07.2E AN U7P2 (PART E) Homeostatic Imbalances of the Nervous System
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Traumatic Brain Injuries (TMI)
Examples include concussions, contusions, and cerebral edema
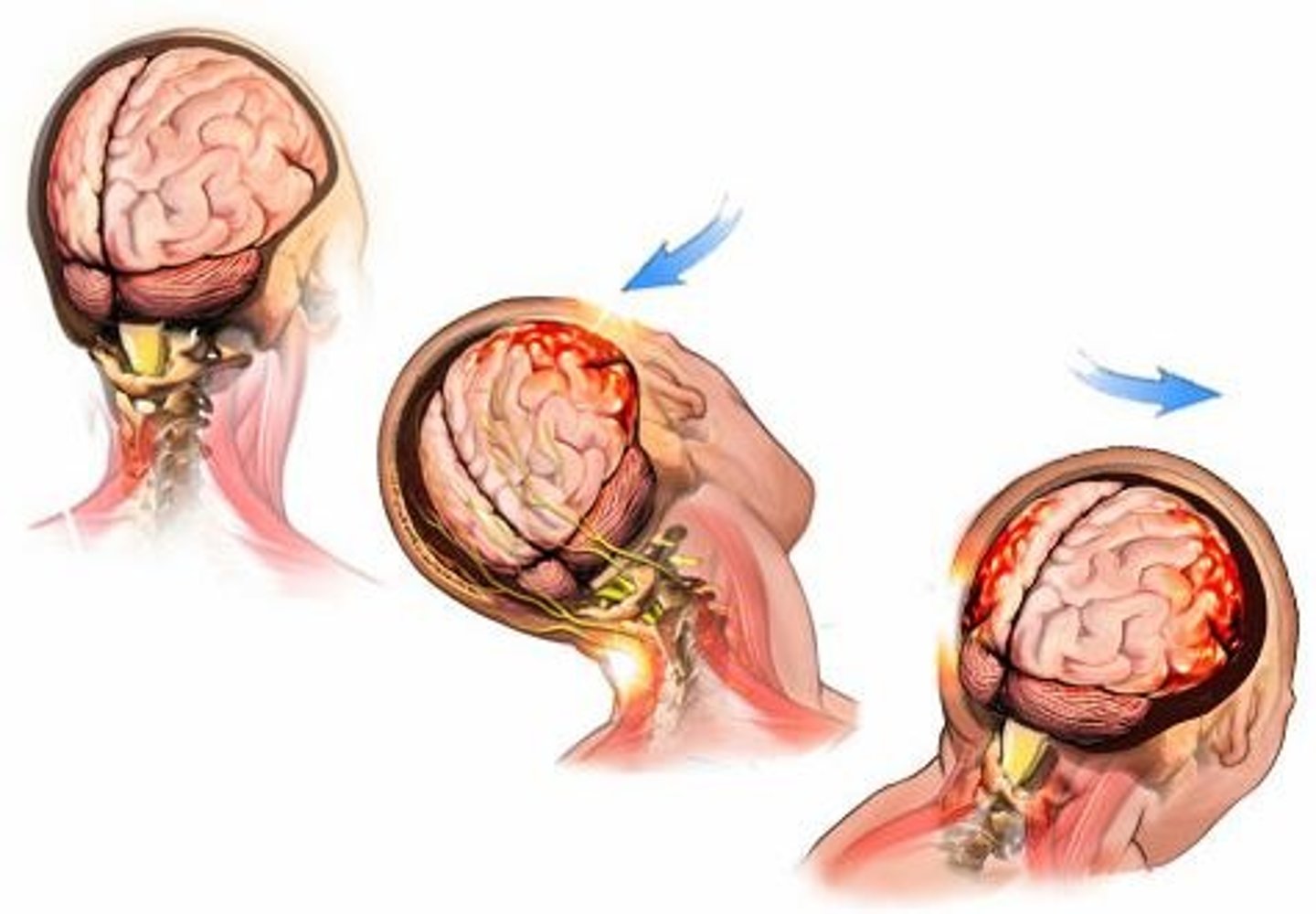
Concussion
Slight brain injury in which there is typically no permanent brain damage; person may feel dizzy and not be able to concentrate
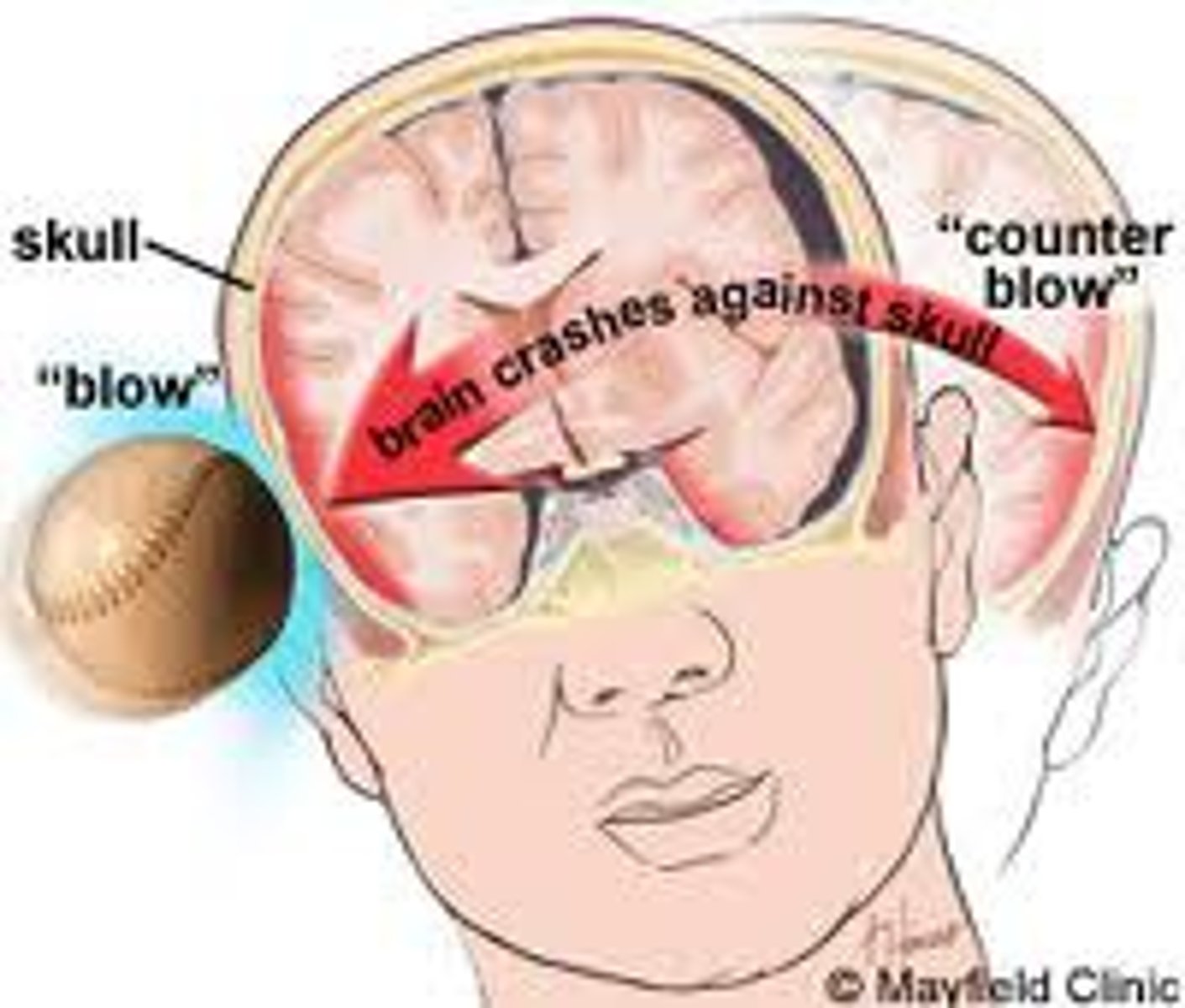
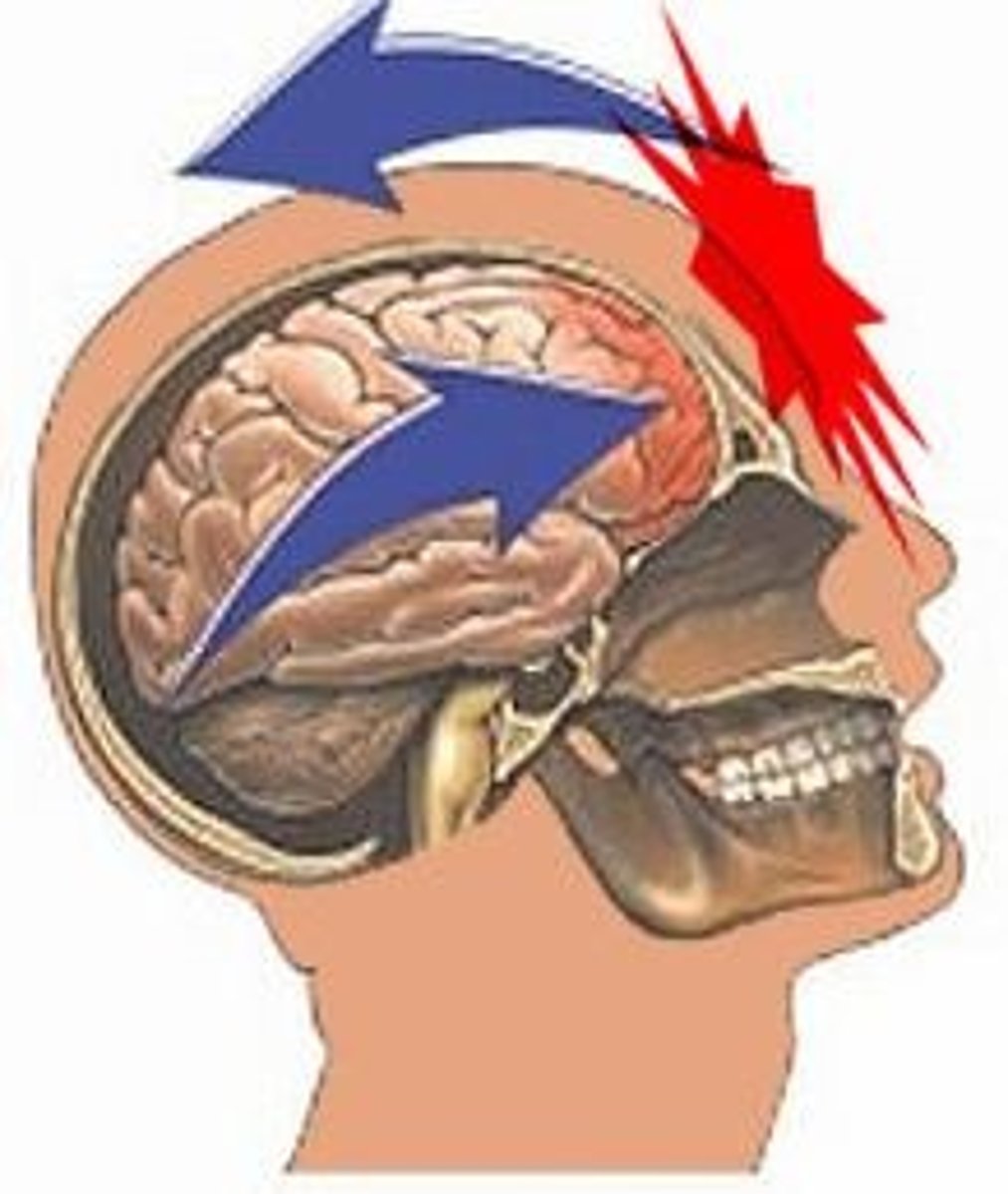
Contusion
A brain injury in which tissue destruction occurs and does not regenerate
Cerebral edema
Swelling of the brain from the inflammatory response; inflammation my cause brain to compress against the skull which can result in brain tissue death
