SHM and CM Questions
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
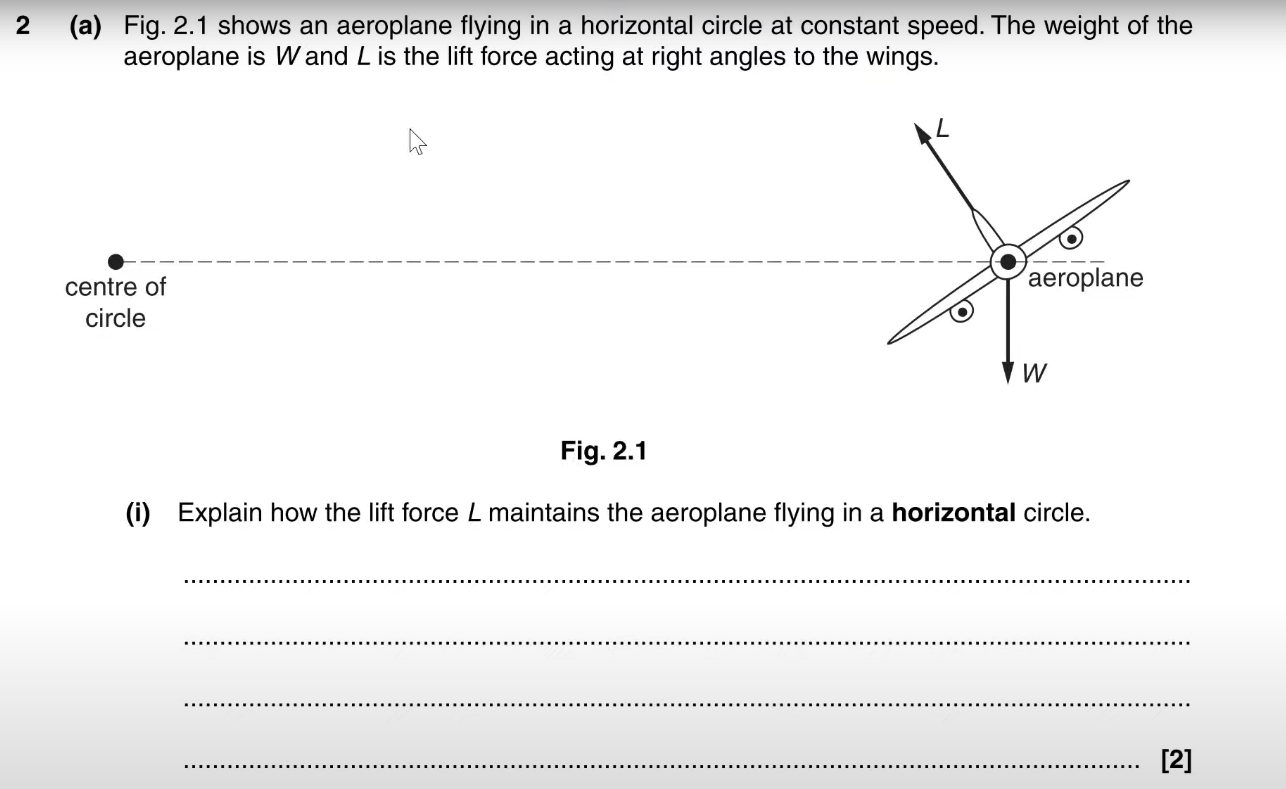
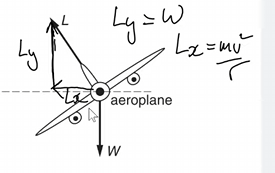
The vertical component of L is balancing the weight (cancelling them out)
This means horizonal component is providing the centripetal force.
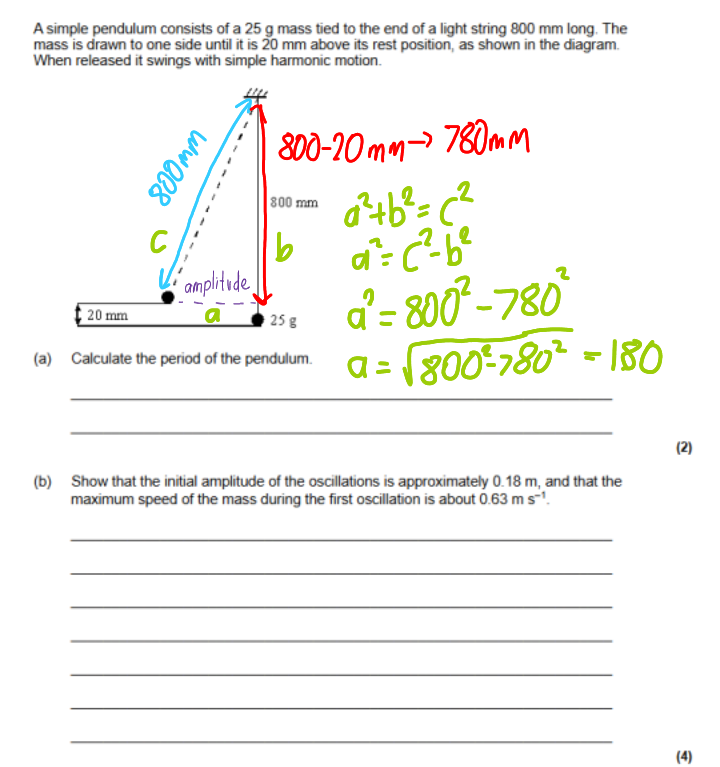
How can you find the amplitude using Pythagoras?
0.18m

