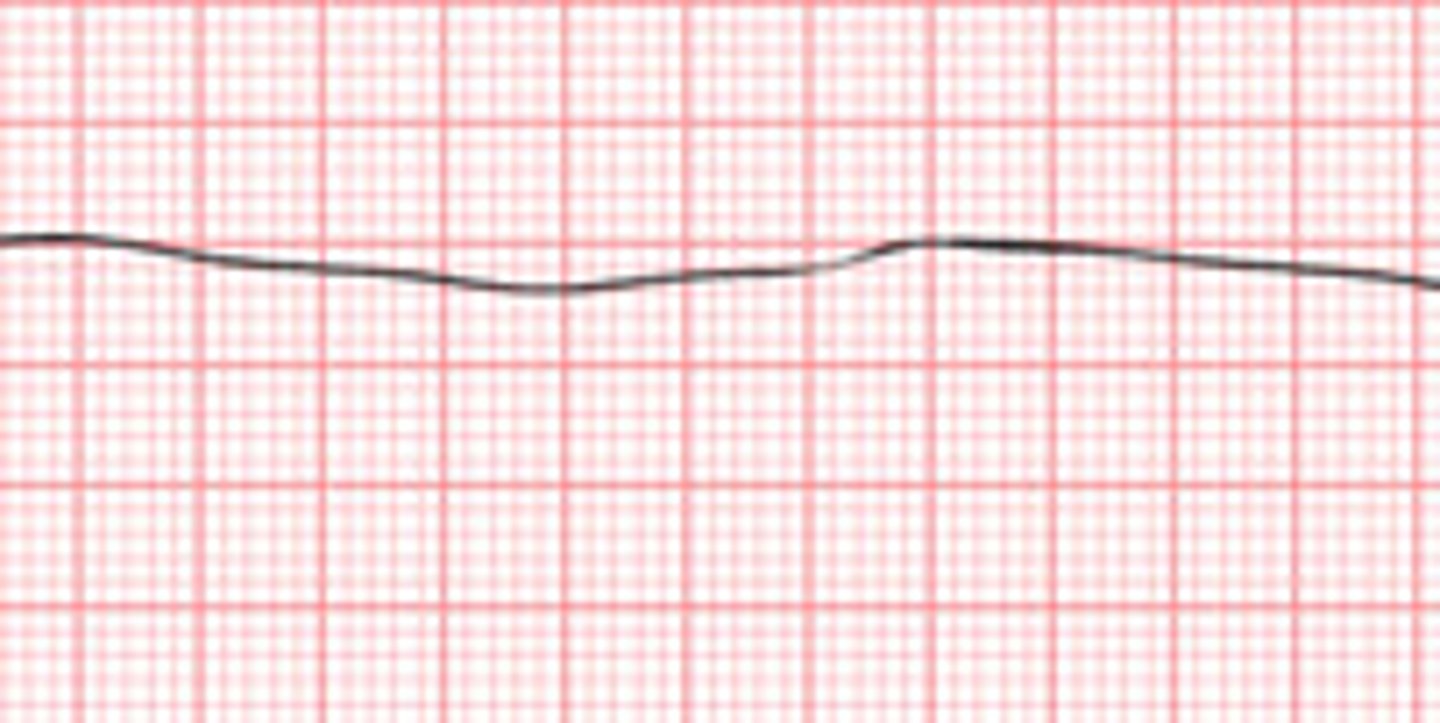
asystole
Heart has lost its electrical activity
EKG = flat line
AV conduction blocks overview
Inability of the AV junction to conduct every normal impulse generated above it to the ventricles within the normal amount of time
abnormal P waves and PR intervals
types of AV conduction blocks
