Urinary System
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Excretion
Process of separating wastes from the body fluids and eliminating them
Components of urea
Ammonia and carbon dioxide
What organ removes the amine groups from proteins to form ammonia
Liver
Why is carbon dioxide added to ammonia to make urea
To dilute ammonia because ammonia is too toxic
Deamination
Break down of amino acids from proteins to make ammonia
What organ filters out the organ from the blood?
Kidneys
What is the functional unit of the urinary system?
Nephron
What body systems are involved in the excretion system?
Respiratory and integumentary
Is the elimination of feces considered excretion?
No!
What vessels branch from the aorta and enters the kidneys?
Renal arteries
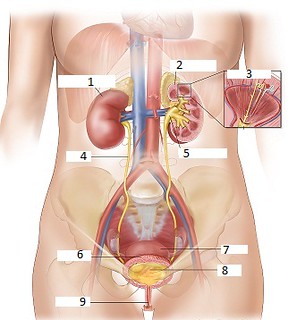
What is number 1 on the diagram?
Kidney
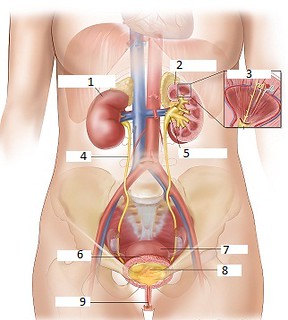
What is number 2 on the diagram?
Cortex
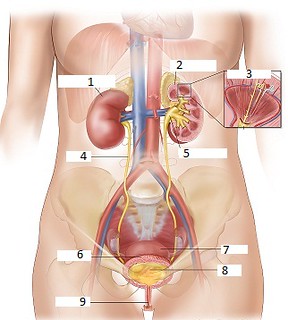
What is number 3 on the diagram?
Nephron
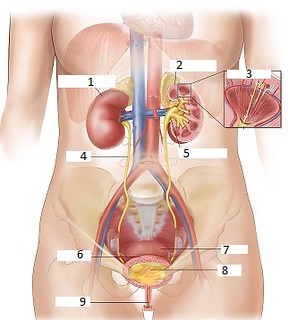
What is number 4 on the diagram?
Ureters
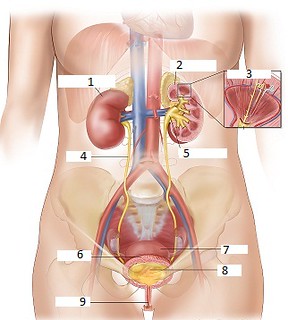
What is number 5 on the diagram?
Renal pelvis
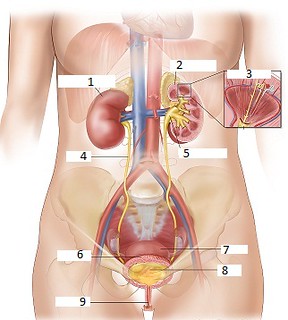
What is number 6 on the diagram?
Bladder
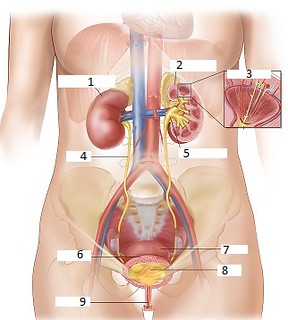
What is number 9 on the diagram?
Urethra
What is at the base of the bladder than releases the urine into the urethra?
Urinary sphincter
Ureters
Tubes that conduct urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder
Urethra
Tube that conducts urine to the outside of the body
Do the Renal arteries carry high or low oxygen and waste?
High
Does the Renal vein have high or low oxygen and waste?
Low
What is the urine volume when the bladder stretches and sends a message to the brain that it needs to be emptied?
200ml
What is the function of the urinary sphincter?
Controls the flow of urine out of the bladder and into the urethra
What are the three sections of the kidney and where are they?
Renal cortex (outer layer and circles the kidney)
Renal medulla (inner layer)
Renal pelvis (hallow chamber that joins the kidney with the ureter)
What type of arteriole supplies the nephron with blood?
Afferent arteriole
What is the arteriole that blood leaves in after transporting its components to the glomerulus?
Efferent arteriole
What is the capillary bed called?
Glomerulus
Where does the efferent arteriole direct its blood to?
Vasa Recta
What is the name of the funnel-like structure that surrounds the glomerlulus?
Bowman’s capsule
What is unique about the capillaries in the glomerulus?
The capillaries are fenestrated
What is the plasma-like solution collected in the Bowman’s capsule? What does it NOT have?
Filtrate
Proteins, platelets, RBC
After collecting into the Bowman’s capsule, where does the filtrate go to?
Into the proximal tubule
List the structures the blood solutes travel through to make urine
Afferent arteriole, glomerulus, bowman’s capsule, proximal tubule, loop of henle, distal tubule, collecting ducts
What structure(s) secrete aldosterone?
Ascending limb of loop of henle
What is the function of aldosterone?
When secreted, it increases the reabsorption of Na+ to increase water osmosis. This is to maintain homeostatic blood volume/pressure when the body is dehydrated.
What structure secretes aldosterone? Where is it located?
The adrenal gland above the kidney.
List the main components of the blood plasma when it’s in the renal artery (as well as it’s concentration)
Glucose (normal)
Urea (normal)
Proteins (normal)
Sodium ions (normal)
RBC (normal)
Hormones (normal)
List the main components of filtrate and what is no longer present (including concentration)
glucose (normal)
Urea (normal)
Sodium ions
Hormones (normal)
Proteins (none)
RBC (none)
List the main components of urine (and concentrations)
urea (very concentrated)
Sodium ions (more concentrated)
Hormones (what has been diffused)
List the main components of the blood plasma when it is in the renal vein (and concentrations)
glucose (normal)
Urea (less)
Proteins (normal)
Sodium ions (less)
RBC (normal)
Hormones (less)
What does ADH stand for
Antidiuretic hormone
What is the function of ADH
Regulates the osmotic pressure in the kidneys to increase water absorption
Where is ADH released from and what happens to it
Hypothalamus and shrinks due to increased solute levels in the blood (becomes hypertonic)
Where is ADH stored?
Posterior pituitary
What structure(s) is ADH released?
Distal tubule and collecting duct
What are the names of two types of diabetes? Which is type 1?
Diabetes mellitus (type 1)
Diabetes Insipidus
What is diabetes mellitus?
When the person has inadequate levels of insulin, it causes blood sugar levels to rise and having glucose be excreted in the urine rather than be used in muscles.
What is diabetes insipidus?
When the ADH-producing cells in the hypothalamus are destroyed, being unable to reabsorb water, resulting in a drastic increase in urine output
What are the two types of dialysis?
hemodialysis
Peritoneal dialysis
Explain hemodialysis
The blood will be filtered through a machine called a dialyzer. It consists of a semipermeable tube immersed in a solution that consists of the same components as blood plasma. Dialysate (the person’s blood) will pass through the semipermeable tube and the wastes will diffuse into the solution, cleansing the blood (but only until equilibrium).
Explain peritoneal dialysis
Putting the solution in the abdominal cavity surrounding the small intenstine, waste particles in the blood vessels that line the small intestine will diffuse into the clean solution creating dirty solution. This dirty solution is then drained.
What type of kidney will most likely last longer and function better in a kidney transplant?
A live, fresh kidney
What are kidney stones? What does it cause? How are they removed?
Collection of mineral salts from the blood. It can cause severe pain from getting lodged in the ureter or pelvis. It is removed by ultrasound waves breaking up the salts so it can pass through.
Is kidney stones an irritant disease?
No.