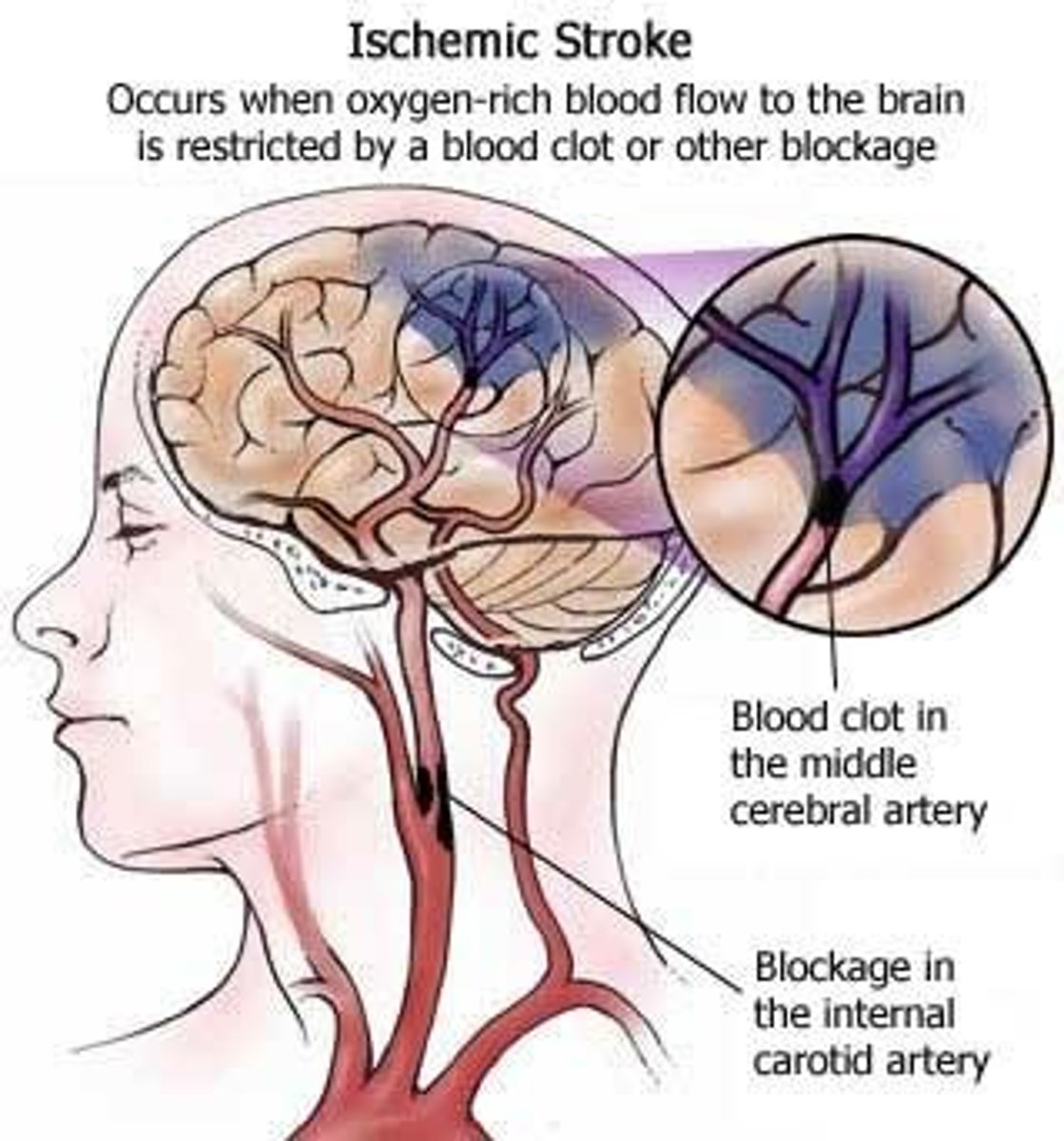
Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)
Commonly called a stroke; results from a blocked blood vessel supplying a region of the brain; can results in death of tissue and loss of function; paralysis
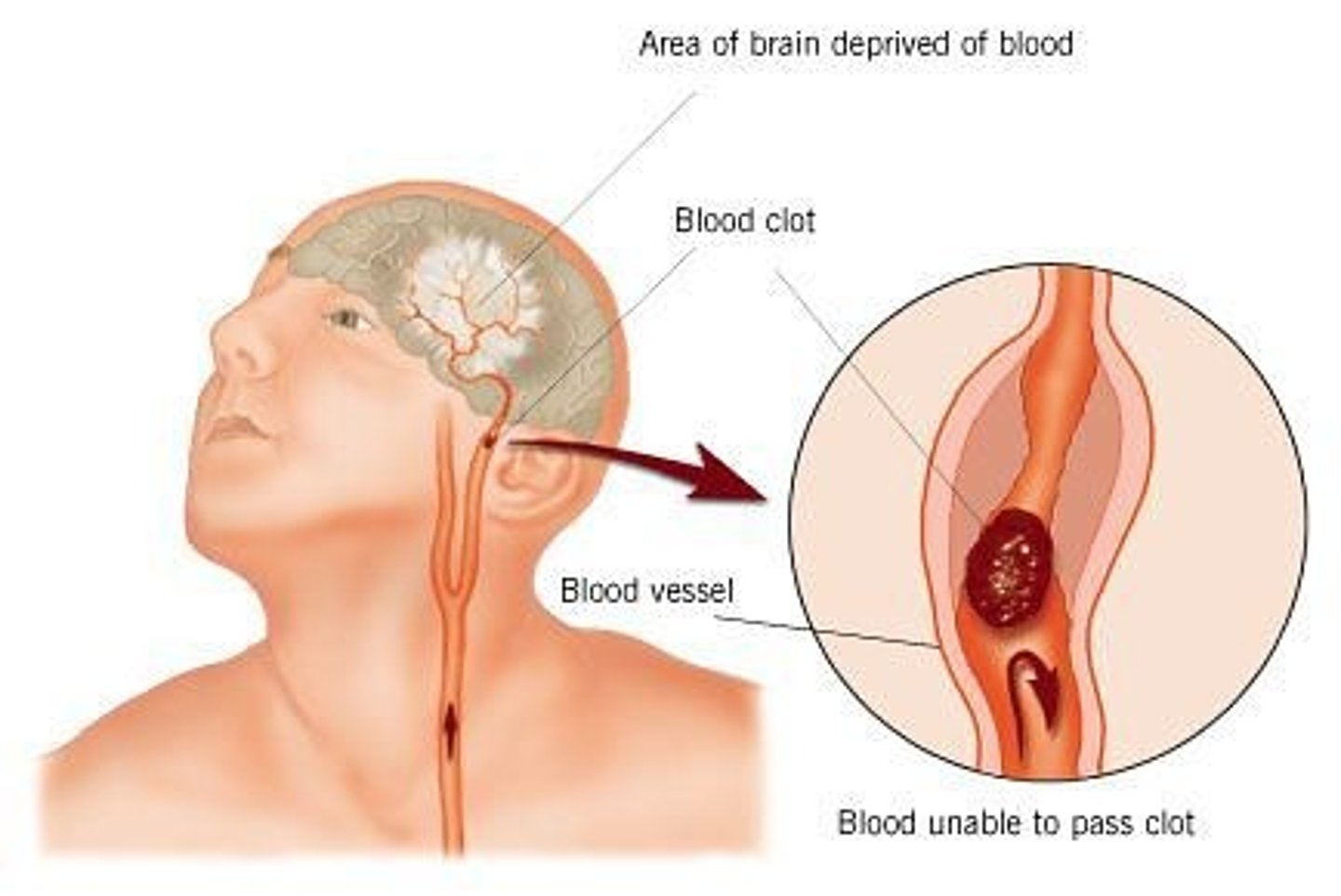
Temporary Brain Ischemia (TIA)
Restriction of blood flow to the brain for 5-50 minutes; results in numbness; paralysis; impaired functions
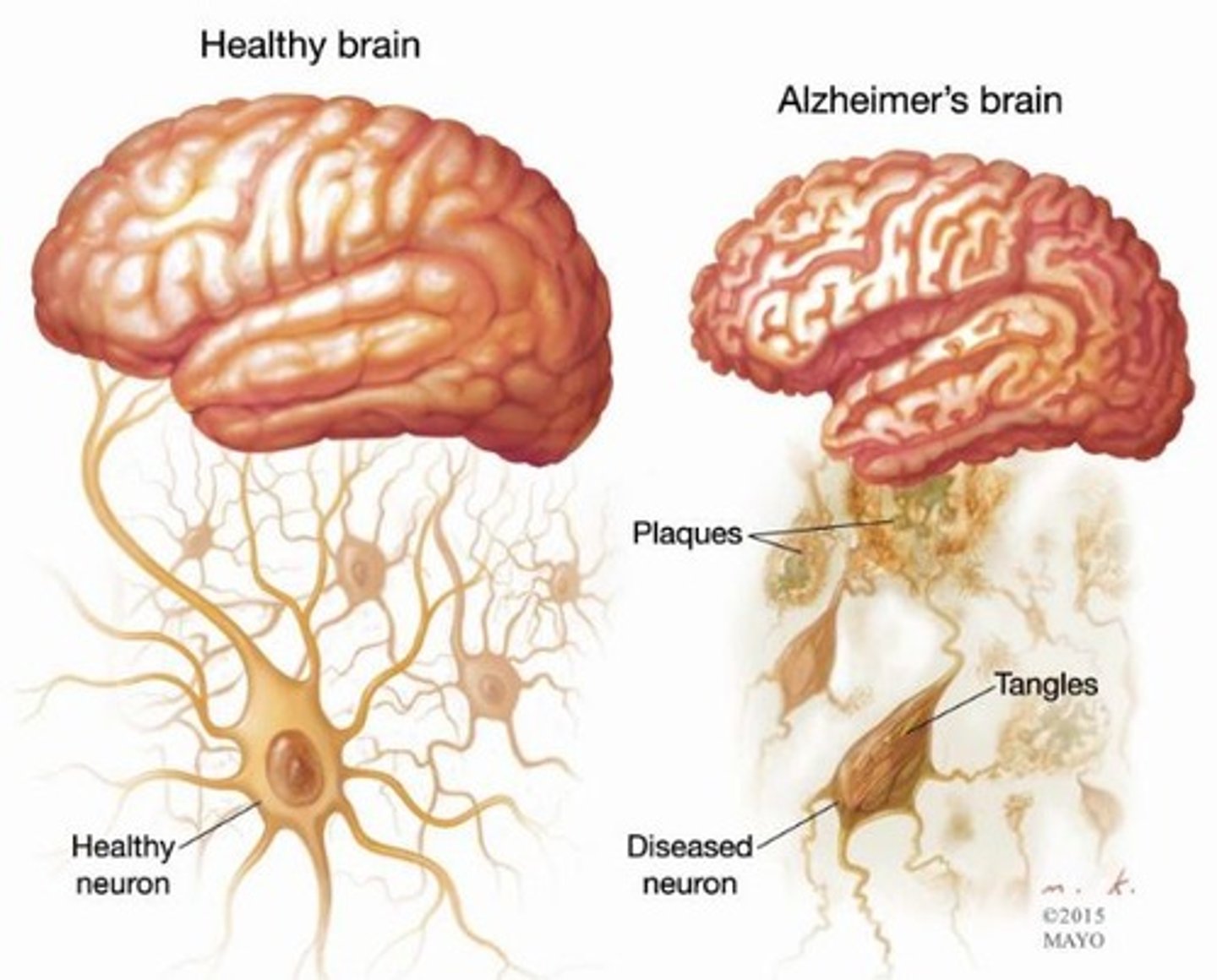
Alzheimer's Disease
