Module 7 Flashcards
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Viruses
Obligate intracellular pathogens that require host cells to complete life cycle
Features of viruses
Not made of cells
cannot reproduce independently
does not undergo self-division
Composition of viruses
Composed of just protein and nucleic acid genome
Describe the nucleic acid genome of viruses
Can be either DNA or RNA
surrounded by protective protein coat = CAPSID
some viruses contain lipid membrane envelope with glycoproteins for attachment
Life cycle of a virus
Attachment to the cell and entry
Production of new viral proteins
Replication of Virus genome within cell
Assembly and exit of new virus particles to go find another cell
Common routes of entry for viruses
skin
conjunctiva
respiratory
GI
genitourinary
Tropism
the specificity of a virus for a particular host tissue or cell type
Types of Virus transmission
Contact transmission
Transmission between humans
Transmission from animals
Contact transmission
transmission via:
aerosols/mucous
fecal-oral
skin lesions
body fluids
Transmission between humans
horizontal transmission from person to person (contact transmission)
vertical transmission from mother to baby (placental, utero, breast milk)
Transmission from animals
Involves:
vectors (birds, insects)
vertebrate reservoirs (dogs and rabies)
3 main ways of viruses spreading within a host
Localized infection
Disseminated infection
Systemic infection
Localized infection
occurs at site of entry
viruses replicate in specific region of body
Disseminated infections
virus begins at primary site of infection and extends beyond to other regions of the body
Systemic infection
involves the spread of viruses throughout the body affecting multiple organs and tissues
Acute infections
rapid onset, fast viral replication, short duration
Persistent infections
slow and chronic, long-lasting, may remain dormant or react periodically
Prions
Infectious agents that cause fatal neuroldegenerative diseases
do not contain nucleic acid
comprised of misfolded proteins that are self-replicating
Prion reproduction
existing prions stimulate the conversion of normal cellular protein (PrPc) into a misfolded disease causing protein (PrPsc) that are resistant to proteinases
What is the SC in PrPsc
stands for "scrapie," a prion disease that was discovered in sheep
originally thought to be a virus - but after resisting heat, chemicals, UV, determined that scrapie lacked nucleic acid (unique to prions)
Human spongiform encephalopathies
caused by buildup in PrPsc in neurons leading to brain damage
Disease can be:
acquired from environment
genetic
sporadic / spontaneous
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD)
