B7.3 Digestion
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is mechanical digestion?
Mechanical digestion is the breakdown of food into smaller molecules without a chemical change to the molecules
Where is mechanical digestion carried out?
- Teeth in the mouth
- Muscle walls in the stomach
What happens during mechanical digestion?
Food is chewed in the mouth then churned in the stomach, which turns the food into smaller pieces. By turning the food into smaller pieces, the surface area to volume ratio (SA:V) increases, which allows the enzymes to act more effectively during chemical digestion.
What is the equation for volume and surface area of a cube respectively?
Volume: a^3
Surface area: 6a^2
What is chemical digestion and what are some examples of insoluble molecules?
Chemical digestion is the breakdown of food from large insoluble molecules to small soluble molecules that can be absorbed.
Examples of insoluble molecules: starch, proteins, fats
What is an emulsifier?
A substance that helps mix together two liquids that don't normally mix to form a stable emulsion
What is bile and what does it do?
- Bile is an alkaline mixture which neutralises the pH of the acidic mixtures entering the duodenum from the stomach. - It also acts as an emulsifier which is able to emulsify fat into small droplets which increases its surface area. This allows lipase (enzyme) to digest the fats faster into fatty acids and glycerol
What are the three main enzymes involved in chemical digestion?
1. Amylase
2. Protease
3. Lipase
What is the function of amylase?
Digests starch into simple reducing sugars or simple sugars
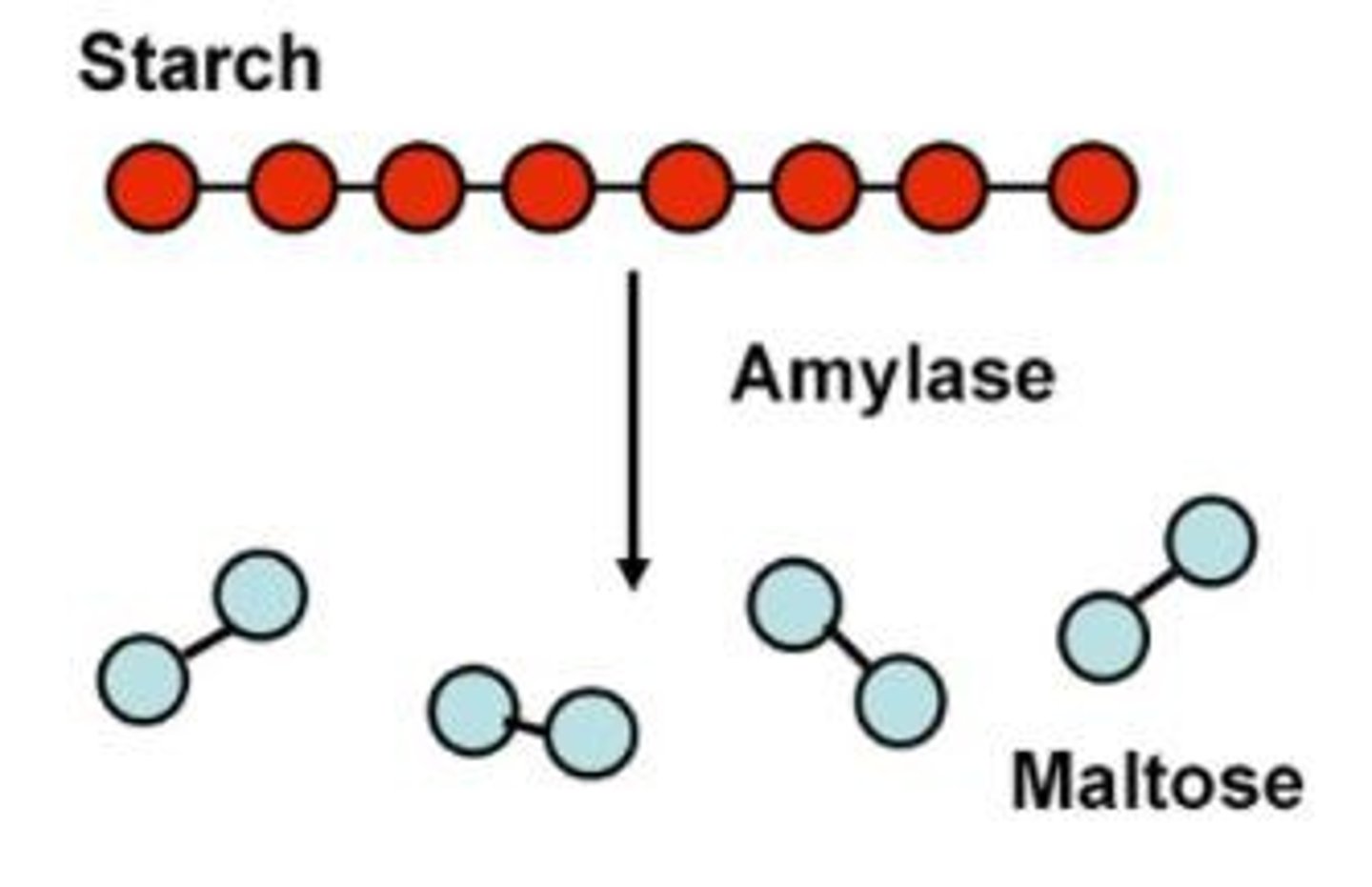
Where is amylase secreted and where does it act?
