AP Psychology: Topic 4.5 - Social-Cognitive and Trait Theories of Personality
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Social-cognitive theory
a psychological theory that emphasized the dynamic interaction between people (personal factors), their behavior, and their environments
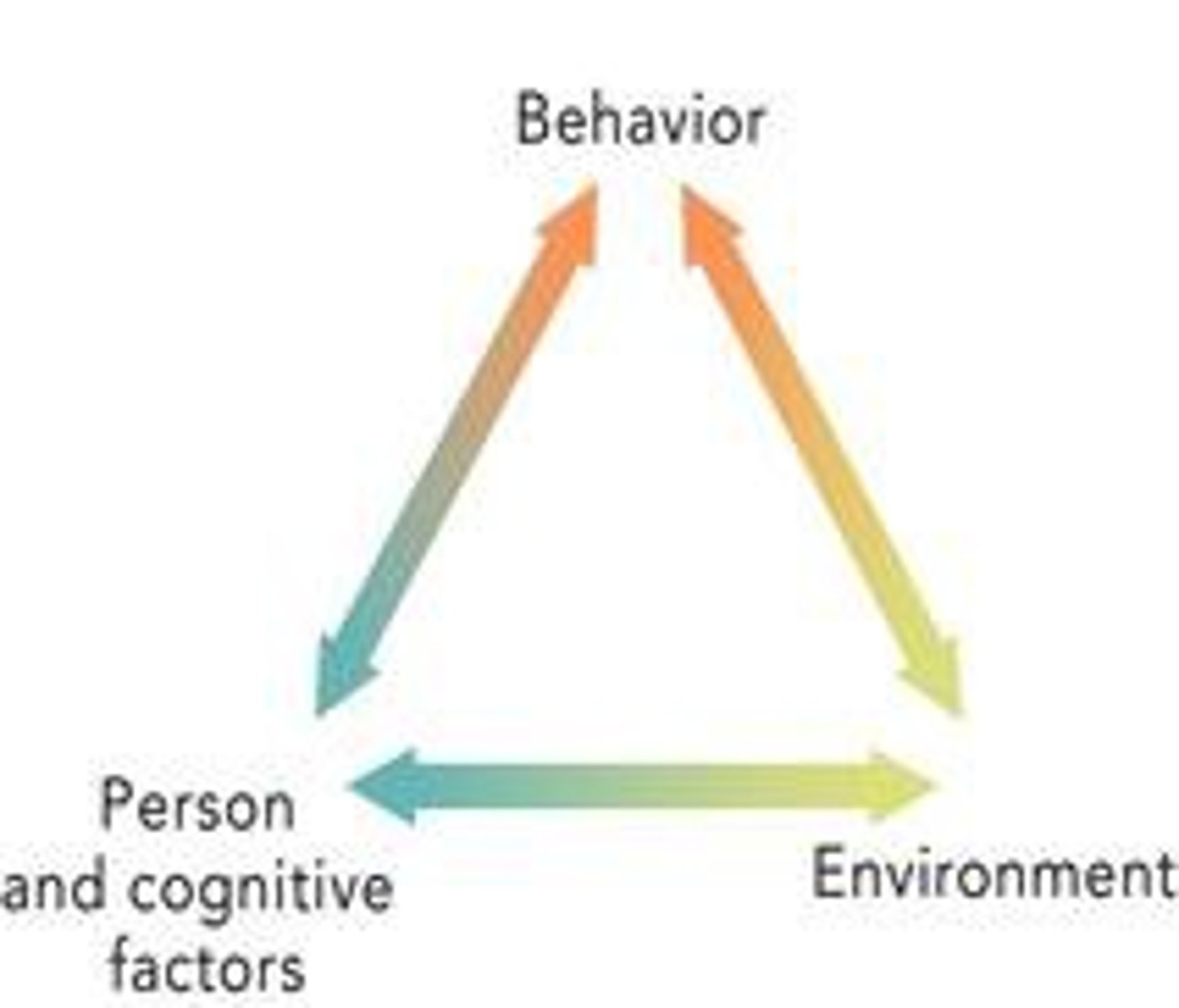
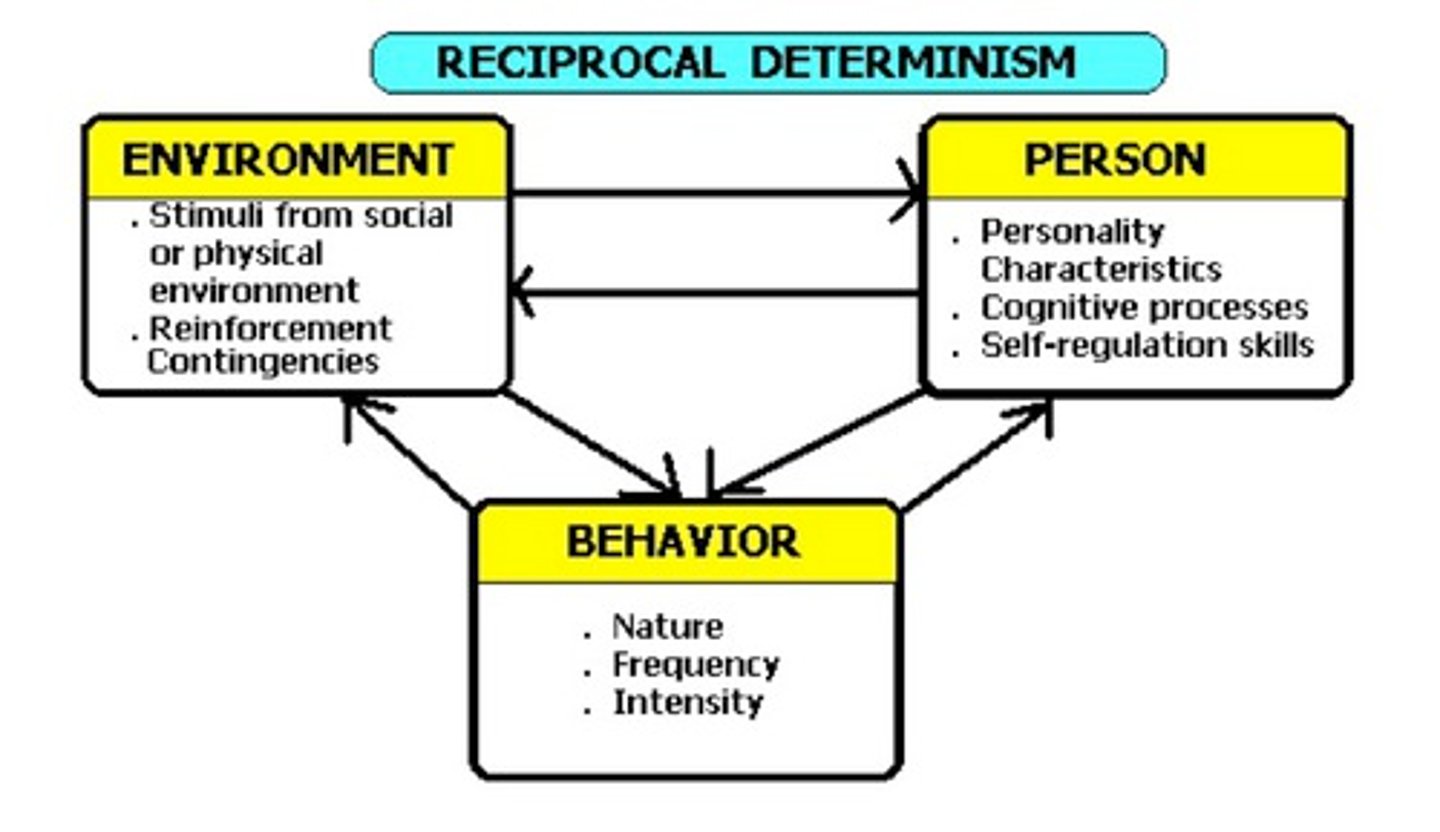