fatal neural disease sure to PrPsc in brain leading to death of neurons
a subset of spongiform encephalopathies
Can arise via:
Sporadic CJD
Genetic CJD
Acquired CJD
Three types of CJD: Mad Cow Disease, Variant CJD (vCJD)
Sporadic CJD
arises from spontaneous PrPc → PrPsc change
Genetic CJD
inherited mutation in PRNP gene causing CJD
specifically causes Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker Syndrome (GSS) and Fatal Familial Insomnia (FFI)
Acquired CJD
rare but involves human-human transmission
Mad Cow Disease
neurodegenerative disease of cattle
in 1985, revealed to be new transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (Bovine spongiform encephalopathy - BSE)
caused by cattle on high protein diets
Variant CJD
a form of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease associated with the consumption of beef products contaminated with BSE
Mode of prion transmission
ingestion
blood transfusion
treatments involving human cadaver products
contaminated surgical instruments
hormone replacements
brain tissue grafts
ocular tissue grafts
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
Belongs to Herpesviridae family and Alphaherpesvirus subfamily
Includes:
HSV-1
HSV-2
Varicella Zoster Virus
Virus has latent infection in sensory/peripheral neurons
Transmission via direct contact or body fluids
Similarities between HSV1 and HSV2
double strand viruses
replication occurs in host cell nucleus
similar genomes
both can cause oral and genital infections
Differences between HSV 1 and 2
HSV 1
more commonly associated with cold sores
often transmitted through oral-oral or oral-genital contact
HSV 2
more commonly associated with genital infections
often transmitted through sexual contact
Primary infection of HSV
break in skin/mucosa → virus accesses mucosa → infection in epithelial cells → virus replication → new viruses released → new viruses access sensory nerve endings to the sensory ganglions (retrograde transport)
Latent infection of HSV
occurs after primary infection
virus is contained in non-replicative state within sensory neurons - hidden from immune system
virus will later enter replicative state and travel from ganglion to sensory nerve endings (anterograde transport)
this process ensure herpes for life
Human Papilloma Virus
a non-enveloped virus with ciruclar dsDNA genome (6-8 kilobase pairs)
Contains 8 different gens in its genome
6 early genes: E1, E2, E4, E5, E6, E7
2 late genes: L1, L2
Transmission of HPV
Skin or mucosal contact
Infection is latent for 3-4 months before symptoms appear
forms hyperproliferative lesions (cancerous lesion) and benign warts
Infection cycle of HPV