Objects move tangentially when the string breaks—initially. However, gravity acts immediately after the string breaks, causing the motion to curve downward into a parabolic path.

Definition of Simple Harmonic Motion? (2 marks)
Motion in which the acceleration is directed towards a fixed point (or equilibrium position) AND is directly proportional to the negative of the displacement.
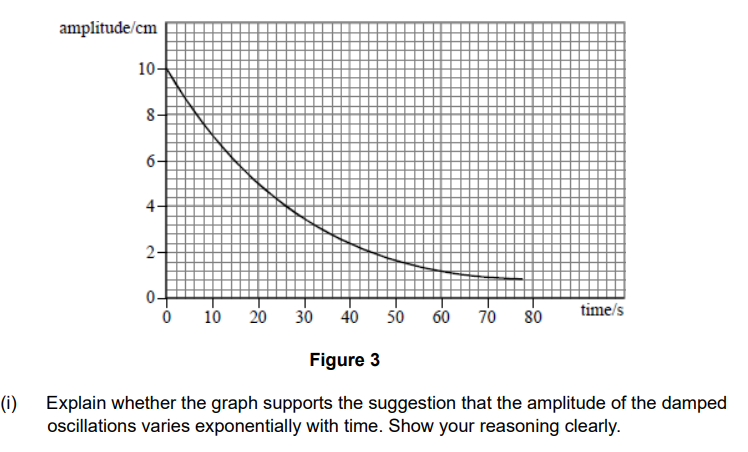
If no calc, how would it be done?
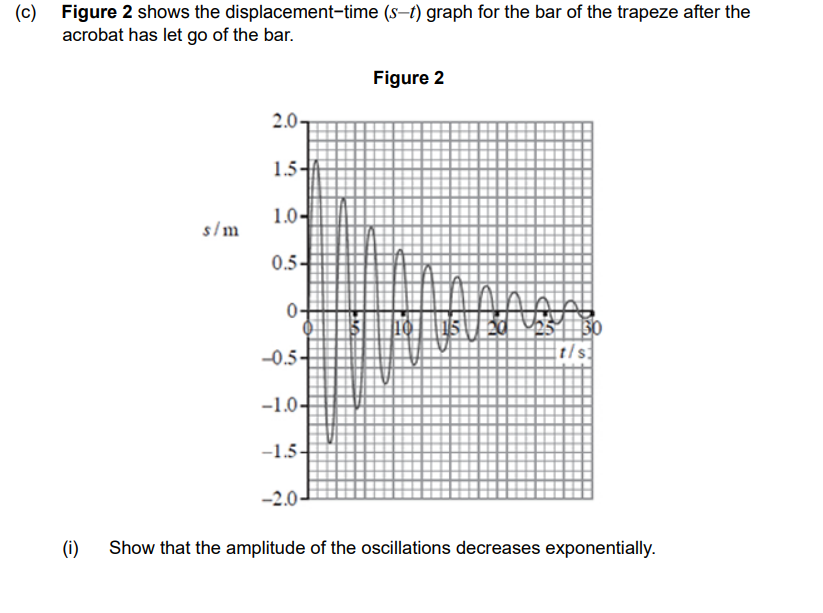
Since you know the equation A = A0 x e^-kt , where A is the amplitude, you can re arrange to find:
A/A0 = e^-kt
Now, pick equal time intervals (10s apart for example), and you know e^-k must be roughly constant if the system is exponentially decreasing!