Progressively degenerative brain disease; mostly seen in elderly; structural changes in the brain occur; protein deposits result in death of neurons; victims experience memory loss, mood changes and ultimately death
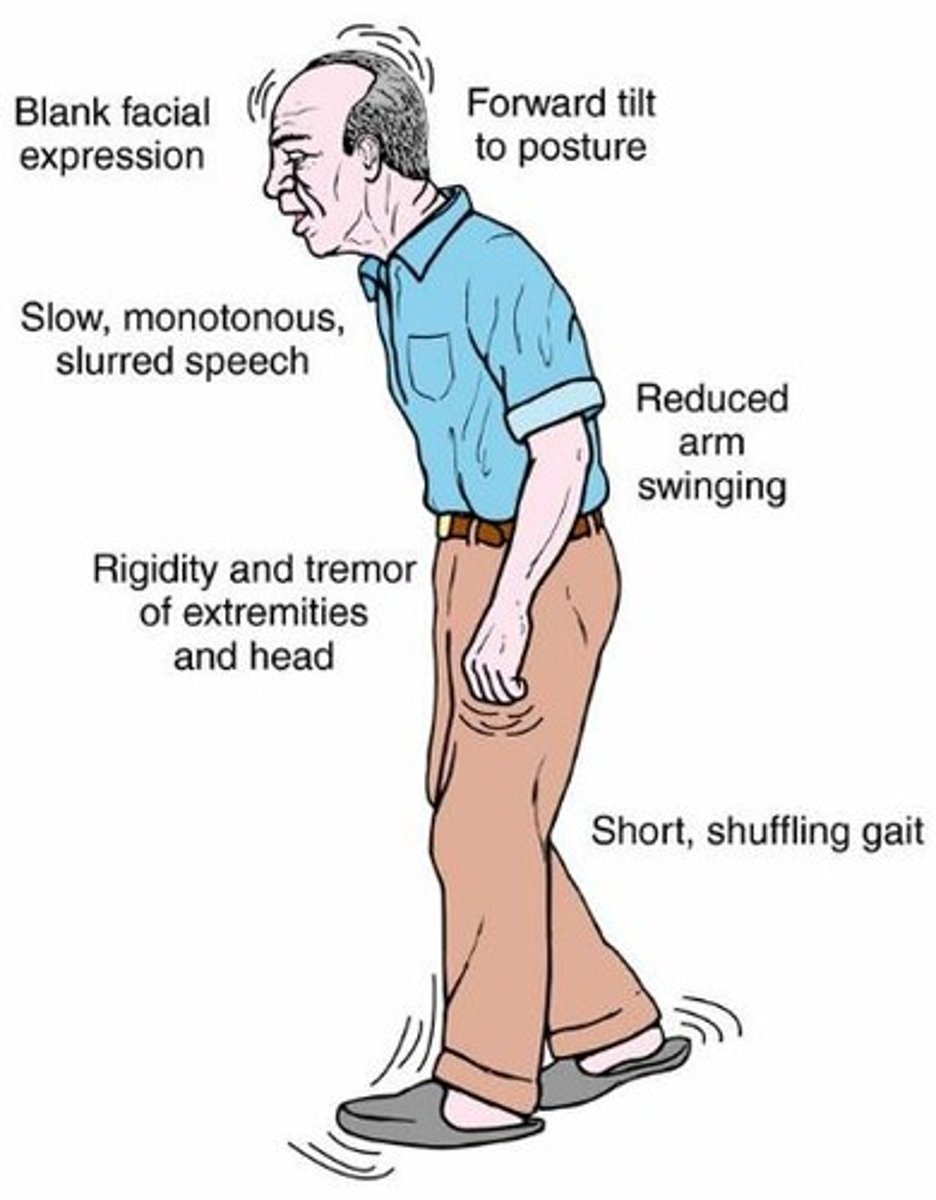
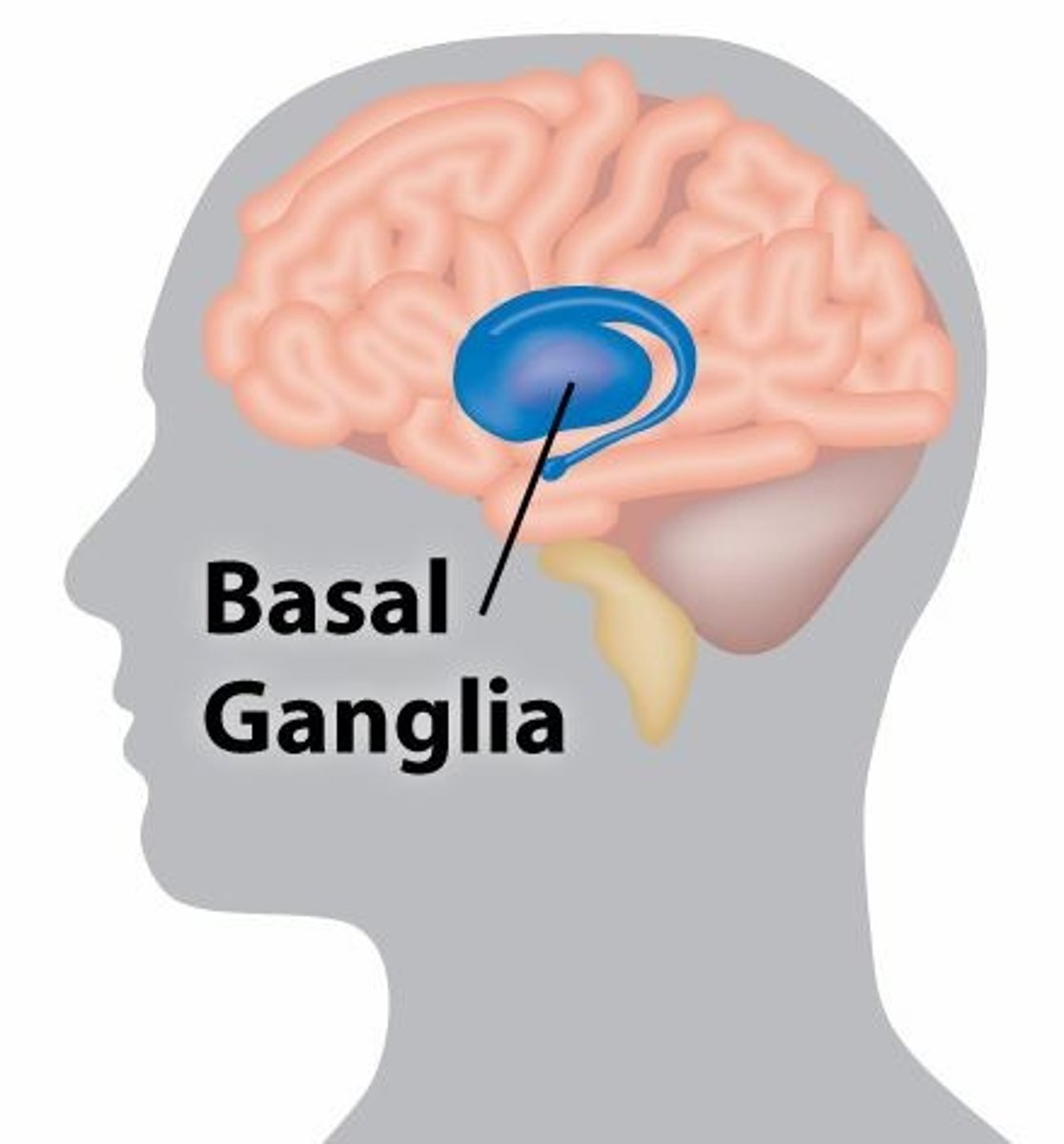
Parkinson's Disease
Effects basal nuclei; results in trembling of hands, stiffness in limbs, slow movement, impaired balance, administer drugs that increase dopamine, including anticholinergics and MAO-B inhibitors; can also use deep brain stimulation
Huntington's Cholera
An autosomal dominant genetic disease common in Venezuela that affects the basal ganglia; brain degeneration results in uncontrolled movement, loss of