ULL Bio 221 Exam 2
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
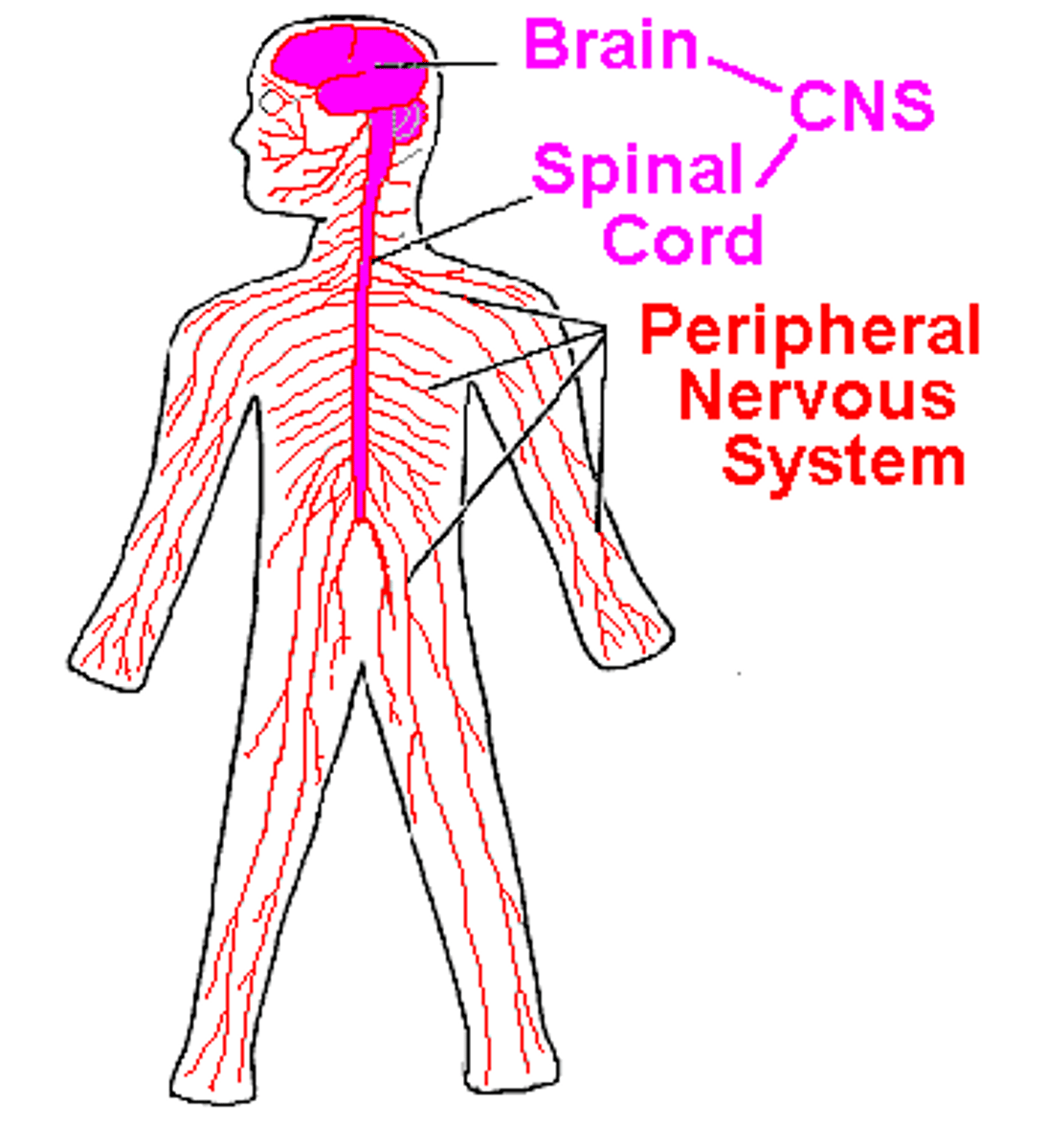
central nervous system (CNS)
