IB Psych SL Cognitive Approach
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
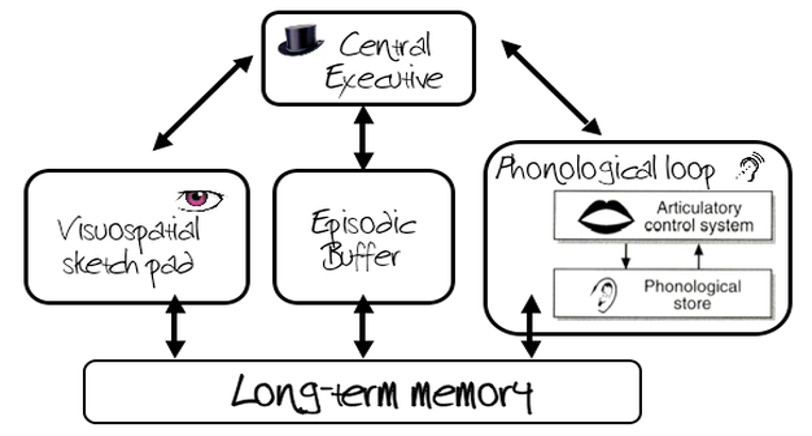
Working Memory Model
Model that relates to the formation of the short term memory, 4 parts
Central Exectutive: controls attention and coordinate subsystems; “manager”
Episodic Buffer- temporary store that holds visual, auditory info
Phonological loop: processes auditory info for (1.5-2 seconds)
“Inner Ear”
Visuospatial Sketchpad- processes visual information
Inner Eye
Studies:
KF: case study, damage to STM
Remembered verbal information but not visual; suggests there are separate stores for visual and verbal info
Robbins
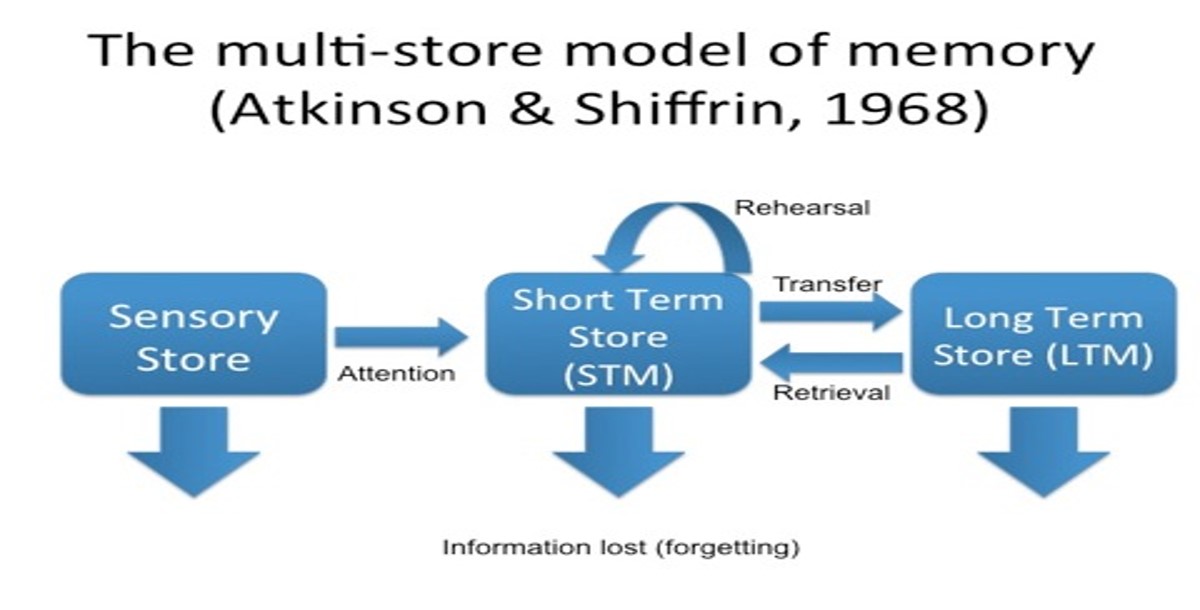
Multi-Store Model
Model that suggests information from the short-term memory needs to recieve attention to transfer to long term memory
If info in STM is rehearsed, it moves to LTM
Studies that support:
HM,
Schema Congruence
Information that is in line with our past experience and knowledg
Schema Incongruence
Info is not align with our prior experiences and knowledge
Schema
Mental representations derived from prior knowledge and experiences
Help us to predict what to expect
Used to organize knowledge, assist recall, guide behavior, and make sense of current experiences
Dual Process Model
Theory that decision making and thinking is split into two systems
System 1 (Dual Processing Model)
Intuitive
Fast, Non conscious and automatic form of thinking
Uses heurisitics
More Prone to errors
System 2 (Dual Processing Model
Rational
slow, effortful thinking
Requires thinking about all possibilities and gradually eliminating them
Slower but less prone to errors
Heurisitic
Rules of thumb that can be applied to guide decision making based off of available information
Rely on less information
Makes decision making faster
Cognitive Misers
Theory that states we tend to minimize the amount of effort to think
Cognitive Load
used amount of working memory resources
When cognitive load is high, we are more likely to use system 1 thinking
Reconstructive Memory
act of remembering is influenced by other cognitive processes such as perception, past experience, imagination, and beliefs
Misinformation Effect
Tendency for post-event information to interfere with the memory of the original event
Flashbulb Memories
highly detailed snapshot of a moment in which a shocking event took place
Brown and Kulik, talarico and ruben
Adrenaline
hormone linked to the human flight or fight response
Amygdala
responsible for encoding emotional memories
Ethic Go- tos (Cognitive)
Deception
Brewer and Treyens
schema theory
AIM: see if schema affects memory
METHOD: correlational
PROCEDURES:
30 University Students taken into an office for 35 seconds
Taken out and asked to recall objects in the room, werent told they would need to.