intellect, emotional outbursts; medication is used to control movements and emotions but there is no cure; genetic studies are ongoing
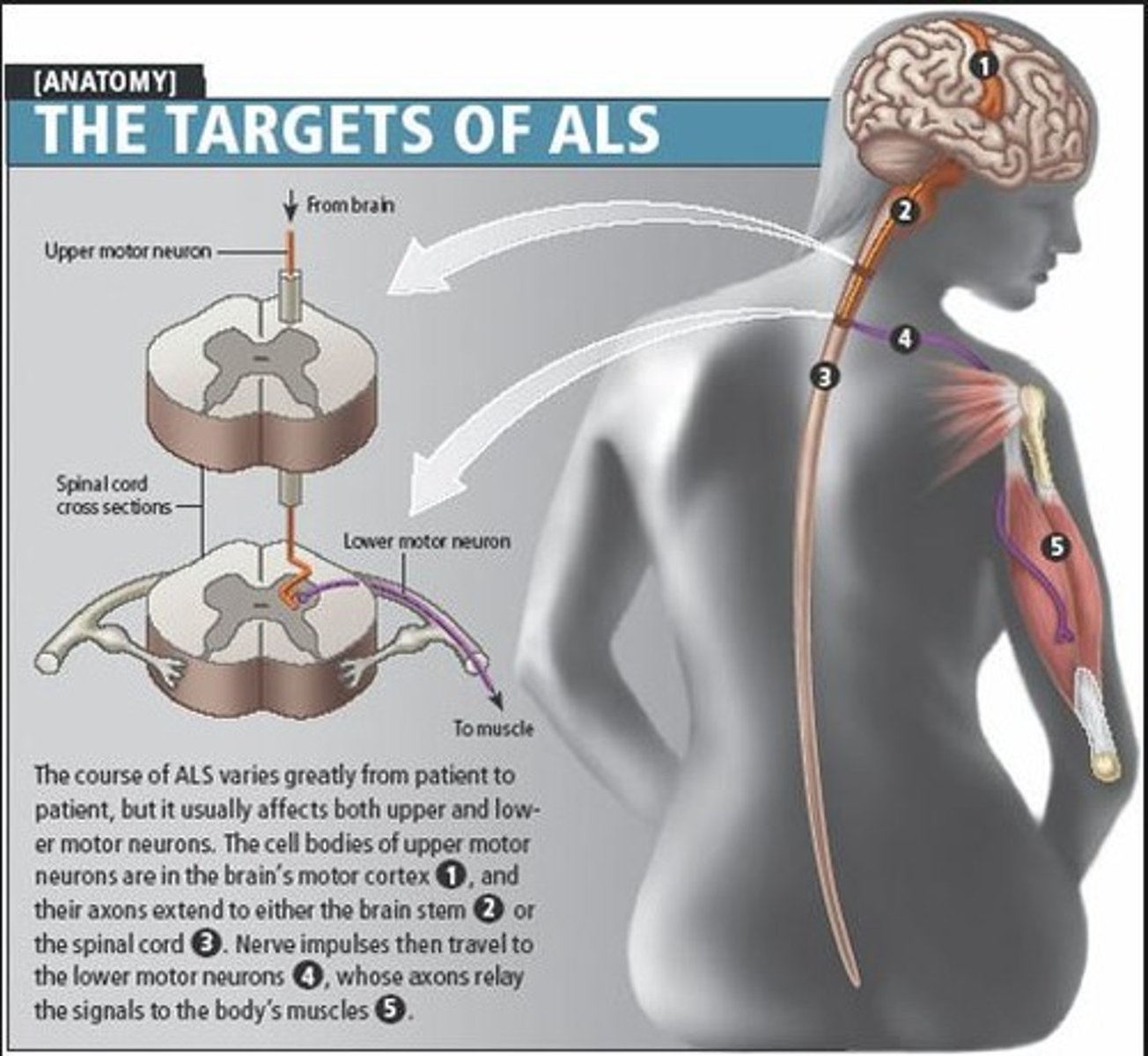
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Also known as Lou Gehrig's Disease; a progressive neurological disease that causes motor neurons not to function properly; over time, this leads to muscle weakness, gradually affecting how the body functions; the condition eventually affects nerves that control breathing and other vital bodily functions, resulting in death; there is no cure, medicines (i.e. Riluzole) control symptoms; symptoms are treated with physical therapy
