Lecture 4 - Prenatal Development
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
organogenesis
• process of organ formation in very early development
• in humans this is from first cell divisions until about 8 weeks
prenatal development
• the development of human individuals before they are born.
What are the phases of prenatal development?
• zygote → embryo → foetus
zygote
• from fertilization to week 2
What stages of the zygote are there?
• stages progress over week 1
• zygote: day 1, fertilized egg
• morula: day 3, ball of 17 cells, cell differentiation starts
• blastula: day 4-7, cavity arises, embryo arises out of inner cells, implantation in uterus
embryo
• the developing organism during the period when organs are forming
• in humans from week 2 until about 10 weeks.
embryogenesis
• formation and development of an embryo
foetus
• in human prenatal development, the organism 10 weeks after conception until birth.
neonate
• an infant less than a month old.
postnatal development
• the development of a human individual after he or she is born, particularly during early infancy
synapses
• the connections between neurons which enable them to transmit information.
synaptogenesis
• the building of connections (synapses) between nerve cells.
apoptosis
• programmed cell death.
neurons
• nerve cells within the central nervous system which transmit information in the form of electrochemical impulses.
axon
• the tail-like part of a neuron which transmits impulses (the actual message) away from the cell body.
gastrulation
• during week 2
• formation of 3 germ layers by migration and differentiation of blastula cells → ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
ectoderm
• the outermost of the three primary germ layers → foundation for organ formation (skin, hair, nervous system)
mesoderm
• middle layer of germ layers → foundation for formation of muscles and bones
endoderm
• innermost of primary germ layers → foundation for formation of most other organs
neurulation
• starts week 3 → marks beginning of formation of CNS
• formation of neural plate, neural groove and neural tube from ectoderm
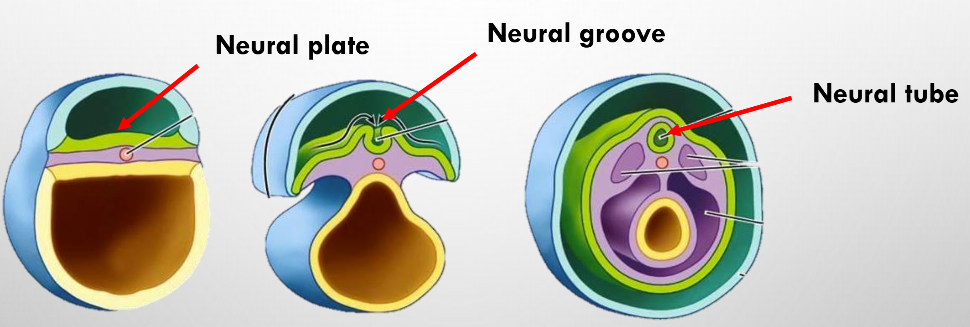
neural plate
• a thickening of ectoderm cells that will give rise to the brain.
neural tube
• a hollow structure in the embryo that gives rise to the brain and spinal column.
consequences when closing of neural tube fails
• anencephaly: open skull
• spina bifida: open back
What causes neural tube defects and how can they be prevented?
• defects in neurulation
• folic acid use during first 12 weeks of pregnancy
neurogenesis
What happens during embryogenesis?
• first primitive brain areas due to neurogenesis, differentiation and migration of cells from neural tube → forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
• cranial-caudal orientation arises
cranial-caudal
• the direction beginning with the head end and moving toward the opposite end or feet in humans.
cerebral cortex
• the area of the brain that is associated with complex tasks such as memory, language, and thoughts and the control and integration of movement and the senses
• begins to develop at ~9 weeks
• neurogenesis + migration after embryogenesis
• axons and dendrites start growing
• cortex gets 6 layers
sulci
• the deep narrow grooves of the outer surface of the brain
• appear in 6th month of pregnancy
gyri
• the prominent ridges on the outer surface of the brain
• appear in 6th month of pregnancy
myelin
• a fatty insulator which prevents leakage of the messages travelling along the nerves, and increases the speed of neural transmission.
• = white matter
myelination
• The process by which myelin is formed around the neurons. Myelination begins in the 6th month of life in the foetus but continues through childhood, not complete until third decade of life
How does the brain of a newborn compare to that of an adult?
• sensory and motor networks similar
• networks associated to higher cognitive functions dissimilar
gestation
• = pregnancy
• behavior of foetus becomes progressively more organised as gestation proceeds
quiet sleep
• by week 34, foetus spends 20-30% of time in quiet sleep
• quiet, motionless sleep-like state
• steady heartbeat and breathing movements when they occur
active sleep
• most of rest of time in active sleep
• many different body movements
• eyes moving rapidly back and forth, periodically open
• heart rate and breathing patterns irregular
• responsive to sensory stimuli
term
• the end of pregnancy.
When does feeling of touch develop?
• develops first → from head (lips week 8) to hands (week 10) to feet (week 12) → cranial-caudal
• first moving away from touch, later towards it
• rich environment: wall of uterus, umbilical cord, parents, itself
rooting reflex
• the reflex that causes newborn babies to respond to one of their cheeks being touched by turning their head in that direction.
How many pregnancies end with miscarriage?