1st degree AV block
2nd degree AV block (type I and type II)
3rd degree AV block
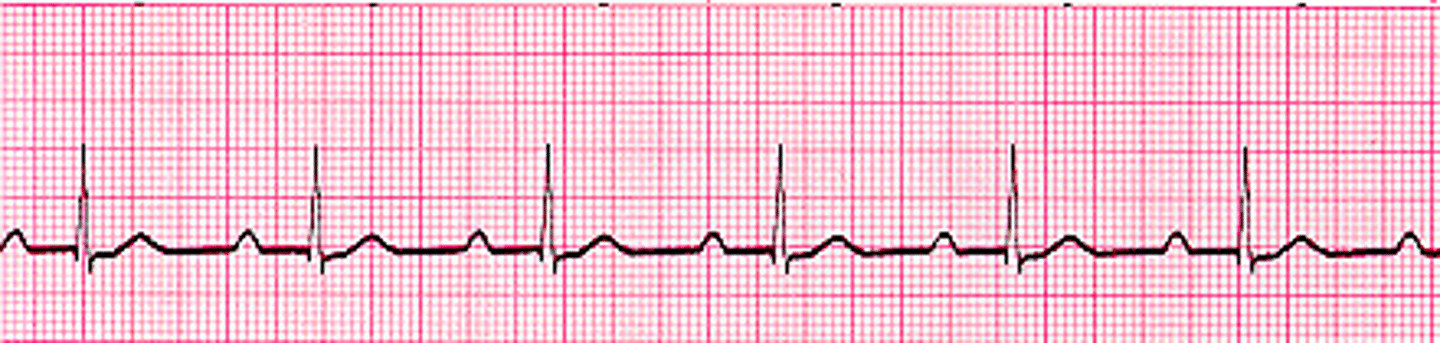
1st degree AV block
The AV node holds each sinus impulse longer than normal before allowing the conduction through the ventricles
PR interval = prolonged (> 0.20 seconds), but consistent
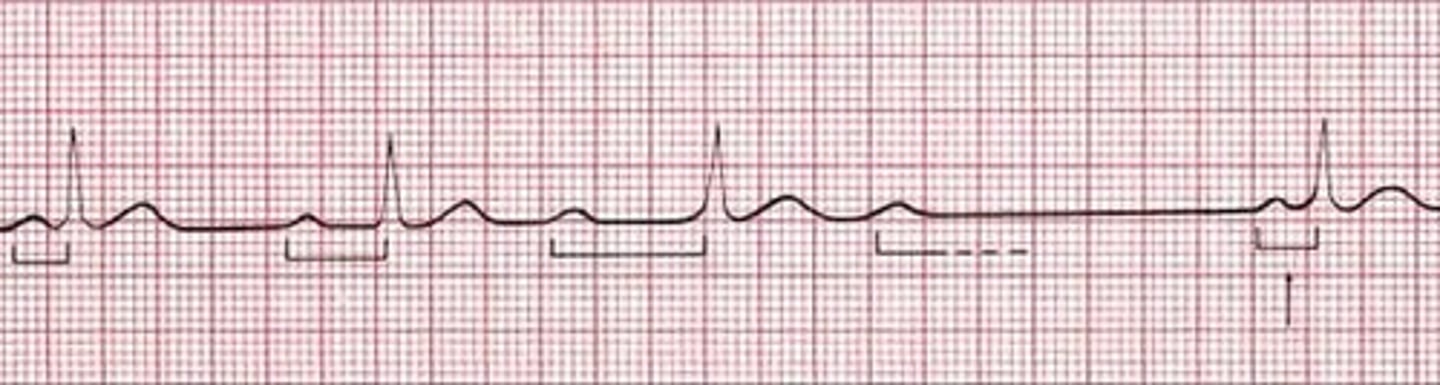
