Physics - Electricity - 3.4 - capacitors
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is a capacitor?
A component that stores electrical energy and charge.
What is the structure of a capacitor?
Two plates of metal separated by a layer of insulation.
What is the symbol for a capacitor?
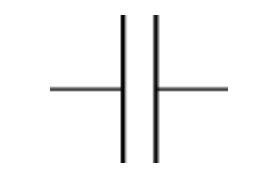
What is capacitance measured in?
Farads (F), more commonly microfarads (Fx10^-6) or nanofarads (Fx10^-9)
What does the capacitance of a capacitor depend on?
Its construction, NOT the charge on it or the potential difference across it.
What happens to the charge on a capacitor as the voltage across it increases?
The charge increases.
What happens when there is an electric field between the plates of a capacitor?
There is a potential difference (voltage) across them.
Is the relationship between voltage and charge on a capacitor linear?
Yes.
Equation: Q=…
Q= CV
Equation: C=…
C = Q/V
What is C?
The capacitance.
What is capacitance?
The ability of a system to store electric charge. The ratio of electric charge to potential difference between two conductors separated by an insulating material.
For a parallel-plate capacitor, what does capacitance depend on?
The surface area of the plates, the distance between the plates and the insulating material between the plates.
Is 1F a capacitance that you would come across in practice?
No, one farad is a very large capacitance.
Work has to be done to move an electron from the negative plate to the positive plate, what would make this even harder?
If the charge on the plates was higher.
The more charge stored on a capacitor…
The greater the stored potential energy.
The area under a charge against voltage graph across a capacitor is equal to what?
The work done in charging the capacitor.
Equation: E c = …
E c = ½ QV
What equation could you use to find the work done in charging the capacitor if the voltage and capacitance was known?
E c = ½ CV²
What equation could you use to find the work done in charging the capacitor if the charge and the capacitance was known?
E c = ½ x (Q²/C)
1 Farad is equal to
1 C V^-1
What is the difference in use between E = QV and E = ½ QV?
E=QV is used when charge is being moved through a fixed voltage, whereas E= ½ QV is used for a capacitor because the voltage increases from 0 to V as the capacitor charges.
What happens to the current when charging a capacitor by a d.c. source?
The current gradually decreases to zero.
What does the rate of current decline depend on?
It depends on the capacitance of the capacitor and the resistance of the circuit.
What does a higher resistance in a circuit mean for the rate of build up of charge in a capacitor?
It will be slower if the resistance is higher.
What happens to the current if a variable resistor is introduced?
The current can be kept constant.
How is it possible to see how long it takes a capacitor takes to charge?
If the current is kept constant.
How can the charge on the capacitor be determined?
By knowing the time and the current, the charge can be determined.
Equation: Q = (current and time)
Q = It
Does charge flow across a capacitor?
No.
As the capacitor gains charge, is it easier or harder to add more charge?
Harder.
What will the final charge of the capacitor equal?
It will equal the e.m.f. of the supply.
What does a current against time graph look like for a capacitance circuit? (Current - y axis, time - x axis)?
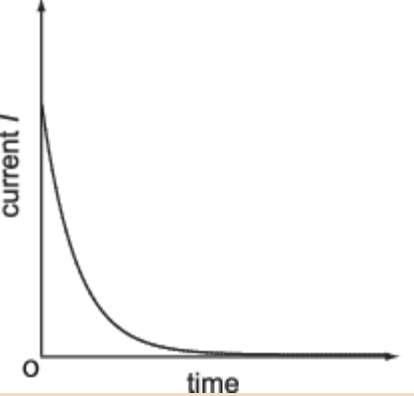
What does a charge against time graph look like for a capacitor? (charge - y axis, time - x axis)
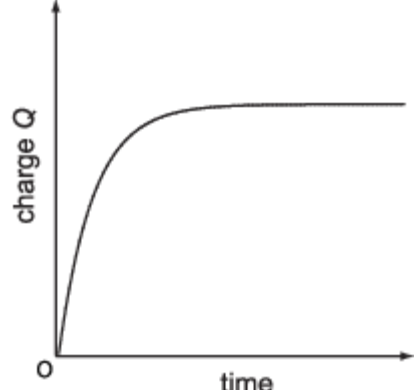
If the battery in a capacitance circuit has a negligible internal resistance then what is an equation for the e.m.f?
E = VC + VR
The voltage across a capacitor is proportional to …
The charge stored on it.
Give an equation for the current, the instant that the switch on the circuit is closed.
I = E/R
As charge builds up on the capacitor, what happens to the voltage across it?
It decreases.
As charge builds up on the capacitor, what happens to the voltage across the resistors?
It decreases.
What does a current against time graph look like for when a capacitor is charging and when it is discharging?
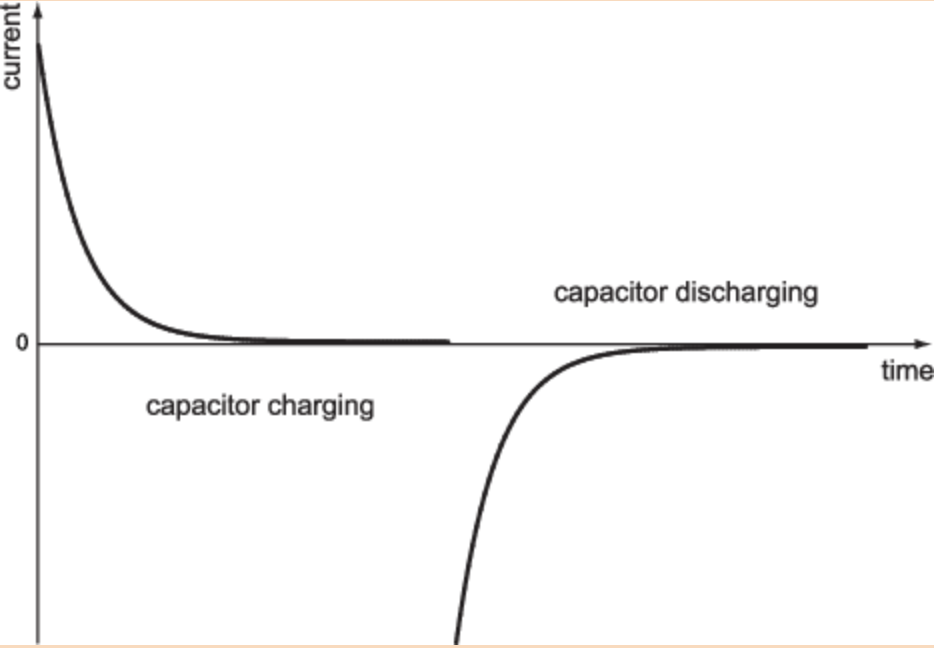
What is the equation for current when the capacitor initially starts charging?
I = Vsupply / R
What is the equation for current when the capacitor initially starts discharging?
I = Vcapacitor / R
Why is the equation when the capacitor starts discharging Vcapacitor and not Vsupply ?
The circuit is disconnected from the supply.