Reciprocal determinism
the idea that a person's behavior both influences and is influenced by personal factors and their social environment
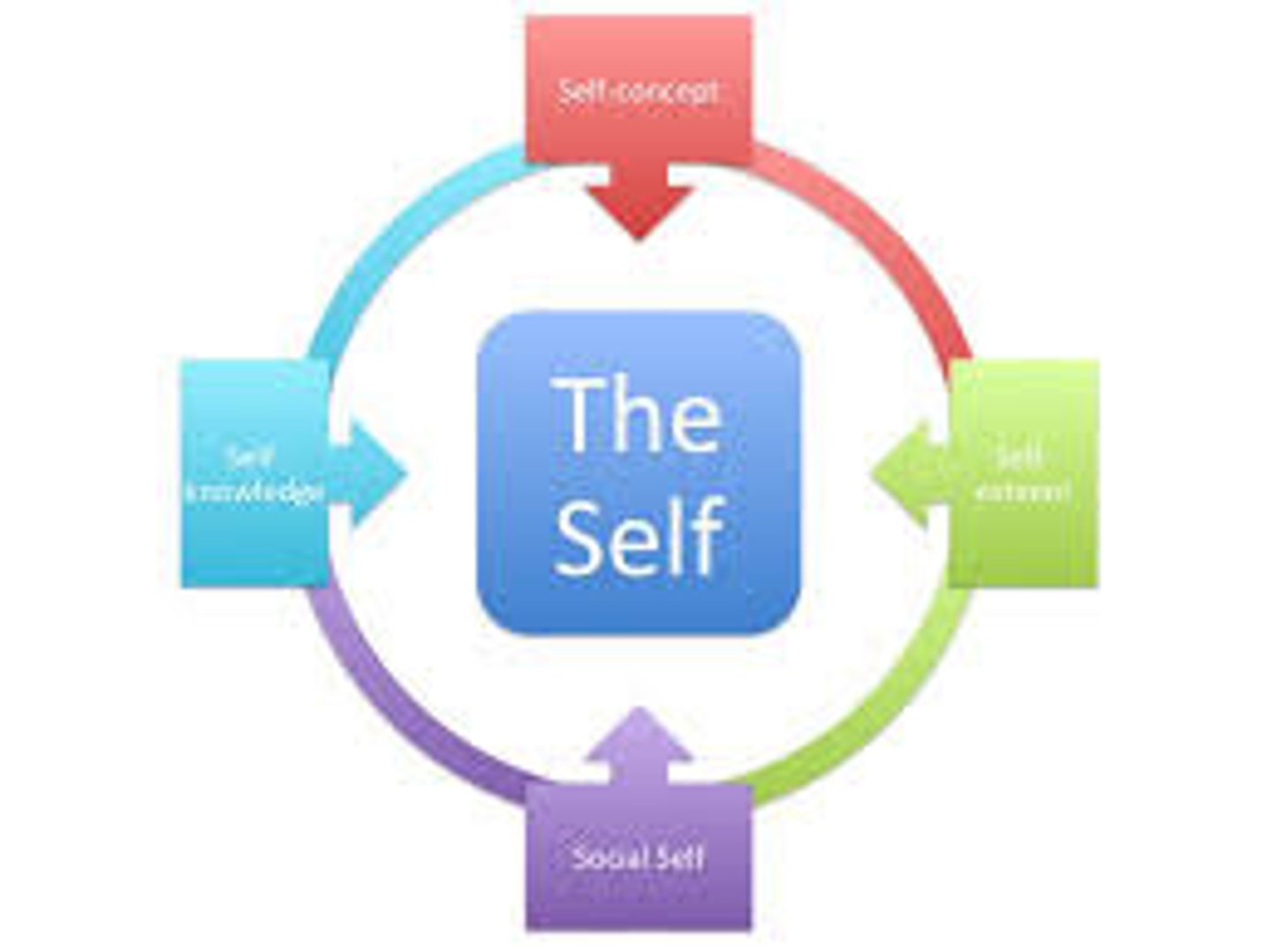
Self-concept
the overall view a person has of themselves, including their beliefs, physical and mental attributes, and social interactions
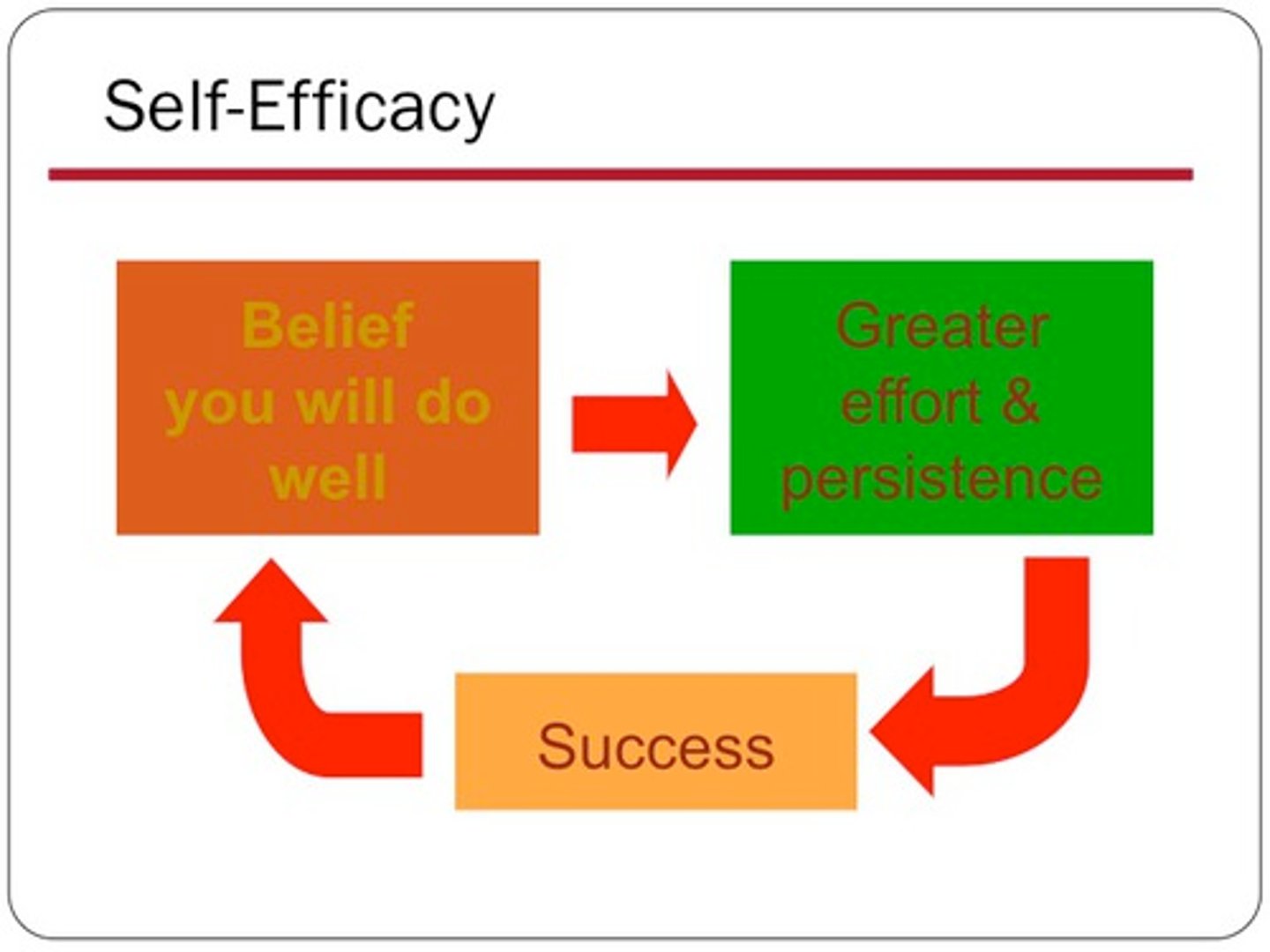