2nd degree AV block wenkebach
Not every atrial impulse is able to pass through the AV node into the ventricles
extra P wave, where there is no QRS
PR interval = progressively lengthening, until a P wave (atrial conduction) is blocked from entering the ventricles (not conducted)
ventricular rate < atrial rate
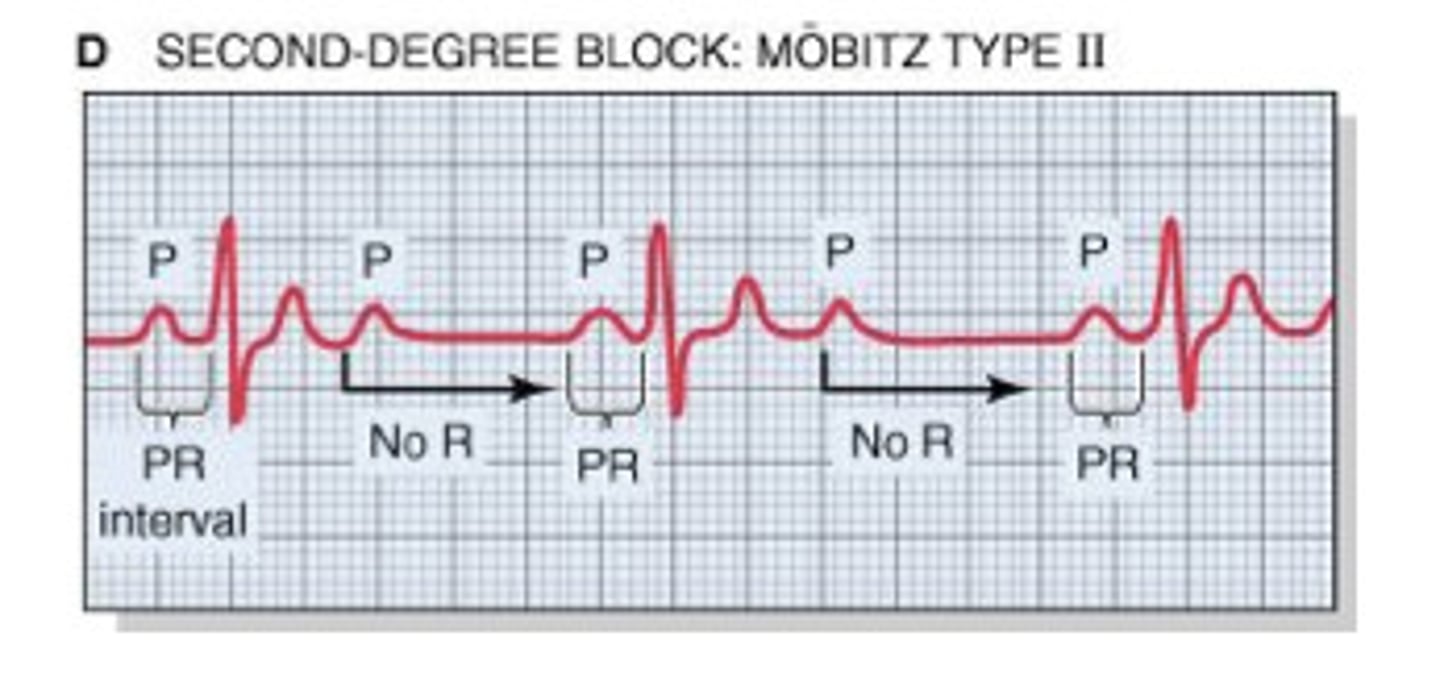
