Week 1-3: Fluid Balance, IV Access, and Cardiac Health
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Intrinsic Pathway
Triggered by blood vessel damage; leads to clotting.
Calcium and VWF
Essential for clot formation and stabilization.
Prothrombin Time (PT)
Measures extrinsic pathway clotting time in seconds.
International Normalized Ratio (INR)
Standardizes PT; normal range 0.8-1.1.
Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT)
Measures intrinsic pathway clotting time; normal 25-30 seconds.
Hypocoagulability Disorders
Conditions increasing bleeding risk due to clotting issues.
Thrombocytopenia
Low platelet count leading to bleeding risk.
Hemophilia
Genetic disorder causing deficiency in coagulation factors.
Von Willebrand's Disease
Deficiency or defect in von Willebrand factor.
Leukemias
Hematological malignancies affecting blood cell production.
HELLP Syndrome
Pregnancy complication with hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes.
Signs of Bleeding
Symptoms include bruising, hematuria, and excessive menstruation.
PT (INR)
Prothrombin Time; measures blood clotting time.
PTT
Partial Thromboplastin Time; assesses intrinsic pathway.
Vitamin K
Essential for synthesizing clotting factors.
Vitamin K Deficiency
Increased bleeding risk; high PT & PTT.
Warfarin Overdose
Reversed with Vitamin K administration.
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Condition causing widespread clotting and bleeding.
DIC Causes
Includes infection, trauma, and obstetrical emergencies.
DIC Pathology
Uncontrolled thrombin leads to microclots.
DIC Symptoms
Petechiae, bruising, fatigue, shortness of breath.
Hypercoagulability
Increased tendency to form blood clots.
Thrombocytosis
Elevated platelet count; risk for clotting.
Thrombophilia
Genetic predisposition to abnormal clotting.
Protein C Deficiency
Inherited condition; increases clotting risk.
Factor V Mutation
Genetic defect leading to clotting disorders.
Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Autoimmune disorder increasing clotting risk.
Sepsis
Severe infection that can lead to clotting issues.
Acetylsalicylic Acid (ASA)
Aspirin; mild anticoagulant and anti-inflammatory.
Heparin
Anticoagulant that inactivates thrombin.
Protamine sulfate
Antidote for heparin overdose.
Apixaban
Anticoagulant that requires monitoring for bleeding.
Transfusion reactions
Adverse responses to blood transfusions.
Antigens
Substances that trigger immune response in blood.
Pre-transfusion assessment
Vitals signs
Respiratory
Cardiovascular
Integumentary
Pre-medication may be required if prior reaction
Blood Pickup Timing
Start within 30 minutes, complete within 4 hours.
5 Rights of Transfusion
Right Patient, Product, Amount, Rate, Time.
Initial Monitoring Period for transfusion
Monitor closely for first 15 minutes.
Transfusion Rate Increase
Adjust rate after 15 minutes if stable.
Packed Red Blood Cells (PRBCs)
Most common transfusion for bleeding or anemia.