C, JUST RE ARRANGE FOR L! (Don’t forget to square root)

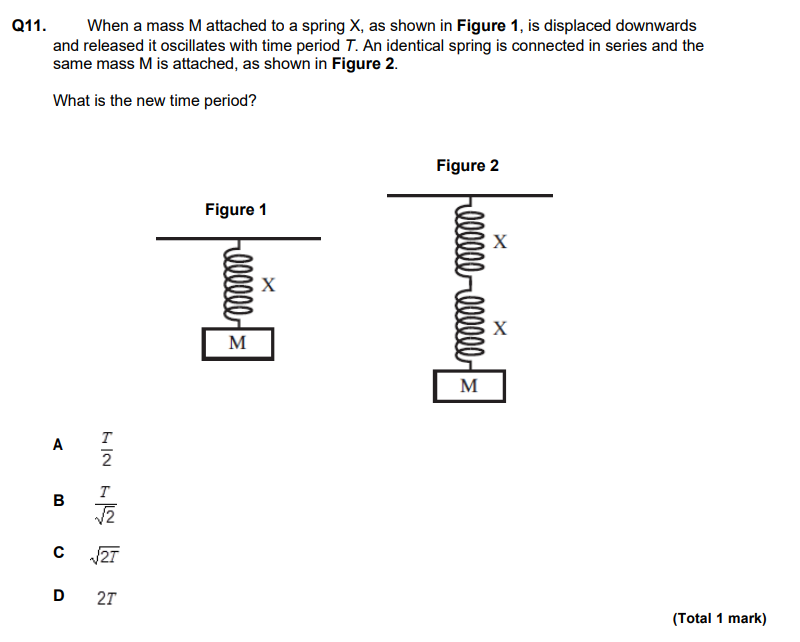
REMEMBER that calculating spring constants is the opposite to how you calculate resistance in circuits.
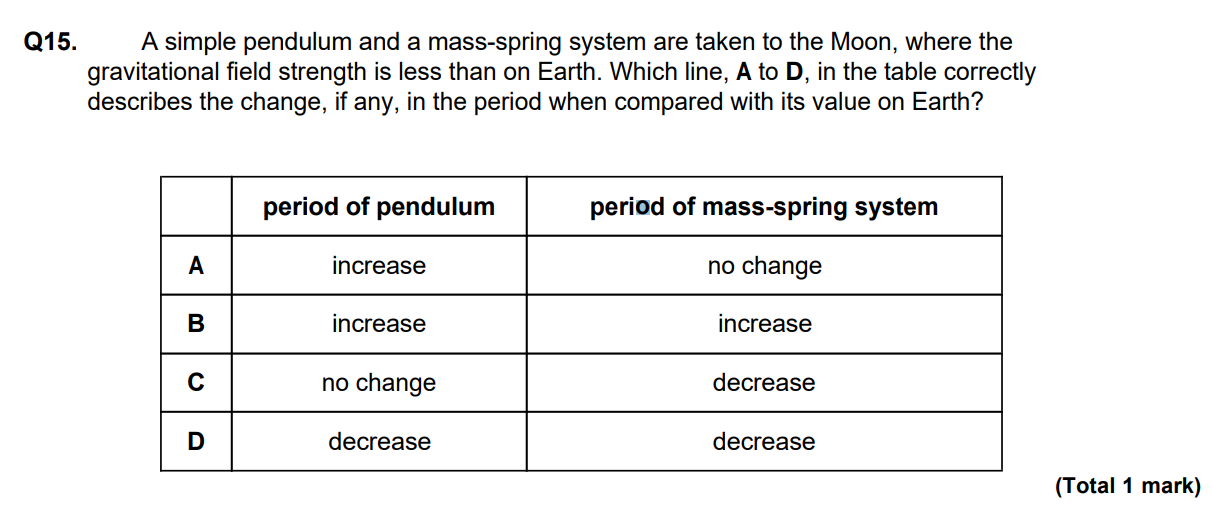
A
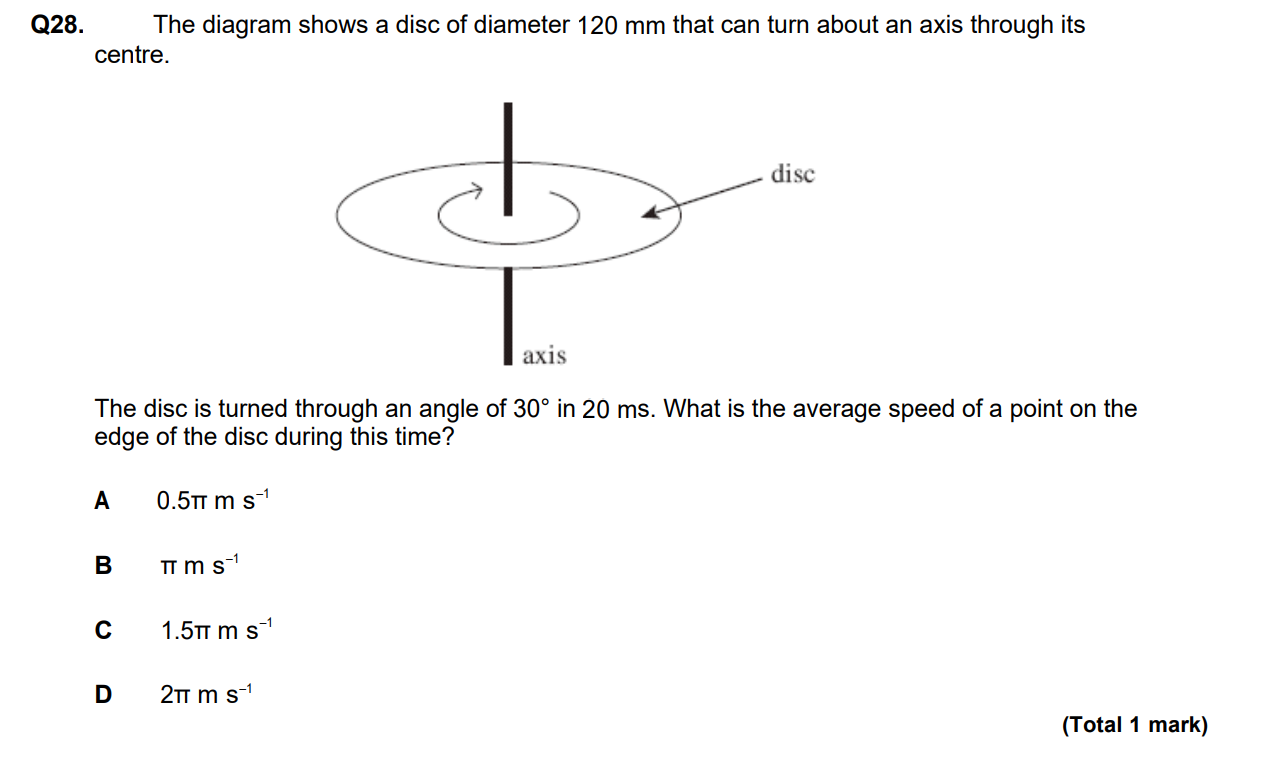
Find distance travelled and divide by time OR using w = theta / t where theta IS IN RADIANS!
How could you calculate the energy of a spring system, given only the amplitude?
E = ½ k x e²
e = Amplitude
So ignoring ½: E1 = k x A² and E2 = k x A2², make k equal
E1/A1² = E2/A2² so then E1/E2 = (A1/A2)² .
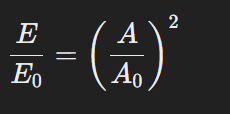
What is the definition of a newton?
The force required to accelerate a mass of 1kg to 1ms^-2.