2nd degree AV block mobitz type II
blocked atrial contractions (extra P waves with no QRS)
PR interval = within normal limits/consistent until a P wave is not conducted (stranded P waves are seen); no progressive lengthening of PR interval
ventricular rate < atrial rate
NOT SEEN IN NORMAL HEARTS
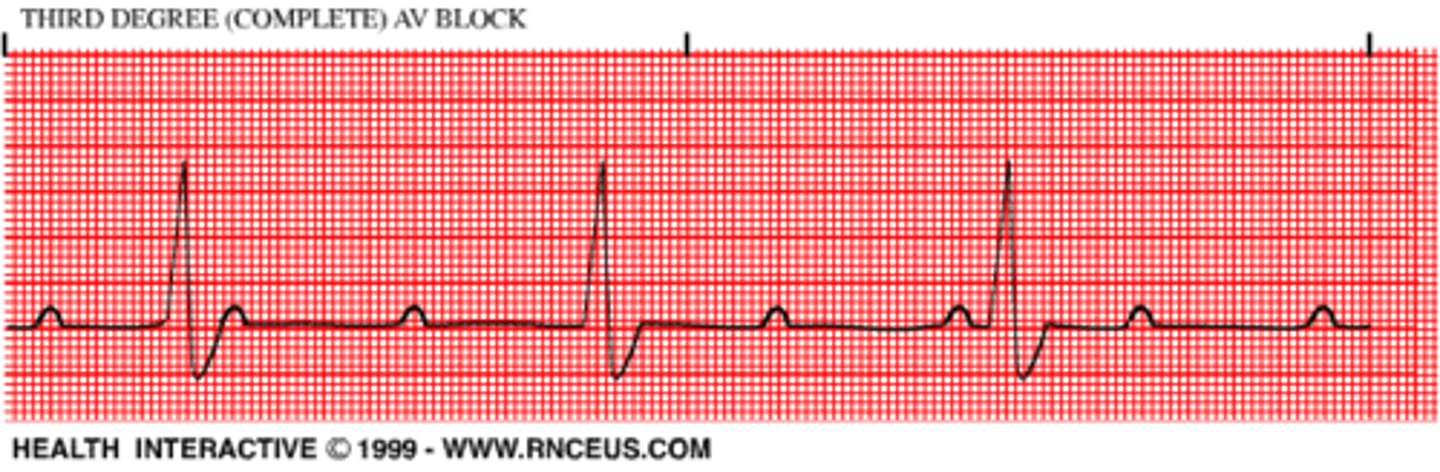
