Economics - Chapter 3: Microeconomic Decision Makers
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/234
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
235 Terms
1
New cards
What is a barter?
To exchange goods or services for other goods or services without using money
2
New cards
What did traditional economic systems depend on to trade goods and services?
Depended on bartering for the trade of goods and services between individuals and communities
3
New cards
What is money?
Anything that is widely accepted or used to exchange for goods and services
4
New cards
How many functions of money is there in an economy?
4: Medium of exchange, store of value, unit of account, standard for deferred payments
5
New cards
What is medium of exchange?
Money is widely accepted and can be used in exchange for goods and services
6
New cards
What is store of value?
Money can be stored for some period of time and still remain valuable in exchange
7
New cards
What is unit of account?
Money provides a common measure of the value of goods and services being exchanged
8
New cards
What is standard for deferred payments?
Money is a widely accepted way to value a debt; thereby allowing goods and services to be acquired now and paid for in the future
9
New cards
If you bought a coffee for $25, what is the function of money used?
Medium of exchange
10
New cards
If you are selling an apple for $10 and keeping the money to spend on an orange for $10 next month, what is the function of money used?
Store of value
11
New cards
If you are comparing a small soft drink ($21) against a medium ($26) and a large ($28), which function of money is used?
Unit of account
12
New cards
If you are buying a house in the UK and borrowing money (a mortgage) to pay for it over the next 25 years, what function of money is used?
Standard for deferred payments
13
New cards
What is a commercial bank?
A financial intermediary that brings together customers deposits they wish to save and customers that want to borrow
14
New cards
What is a central bank?
A single national bank that provides financial and banking services for its country's government and commercial banking system
15
New cards
What is an interest rate?
The return on savings and the cost of borrowing
16
New cards
What is the banking cycle?
1. People and businesses deposit money into commercial banks that hold this money in their reserves.
2. The banks pay interest to the depositors to encourage them to deposit money with them (eg. an interest of 2% of the deposited amount per annum)
3. The banks then loan out these reserves to individuals and businesses who spend this money on goods and services (or invest in the case of businesses)
4. The banks charge interest to the lenders to make a profit
2. The banks pay interest to the depositors to encourage them to deposit money with them (eg. an interest of 2% of the deposited amount per annum)
3. The banks then loan out these reserves to individuals and businesses who spend this money on goods and services (or invest in the case of businesses)
4. The banks charge interest to the lenders to make a profit
17
New cards
What are the functions of commercial banks?
- Accept deposits of money and savings
- Help customers make and receive payments
- Make personal and commercial loans
- Help customers make and receive payments
- Make personal and commercial loans
18
New cards
What are commercial banks able to do?
- buy and sell shares for customers
- provide insurance
- operate pension funds
- provide financial and tax planning advice
- exchange foreign currencies
- provide insurance
- operate pension funds
- provide financial and tax planning advice
- exchange foreign currencies
19
New cards
What is the initial public offering?
Where investors can bid for the first publicly available shares in the public limited company on the stock exchange
20
New cards
What is a stock market?
A market where shares in companies and other securities are bought and sold
21
New cards
How does economic growth affect the price of shares in the stock market?
Higher economic growth or better growth prospects may been an increase in profits for firms due to an increased demand for goods and services. This may increase company dividends and therefore increase share prices.
22
New cards
How do interest rates affect the price of shares in the stock market?
Lower interest rates help boost economic growth, this increasing profits for firms. also, lower interest rates increases the return on bank deposits and bonds, thus increasing the attractiveness of shares
23
New cards
How does stability affect the price of shares in the stock market?
Stock markets react negatively to shocks that could threaten future macroeconomic stability and growth. Bad news, political instability and poor economic policies will decrease stock prices.
24
New cards
How does confidence and expectations affect the price of shares in the stock market?
Economic news that makes investors optimistic about the future will increase demand for shares and increase share prices. Investors are always trying to predict future movements in share prices
25
New cards
How does the bandwagon effect affect the price of shares in the stock market?
People at times tend to follow the crowd. If price falls, people may feel the need to exit the market and sell their shares too. This will decrease share prices further
26
New cards
How do related markets affect the price of shares in the stock market?
Investors can invest in multiple markets, including bond and commodity markets. If they feel these other markets are overvalued, they may sell these and buy stock. This would decrease share prices.
27
New cards
How does price to earnings ratio affect the price of shares in the stock market?
If the price of a share rises and the earning of the company remin the same, then the company's price earnings (price / earnings) ratio will increase. This could be a sign that the shares are overvalued and could prompt a correction.
28
New cards
What is a bull market?
A persistent growth in a stock market, when the value of shares is growing rapidly
29
New cards
What is a bear market?
A persistent fall in the stock market, when the value of shares is falling rapidly
30
New cards
What are the wage related factors of choosing an occupation?