Ataxis
Gross in-coordination of muscle movement
Symptom of different things
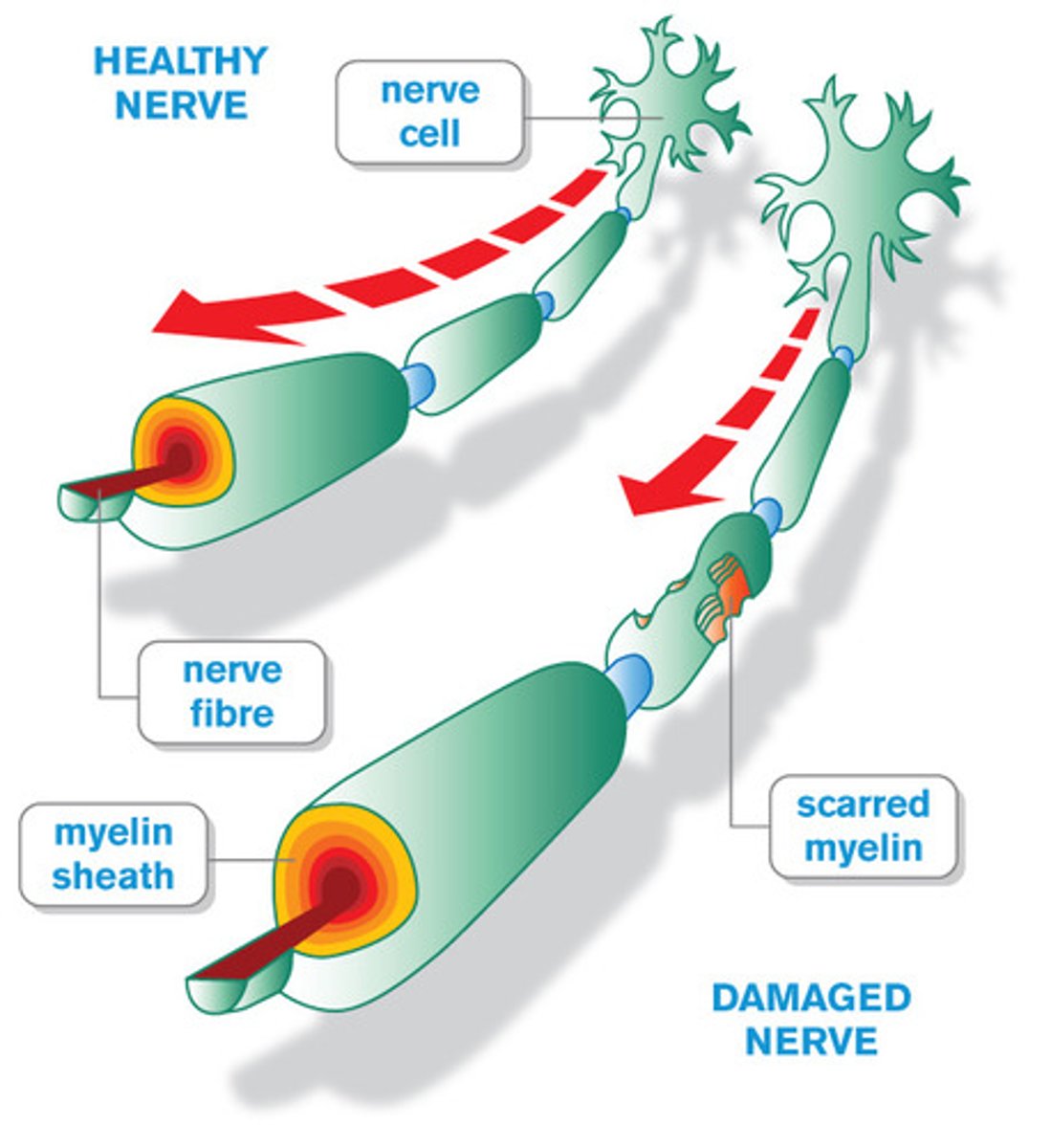
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Autoimmune disorder that results in numbness, loss of balance, weakness of limbs, blurred vision, fatigue; treated with medication and physical therapy
Encephalitis
Brain inflammation that usually is the result of a viral illness; resembles the flu and lasts 2-3 weeks; treated with IV fluids
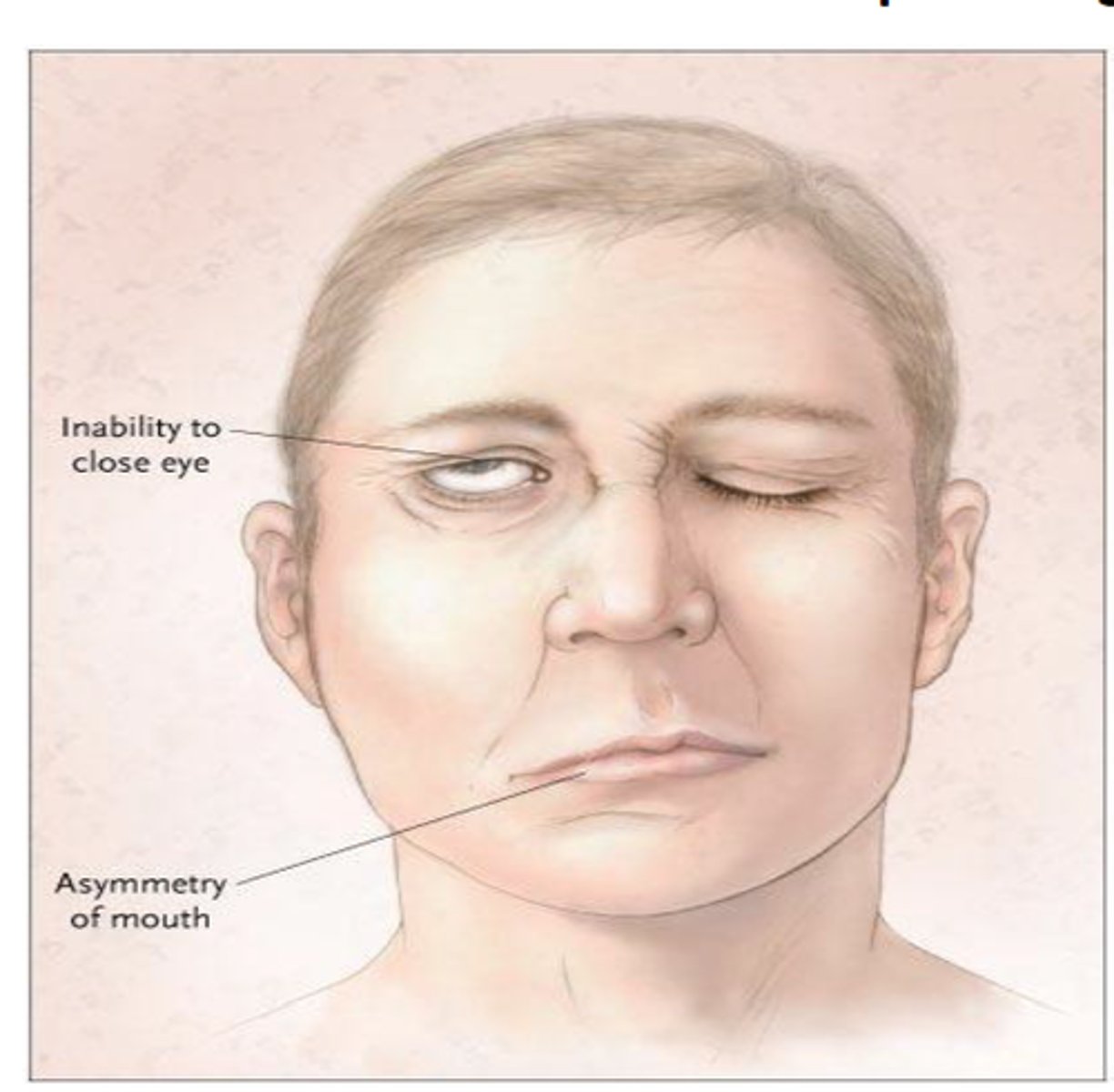
Bell's Palsy
Facial paralysis caused by irritation of cranial nerve VII; cause unknown, most patients recover; inflammation treated with steroids; eye irritation treated with eye ointment and sunglasses; in some cases surgery is necessary