3rd degree AV block
P and QRS are NOT communicating (atrial and ventricles function normally, but are completely dissociated)
AV node cannot conduct impulses, ventricles generate an escape rhythm (20-40 bpm)
PR interval = cannot determine (random P waves)
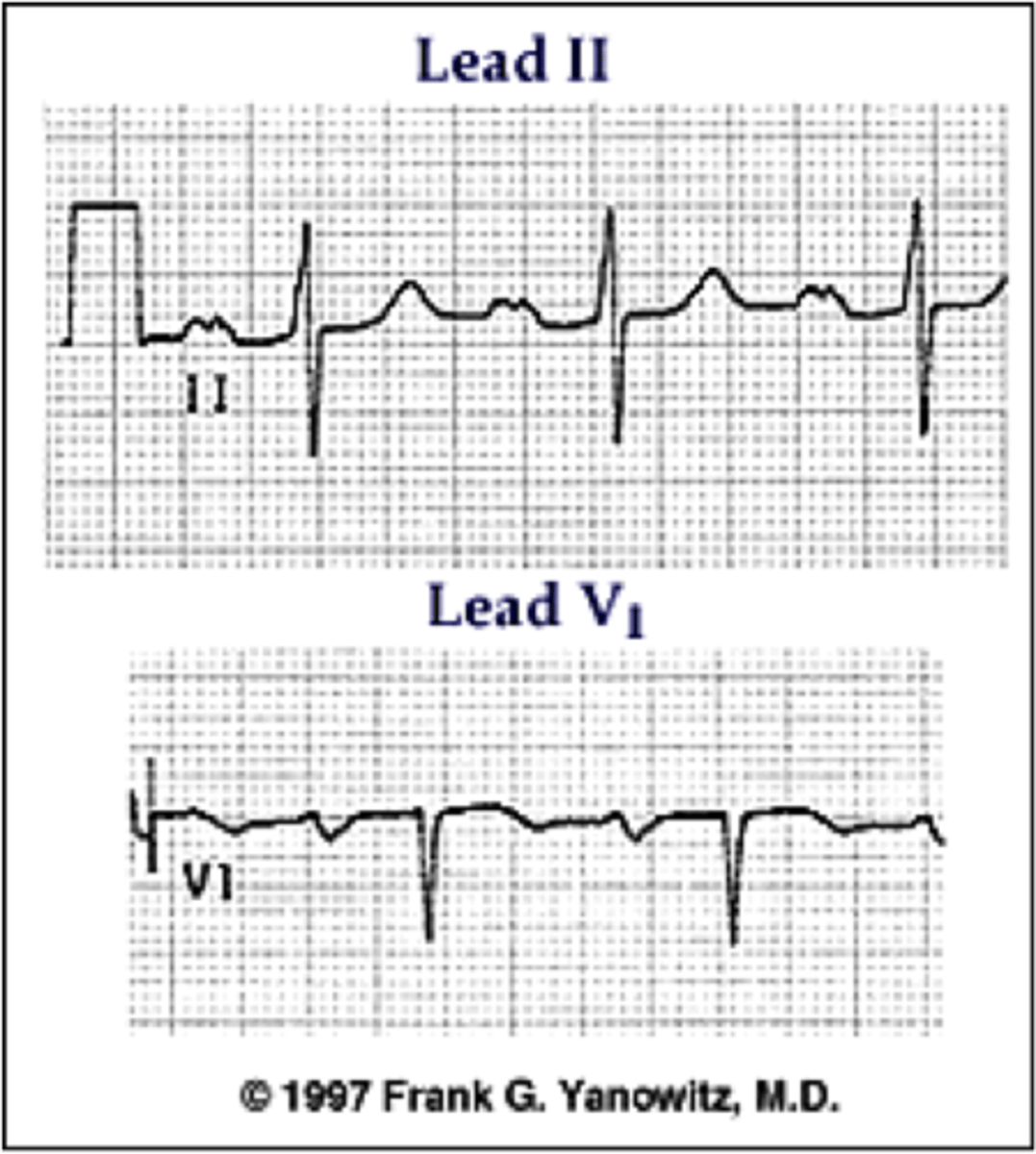
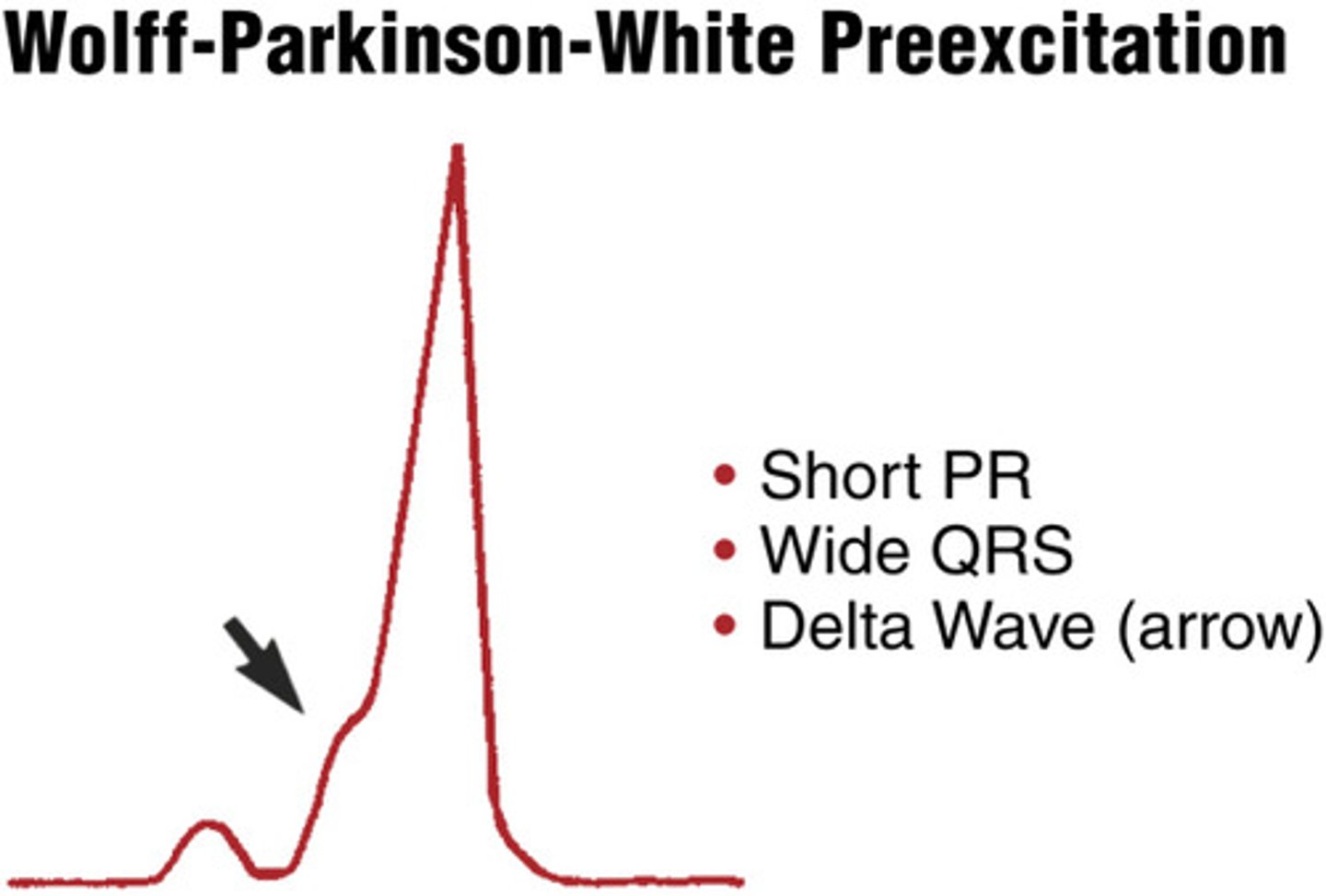