ALWAYS towards the centre of the circle
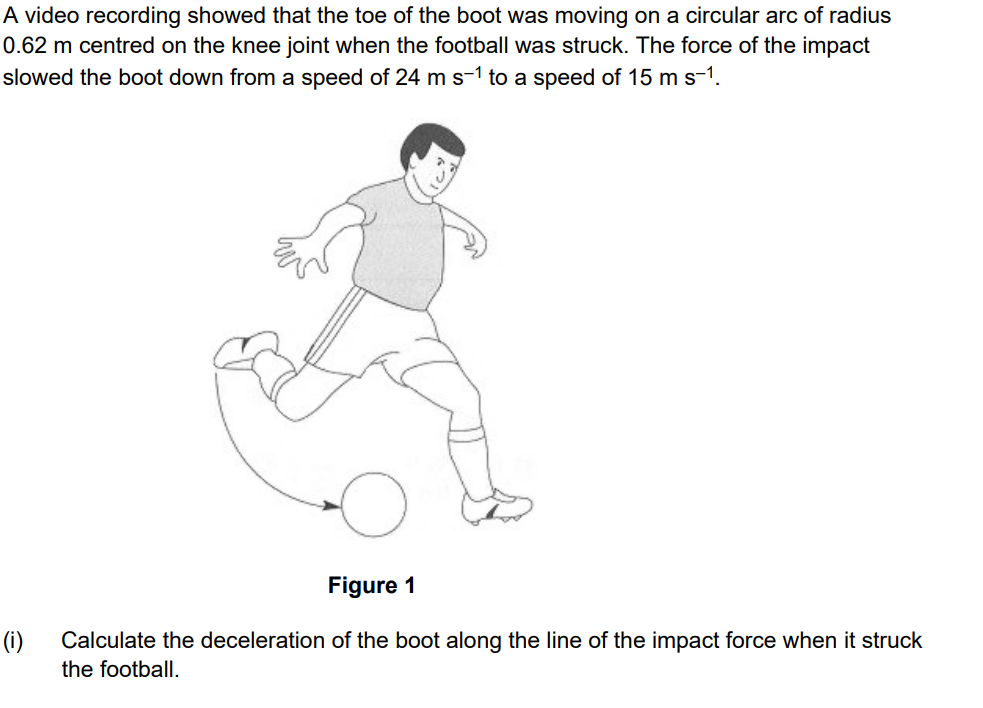
Given t = 9.2ms
Remember, acceleration is:
CHANGE IN Velocity/Time
Therefore:
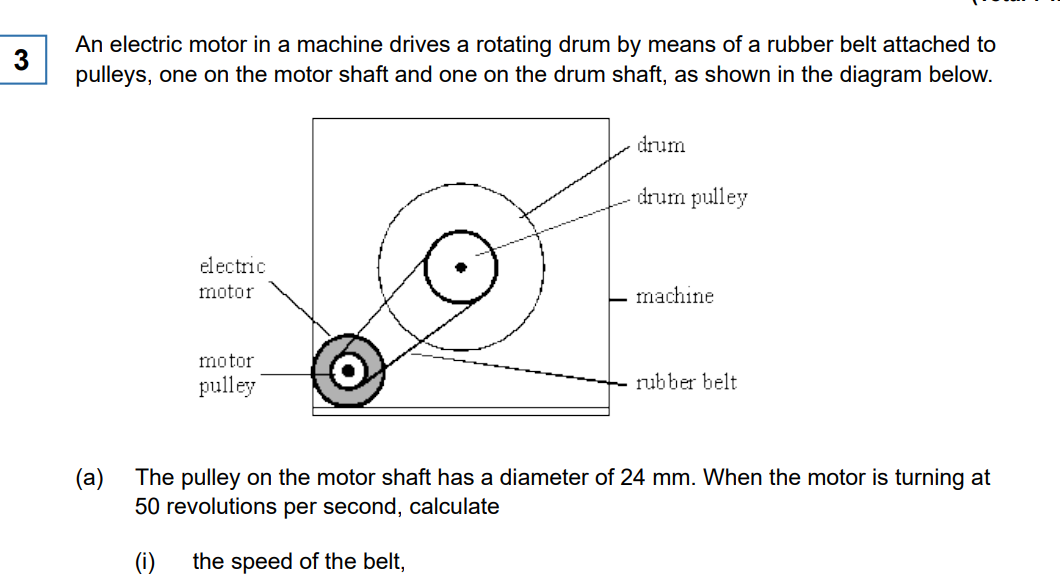
Rev s^-1 is w, and w = v/r