Basic pay, overtime, bonus, commission
31
New cards
What is basic pay?
The amount of money received by an employee before any increments or deductions are made
32
New cards
What is overtime?
Hours worked in addition to the basic contracted hours, overtime is usually paid at a higher rate than normal hours. The purpose of giving overtime pay is to encourage people to work at 'unsocial hours'
33
New cards
What is a bonus?
A one-off monetary incentive to encourage workers to work harder or longer, eg. meet a particular sales or production target
34
New cards
What is a commission?
A payment made as a percentage of sales revenue that a salesperson makes or as an amount per unit; this will encourage the salesperson to be enthusiastic about selling more
35
New cards
What are the non-wage factors of choosing an occupation?
Job satisfaction, career prospects, fringe benefits, job security, length of holidays, travelling distance
36
New cards
What is job satisfaction?
Many people are prepared to work for lower pay if they enjoy the work, some people prefer a company, others prefer the freedom of working for themselves, others want to travel with work
37
New cards
What are career prospects?
Many people want to work in occupations where there is an opportunity for promotion. This may provide an opportunity to take on more responsibility or earn a higher wage
38
New cards
What are fringe benefits?
These are non-financial incentives given to employees, eg. subsidised housing, company car/subsidised transport, subsidised company products, company pension
39
New cards
What is job security?
Most people want to be sure that the job they choose to do will be secure and that they will not be laid off
40
New cards
How is length of holidays a non-wage factor for choosing an occupation?
Many countries have implemented labour laws requiring that the workers get a certain number of days as holidays. Additional days may act as an incentive
41
New cards
How is travelling distance a non-wage factor for choosing an occupation?
Having to travel a long distance to attend to the work may make an individual seek employment at a firm which is nearer to home, even if the firm nearer to home pays a lower salary
42
New cards
What are the income patterns over an individual's lifetime?
People borrow money for college, buying a home
People are saving and earning money during their prime working years
people are dissaving during retirement
People are saving and earning money during their prime working years
people are dissaving during retirement
43
New cards
What is wealth?
A stock of assets including money held in bank accounts, shares, bonds, cars, houses
44
New cards
What is disposable income?
Income left after direct tax
45
New cards
What are the three main sources of income?
Active: generated from working
Portfolio: capital gain from selling stocks, assets, property
Passive: generated from assets you own (dividends, interests, rent)
Portfolio: capital gain from selling stocks, assets, property
Passive: generated from assets you own (dividends, interests, rent)
46
New cards
What is saving?
The process of setting aside a portion of current income for future use
47
New cards
What is borrowing?
Act of receiving something which will be returned in the future
48
New cards
What are the factors affecting borrowing levels?
- income and wealth levels
confidence in the economy and future prospects
- interest rates
- cultural attitudes to borrowing
- state provision of education and healthcare
- house prices
confidence in the economy and future prospects
- interest rates
- cultural attitudes to borrowing
- state provision of education and healthcare
- house prices
49
New cards
What is the labour market?
The place where businesses and employees interact with each other
50
New cards
What happens to labour in an economy?
People supply labour and firms demand labour in an economy
51
New cards
What is the graph for wage and workers?
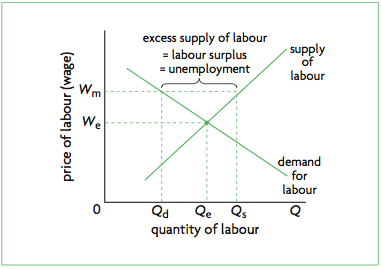
52
New cards
What is derived demand?
The demand for a commodity, good or service comes from the demand for something else
53
New cards
Example of derived demand
- If the demand of hotels increase, the demand for the number of workers will increase
- If the demand for cars increase, the demand of petrol will increase, petrol being derived demand
- If the demand for cars increase, the demand of petrol will increase, petrol being derived demand
54
New cards
What are the factors that affect the supply for labour?
Social trends, changes in net migration, changes in benefits that change employee's incentives to work, income tax changes
55
New cards
What are the factors that affect demand for labour?
Changes in cost of hiring and training workers, price of other factors of production, government employment regulation changes
56
New cards
If the price of machinery used to harvest wheat falls, what is the effect on the market for farm worker?
There is a decrease in the demand of labour. The wage rate falls from W1 to W2. The new equilibrium quantity is Q2
57
New cards
If the school leaving age is increased from 16 to 18, what is the effect on the market for waiters?
There is a decrease in the supply of labour. The wage rate falls from W1 to W2. The new equilibrium quantity is Q2
58
New cards
If legal documents must be rewritten following Brexit, what is the effect on the market for lawyers?