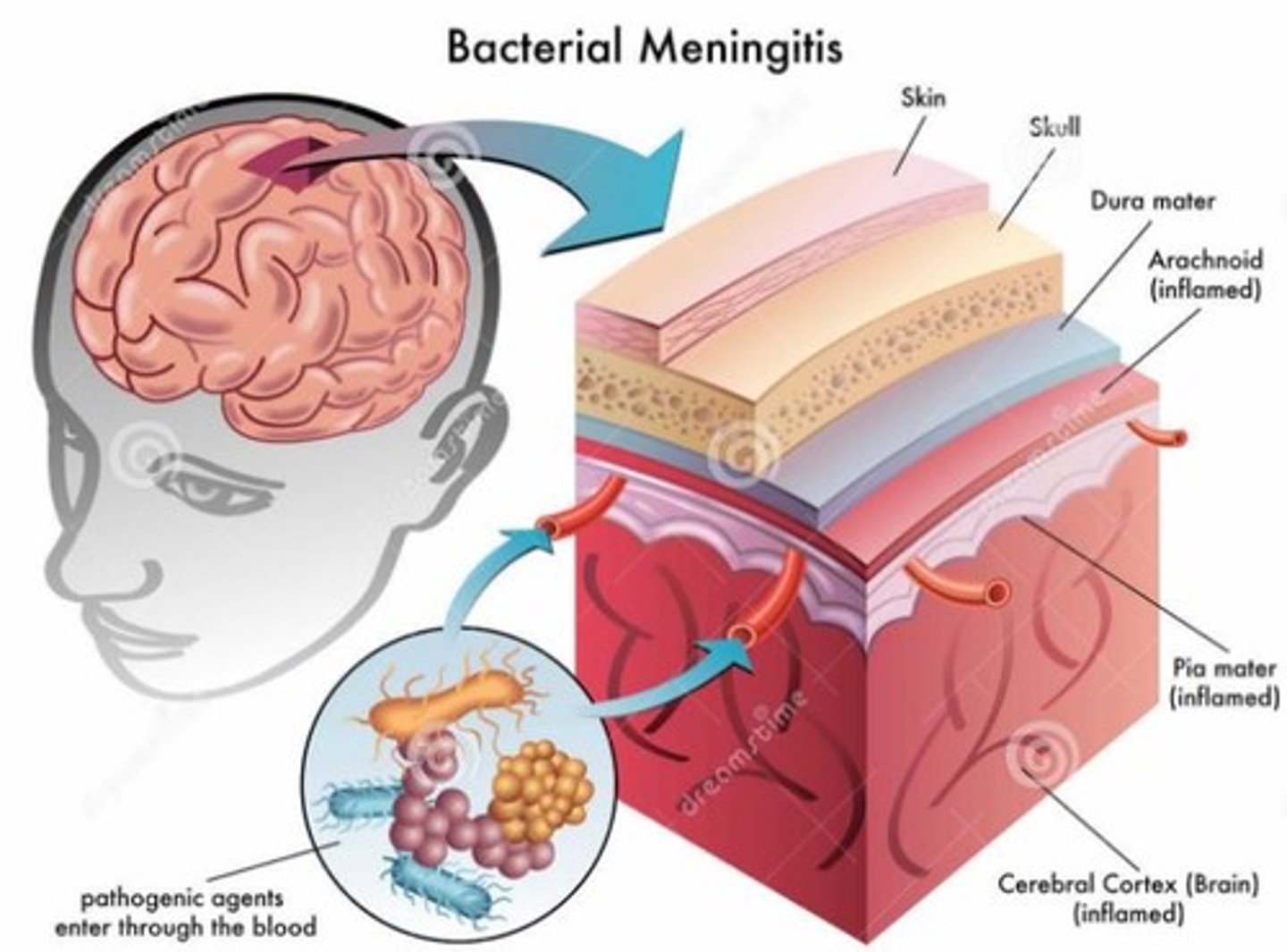
Meningitis
Inflammation of meninges (layers covering the brain) caused by a bacterial or viral infection; life threatening; 20-25% fatal
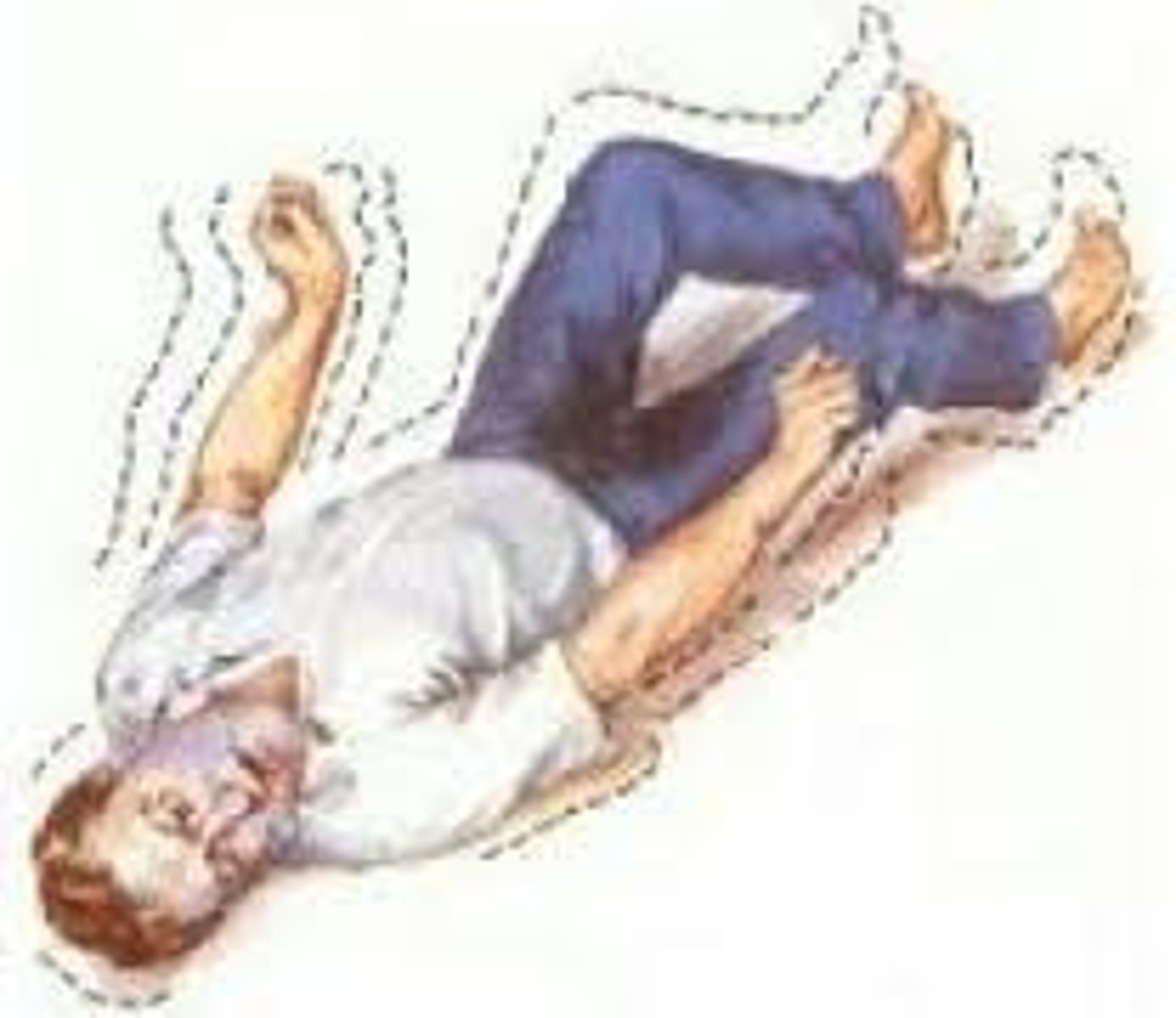
Epilepsy
Abnormal brain cell activity; results in confusion, uncontrolled movements; treat with anti-epileptic drugs and removal of defined area within the brain
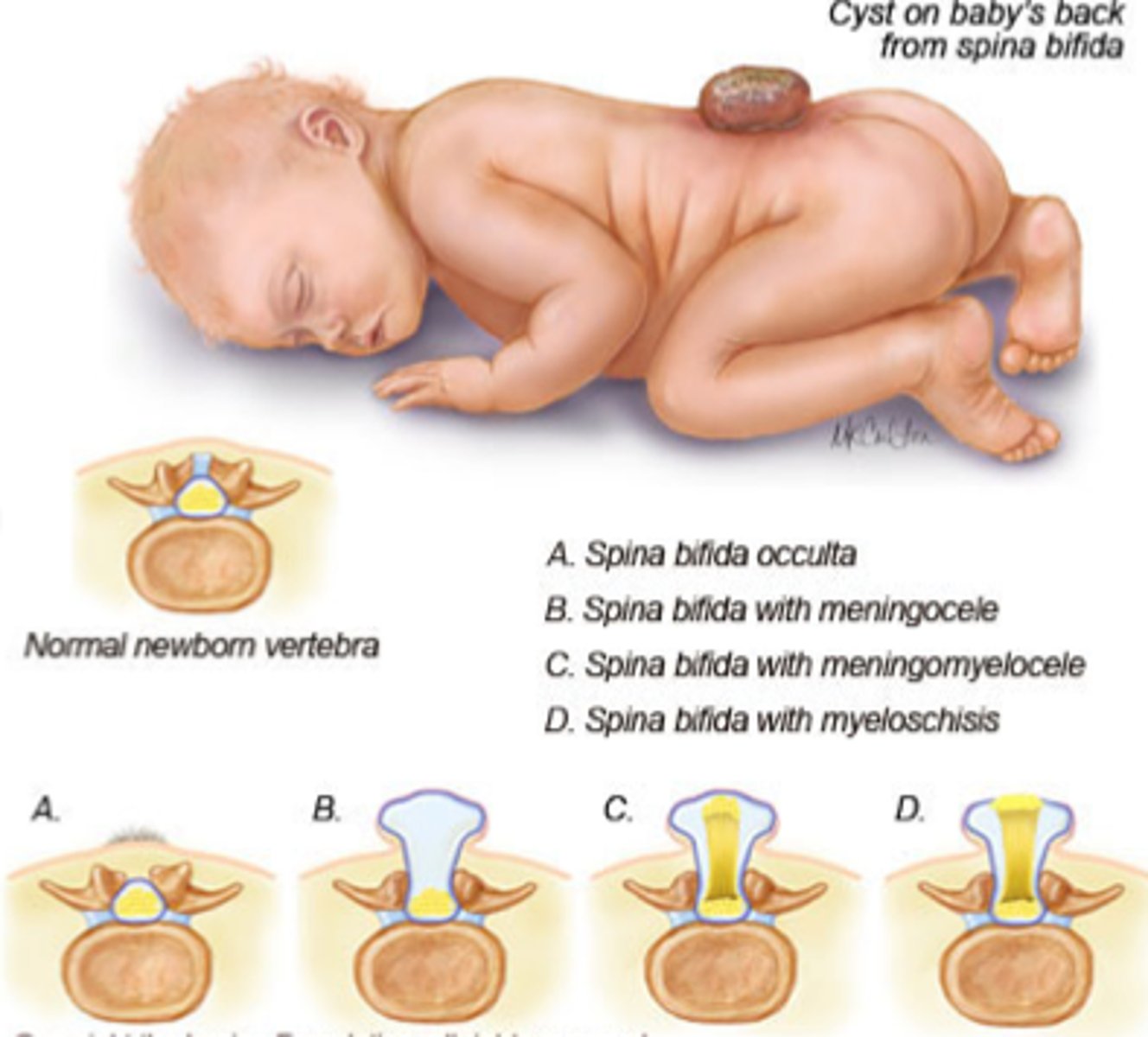
Spina Bifida
Affects 1 out of 1000 newborns; vertebrae form incompletely; sometimes protrusions are evident; paralysis and loss of feelings in limbs, bowls and bladder can result; treated surgically