Secreted in the salivary glands and pancreas
Acts in the mouth and small intestine
What is the function of protease?
Digests proteins into amino acids
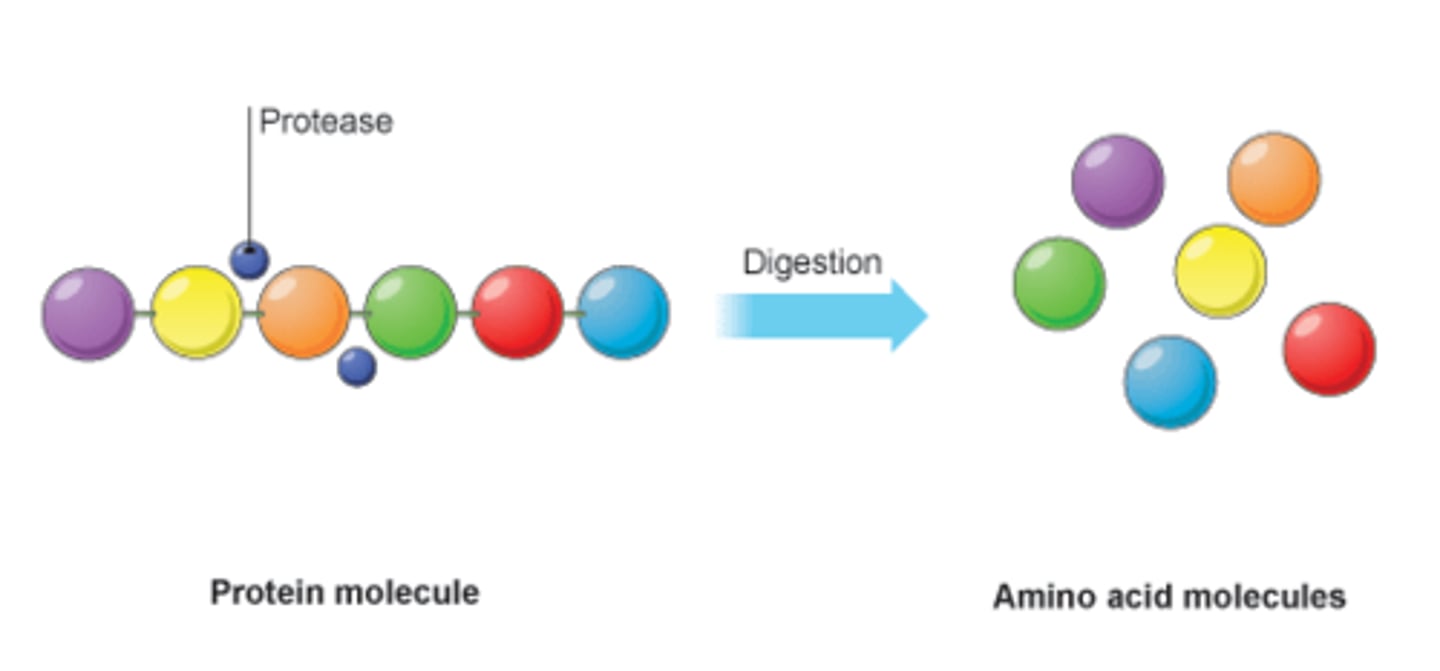
Where is protease secreted and where does it act?
Secreted in the stomach and small intestine
Acts in the stomach and small intestine
What is the function of lipase?
Digests fats into fatty acids and glycerol
Where is lipase secreted and where does it act?
Secreted in the pancreas
Acts in the small intestine
What is gastric acid and what is its function?
Gastric acid is a mixture secreted into the stomach which contains hydrochloric acid (pH range of 1.5-3.5)
Function: provides optimum pH for protease in the stomach to work, denatures enzymes in harmful microorganisms, kills bacteria in food