There is an increase in the demand of labour. The wage rate rises from W1 to W2. The new equilibrium quantity is Q2
59
New cards
If immigration quotas into the UK are increased, what is the effect on the market for shop workers?
There is an increase in the supply of labour. The wage rate falls from W1 to W2. The new equilibrium quantity to Q2
60
New cards
What is a trade union?
An organisation of workers that come together to achieve common goals
61
New cards
How do trade union workers negotiate?
Trade union represents their members in meetings and user collective bargaining to negotiate better pay and conditions
62
New cards
What are the benefits of a trade union?
• Protect employment rights
• Provide information on rights and entitlements
• Facilitate bargaining by speaking in behalf of every union member
• Simplify the communication and bargaining process of employers
• Negotiate on behalf of their members with employers
• Provide services such as insurance and saving schemes
• Represent their members concern to the public through the media
• Fight for equality for a fair society
• Provide information on rights and entitlements
• Facilitate bargaining by speaking in behalf of every union member
• Simplify the communication and bargaining process of employers
• Negotiate on behalf of their members with employers
• Provide services such as insurance and saving schemes
• Represent their members concern to the public through the media
• Fight for equality for a fair society
63
New cards
What are the aims of trade unions?
- Represent workers with regard to pay and working conditions
- Bargain for higher wages with the possibility of going on strike to target higher wages
- Co-ordinate with firms to implement new working practises and negotiations with workers
- Bargain for higher wages with the possibility of going on strike to target higher wages
- Co-ordinate with firms to implement new working practises and negotiations with workers
64
New cards
Why has trade union membership declined?
The large advancements structurally in today's economies change, moving away from manufacturing. The power has also been eroded from trade unions
65
New cards
Why does the government intervene in labour markets?
- raise wages for the lowest paid workers
- protect the rights of employees (health, safety, gender and age equality, working hours)
- protect the rights of employees (health, safety, gender and age equality, working hours)
66
New cards
What is the national minimum wage?
A minimum wage is a legally-enforced pay floor in a labour market
67
New cards
How does NMW ensure protection of employees' wages?
The government ensures that employees are paid a high enough wage is to introduce a national minimum wage
68
New cards
What is the effect of the NMW on the market for labour?
As wage increases, less people are employed as firms can't afford that many workers
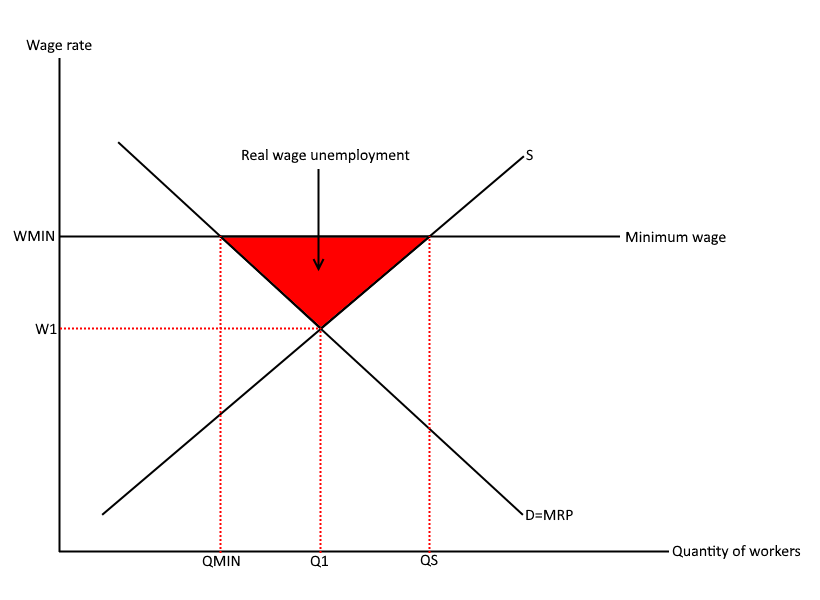
69
New cards
How does the national minimum wage cause unemployment?
The national minimum wage is above the market equilibrium, the quantity supplied of labour will be higher than the quantity demanded by firms. This leads to the excess supply of labour - unemployment
70
New cards
How will the national minimum wage reduce relative poverty and inequality?
A NMW increases the wages of the lowest paid workers in society, this increase in income will reduce relative poverty and inequality
71
New cards
How does the national minimum push inflation?
Higher wages mean higher costs of production for firms. To maintain profit margins, firms may this increase onto consumers via higher prices. The NMW may cause cost push inflation
72
New cards
How does the national minimum wage increase productivity?
Firms may invest more into training their workers to make them more efficient. This increase in productivity will help counteract the increase cost of labour
73
New cards
Why is the lowest income group in society not affected by the NMW?
Those members of society on unemployment benefits will not be affected by the change in the NMW. The lowest income group in society is not affected.