Resonance occurs
Since motor’s frequency = natural frequency of metal panel.



Remember to add on all the distance travelled (1.6m)

C
Discuss the motion of the ball being spun in circular motion in terms of the forces that act on it. In your answer you should: • explain how Newton’s three laws of motion apply to its motion in a circle • explain why, in practice, the string will not be horizontal. (6 marks)
N1L: Ball doesn’t travel in straight line, meaning a force must be acting on it. It has a constant speed, NOT a constant velocity, since its direction is changing, meaning its acceleration is changing
N2L: Force of ball causes it to accelerate in the direction of the force (towards centre of circle)
N3L: Ball must pull on the central point of support with a force that is equal and opposite (centrifugal force).
Ball cannot be completely horizontal, since the weight of the ball acts vertically downwards, and needs to be balanced by the vertical component of the tension (think equilibrium triangle). If the string were horizontal, there would be no component of tension to balance the weight, so the ball would simply fall.
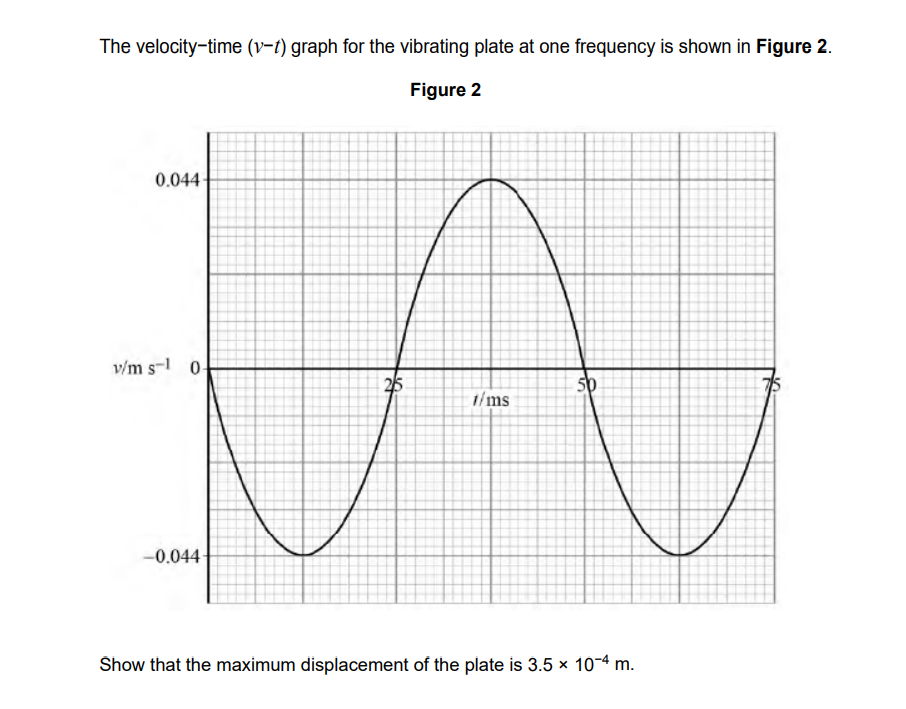
vMax = w A
0.044 / (w = 2 pi / T)

No extra info needed








to find oscillations, multiply frequency x length of time (since fequency is how many occurs in 1 second!)




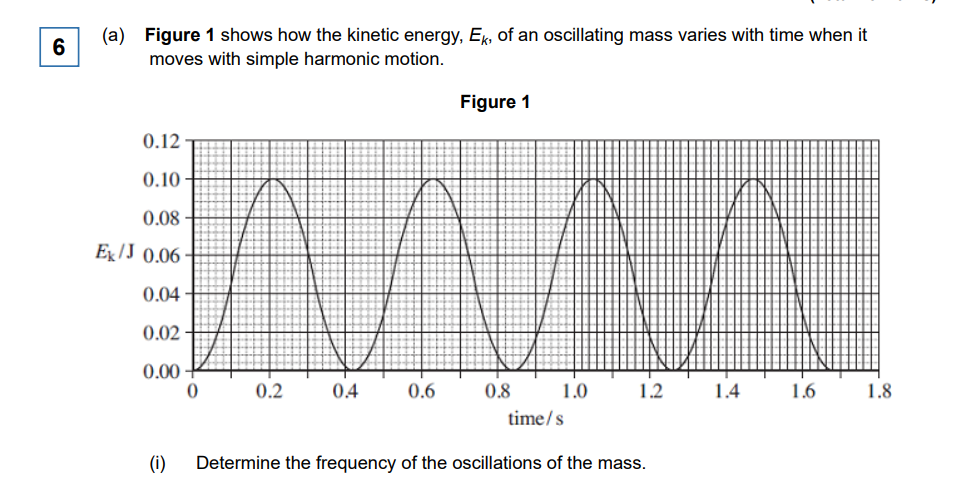
This is important to realise. If talks about energy-time graph, remember that 2 wavelengths will occur for 1 oscillation since each “wavelength” is one half of the cycle (From max amp to 0 and to opposite max amp is 1 wavelength, and it must do another to get back to original max amp (say on the left). This then would be 1 period!