Senility
Loss of mental capabilities as a result of the normal aging process

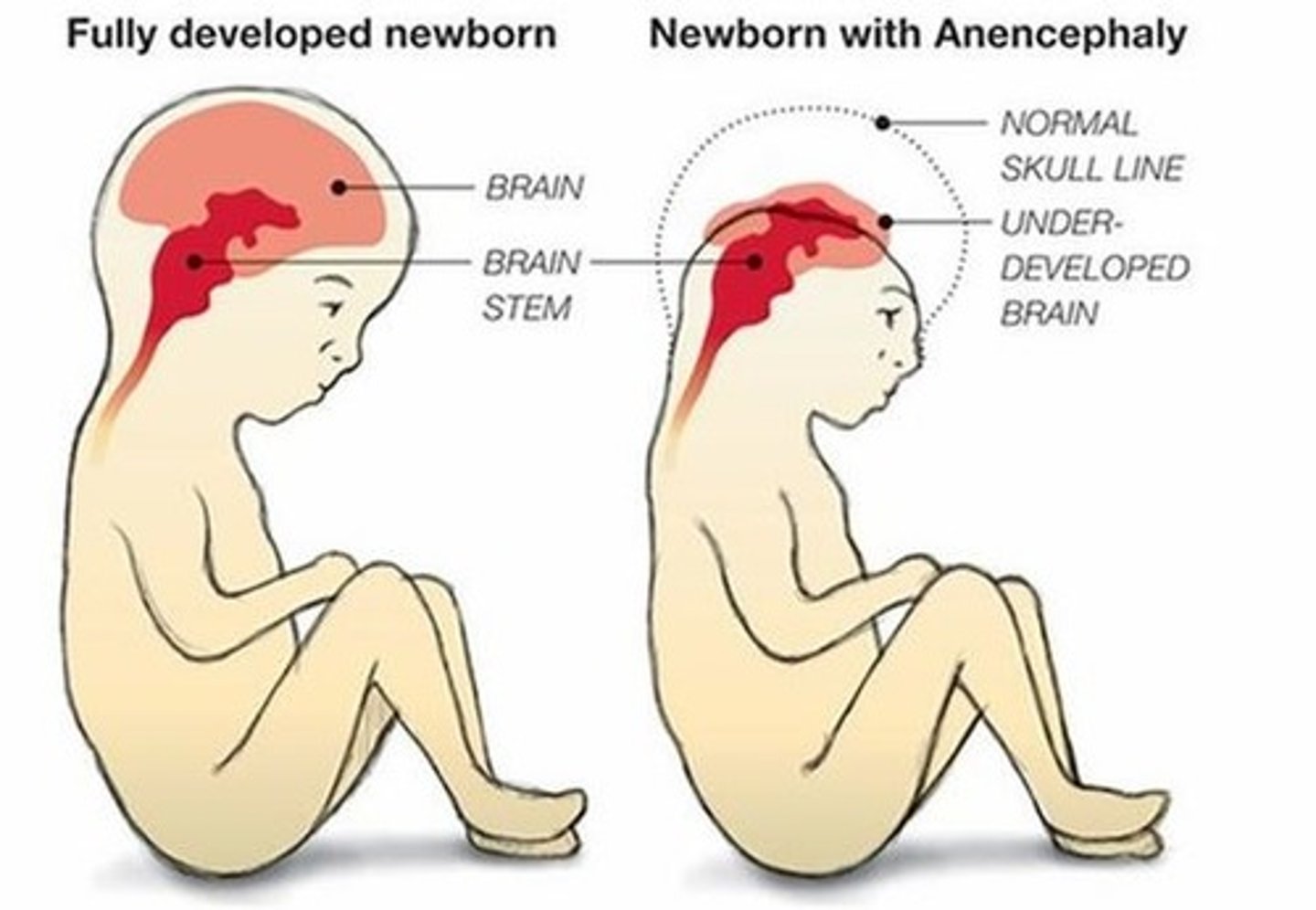
Anacephaly
Failure of the brain to form; can be caused by low levels of folic acid during preganancy
Cerebral palsy
A condition characterized by paralysis, weakness, lack of coordination and other type of motor problems; caused by damage to parts of the brain, before, during or shortly after birth; some individuals have mental retardation and some do not. The severity depends on the parts of the brain that are damaged and the extent to which they are damaged.