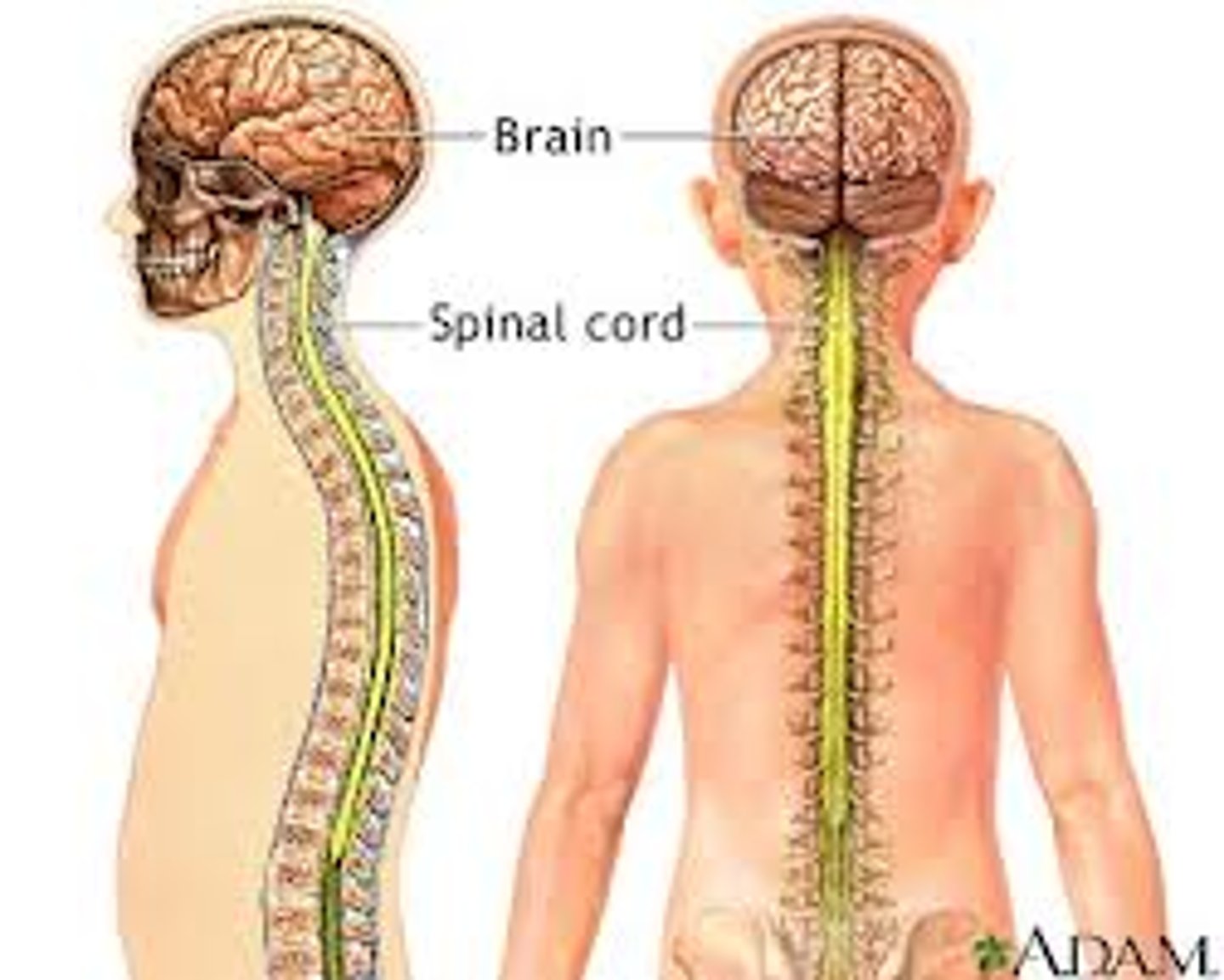
central nervous system (CNS)
consists of the brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
