AP Human Geo. Unit 6 vocab
1/64
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
City
large settlement whose population is engaged in secondary and tertiary activity
central city
urban settlement that has been incorporated into an independent, self governing unit. (EX Tampa)
MSA (metropolitan statistical area)
the county that the central city is located in and its surrounding areas that are socioeconomically tied to the urban core (ex Hillsborough)
forward capitals
cities that are deliberately located in a country to promote development in less populated areas. These capitals are intended to further economic growth, political influence, and cultural significance.
site
the actual location of a city or settlement, characterized by its physical attributes and resources.
situation
the location of a city relative to its surrounding environment, including other cities and natural features.
urbanization
the process by which cities grow as populations increase, leading to the expansion of urban areas and changes in land use.
suburbanization
movement of the upper/middle class of people from urban areas to the surrounding outskirts
boomburbs
rapidly growing suburban cities that represent a new metropolitan form.
urban sprawl
unrestricted growth in urban areas
megacity
city of 10 million or more residents
metacity
city of over 20 million or more residents
edge city
economic center on the edge of a city with very large infrastructure that is located off the side of a major highway or road.
exurb
residential districts that are located beyond the suburbs.
world city
a very influential city that’s name is very recognizable and functions at the very top of the worlds hierarchy (ex: Tokyo, New York, London)
megalopolis
when multiple large and expanding cities overlap with other nearby cities creating even larger urban areas.