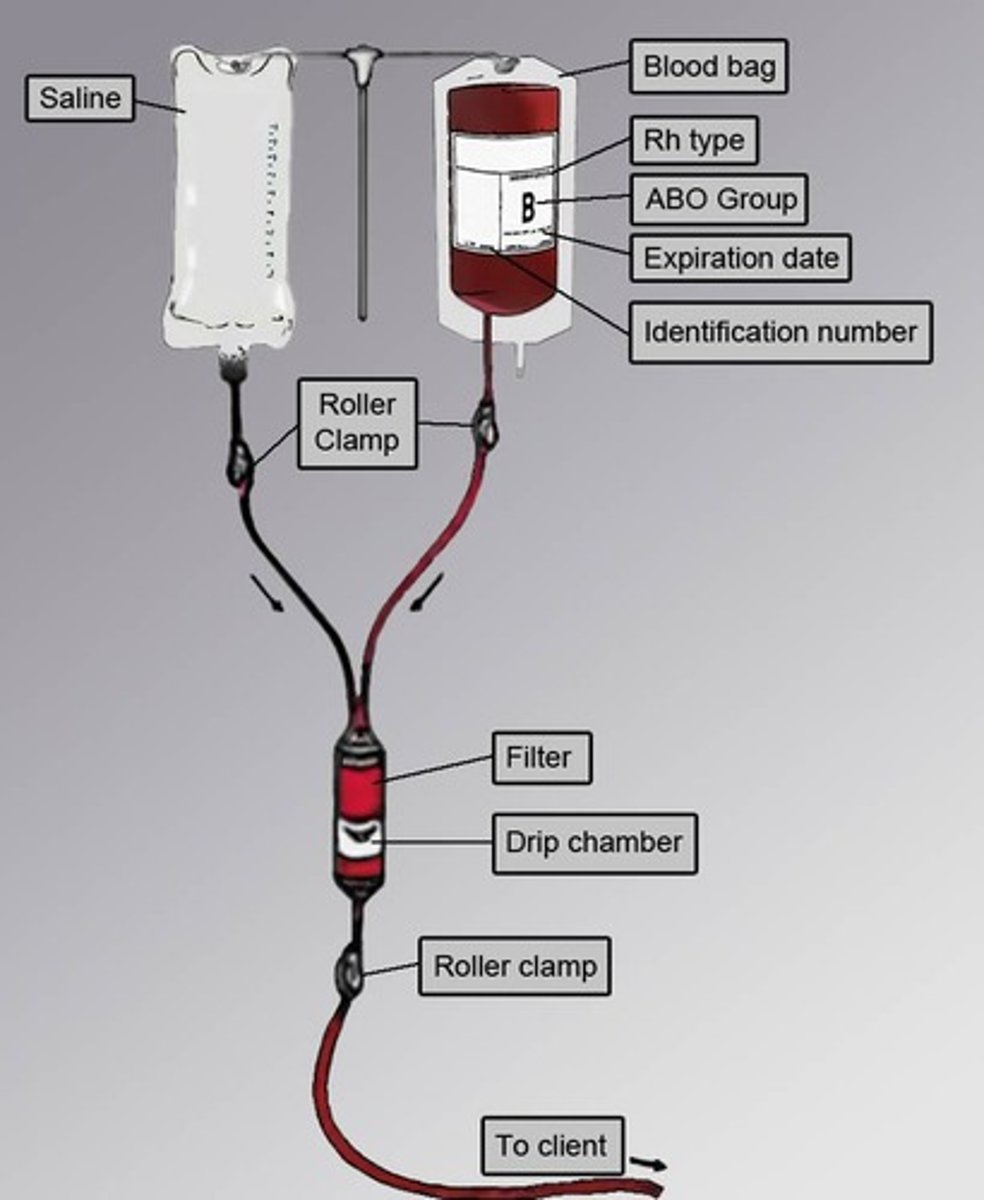
PRBCs Administration
Initiate transfusion slowly
Transfuse over 1.5 to 2 hours typically.
Expected Hgb Change after PRBCs
Increase of ~10g/L in 4-6 hours.
Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
Used for volume expansion and clotting factors.
Administered over 30 minutes - 2 hours
Platelets Administration
Control bleeding in thrombocytopenia patients.
Administered over 60 minutes
Transfusion Reaction S&S
Monitor for fever, chills, rash, hives, itchiness, dyspnea, nausea, headache,
Minor Allergic Reaction
Mild rash, itching, warm; treat with antihistamines and slow transfusion
Anaphylaxis Reaction
Difficulty breathing, loss of airway, hives; emergency response required; stop transfusion.
Febrile Non-Hemolytic Reaction
Low-grade fever and rigors; administer antipyretics and slow transfusion
Bacterial Sepsis
Potentially fatal reaction from contaminated blood.
Rigors, high fever, severe chills, hypotension, tachycardia, nausea, dyspnea; stop transfusion
Acute Hemolytic Reaction
Fatal reaction from blood group incompatibility; hypotension, back pain, fever, dark urine; Stop transfusion
TRALI (transfusion related acute lung injury)
Acute hypoxemia; emergency; rapid onset dyspnea and tachypnea, spo2 < 90 on RA, fever, cyanosis, hypotension; Stop transfusion
TACO (transfusion associated circulatory overload)
mild fluid volume overload; hypertension, crackles, increased RR, dyspnea, increased HR; administer diuretics and slow transfusion
Hypotensive Reaction
Rare bradykinin-mediated hypotension; Emergency; rapid drop in BP; stop transfusion.