cerebral hemispheres
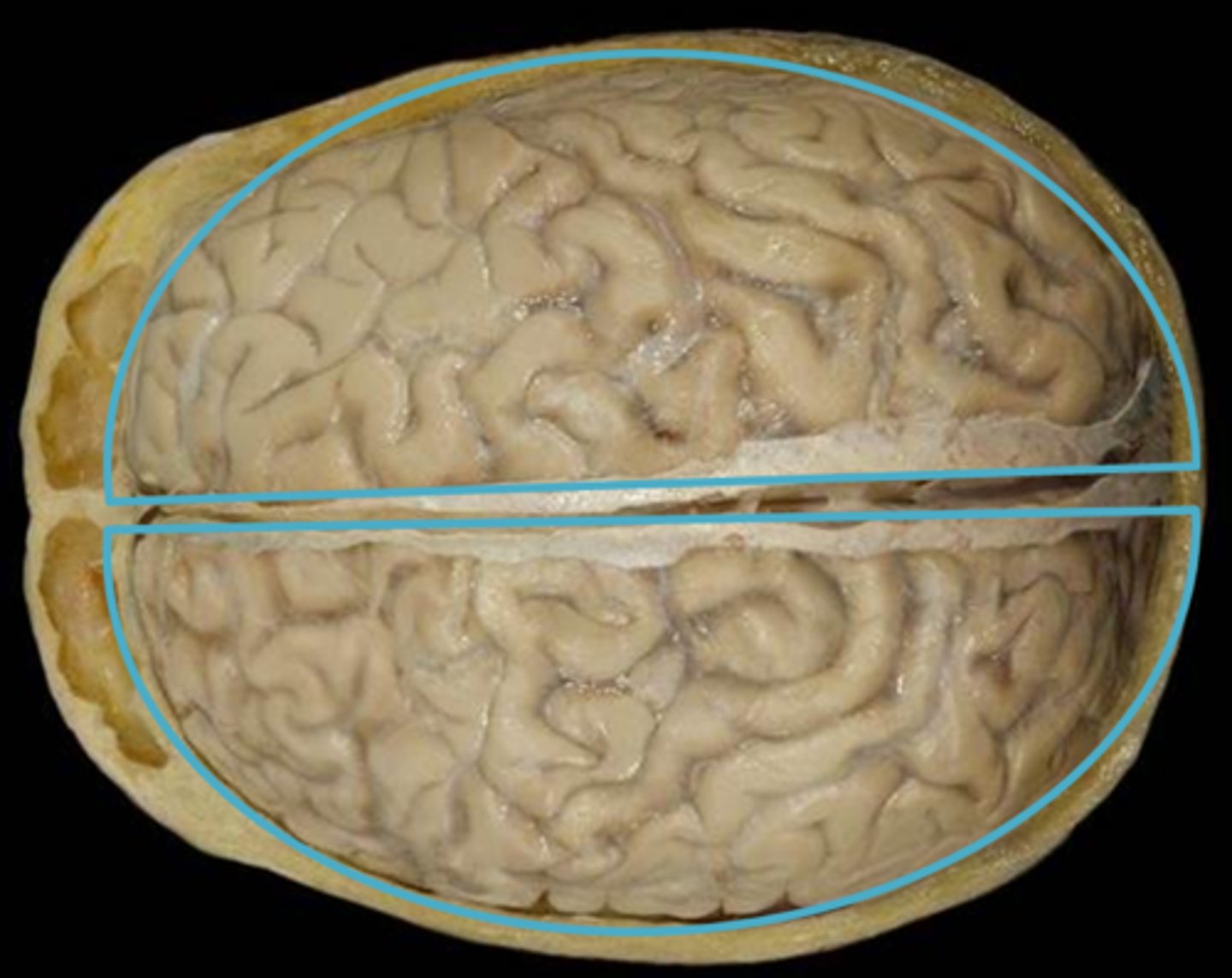
cerebral hemispheres
The right and left halves of the cerebrum