Self-efficacy
a person's belief in their ability to perform a task or reach a goal
Self-esteem
the degree of confidence and value a person has for themselves

Trait theories
categorizes and describes the characteristics that make up human personality in an effort to predict future behavior

Big Five theory
identifies five main characteristics that account for most individual differences in personality (agreeableness, extraversion, conscientiousness, openness to experience, and emotional stability (neuroticism))

Agreeableness
a person's concern for social harmony and their tendency to get along with others

Extraversion
describes people who are sociable, talkative, assertive, and active

Conscientiousness
describes a person's level of organization, persistence, and motivation to accomplish a goal

Openness to experience
describes how open-minded, imaginative, creative, and insightful a person is
Emotional Stability
the extent to which people feel secure and unworried and how likely they are to experience negative emotions under pressure

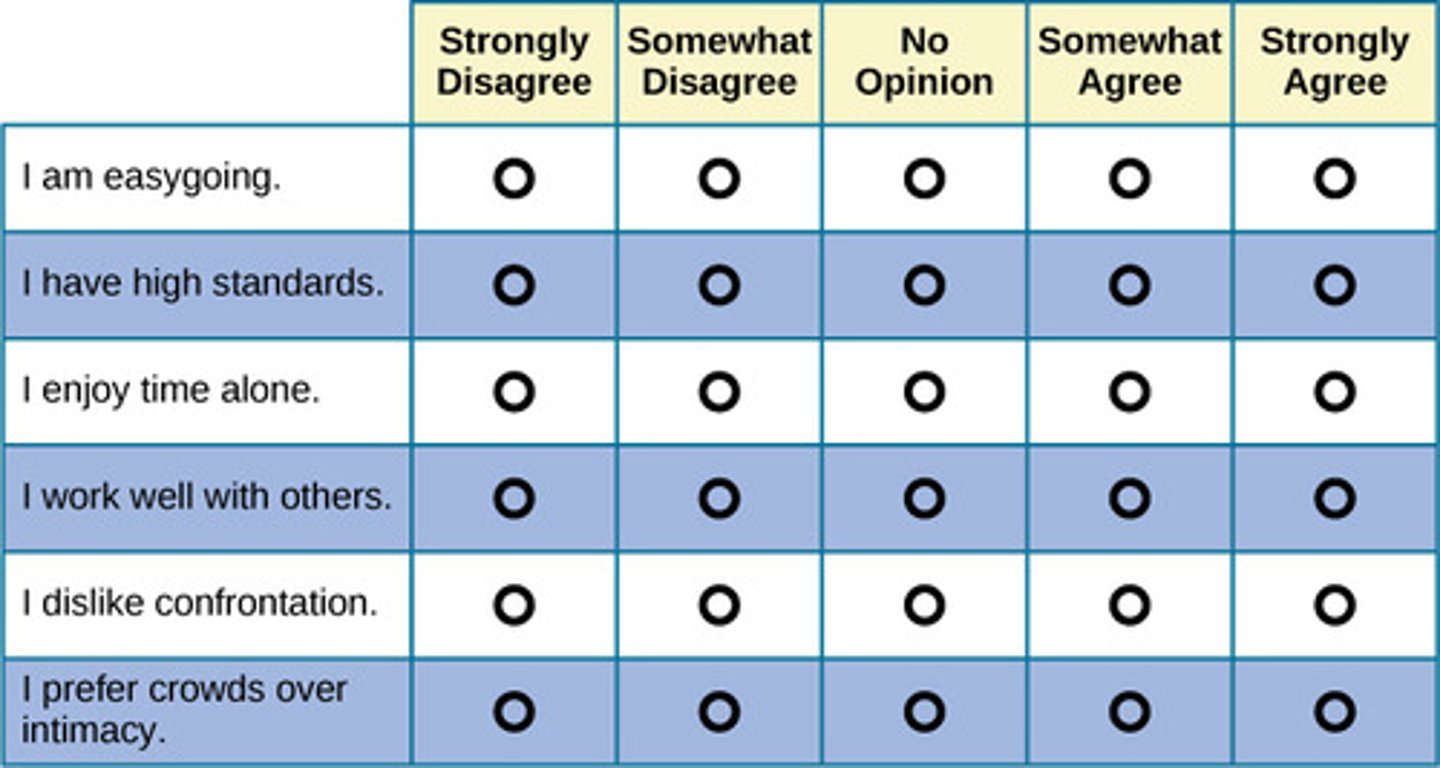