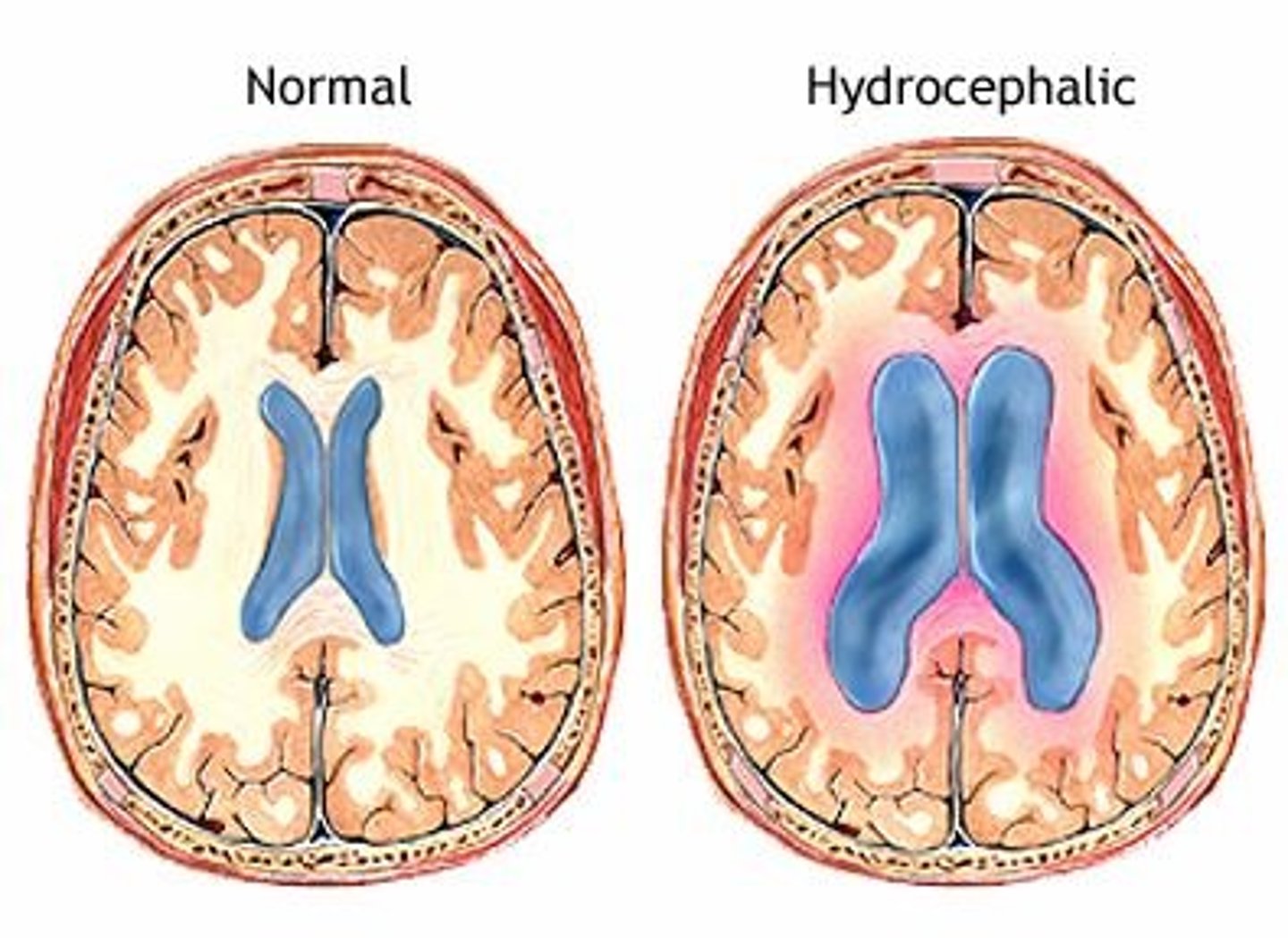
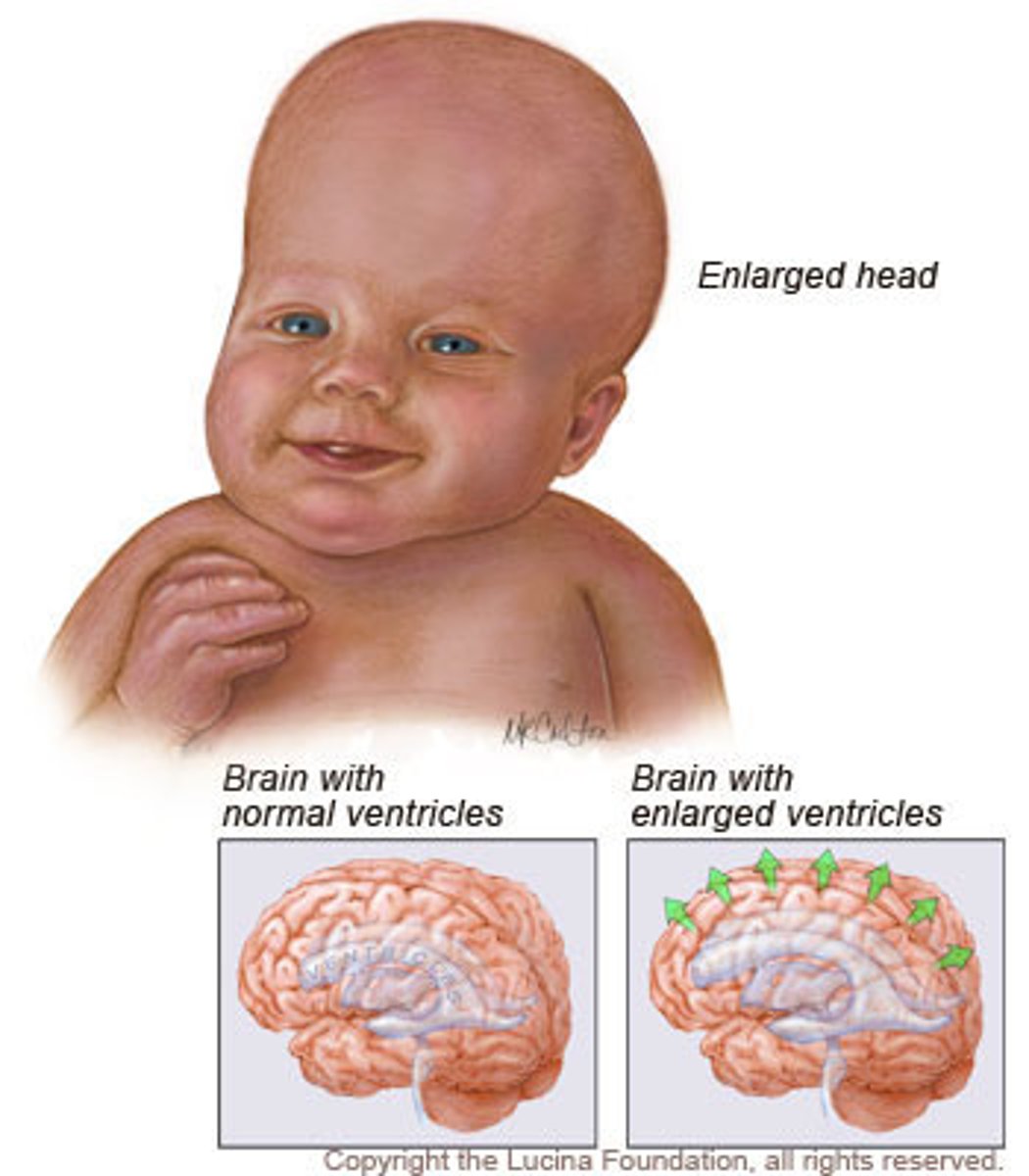
Hydrocephalus
Condition in which excess cerebrospinal fluid accumulates within the ventricles.
Degenerative Diseases
Diseases that result in the loss of brain tissue and brain function include ALS, Alzheimer's, Huntington's and Parkinson's