wolff-parkinson-white pattern (pre excitation)
PR interval is shortened < 0.12 seconds
P wave blends in with QRS (delta wave)
The QRS is widened secondary to early stimulation of the ventricles
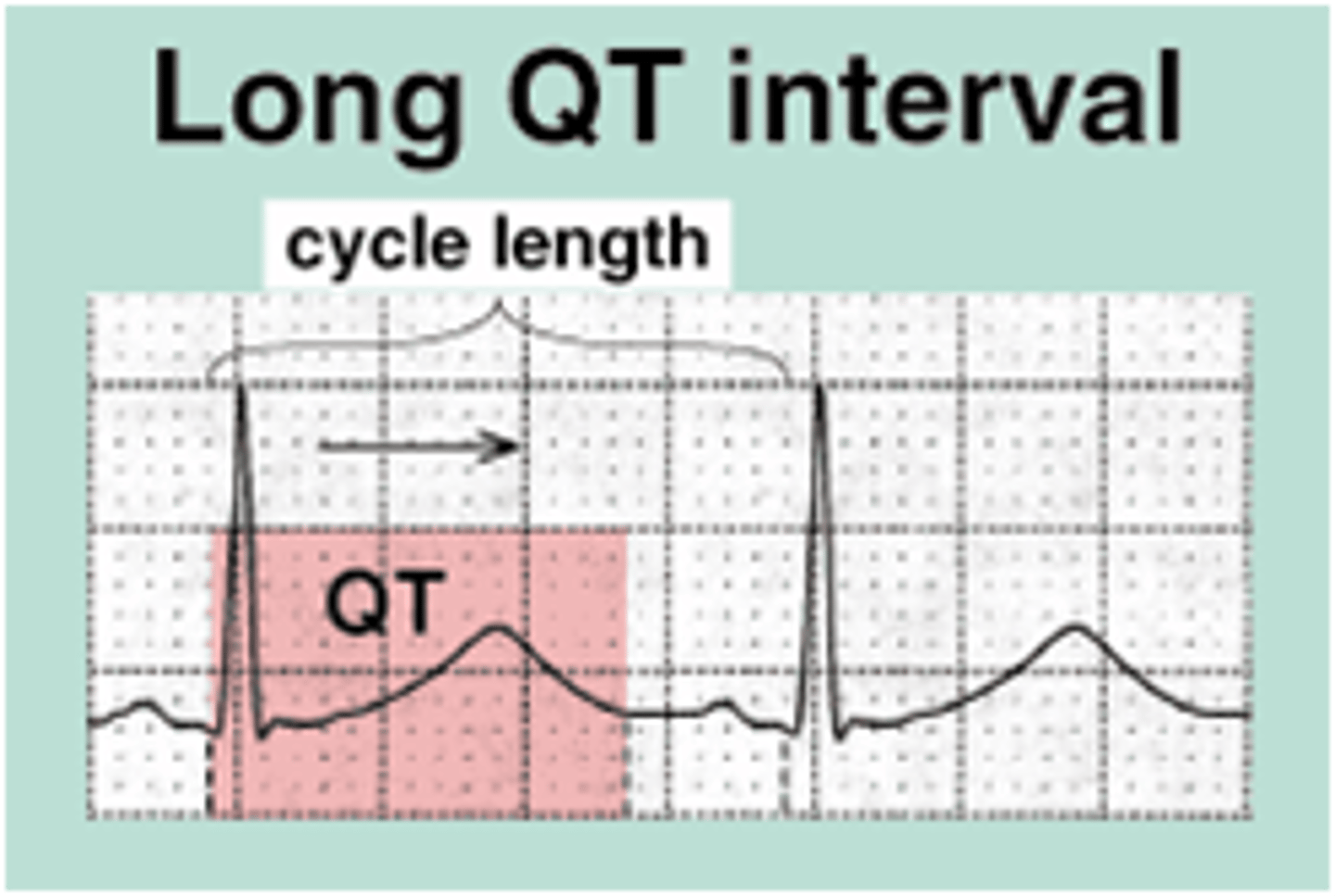
long QT syndrome
Increased risk for sudden death (genetic predisposition)
QTc > 460 msec
