ECON 248 14.2 Explaining Short-Run Economic Fluctuations
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
A theory which assumed nominal variables like price levels do not influence real variables such as unemployment and output.
Classical Economic Theory(Monetary Neutrality)
Most economists believe that classical economic theory only accounts for the ().
Long Run
Economists analyze short run economic fluctuations through the model of ().
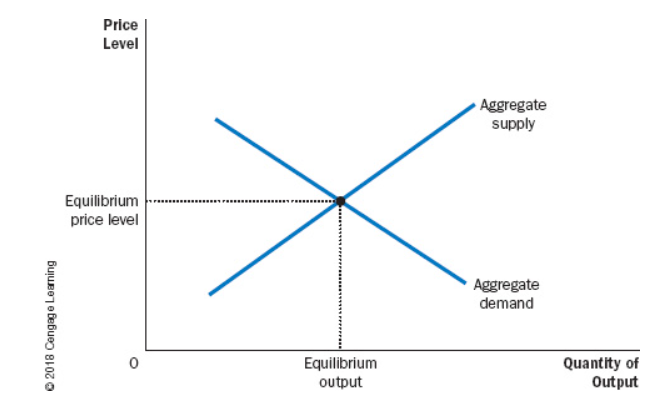
Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply.
The first variable(x axis) on the model for aggregate supply and demand is the economy’s total () of goods and services.
Output
The 2nd variable(Y axis) on the model for aggregate supply and demand is the ().
Price Level
The () shows what goods households, firms, and governments are willing to buy at each price level.
Aggregate Demand Curve
The () shows the quantity of goods and services that firms choose to produce and sell at each price level.
Aggregate-Supply Curve
In the model for aggregate supply and demand, short-run macro economic equilibrium occurs when () equals ().
Real GDP Demanded, Real GDP Supplied
Shifts in aggregate demand and supply curves are responsible for short-run ().
Economic Fluctuation