cortex
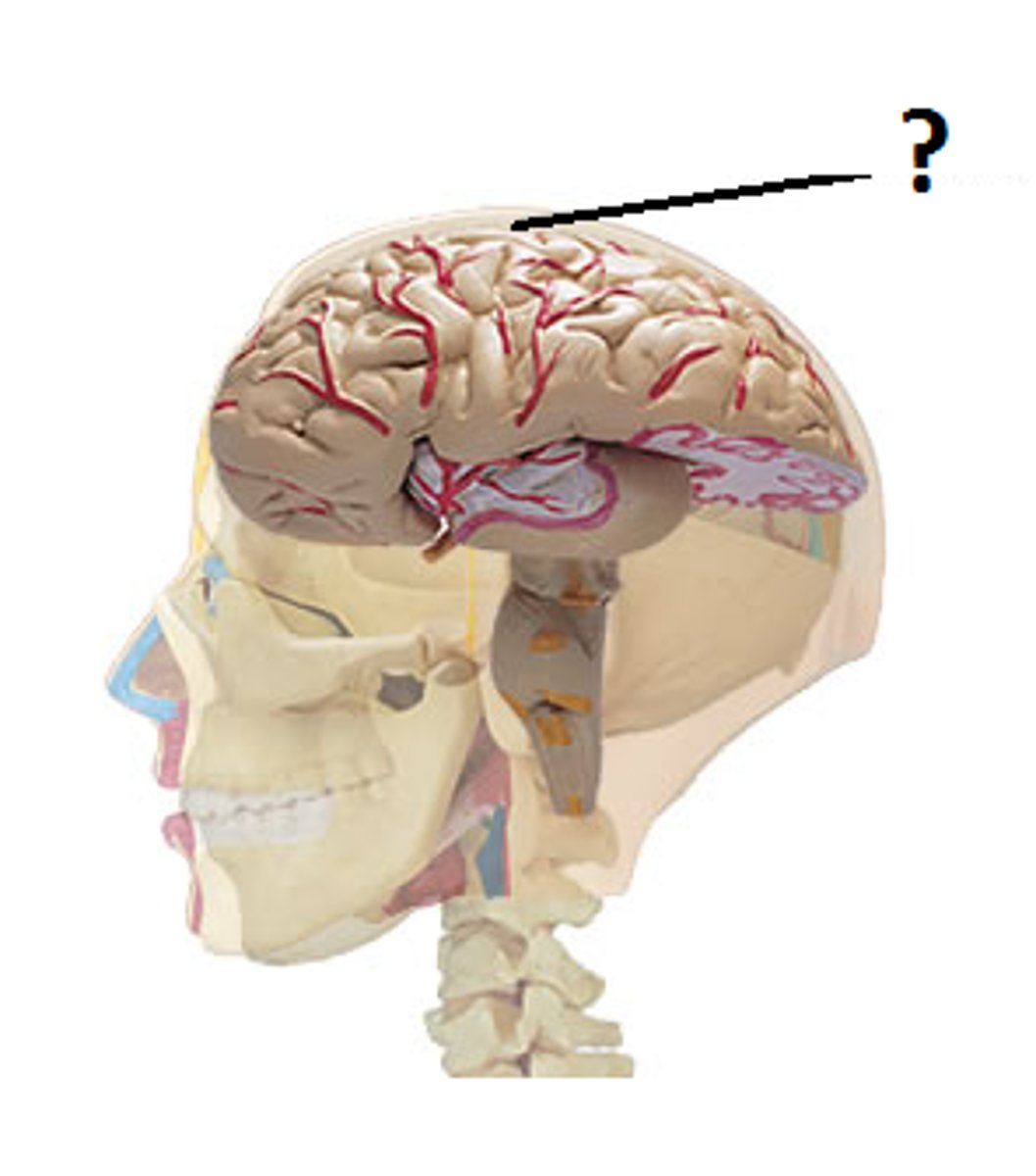
cortex
outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input
gyri