Personality inventories
an assessment tool (usually a questionnaire that measures and evaluates an individual's personality, such as traits, behaviors, and attitudes
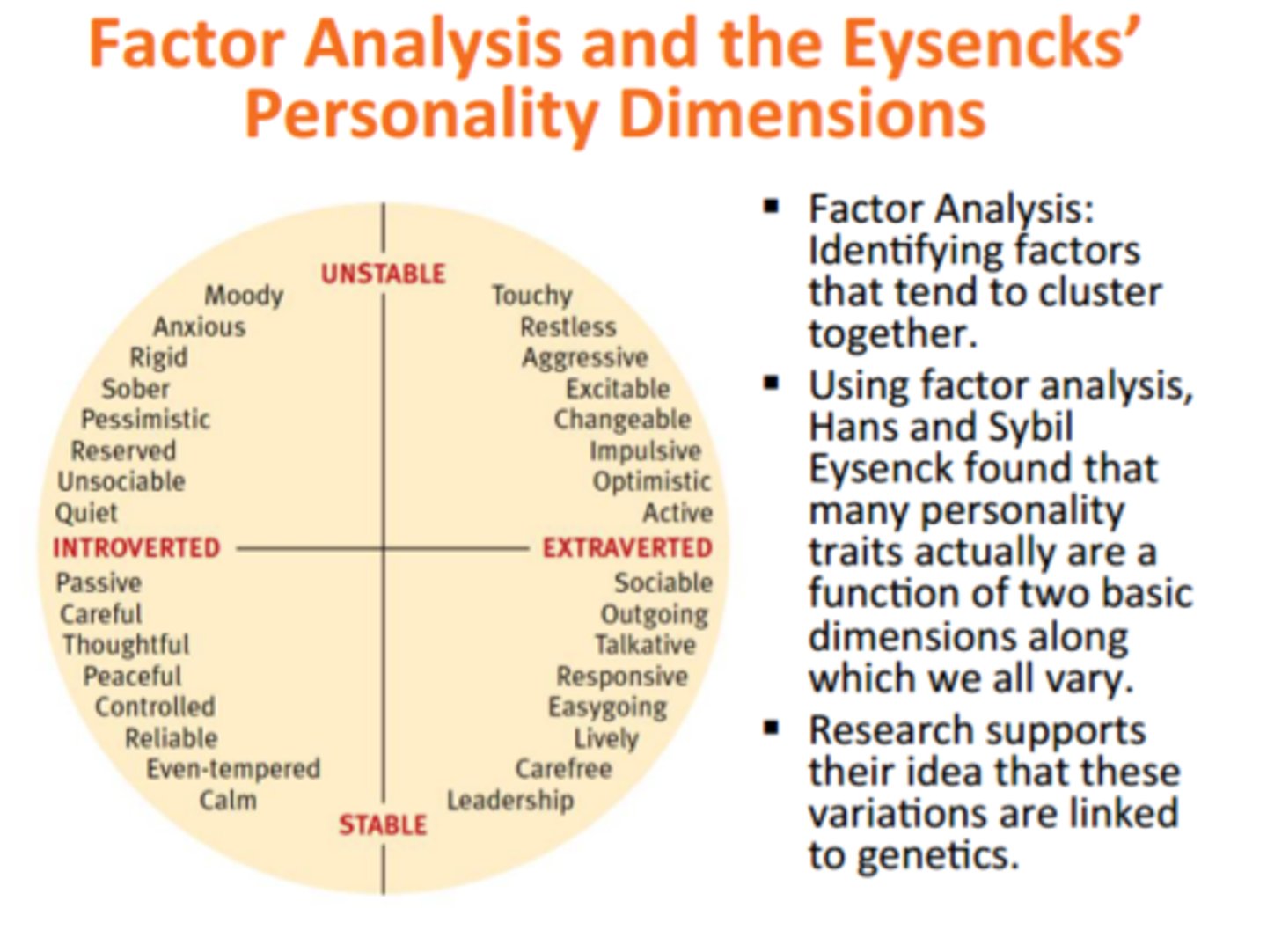
Factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items on a personality test to identify things that help interpret a person's total score