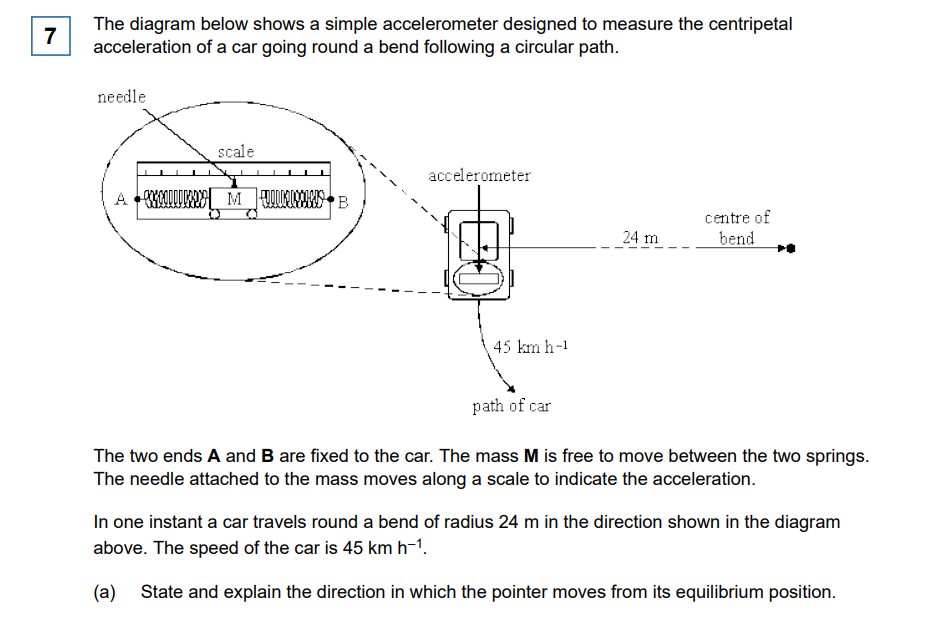
force is needed toward the centre or there is acceleration toward the centre B1
movement to the left/toward A/away from the centre (or indicated on diagram) M1
right hand spring (attached to B) has to stretch to provide force A1 ???