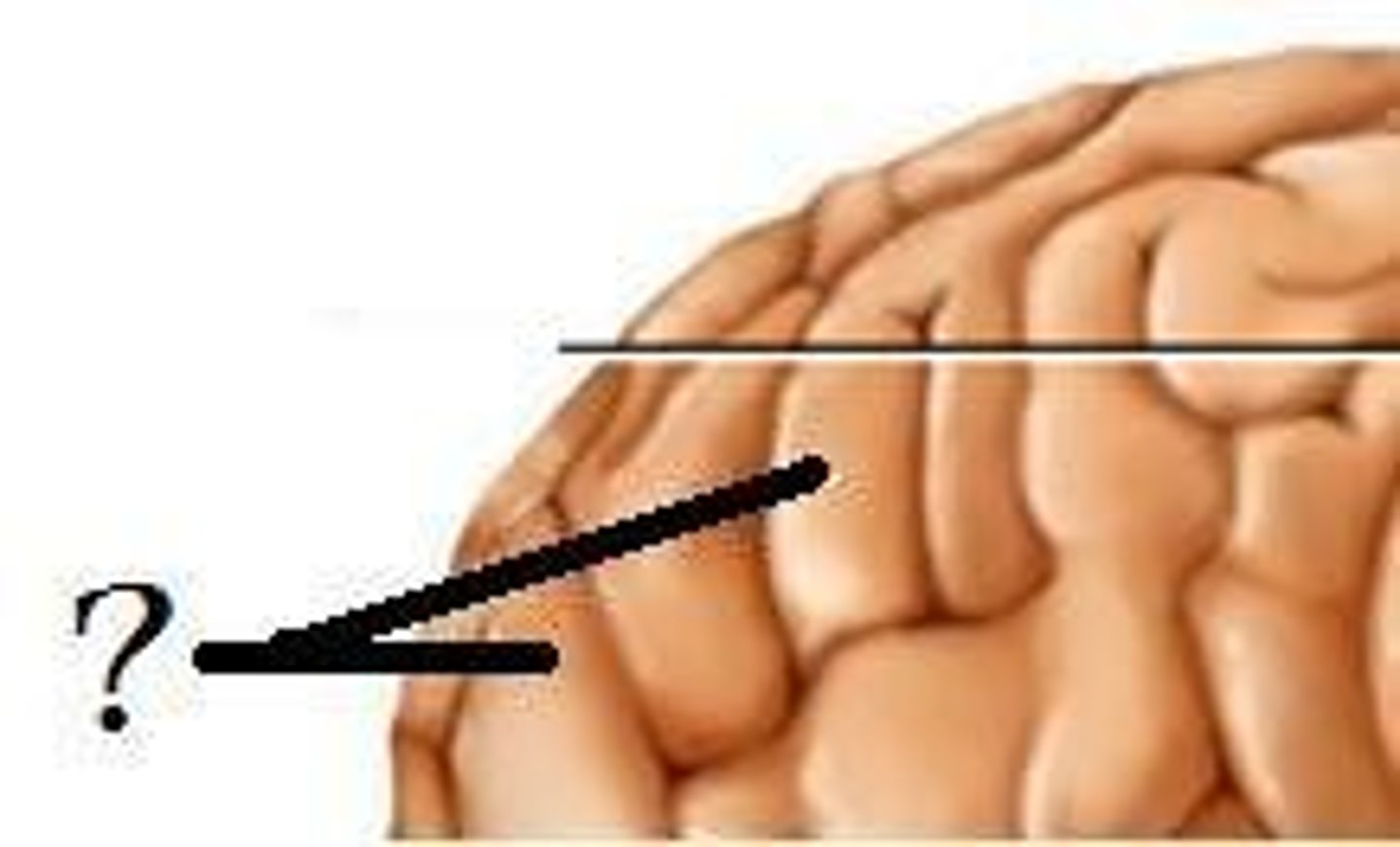
gyri
ridges of the brain
sulci
sulci
shallow grooves that separate gyri
fissures
fissures
deep grooves in the brain