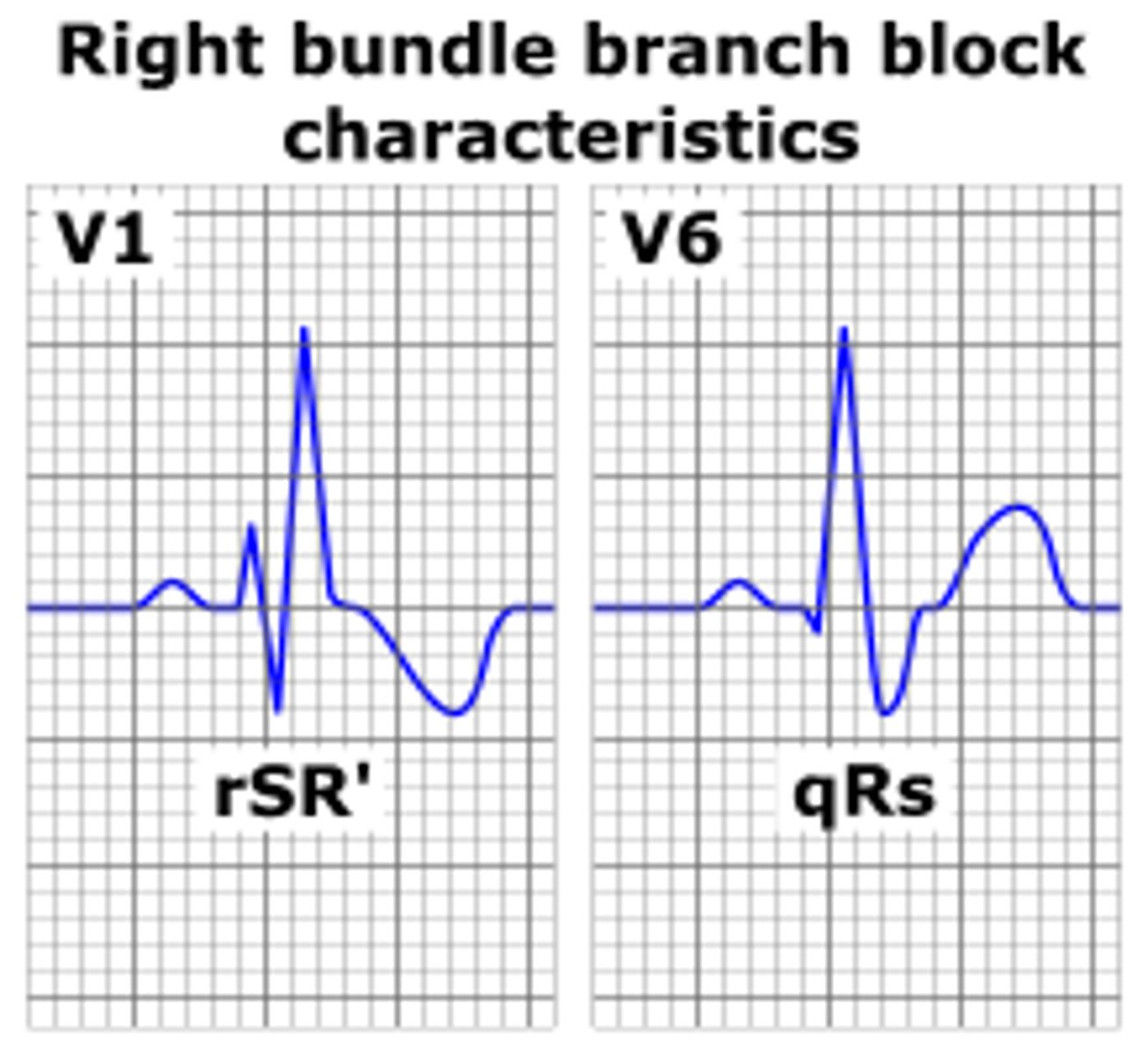
right bundle branch block
widened QRS (>0.12s)
double/notched R waves (best to look in V1 and V2)
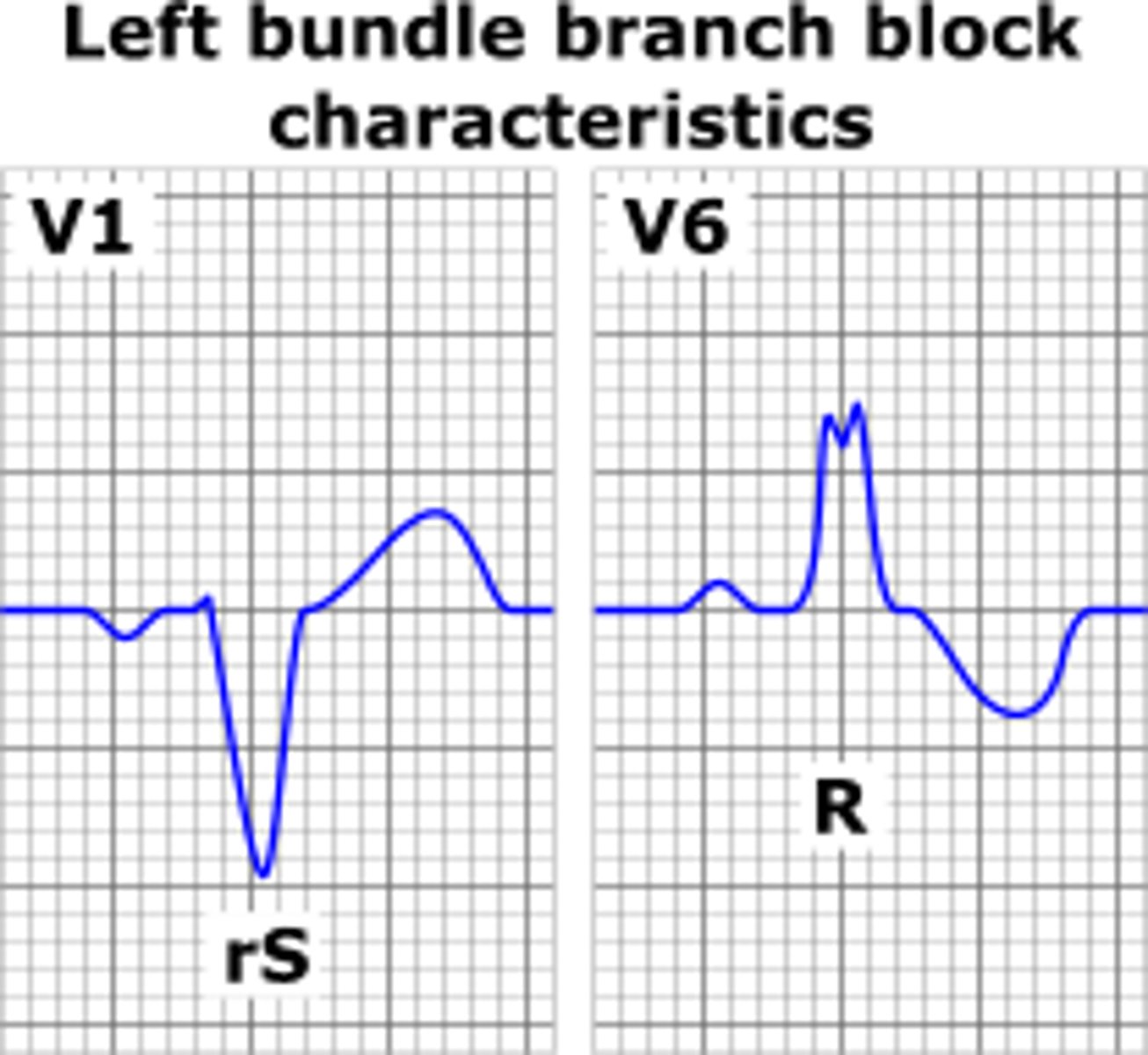
left bundle branch block
V1 and V2 have neg deflection with wide QRS
widened QRS
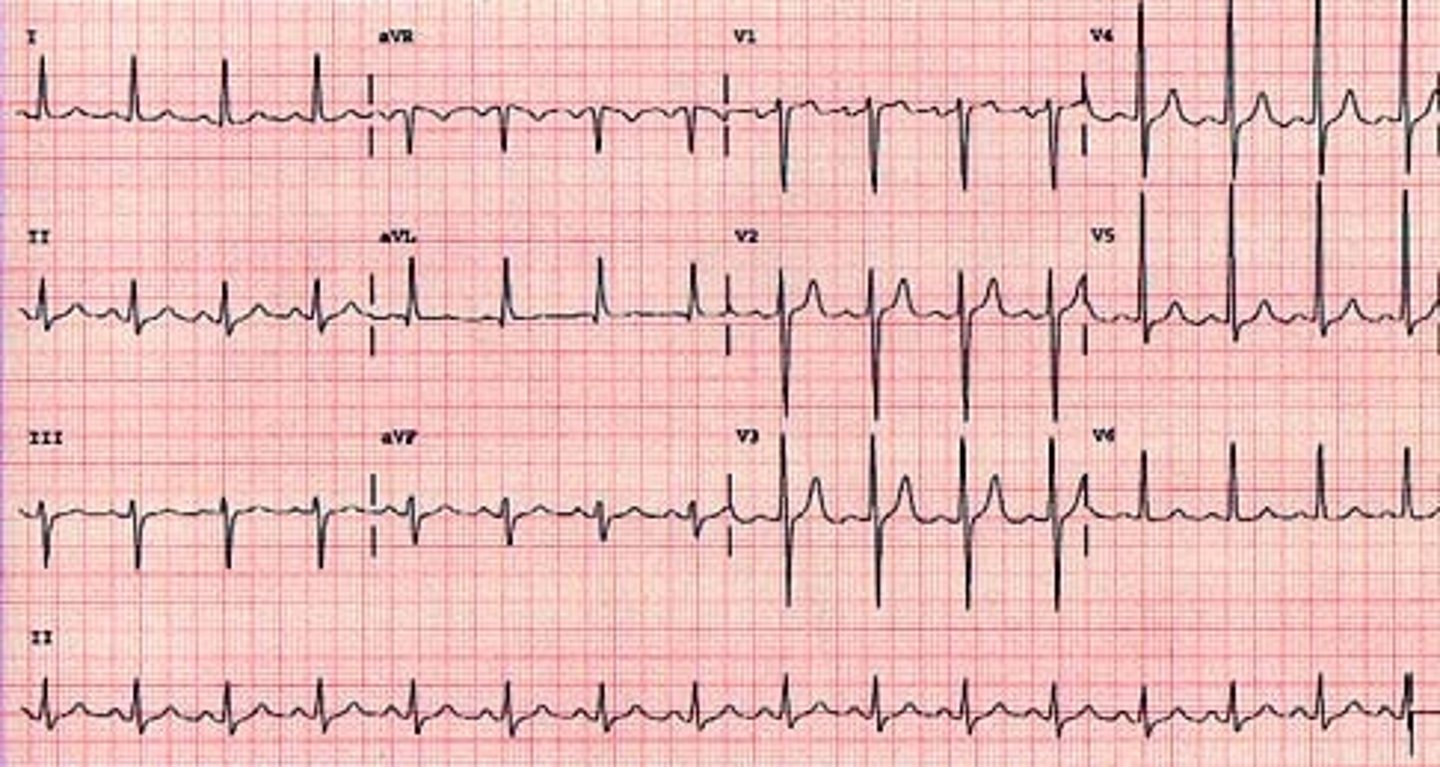
right ventricular hypertrophy