beings with abrasion of skin/mucosa that exposes basal membrane to epithelial cells → HPV is replicated within basal cells → expression of viral gene products as basal tissue differentiates and ascends into surface epithelia
Oropharyngeal HPV
spread through mouth-mouth or mouth-genital contact
often forms benign warts on lips, mouth, throat - can be cancerous in rare cases
Oral Papillomas
3 Types: Squamous papilloma, Verruca Vulgaris, Condyloma Acuminatum
Squamous Pailloma
Usually a single lesion on the lip, palate, or tongue
Verruca Vulgaris
Wart of gums - seem in children with warts on fingers that touch their mouth
Condyloma Acuminatum
Lesion on labial mucosa, lingual frenum, and soft palate
Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
cancer found on pharyngneal walls, soft palate, base of tongue, tonsils.
72% of the time, this cancer is caused by HPV
Oral tuberculosis
Caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Type IV Hypersensitivity (granulomatous inflammation)
Primarily occurs in lung - occasionally progresses to tongue (uncommon)
causes chronic ulcerations or swellings
Oral Syphilis
Caused by Treponema Pallidum
3 Three:
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Primary Syphilis
Characterized by Chancre
forms 3 to 90 days post infection
mainly in genital areas but can also occur on lips
Painless ulceration
Secondary Syphilis
Characterized by Mucous patches
4-10 weeks post infection
systemic symptoms (fever, headache, malaise, pain, etc)
Maculopapular cutaneous rash
Tertiary Syphilis
Characterized by Gumma (Granulomas)
30% of syphilis progresses to tertiary
may cause perforation in the palate into the nasal cavity
interstitial glossitis (lobular pattern on tongue)
luetic glossitis (loss of lingual papillae on dorsal surface of tongue)
Oral Candidiasis
Caused by Candida Albicans and Erythematous Candidiasis
Associated lesions:
denture stomatitis, Angular Cheilitis, Median Rhomboid Glossitis, Linear Gingival Erythema
Other types of Candidiasis
Pseudomembranous Candidiasis (ORAL THRUSH)
Chronic Hyperplastic Candidiasis
Chronic Mucocutaneous (occurs on skin outside the oral cavity)
Other types of Herpes Viruses
HHV 4: Epstein-Barr Virus → “mono"
HHV 5: Cytomegalovirus (CMV) → opportunistic infections in immunocompromised patients
HHV 6: Roseola → affects young children
HHV 8: Kaposies Sarcoma → associated with HIV patients
Acute Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
Gingival ulcer that is caused by HSV 1 → painful, enlarged, red gingiva
generally in infants and young children
Two types of fungal infections
Mold and Yeast
Mold
furry growth on surface of organic matter caused by fungi in for of multicellular filaments called hyphae
Yeast
single celled fungus that reproduce by budding