longitudinal fissure
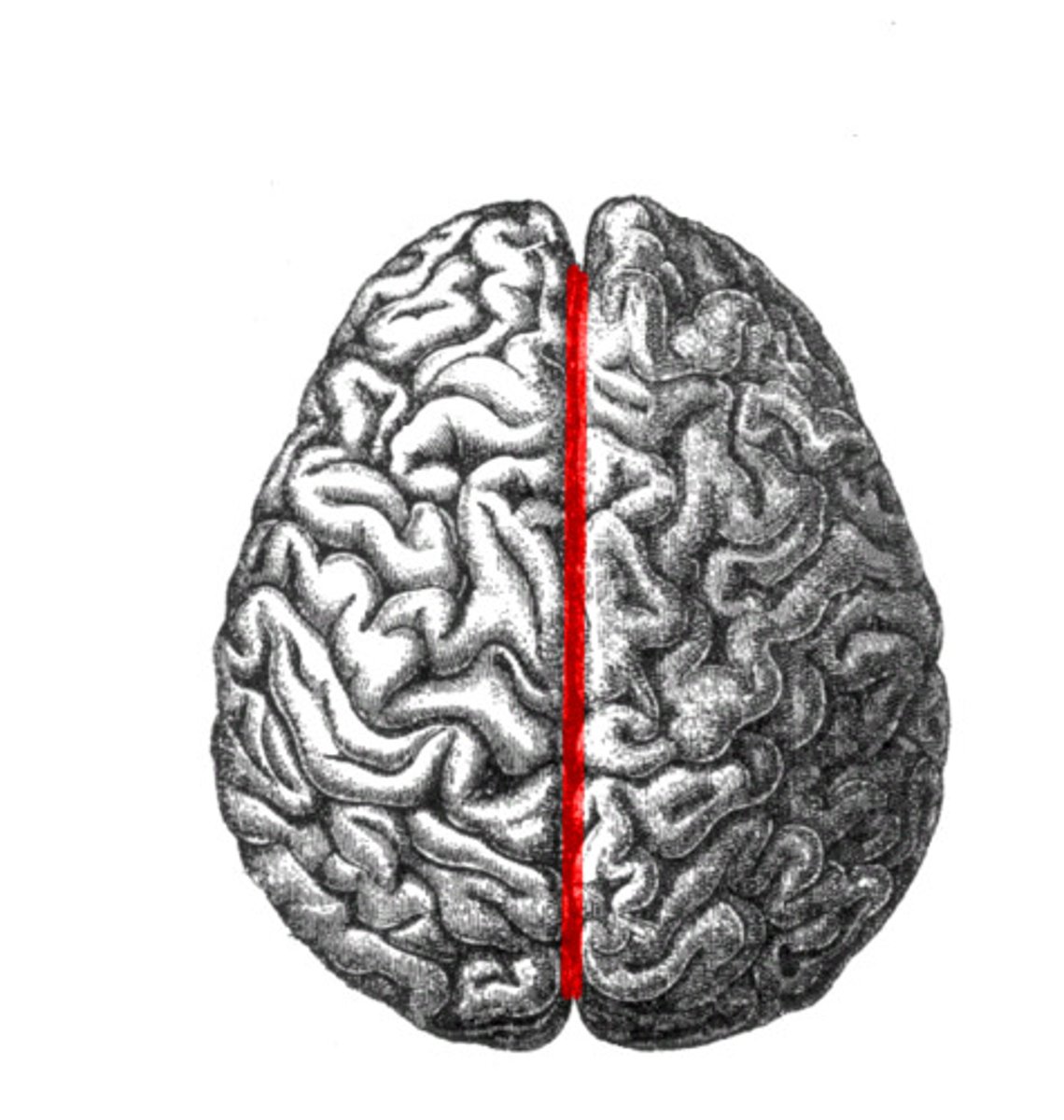
longitudinal fissure
separates cerebral hemispheres
