nerons+ seminar
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Finished
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
what is in the skin to allow it to detect pain?
In the skin we have free nerve endings – loads of these witch are breached
those free nerev endings converge onto an axon
how does the free nerve ending create a action potental
when pressure is added to the free neurve endings pressure gated na+ chanles open letting soduim past the membbrain, making the mebrain more postive (depolirising)
Noctercepters
is a sensory neuron that responds to damaging or potentially damaging stimuli by sending "possible threat" signals to the spinal cord and the brain
what is the resting mebrain potentlal
-70mv
what is a mebrain potental
what is the relative diffrence between inside the meron and outside the membrain
sodium
postive
cloride
negative
hyperpolirising
makes mebrain potental more negative
depolirising
makes more postive
what happens after the pressure gated sodium channels are open?
sodium flows into of the membrain meaning that the membrin potential becaimes more postive Witch then triggars the voltage gate Na+ chnales- it is senstive to the membrain potental till it reaches action potential
what haopens when they reach the action potential
the action potental spreds along the axon. the the membrane potential attains +30 mV, the voltage-gated channels specific to K+ ions open. As the membrane repolarizes, the sodium channels de-inactivate and return to the initial state, ready to open after receiving a stimulus. The potassium channels also close but remain open long enough to undershoot as potassium moves toward its equilibrium potential of -80 mV
How dose action potentals move up the axon?
There are spodium channales all over the axon witch will spered the mabrains potential witch will triggar more sodium chanles oping. Witch will casue more action potentials Is the axions mylinated it jumps because of the nodes of ravror
where do the axons go to?
This axon runs to the spinal cord.
To the dorsal horb in the spinal cord
the dorsal horn
Dorsal- towards back
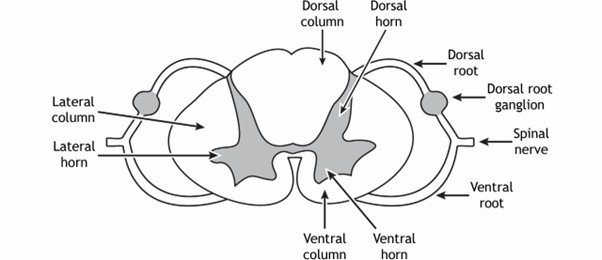
dorsal root
is a bundle of axons coming into the dorasl part
dorsal root gangluar
cell bodies collection
where is the cell body of the axon
The cell body of the nerve witch sits on a stallk next to the axon and the axon potental dosnet go through the cell body just next to it. All the the cell body sit close together in the doral root gangular.
what dose the axon go to ?
onto the 1st order spinal neron
what happens when the axon potental gets to the presysnaps
th emebrain potental is postive witch Wicth then triggaes voltage gated calcuim chanles to open.
what dose calcium do in the presynaps
Calcuim is postive. But also a magor intercellulart signiloing molecule and when intracts with proteens it can change the shapes of those proteens
how do the vicecals go into the synaptic cleft
Clacium intracts with the proteens that are in the vesicles. The proteens that make the vesical open into th synaptic gap are controlled by calcium concentraits.
what are the nerons in the 1st order sensory neron synaps
substace p
glutimate
if there is a lot of pain what happens diffrently at the sensory and 1st order spin synaps
Lots of action potential both will relace but only a few just glutamate is reliced
What substace p is reliced then we feel a lot more pain.
what happens whe the nerotrasnmitters diffuse at th epost synaptic neuron
nerotransmitters bind to the to receptors that depolirises the mebrain potential ( makes more positive). The rectptors are ligand- gated na+ chanles. Wich allows sodium to go into the cell. If this happen in enough recptors/ close together. To reach the threshold for the voltage gated sodium chanles to open with will then generate an action potential.
whatr types of gates are at the postsynaptic recetpters
ligand- gated na+ chanles
where dose the Desendig angisal circuit start
Starts in the PAG(Periaqueductal gray) is in the mid brain, gray and located near the aqueduct. has a collection of nerisn witch are respnsable for the DAC
Internerons
Short axon, in the same area, inhibitory most common one is GABA
Projection neron
long axon that comunictaes with different parts of the cns
how do inhibitory post synaps fire randomly?