primate cities
when the largest city in a country is more than twice the size of the second largest city in that country.
rank size rule
the “nth” largest city in a country should be “1/n” the size of the largest city
gravity model
predicts the degree of interaction between 2 places —— as distance increases there will be less movement between them
central place theory
Central place theory is a concept that explains how cities and towns are organized. It suggests that larger cities provide more services and goods than smaller towns, acting as central hubs for surrounding areas.
threshold
the amount of people and traffic needed to keep an area alive and open.
range
the distance that people will travel for a certain experience or service. ( bigger and scarcer places often have a much larger range)
CBD (Central business district)
the “downtown” of a city
zoning
local regulations that dictate how land can be used (residential, commercial, industrial, etc.), influencing urban development patterns and density
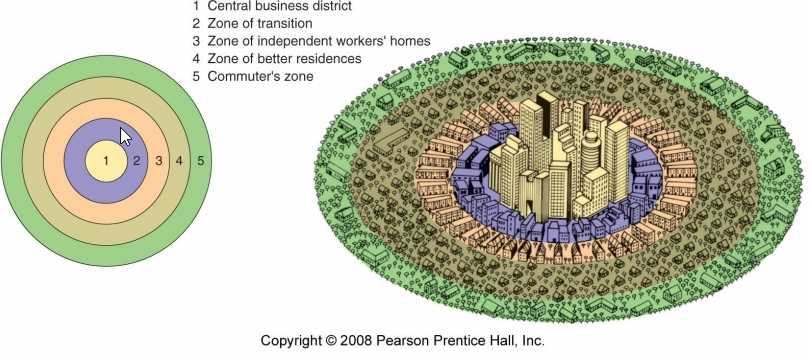
concentric model
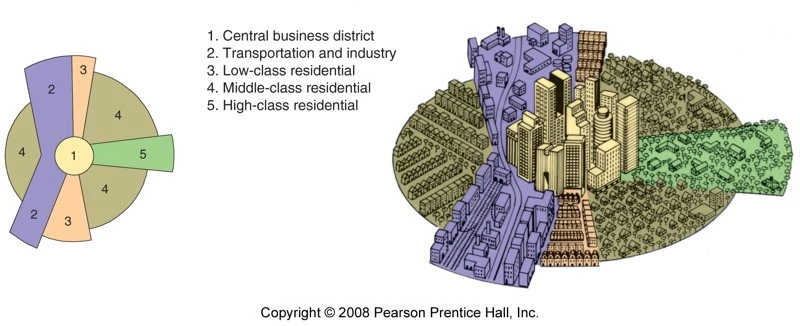
sector model
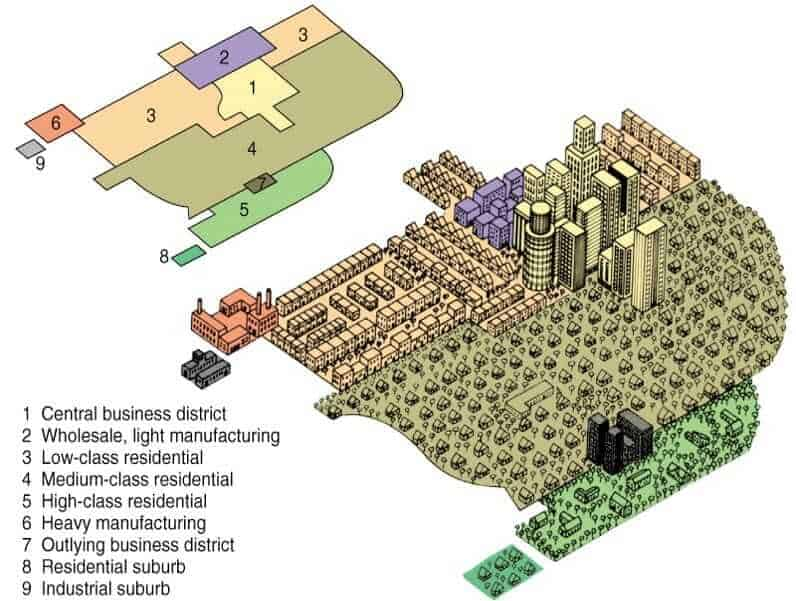
multiple nuclei model
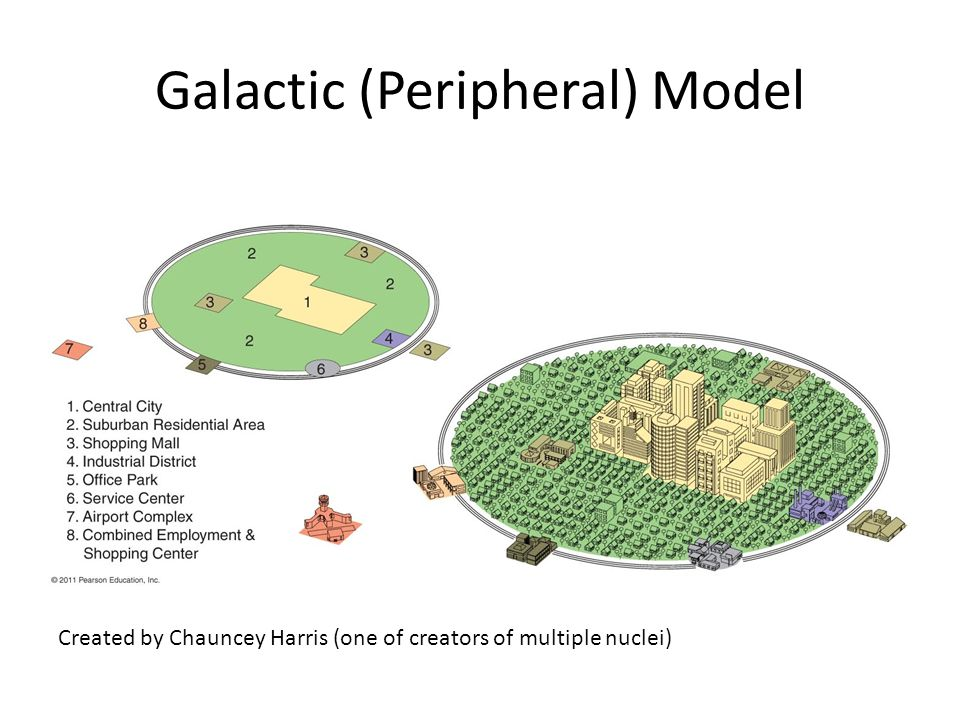
peripheral model
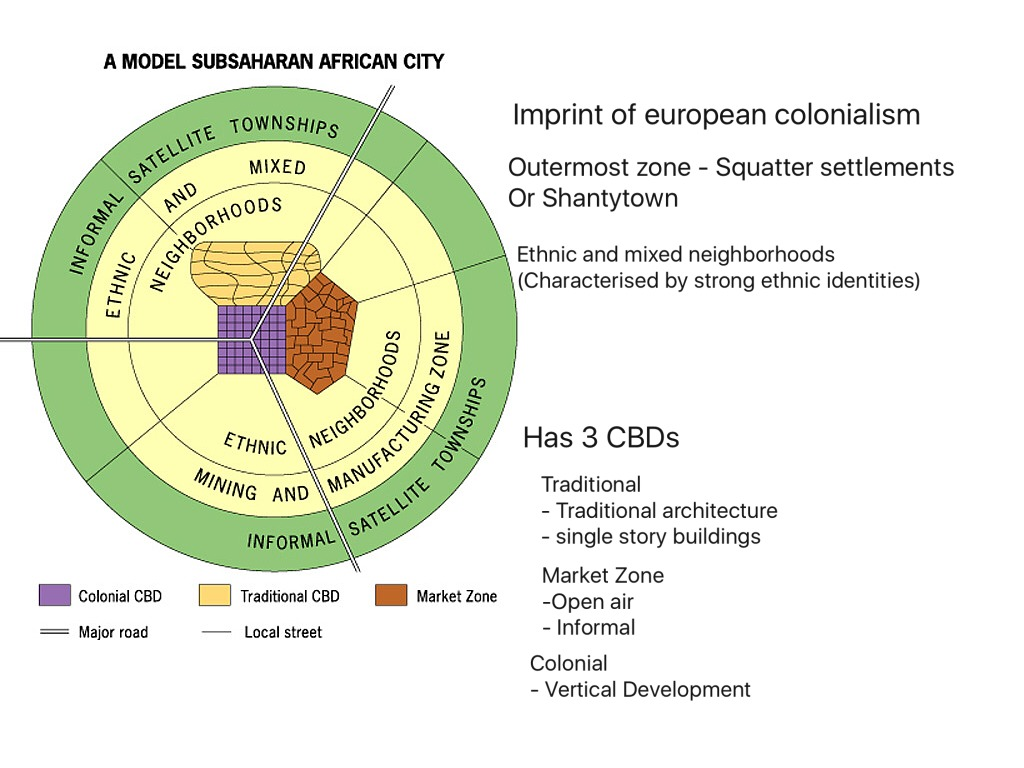
African city model
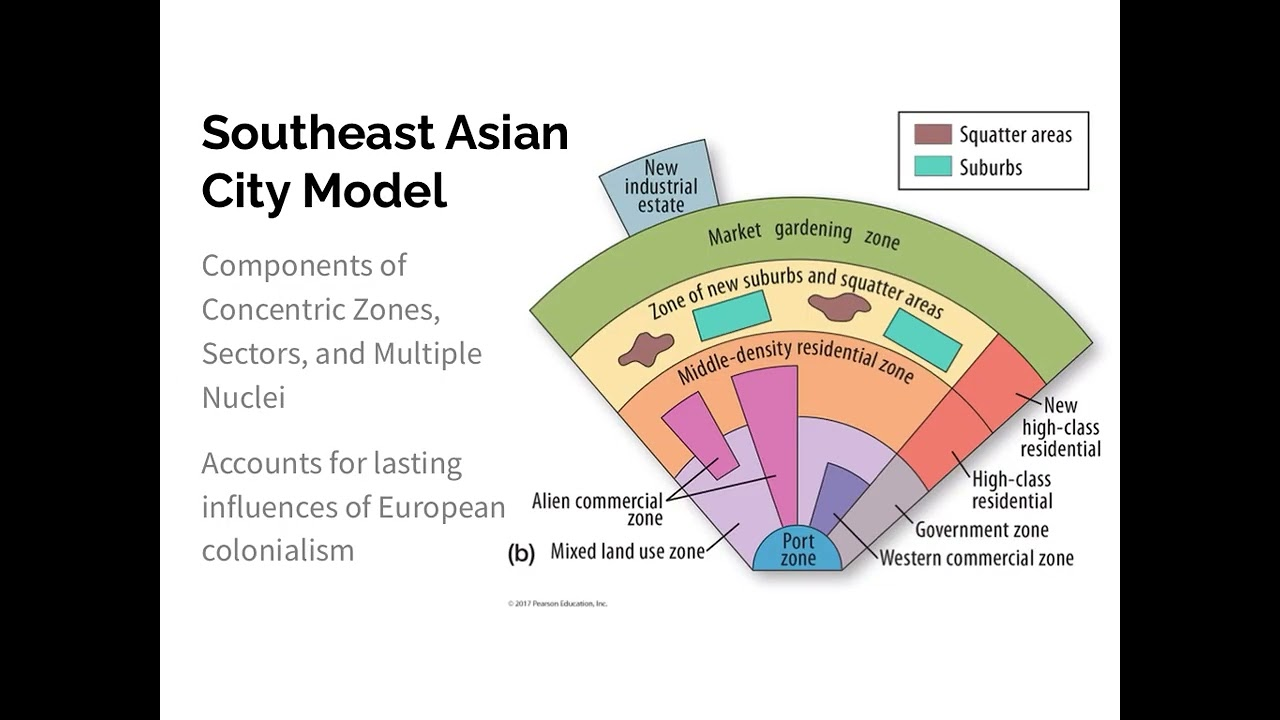
southeast Asian city model
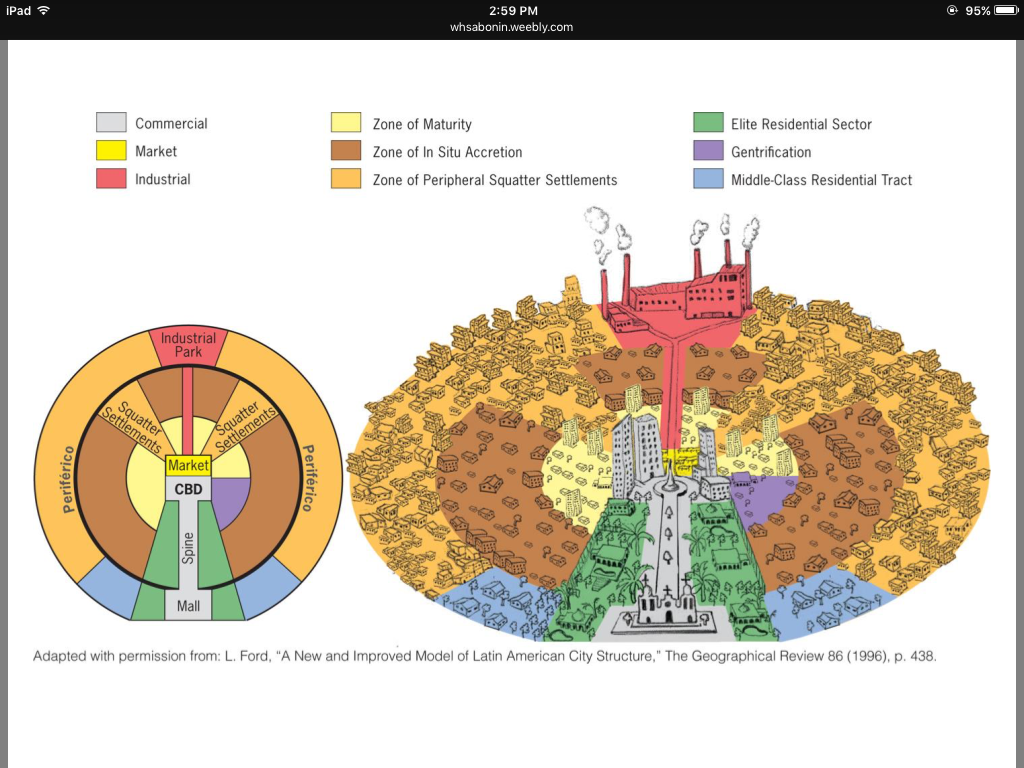
Latin America ciyt model
greeenbelt
designated areas of open land surrounding urban areas, often used to restrict development, preserve natural habitats, and enhance the quality of life for residents
bid rent theroy
explains how land prices and demand change as the distance from a city's central business district (CBD) increases
