Antigen-Antibody Interactions
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Antigen
Immunogen = induce immune response
Refers to thesubstance that react with antibody or sensitized T cell
It is not able to trigger an immune response on its own
Immunogen
Refers to the substance that is capable of induding an immune response on its own
All immunogen are antigen, but not all antigen are immunogen
All _______ are _______, but not all ______ are immunogen

Autoantigen
TYPE OF ANTIGEN:
Antigen of the same individual

Alloantigen
TYPE OF ANTIGEN:
Antigen of different individuals but the same spp

Heteroantigen
TYPE OF ANTIGEN:
Antigen of two different spp

Heterophile Antigen
TYPE OF ANTIGEN:
Antigens in unrelated plants or animals but are identical or closely related in structure
Epitope = antigen
Paratope = antibody
Epitope is found in _______
Paratope is found in _______
Haptens
A substance that requires carrier molecule to elicit immune response (turns to immunogen)
Example: Therapeutic Drugs
Adjuvants
A substance that is added to increase and itensify immune response (e.g vaccines)
Papain
What enzyme causes breakdown of antibodies above the hinge region
[ 2 Fab + Fc = 3 fragments]
Pepsin
What enzyme causes breakdwon of antibodies below the hinge region
[ F(ab’)2 + Fc’ ]
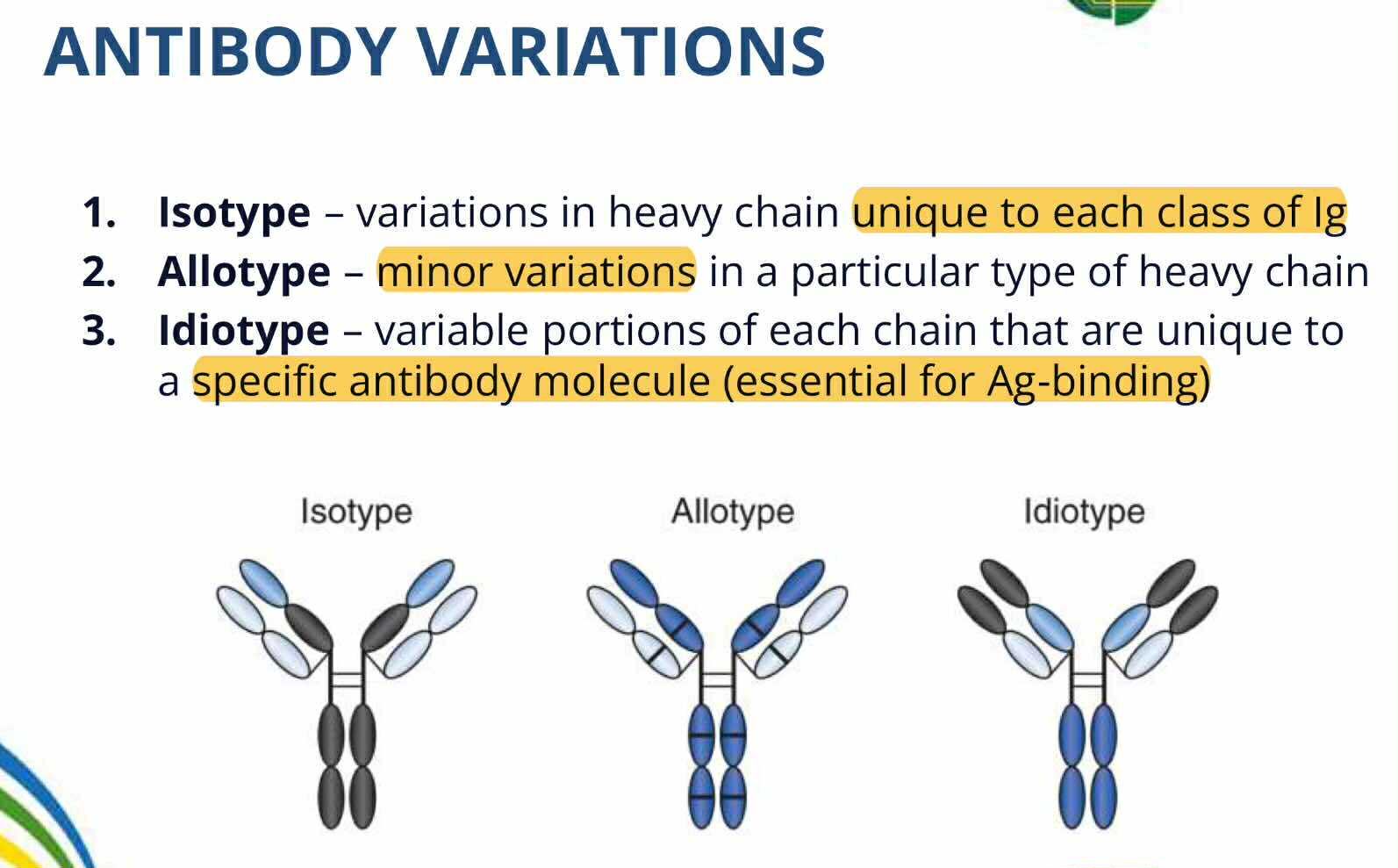
Isotype
ANTIBODIES VARIATION:
Variation in the constant region of heavy chain
specifies what type of Ig class
[Heavy Chain: gamma, mu, alpha, epsilon, delta]
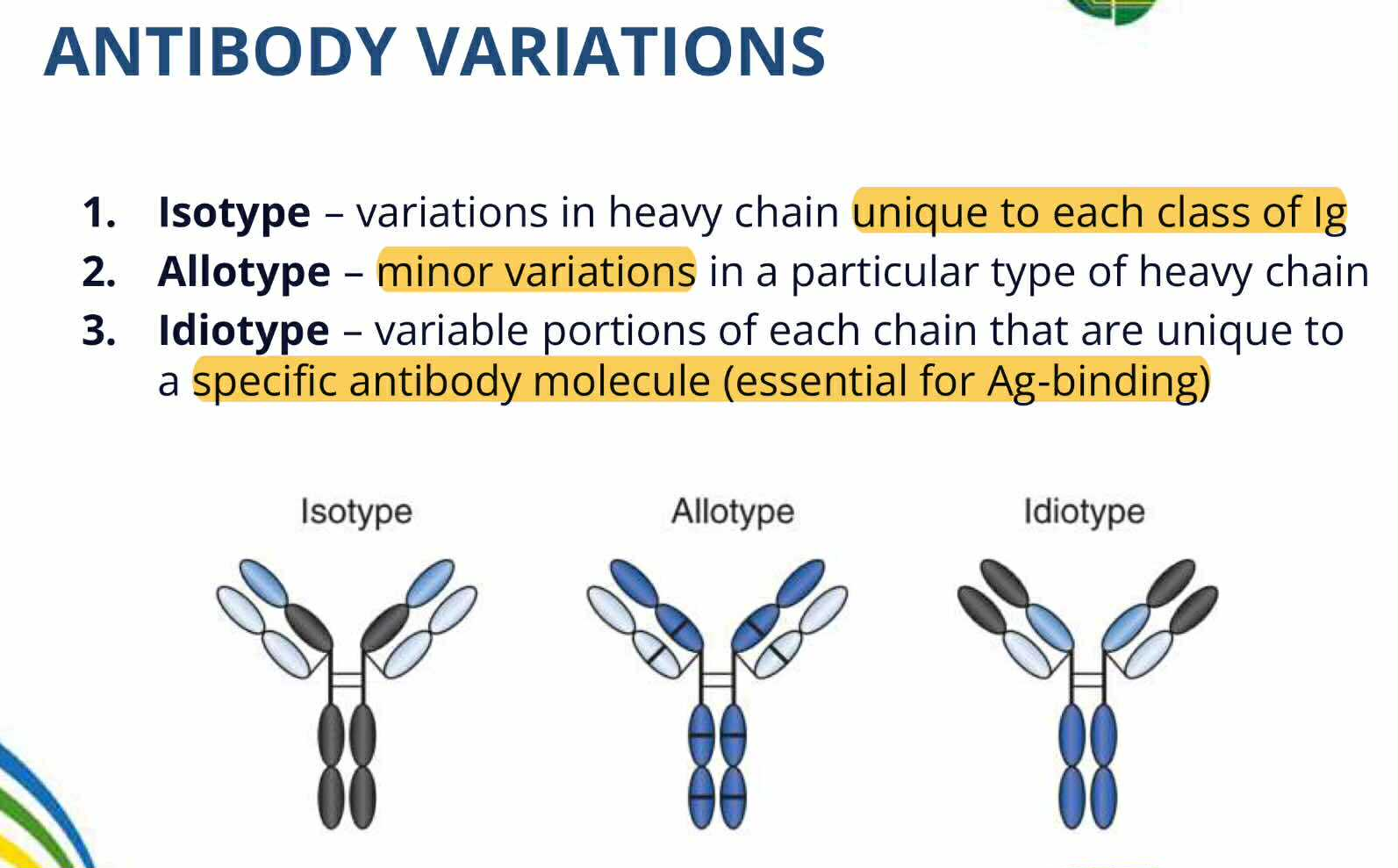
Allotype
ANTIBODIES VARIATION:
Variation of constant region of light and heavy chain
specifies the subclasses of each immonoglobulin
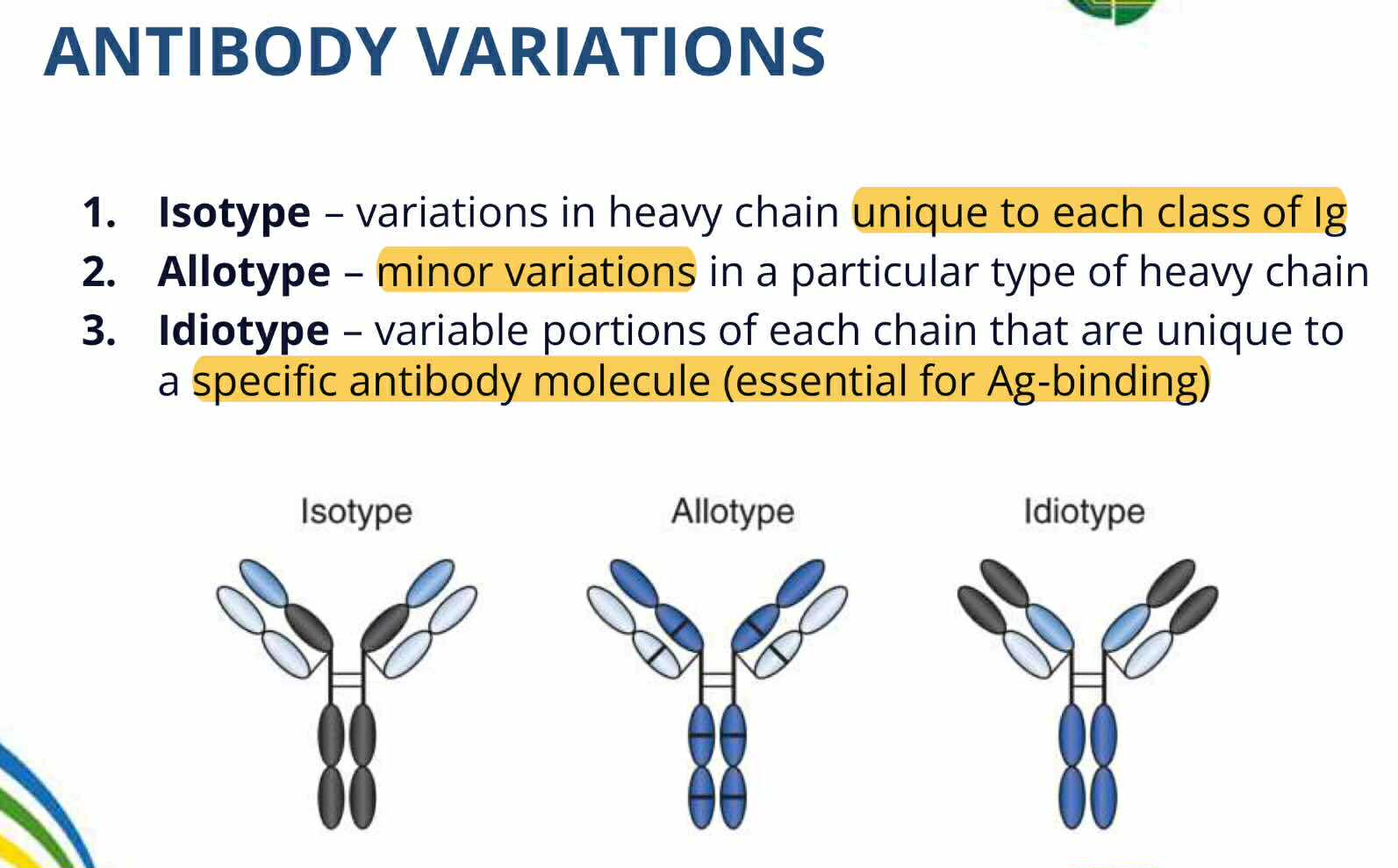
Idiotype
ANTIBODIES VARIATION:
Variation of variabe region of light and heavy chain
determine why antibodies are specific to an antigen
IgG
CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS:
most abundant in serum
IgG
CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS:
for inflammation
IgG
CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS:
participate in Complement Fixation
IgG 1
IgG 3
IgG 4
IgG 2 = can’t cross placenta
CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS:
Subclasses of Immunoglobulins that passes through placenta (in order)
IgG 3
IgG 1
IgG 2
IgG 4 = can’t
CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS:
Subclasses of Immunoglobulins that participates in complement fixation (in order)
IgM
CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS:
pentamer
IgM
CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS:
Most primitive
1st form in babies
IgM
CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS:
found only in blood vessels
IgA 2 = resistant
IgD = susceptible
CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS:
most resistant to proteolysis
most susceptible to proteolysis
IgD
CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS:
anti-idiopathic antibody
IgE
CLASSES OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS:
Reagenic
Participates in allergic reaction

Lag = longer
Log = increase
Plateau = short
Rapid decline
Describe the kinetic of PRIMARY immune response

Lag = shorter
Log = sudden decrease
Plateau = longer
Gradual decline
Describe the kinetic of Secondary immune response