Things that increase risk of fungal infections
Acute leukemia
Neutropenia
Immunosuppressive therapy
Glucocorticoids
Mucositis
Central venous catheders
Broad antibiotic use
Genetics
HIV
Lung cavities
Antifungal drug mechanism of action
target cell wall/membrane
ex,, Amforin B and Nystatin create pores in fungal cell wall
Azoles interfere with ergosterol (cell mem component) synth
Echinocandins also attack cell membrane
Oral Thrush
AKA pseudomembranous Candidiasis
caused by candida albicans
occurs in patients that overuse antibiotics or are immunodeficient
Local treatment: nystatin, Amphotercin B, Miconazole
Systemic Treatment: Fluconazole
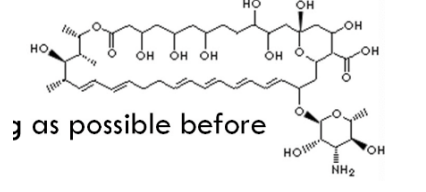
Nystatin oral suspension
Take 4 times daily - 100,000 units → swish in mouth for as long as possible before swallowing
Drug class: polyenes
Mechanism: binds to sterol in fungal cell membrane and creates pores in cell membrane
Use: candida fungi
DDIs: none
Absorption: none
Amphotericin B lozenges
suck on 10mg lozenge 4 times daily
Miconazole oral gel
take 4 times daily, 2.5 ml - swish in mouth for as long as possible before swallowing
Treatment for Aspergillus Infection
Voriconazole loading dose → the maintenance dose
Alternatives:
liposomal, Amphotericin B, lsavuconazole, posaconazole
Treatment of Candida infection
Caspofungin (loading dose then maintenance dose)
Anidulafungin (LD then MD)
Micafungin
Fluconazole (LD then MD)
Purpose of a loading dose
to quickly achieve a therapeutic level of a medication in the bloodstream before switching to a maintenance dose
Fluconazole
Drug class: Triazole
Mechanism of Action: inhibits ergosterol synth for cell wall formation
Use: against candida albicans
treat oral thrush: 50-200 mg daily
treating other invasive fungal infections:
LD up to 800 mg
MD up to 400 mg
DDIs: inhibits CYP3A4, 2C19, 2C9 enzymes
Dose must be adjusted depending on renal function
Voriconazole
Drug class: triazole
Mechanism of action: inhibits ergosterol for cell wall synth
Use: against Candida and Aspergillus infections
treat invasive disease: 400mg LD or 6 mg/kg IV every 12 hours for the first 24 hours, then 200mg MD or 4 mg/kg IV every 12 hours
DDIs: inhibits CYP3A4, 2C19, 2C9
Adverse Effects: hepatotoxicity, hallucinations, rash
Posaconazole
Drug class: triazole
Mechanism of Action: inhibits ergosterol
Use: against candida and Aspergillus + Mucorales
DDIs: p-glycoprotein efflux substrate (reduces drug absorption)
Adverse effects: hepatotoxicity
Typical Characteristics of Fungi
Eukaryotic
lack chlorophyll therefore absorb nutrients from other organisms
reproduce sexually (fusion of two fungi) and asexually (spores)
Reproduction of different fungi
Yeast: circular fungi that reproduce by budding
