ch 5 chemical energetics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
standard enthalpy change of reaction
enthalpy change when molar quantities of reactants as stated in the thermochemical equation react together under standard conditions
heat capacity
C=mc
standard enthalpy change of neutralisation (exothermic)
energy evolved when one mole of water is formed during the neutralisation of an acid and an alkali under standard conditions
standard enthalpy change of combustion (exothermic)
energy evolved when one mole of substance is completely burnt in excess ixygen under standard conditions
standard enthalpy change of atomisation of elements (endothermic)
energy absorbed when one mole of gaseous atoms is formed from its element under standard conditions
standard enthalpy change of atomisation of a compound (endothermic)
energy absorbed when one mole of compound is converted to its constituent gaseous atoms under standard conditions
standard bond dissociation enthalpy (endothermic)
energy needed to break one mole of covalent bonds between two atoms in the gaseous state under standard conditions
first ionisation energy (endothermic)
energy absorbed when one mole of electrons is removed from one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of singly-charged gaseous cations
first electron affinity (exothermic)
energy change when one mole of electron is added to one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of singly charged gaseous anions
standard lattice energy (exothermic)
energy evolved when one mole of ionic compound is formed from its constituent gaseous ions under standard conditions
standard enthalpy change of hydration (exothermic)
energy evolved when one mole of gaseous ions is surrounded by water molecules, forming a solution at infinite dilution under standard conditions
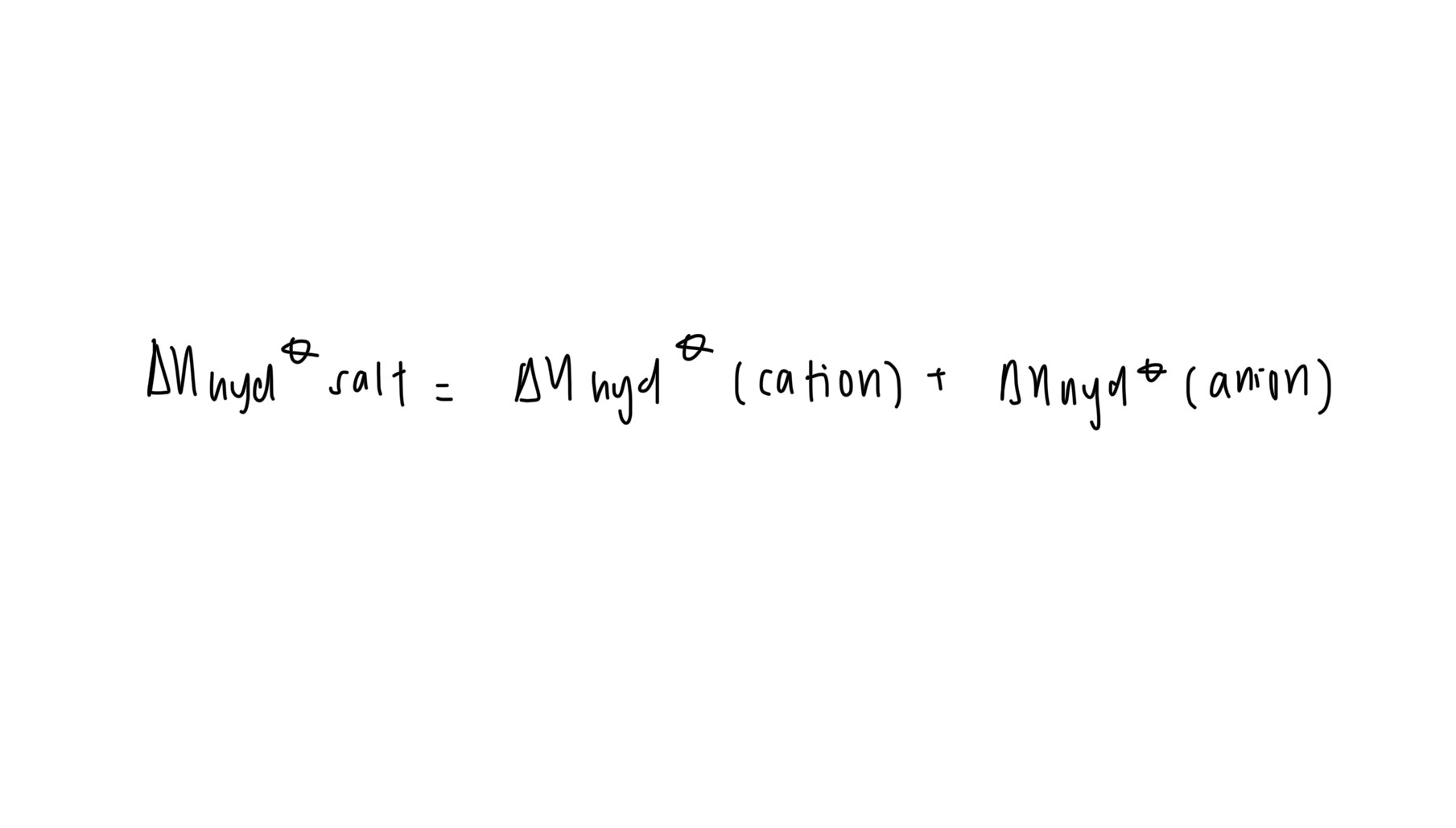
standard enthalpy change of solution (can be exo/endo)
energy change when one mole of substance is dissolved by solvent such that further dilution produces no more energy change under standard conditions
standard enthalpy change of formation (can be exo/endo)
energy change when one mole of compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states under standard conditions
🔼Hf of an element in its standard state is always zero
Hess’ law of constant heat of summation
states that the enthalpy change for a chemical reaction is the same regardless of the route of reaction it takes, provided that the reactants, products, initial and final conditions are the same.
entropy, S
a measure of the randomness or disorder of a system