74
New cards
How does the national minimum wage incentivise workers?
Higher wages can incentivise people to work harder. A higher wage could increase the productivity of the workers it affects.
75
New cards
How does the national minimum wage increase participation in the workforce?
An increase in NMW will increase the difference between unemployment benefits and income from employment. This could increase the participation rate in the workforce.
76
New cards
How does the national minimum wage encourage workers to participate in the black market?
The NMW may increase the number of workers int he black market so firms can avoid paying the NMW. Workers in the black market are not protected from exploitation.
77
New cards
How does the national minimum wage not affect some of those who live in countries with higher costs of living?
The cost of living varies depending on where you live in a country. Costs may be higher in certain regions and in cities. The NMW is the same for all workers in the country.
78
New cards
What is division of labour?
Division of labour occurs when production is broken down into many separate tasks
79
New cards
How does division of labour increase productivity?
Division of labour raises the output per person as people become proficient through constant repetition of a task
80
New cards
What is specialization?
When a person, business, region or country concentrates on the production of a specific good or service
81
New cards
What are the advantages of division of labour?
- workers spend time doing the same task and quickly becomes highly skilled and more productive, deducting average cost
- no time is wasted moving between jobs, capital equipment can be used continuously in the production process
- workers can specialise in jobs they are most suited to leading to higher productivity and motivation
- less time and resources are required to train workers as they are only completing specific tasks
- no time is wasted moving between jobs, capital equipment can be used continuously in the production process
- workers can specialise in jobs they are most suited to leading to higher productivity and motivation
- less time and resources are required to train workers as they are only completing specific tasks
82
New cards
What are the disadvantages of division of labour?
- demotivated workers due to repetitive tasks that can cause monotony and boredom
- if one group is unproductive or goes on strike, it could slow down or stop the entire production process
- staff turnover may also increase due to repetition and boredom, this leads to increased recruitment and selection costs
- dividing production into simple tasks makes it easier for firms to replace workers with machines, this may lead to structural unemployment
- if one group is unproductive or goes on strike, it could slow down or stop the entire production process
- staff turnover may also increase due to repetition and boredom, this leads to increased recruitment and selection costs
- dividing production into simple tasks makes it easier for firms to replace workers with machines, this may lead to structural unemployment
83
New cards
What is a firm?
An organisation that brings togethers factors of production in order to produce output
84
New cards
What sectors do firms exist in?
private or public sector
85
New cards
What is the public sector?
The sector of the economy involving assets owned and operated by the government
86
New cards
What is an example of a public sector firm?
Education, emergency services, BBC
87
New cards
How are public sector firms funded by?
- tax revenue
- borrowed money
- charges for some services
- borrowed money
- charges for some services
88
New cards
What is the private sector?
The sector of the economy involving assets owned and operated by individuals or groups
89
New cards
What are the examples of a private sector firms?
Apple, H&M, M&S
90
New cards
What are the four main types of private sector firms?
- sole trader
- partnership
- private limited company
- public limited company
- partnership
- private limited company
- public limited company
91
New cards
What is a sole trader/proprietor?
A business owned by one person who is personally responsible for its debts
92
New cards
What type of liability does sole traders have?
A sole trader has unlimited liability. In the eyes of the law, the sole trader and their business are the same legal entity. Any debts accrued by the business have to be paid by the owner if the business fails.
93
New cards
What is the advantage of setting up as a sole trader?
There are relatively few legal formalities involved in setting up as a sole trader, making it easy to do compared with other types of business ownership
94
New cards
What is the advantage of having personal contact with the consumers for sole traders?
The owner of the business will have personal contact with their customers and staff. This the owner can find out and react to what people want. The personal contact may improve customer loyalty.
95
New cards
What is the disadvantage of being the manager of the business for sole traders?
A sole trader takes on all of the responsibility of managing the business meaning very long hours for the owner. If the owner is ill or goes on holiday this could result in a loss of revenue.
96
New cards
What is the advantage of having full control of the business for sole traders?
The owner has full control over the business and can make decisions quickly. This increases flexibility allowing the firm to be more dynamic and able to react quickly to new problems.
97
New cards
What is the disadvantage of expansion for sole traders?
Most sole traders fund their business through personal savings, borrowing from friends or bank loans. Capital for expansion may be hard to come by as banks can be reluctant to lend to small businesses.
98
New cards
What is the advantage of profits for sole traders?
The sole trader receives all of the profits of the firm and does not have to share them with other partners or shareholders.
99
New cards
What is a partnership?
An arrangement in which two to twenty individuals share the profits and liabilities of a business venture
100
New cards
What is the advantage of skills that partnerships have?
Partners can bring new ideas and skills to a business. Having the skills, client base and experience of more owners could improve the quality of the product and help the business run more effectively.