Rate of Reactions
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Effective collision
sufficient energy
right orientation
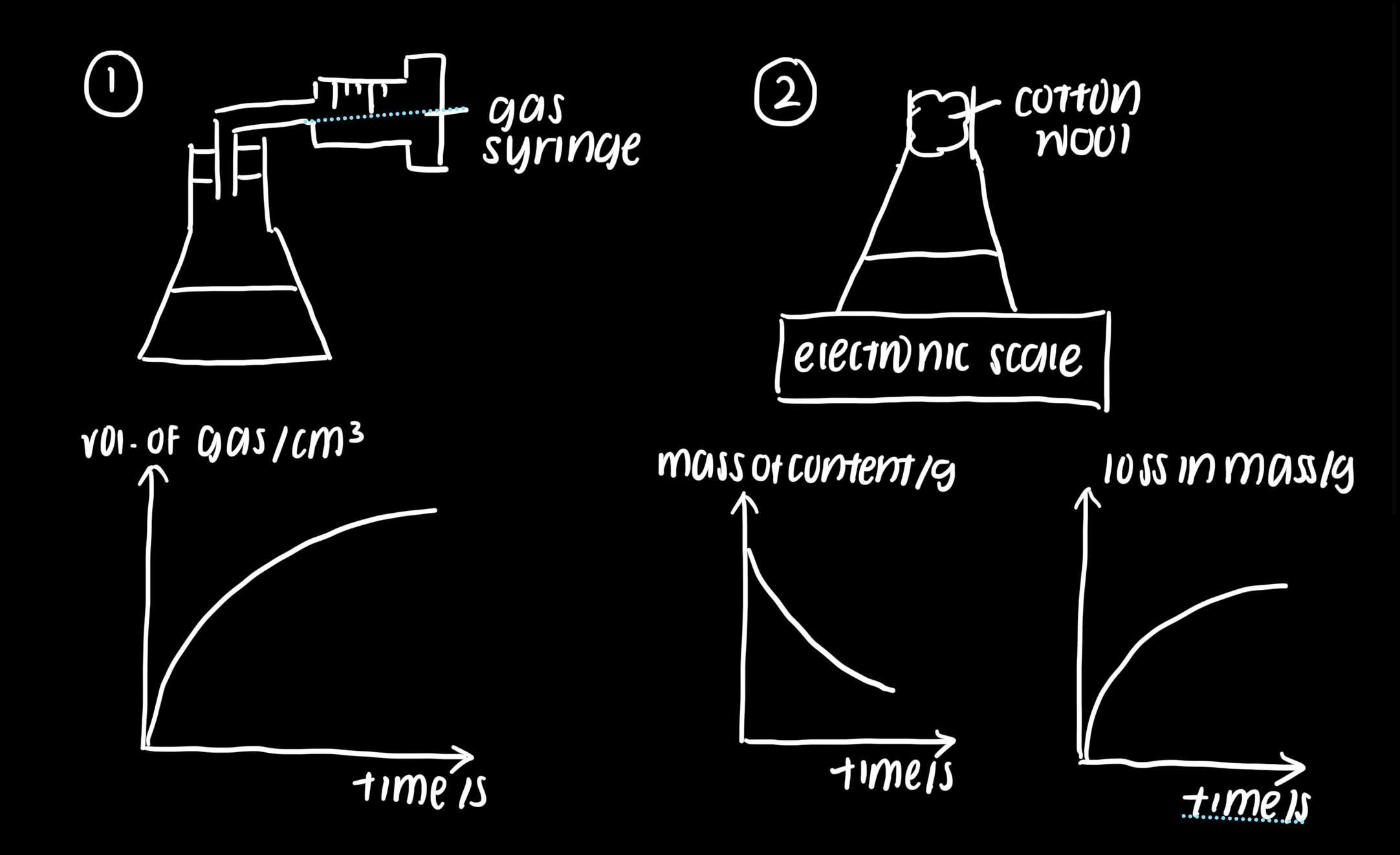
methods to measure rate of reaction
volume of gas produced per unit time
decrease in mass when gas is released per unit volume
(Factors) Size of reactant particles
Greater exposed surface area to volume ration
Frequency of effective collision between reacting particles increases
Rate of reaction increases
Concentration & Pressure
More particles per unit volume
Frequency of effective collision between reacting particles increases
Rate of reaction increases
Temperature
Higher kinetic energy and move faster
More particles have more than or equal energy to overcome activation energy
Frequency of effective collision between reacting particles increases
Rate of reaction increases
Catalyst
Speeds up reaction by providing an alternative pathway
More particles have sufficient energy to overcome lower activation energy
Frequency of effective collision between reacting particles increases
Rate of reaction increases
characteristics of catalyst
Yield remains unchanged throughout
Remains chemically unchanged
only small amount of catalyst is required
Transition metals due to their variable oxidation states
enzymes
Biological catalysts to increase rate of chemical reactions
characteristics —> highly specific/sensitive (temp & pH changes)/ selective