• 10% of pregnancies <4 weeks end with miscarriage
How does the risk of miscarriage change over the pregnancy?
• risk of miscarriage decreases rapidly to less than 1% after 8 weeks
• risk of neural deviations decreases to less than 0.1% after 8 weeks
chemosensory system
• encompasses both the gustatory (taste) and olfactory (smell) senses.
What can the baby smell and taste in the womb?
• from 16 weeks: everything in amniotic fluid
• blood of mother with nutrients
→ rich environment
colostrum
• the breast fluid that precedes true milk
• rich in minerals and antibodies, and it helps populate the newborn’s gut with ‘good’ bacteria.
vestibular system
• the sensory system that contributes to balance and spatial orientation.
vestibular apparatus
• in inner ear
• muscle tension, hearing, vision, feeling
What is the environment for the vestibular system like?
• rich environment: movement of mother and foetus, gravity
→ foetus active when mother is resting
preterm
• born prematurely. Human infants are regarded as preterm if they are born before 38 weeks of pregnancy.
kangaroo method
• skin to skin contact, baby moves together with parent
• for preterm babies: shorter time in incubator, positive effect on heart rhythm, stress/pain response, cognitive/physical development
→ movement is important but we don’t know why
circadian rhythm
• bodily cycles within the body that occur on a 24-hour cycle, such as patterns of sleeping/ waking.
How does the eye develop?
• week 4: thickening of ectoderm → optic cup with two layers → week 8: epithelium with pigment cells and blood vessels (retina with rods and cones)
rods and cones
• light-sensitive cells found in the retina of the eye which translate light into electrical signals that are then transferred to the brain so that the image can be interpreted.
How does the optic nerve of the visual system develop?
• week 8: clearly visible
• week 9: part of fibers of it cross
• week 15: crossing complete and fibers go via thalamus to visual cortex
• week 28: finished
What does the baby see in the womb?
• nothing → very poor environment
• eye lids open only between 5-7 months
trimester
• a period of three months. The course of human pregnancy is divided into three trimesters.
How does the ear develop?
• week 5: groove
• week 6: instilling, start formation middle ear tube
• week 7-8: auricle, start formation eardrum
• week 8: inner ear; vestibular system
Which visual abilities do preterm infants have when?
• 28 weeks: distinction between light and dark
• 30 weeks: distinction between different shapes
cochlea
• the inner ear, a structure encased in bone that contains the receptors for sound.
transnatal learning
• learning that occurs during the prenatal period which is remembered during the postnatal period.
What can the baby hear in womb?
• very rich environment: heartbeat, digestion, voices
• low frequencies by filtering of amniotic fluid
In which order do sensations develop?
• touch → first signs at 8 weeks
• gustation, olfaction
• vision (begins at ~5 weeks, finished during first month after birth)
• audition (begins at ~6 weeks)
electroencephalogram
critical period
• period in which development is optimal (sensitive period) → e.g. language development
• period in which system is vulnerable for lesions
Which internal and external factors can influence development negatively?
• age of parents
• nutrition, drugs, alcohol, smoking
• stress
• mental disorders & medication
• infections
perinatal
• the period just before and after birth
→ perinatal complications can have origins in parental preconception conditions and gene-environment interactions through embryogenesis and gestation
meiotic cell division
• the type of cell division that occurs in sexually reproducing organisms which halves the number of chromosomes in reproductive cells (sperm and ova).
chromosomal defects
• congenital defect
• whole chromosomes or parts of them are missing or duplicated
• caused by error during meiotic cell division
• age of parents has large effect
When is prenatal supervision recommended?
• prenatal care avoiders
• no permanent place of residence/stay
• serious psychiatric disorder with aggressiveness, impulsivity, instability that can results in neglect/abuse
• previous child that is supervised/removed from home
• serious addiction problems
What does the effect of malnutrition during pregnancy depend on?
• timing of nutrition associated with kind of anomaly
• generally: the earlier malnutrition, the more possible anomalies
fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
• causes minor facial anomalies, growth delay, heart defects, mental disabilities, hyperactivity & repetitive behavior
• 6% of children with mother addicted to alcohol has FAS
factors linked to severity of FAS
• mother’s drinking behavior (amount)
• timing alcohol consumption
• mother’s alcohol metabolism
• mother’s age
• genetic predisposition
• mother’s lifestyle and nutrition
Effects of smoking before and during pregnancy
• fertility problems
• increased risk of miscarriage
• delay of growth of fetus
• placenta problems
• preterm birth
• heart defects in baby
Why are pregnant women with mental health problems a vulnerable group?
• both disorder and medication can affect unborn child
microcephaly
• small skull, limited brain growth, often in combination with intellectual disability and organ defects
DNA methylation
• a process with an important role in gene regulation, consisting of the addition of methyl groups to DNA.
autosomal genetic disorders
• disorders resulting from a mutation in a gene in one of the non-sex chromosomes. Wellknown examples are cystic fibrosis (a recessive type) and achondroplasia (dwarfism, a dominant type).
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)
• a class of drugs typically used to treat depression or anxiety.
developmental programming
• the hypothesis that prenatal conditions have detrimental effects on health into adulthood → also on mental health
ultradian rhythm
• rhythms or cycles that repeat in less than a 24-hour period.