In some mebrains of nerons the mebrain potential is very closte to csing a action potential witch causes the neorn to fire by random fluctuation is mebarin potentiual.
what neons are used in teh PAG
internurons that are inhibitory witch use GABA
what happens at the PAG to progection neron
Releces Gaba and bind to the postsytptic receptors wich cayses the projecting neron hyperpolarise ( become negative so it less likely to fire a action potential)
how dose the post synaptic mebrian in the PAG and projection neoron
Gaba chnales are chloride chanles witch allow chloride to come into the neon and the inside becomes more negative. Membrain hyperpolirises- no chance of action potential
what happens when the ingibatiry interanl nerons in the PAG nt bind to the receptors
they stop releasing Gaba onto the projection neurons, meaning
these membranes depolarise and become closer to 0 as they aren’t inhibited
– when negativity comes small enough it opens channels that allow sodium
ions to flow in making the membrane potential positive on the inside which
starts firing AP’s
what is disihabition
lifing of the inhibition by the inhibitory interneurons that causes circuit to
become active. Inhibition is lifed due to endogenous opioids (released from
other axons from outside the PAG) inhibiting the interneurons
what is the Activation of the descending analgesia circuit is a process of
disinhibition
what starts the circte
1. Endoougous opiods get relice
2. Ther inhibitory so the action potential from the internal to projection synaps dsont happen
3. So GABA isn’t realiced
4. Meaning that the post synaps doesn’t get hyperppolirised (more neg) so the random firing of AP because the mebrain is close to 0
5. So there is action potentials firing down the projection
inhibitory synaps
1. Action potential
2. Relice of gaba
3. Gaba binds-
4. Becomes more negative because gaba chanles are cluride chanles so they open and let in clirine in making more neg
5. Probirbility oif firing becomes less –
where dos ethe projection neron go to
the rafe magnus
what happens at the projection (pre) adn rafe mangus (post) synaps
glutamate binds to the receptor depolirises wicth opens the voltage gate soum chanles witch cause action potential
The rapha magnas relices
- Serotonin
- Neroadreninlin
Can be both excitortaty and inhibortoty
whre dodoe the rafe magnus go to
the dorsal horn- al along the spinal cord
what three synapsis dose the rapa magsnus split to
rafe magnus (pre) to the pre synaps of the senry neron (post)
internerons (inhinbitory)
internurons (inhibioty)
what nror transmitter is reliced by the rafe mganus
serotonin and or adrenalin
what type of symaps is the rapha magnas to presynaptic sesonry neron?
inhibitory
what kind of synaps os the rafoah to the inter nerpons
Exictory
what type of nero transmiteer are seritonin and neroadrenilin
excittoray and ca be inhibitory, it depends on the recepteros on the outher side of the cleftr
what type of nerotraynsmitters on on the internerons binding to the internurons
excitory witch depolirises and caysues action potentals
what are the targest of the internerons that are connected to the rafe magnus
firts order neron
onto the presynaptic termanal of the nocersepeter
what type of neron is the fisrt order neorn and what transmitter dose it use
inhibory
encephilin
so What happens to the membraine of the first order nerton whne encephiln binds to it
hyperpolirises becomes more negative ,menas less likley to fire action potentals
what is pre synapting on the neoticepeter synaps with teh first orner spinal neron
inhibiotory internueron with encehilin
raphe magnoiut with seriotioninn wihc is inhibitory
what will the inhabiron do to the presynaptic terminal of the not9iceptor and 1st order spinal nuron
hyperoplirises with mean that they less likelyr to shoot action potentals witch isnt able start the pain cylcle
they need to hyperpoliris enough though because tehre rae two presynaps
what happens if the nocicepter has so much action potental that it ivverrunss teh depolirisating encephil and sseritoionin
the fisrt order neron is hyperpolirised so it wont be able tp depolirise wenough because it is alredy being deplorised by encephilin
further reducing the likely hood of an action potental to get to the barin
Glial cells
Glial cells are a type of cell that provides physical and chemical support to neurons and maintain their environment. Located in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system, glial cells are sometimes called the "glue" of the nervous system, as well as neuroglia or just glia.
pricniples of the nerosystem
GLIA
NEURONS
Neurons
Within-cell communication: electrical (e.g. Action Potentials)
Between-cell communication: chemical (neurotransmitters)
two inhibitoy and one excitoray nerons feed into a noron will it fire?
NO
one inhibitory and two exsitotay nerons feed into a neron will it fire?
YES
hormones
- Through the bloodstream- definition of a hormone
- Global action
- Effects can be varied, depending on the hormone/receptor combination
Neurotransmitters
- From one neuron to the next
- Local action
- Effects can be activation or inhibition, depending on the transmitter/receptor combination