RESULTS:
People remembered things that werent there- stereotyical office items such as a pen stapler and books
Forgot items that were there that werent stereotypical to an office
Suggests that Schema can have an impact on memory
Robbins
working memory model
HM
multi-store model
loftus and palmer
schema theory, reconstructive memory
englich and mussweiler
thinking and decision making- anchoring bias
AIM: wanted to know if a request for the length of a prison sentence would influence the decision by the judge
PROCEDURES: experiment, independent measures
44 german law students in last year, control for courtroom experience
case of alleged rape, prosecuter recommended ½ sentences
low anchor: 12 months
high anchor: 34 months
given case materials and copies of penal code and asked to read materials and form opinion about case
RESULTS:
low anchor: 12 months: average sentence 18.78 months
high anchor: 34 months: average sentence 28.7 months
tversky and kahnanmen
anchoring hueristic
AIM: see if first number seen would influence estimate of value by participant
PROCEDURES:
experiment: independent measures: high school students
quickly estimate sum of product:
ascending condition: 1×2×3×4×5×6×7×8
descending condition: 8×7×6×5×4×3×2×1
RESULTS: median ascending condition was 513
median descending condition was 2250
actual answer: 40320
chou and edge
availability heuristic
AIM: test influence of avaliability hueristic on how FB users evaluate themselves in comparison to others
PROCEDURES: survey with 10 point likert scale
collected info on FB users, # of friends they had, time spent with friends in person
RESULTS:
people who spent more time online indicated that people where happier and had better lives than them
people who spent more time with friends were less likely to indicate that people were happier and had a better life
yuille and cutshall
reliability of memory, reconstructive memory
AIM: see if leading questions would affect the memory of an eyewitnesses of real crimes
PROCEDURES: contacted 13 witnesses 4 months after events of crime- 13 agree, gave account, asked questions
= 2 leading questions- broken headlight/ yellow panel
½ “a” - ½ “the”
- nobroekn headlight, panel was blye
- asked to rate stress on day of event on a 7 point scale
RESULTS:
the eyewitnesses were actually very reliable - with an accuracy between 79 and 85%.
talarico and ruben
study of flashbulb memories
AIM:
METHOD:
PROCEDURES:
RESULTS:
EVAL:
brown and kulik
flashbulb memories
AIM:
PROCEDURES:
RESULTS:
EVAL:
Blacker (HL)
positive effects of tech
AIM: investivate the extent to which action video games may improve quantity and quality of information stored in visual component of working memory model
PROCEDURES: train for 30 hours for continuous stretch of 30 days
prior training- self report motivation for visual working memory task (0-9)
another self report about how they engaged and rate level of enjoyment and absorption
action playing condition: asked to play action videogame like modern warfare in single-player mode
non-action game condition: asked to play simcity (control group)
RESULTS:
action game participant demonstrated significant improvement in change detection tasks while non-action game participants did not
loftus and pickerall
reconstructive memory
AIM: determine if false memories of autobiographical events can be created through the power of suggestion
PROCEDURES: 3M, 21F
before: family members contacted and asked 2questions
1. retell 3 participant childhood memories
do you remember a time when the participant got lost in a mall
questionnaires sent to participants in the mail- asked to recall about 3 real memories and the “lost in mall”- told to write “i dont remember” if they didn’t remember- interviewed twice over 4 weeks
asked to recall as much info as possible about the events and rate confidence on a scale of 1-10
2nd interview: debriefed and guessed which memory was false
RESULTS: 25% recalled false mall memory- ranked as less confident than others- wrote less on questionaire when asked to recall
proves that the brain can formulate false memories through suggestion, reliability of memory is weak
avaliability hueristic
cognitive bias in which we make judgements on how accessible information is and how easily it comes to your mind
representative hueristic
we judge something or someone based on how well they fit into our schema/mental category
anchoring hueristic
we judge something based off the first part of information provided