Perfusion
Blood flow through circulatory system to oxygenate cells and remove waste
Perfusion depends on?
cardiac output & blood pressure
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Measures electrical activity of the heart.
Echocardiogram (ECHO)
Assesses mechanical function of the heart.
Lab Values for cardiac health
Includes K, troponin, BNP for cardiac assessment.
Risk Factors in cardiac labs
BUN/Cr, BG, HbA1C
Atrial Fibrillation
Irregular heart rhythm caused by uncoordinated contraction of atrial muscles
rapid, chaotic and irregular contraction pattern of the atria
A-fib heart rate
Usually exceeds 100 beats per minute.
A-fib rhythm
Characterized by irregular heartbeat.
A-fib P wave
Absent in atrial fibrillation.
A-fib causes
hypertension
diabetes
smoking
obesity
alcohol
A-fib outcomes
clot formation (TIAs, stroke, MI, PE, HF)
poor perfusion
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors for A-fib
Age, gender, genetics, family history.
Modifiable Risk Factors for A-fib
Lifestyle choices affecting heart health.
comorbidities of A-fib
HTN, hyperthyroidism, hypokalemia, hypomagnesmia
Pharmacological interventions for A-fib
Calcium channel blockers
Beta blockers
Cardiac Glycoside
Oral anticoagulants
Medications for A-fib target
Heart rate. rhythm, coagulation
Synchronized Cardioversion
shock given at a specific time in cardiac rhythm to convert heart back to normal sinus rhythm
Catheter Ablation
Procedure to destroy tissue causing A-fib.
Angina
Ischemia of partial thickness of myocardial muscle
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
Ischemia of full thickness of myocardial muscle
Causes of Angina
stenosis, vasospasm, thickening of heart wall
Causes of MI
stenosis, plaque lodge
ST-segment elevation (STEMI)
Indicates significant heart muscle damage on ECG.
Non-ST-segment elevation (NSTEMI)
Partial blockage with less severe ECG changes.
Troponin I
biomarker for cardiac muscle damage
elevates 3-6 hours post MI, peaks 12-16 hours
Cardiac biomarkers
troponin, creatine kinase, myoglobin
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
Procedure to open blocked coronary arteries.
Complications of MI
dysrhythmias, pulmonary edema, MI, cardiogenic shock, heart failure.
ST Depression
Suggests angina or ischemia on ECG.
Systolic Dysfunction
Impaired heart contraction leading to reduced output.
Diastolic Dysfunction
Impaired heart filling leading to reduced output.
Left Sided CHF
Heart failure causing respiratory congestion, dyspnea, SOB, crackles and decreased SpO2
Right Sided CHF
Heart failure causing peripheral edema, fluid volume overload, weight gain, ascites, reduced RBCs
B-Type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP)
increase = heart failure
Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF)
Ejection fraction > 50%; indicates preserved heart function.
Mid-Range Ejection Fraction (HFmEF)
Ejection fraction 41-49%; transitional heart failure stage.
Reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF)
Ejection fraction < 40%; indicates significant heart dysfunction.
Complications of HF
Cardiogenic shock
Pulmonary edema
Venous disorder
S&S of Pulmonary Edema
SOB, tachypnea, low SpO2, cyanosis, frothy pink sputum, restlessness, weak peripheral pulses
Nursing Management for Pulmonary Edema
High Fowler's
Apply O2
Initiate IV access/administer diuretics, morphine
Monitor ECG
cardiogenic shock
compromised cardiac function to the point that it cannot maintain cardiac output and adequate tissue perfussion
Venous Stasis Ulcers
Skin excavation due to inadequate perfusion; inflamed tissue.
Stage one heart failure medication
ACEi or ARB
Stage two heart failure medication
ACEi or ARB + Beta Blocker
Stage three heart failure medication
ACEi or ARB + Beta Blocker + Diuretic
Stage four heart failure treatment
Palliative or heart transplant