Pseudohyphae: reproduce by budding - budded cell attaches to parent to form chain
Hyphae: yeast cell that emits a tail-like projection for budding
Mating Projection: rare - cell extends appendage for mating
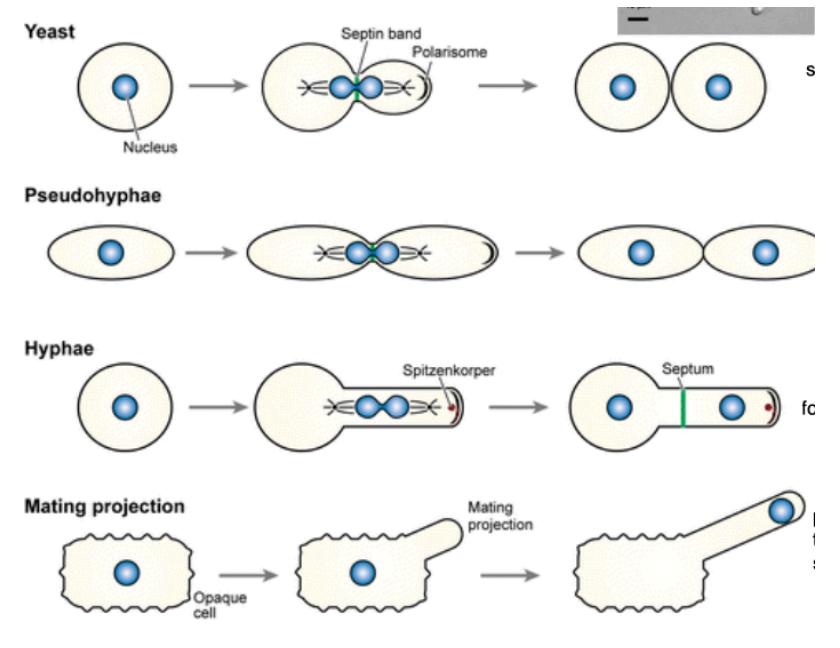
Yeast Cell Membrane
Plasma membrane made of ester-linked phospholipids and sterols
outer wall contains mannose (pro-inflammatory)
inner wall contains chitin and glucans
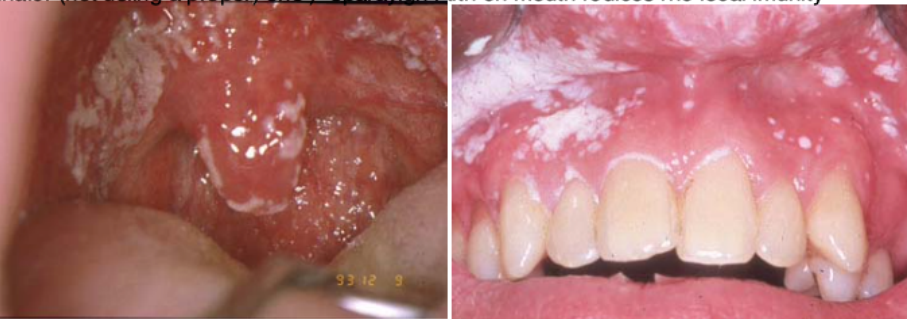
Name the oral candidiasis
Pseudomembraneous candidiasis
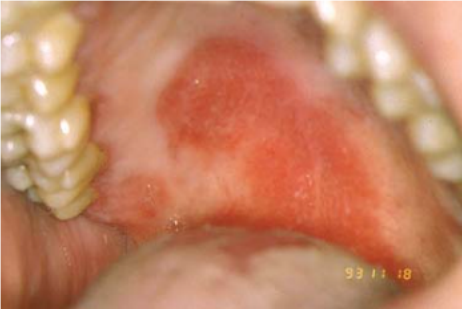
Name the oral candidiasis
Erythematous candidiasis
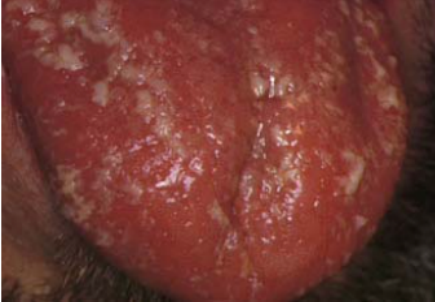
Name the oral candidiasis
Mixed candidiasis from Tc therapy
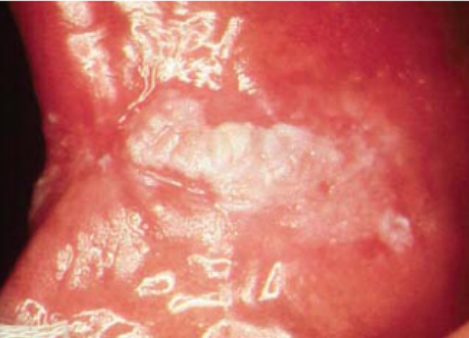
Name the oral candidiasis
Hyperplastic candidiasis
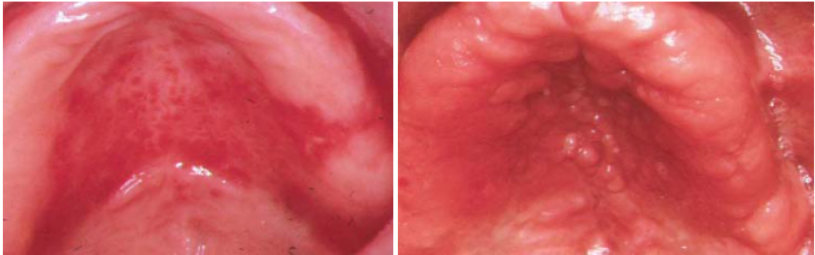
Name the candidiasis associated lesion
Denture Stomatitis
Newton’s Type II (left)
Newton’s Type III (right)
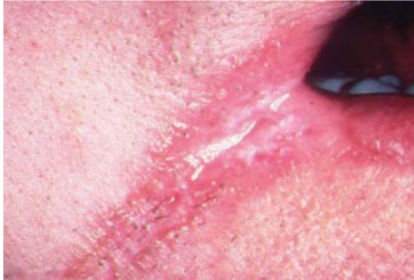
Name the candidiasis associated lesion
Angular cheilitis
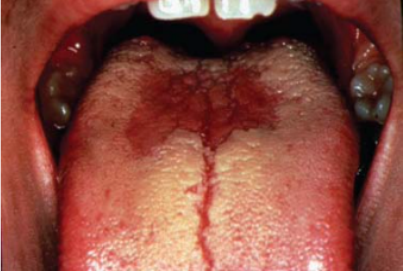
Name the candidiasis associated lesion
Median Rhomboid Glossitis
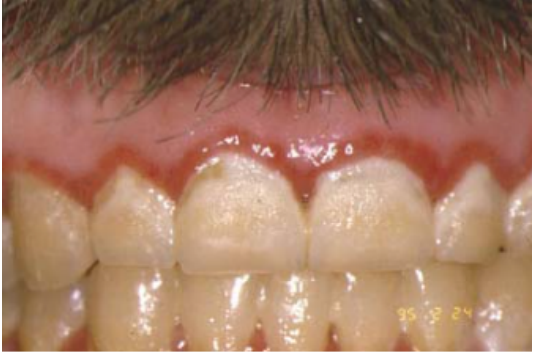
Name the candidiasis associated lesion
Linear Gingival Erythema
Predisposing factors to oral candidiasis
Physiological - age, pregnancy
Local Trauma - mucosal irritation, poor OH
Antibiotics - prolonged or broad use
Corticosteroids
Malnutrition
Endocrine disorders
Blood disorders
Immune deficiencies
Xerostomia
Reproduction of candida
Asexual: budding
Sexual: conjugation of haploids
Parasexual: conjugation of diploids
Yeast-Hyphal transition
Yeast is dormant → transitions in hyphal form which causes the infection
hyphal form better evades immune system
Virulence traits of Candida albicans
Adherence
Invasion
Disarming host defence
Adherence of C. albicans
Yeast agglutin-like sequence (ALS) proteins 1 and 5 bind to buccal epithelia and fibronectin
hyphal proteins bind to buccal epithelia
glycoproteins assist in anchoring to surface
Invasion of C. albicans
a) non-phagocytic cell endocytosis via Als3 Induction
b) active penetration with hyphae into host cells
Disarming host defense by C. albicans
downregulate epithelial TLR4 expression
aspartic proteases degrades C3b
inhibits phagolysosome formation
ROS inhibition
modulation of cytokine signals
Ways that hyphae can evade host immune system
A) if hyphae are phagocytosed, they can grow a hyphae through the phagocyte cell wall, leading to escape
B) hyphae reduces TLR4
C) hyphae blocks the complement system
D) prevents fusion between the phagosome and the lysosome - prevents phagolysosome formation
E) can modulate various immune cell function by modulating cytokine production