R wave progressively smaller from V1 to V4 (abnormal progression)
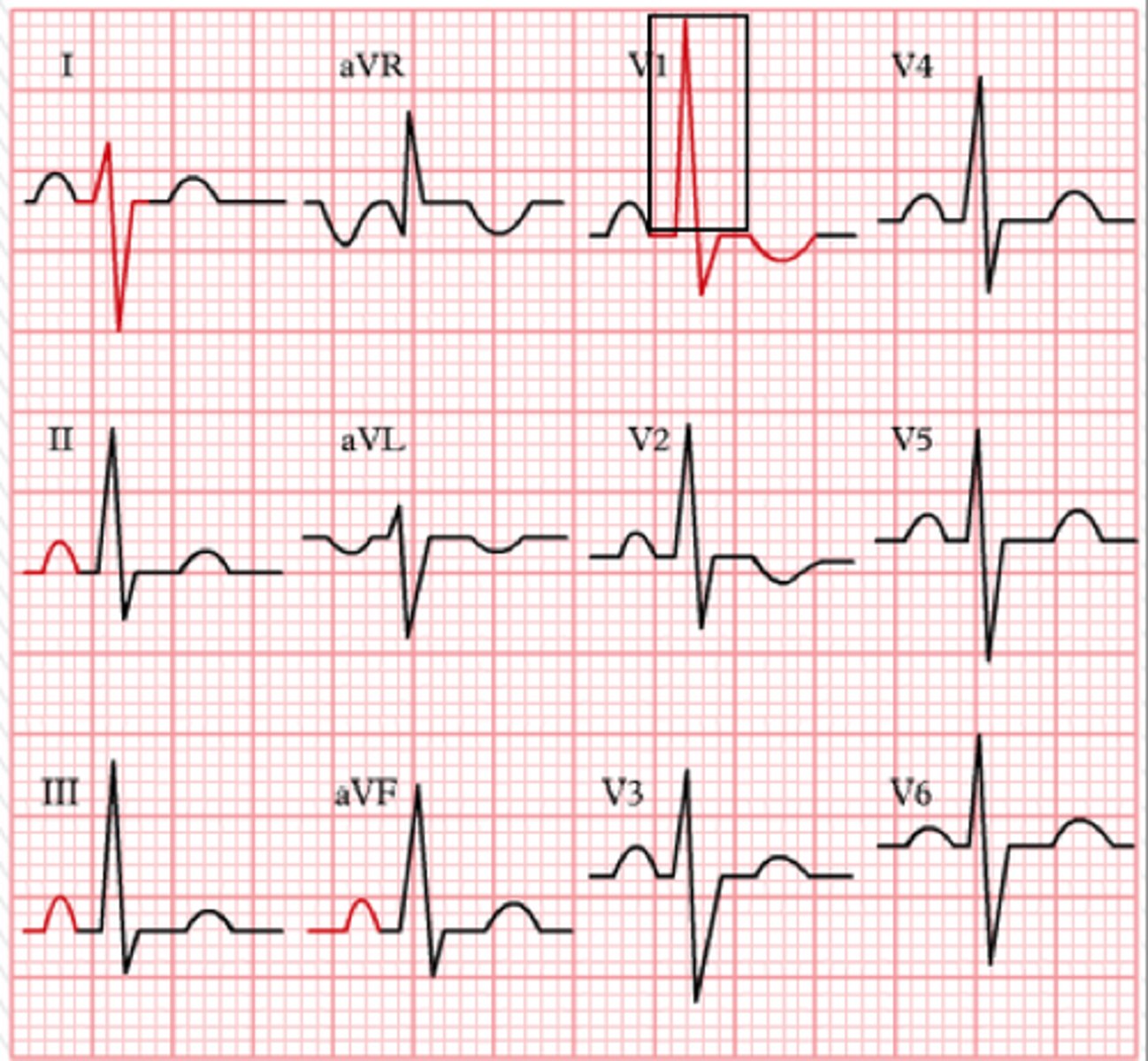
left ventricular hypertrophy
left axis deviation
high R waves in V5 and V6
right atrial enlargement
very tall P wave in right sided leads
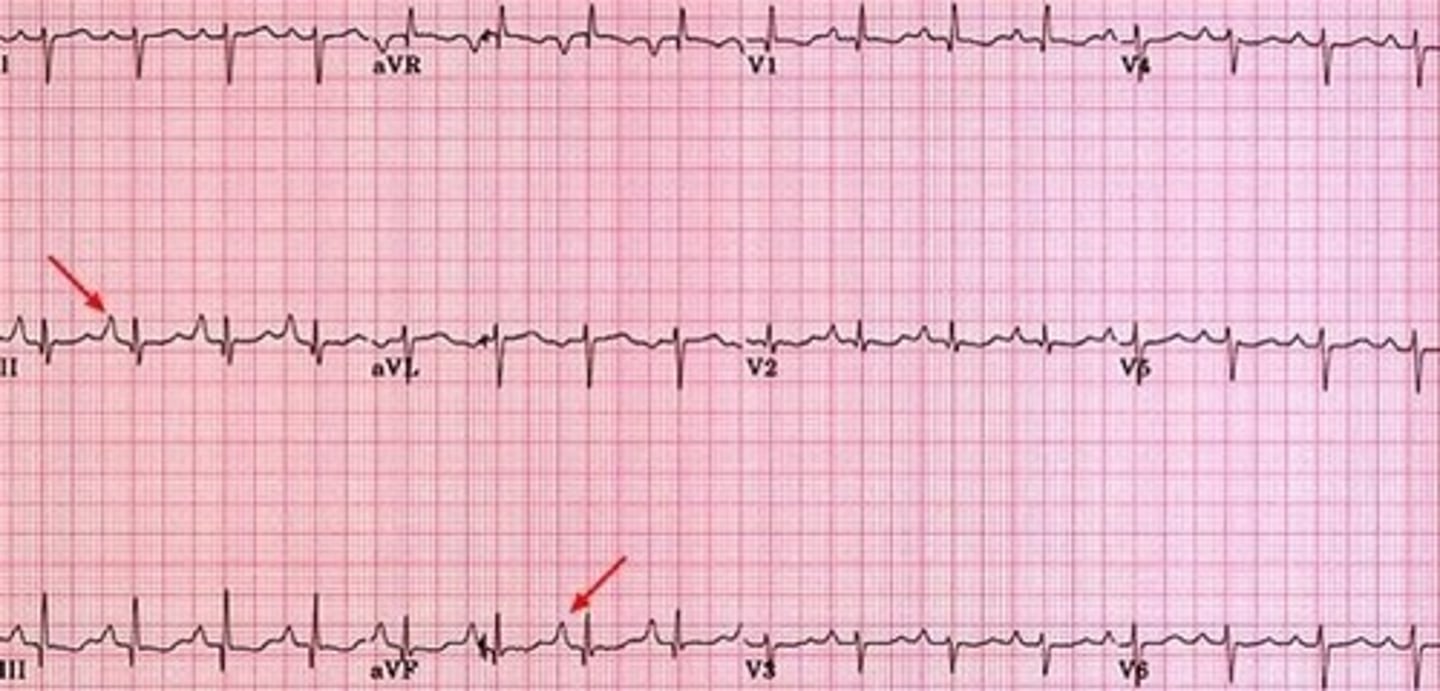
left atrial enlargement
wide/biphasic P wave in left sided leads