D (will be 0 since it is where it is when acceleration is 0)
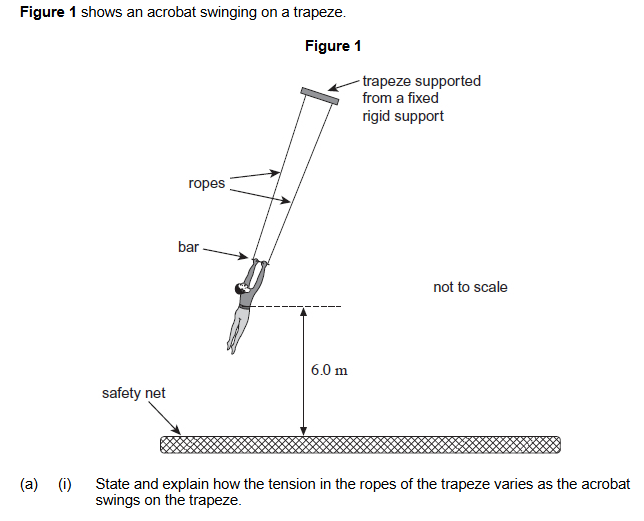
3 marks
Tension minimum at extremities or maximum at middle / bottom
Tension depends on (component of) weight and required centripetal force / velocity
Increases as acrobat moves downwards
Tension at bottom = mg + mv2/r or Tension = weight + centripetal force
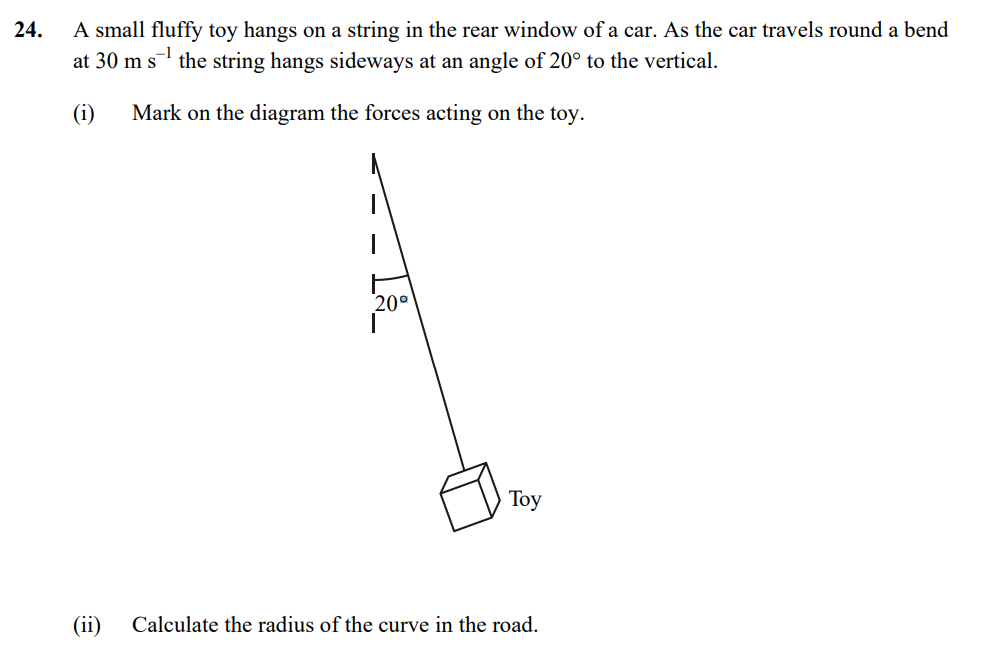
Part b
Resolve the forces, and re arrange! Worth 5 marks.

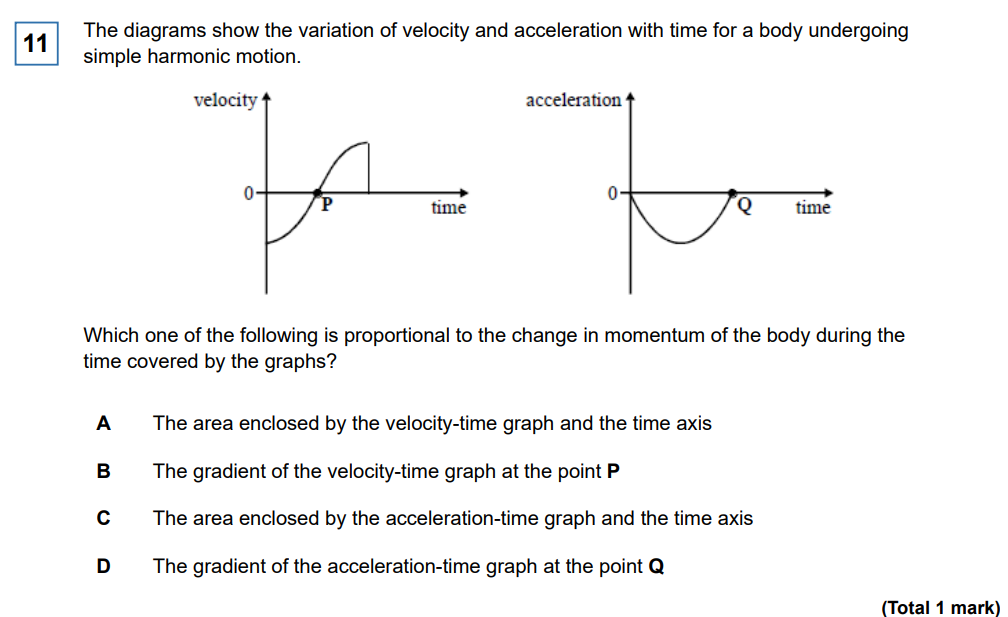
C, Remember, the area under the acceleration time graph is the velocity (integral of acceleration is velocity)


Max displacement from equilibrium (mean) position is 5 (which is when sin(20 pit) =1
Sin(pi/2) = 90 degrees = 1 therefore its A.