high density areas
areas with high density (ex: CBD’s have a high density because everybody is stacked on top of each other)
medium density areas
duh (ex condos or towns homes, people are squished but not on top of each other)
low density areas
duh…(suburbs)
density gradient
the decrease in population density as you move away from the CBD
smart growth
developmental approach that [prioritizes walkability by keeping everything located very close to one another. (EX: Midtown)
New Urbanism
a planning and design philosophy that aims to create sustainable, walkable communities
mass transportation
Busses, trains, subways, metros
Mixed-Use Development
an area providing more than one poupous within a shared building area.
urban design initiative
the focus on creating sustainable, livable and resilient cities
quantitative data
deals with #’s
qualitative data
deals with characteristics and qualities
blockbusting
A process by which real estate agents convince white property owners to sell their houses at low prices because of fear that persons of color will soon move into the neighborhood.
redlining
the discriminatory practice of denying or limiting financial services like mortgages and loans to certain neighborhoods, often based on their racial or ethnic composition
white flight
the historical phenomenon of white residents, particularly middle and upper-class families, moving from urban areas to suburban or outlying areas, often in response to increasing racial diversity and perceived social unrest
ghetto
a spatially confined area where a single ethnoracial group is involuntarily clustered together, often due to extreme racial oppression or other forms of discrimination, leading to unfavorable conditions
restrictive covenant
legally binding agreements that restrict or prohibit certain uses of property, often used historically to enforce racial segregation or other forms of discrimination in housing
food desert
A food desert is characterized by limited access to affordable and nutritious foods, often due to a lack of supermarkets or grocery stores offering healthy options.
Disamenity zone
an area with lots of undesirable features
urban renewal
the clearing out of deserted areas in the inner city to build opportunities for the upper class. Housing, Businesses and more
in-filling
rededication of land in an urban environment to new construction.
gentrification
the act of upper/ middle class people into lower-class urban areas an fixing it up
squatter settlements
illegal housing that springs up on the outskirts of cities
inclusionary zoning
when you designate a couple places to be cheaper to buy than the rest making it more affordable for the poor.
urban gardens
gardens located in the middle of the CBD that help people get access to foods
local food movement
promotes consuming more locally grown foods
“NIMBY”
“Not in my backyard” when people don’t want something located near them.
suburban sprawl
when the suburbs grow massively
ecological footprint
impact of a pero]son or community on the environment
slow growth cities
prioritize sustainable, equitable development over rapid population and economic growth, often focusing on community-specific attributes like small businesses and local initiatives. br
brownfields
a former industrial or
commercial site where future use is affected by
real or perceived environmental contamination
urban growth boundaries
boundaries that limit the growth of the suburbs
farmland protection policies
minimizes the extent to which federal activities lead to the conversion of farm and ranch land to non-agricultural uses