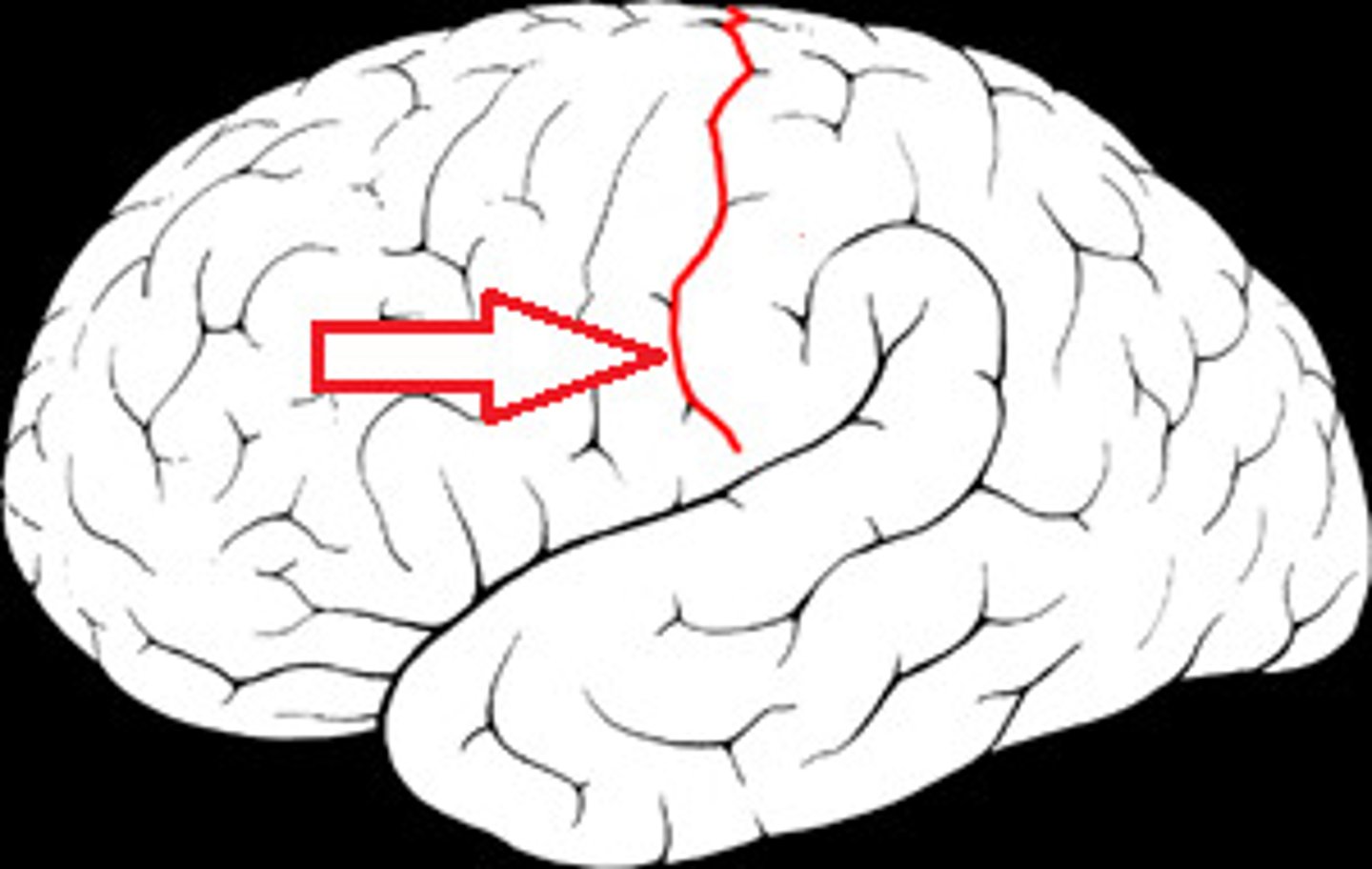
central sulcus
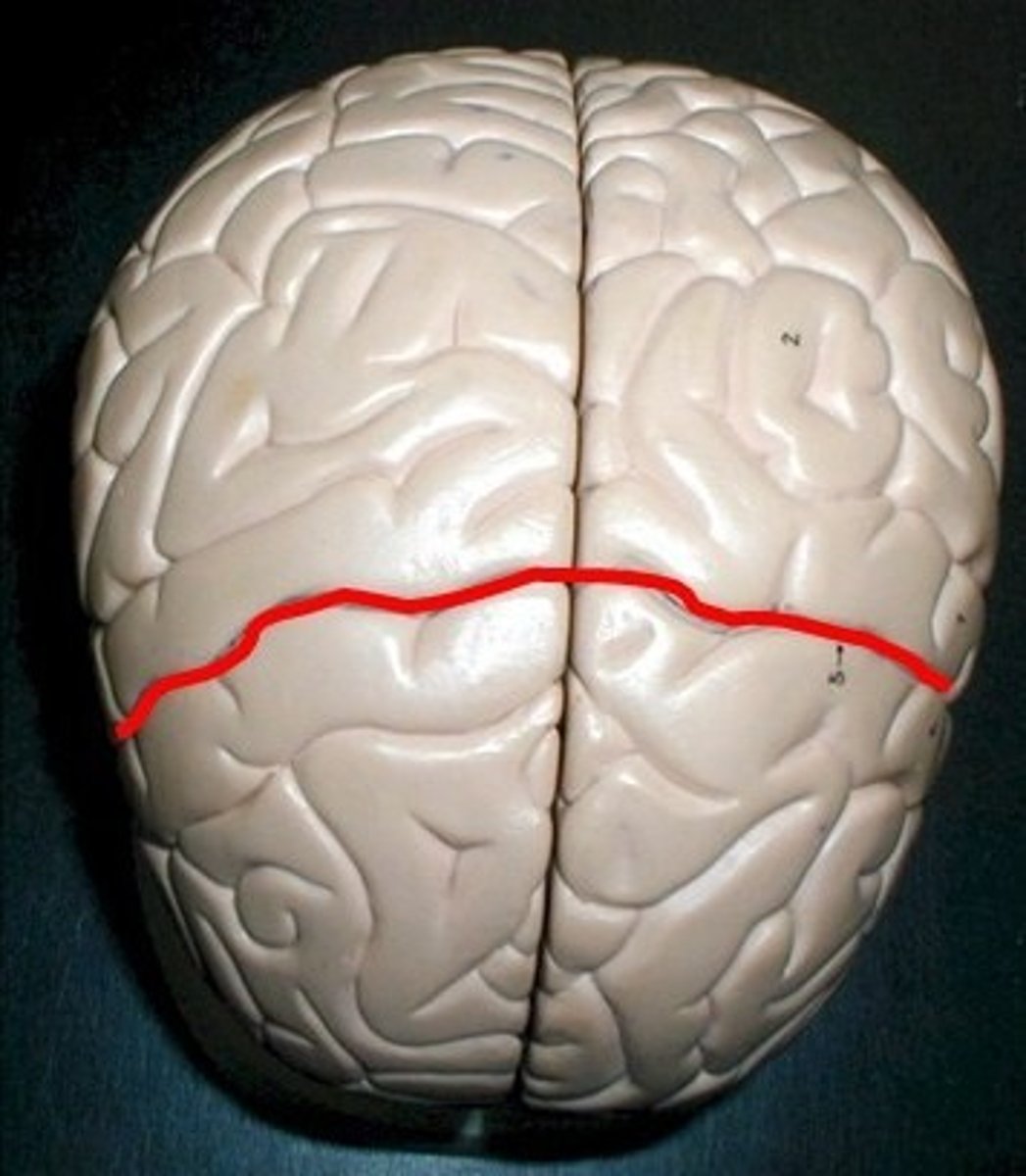
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body
dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information
axon, nucleus, and dendrites
What are the parts of the neuron?
cerebrum
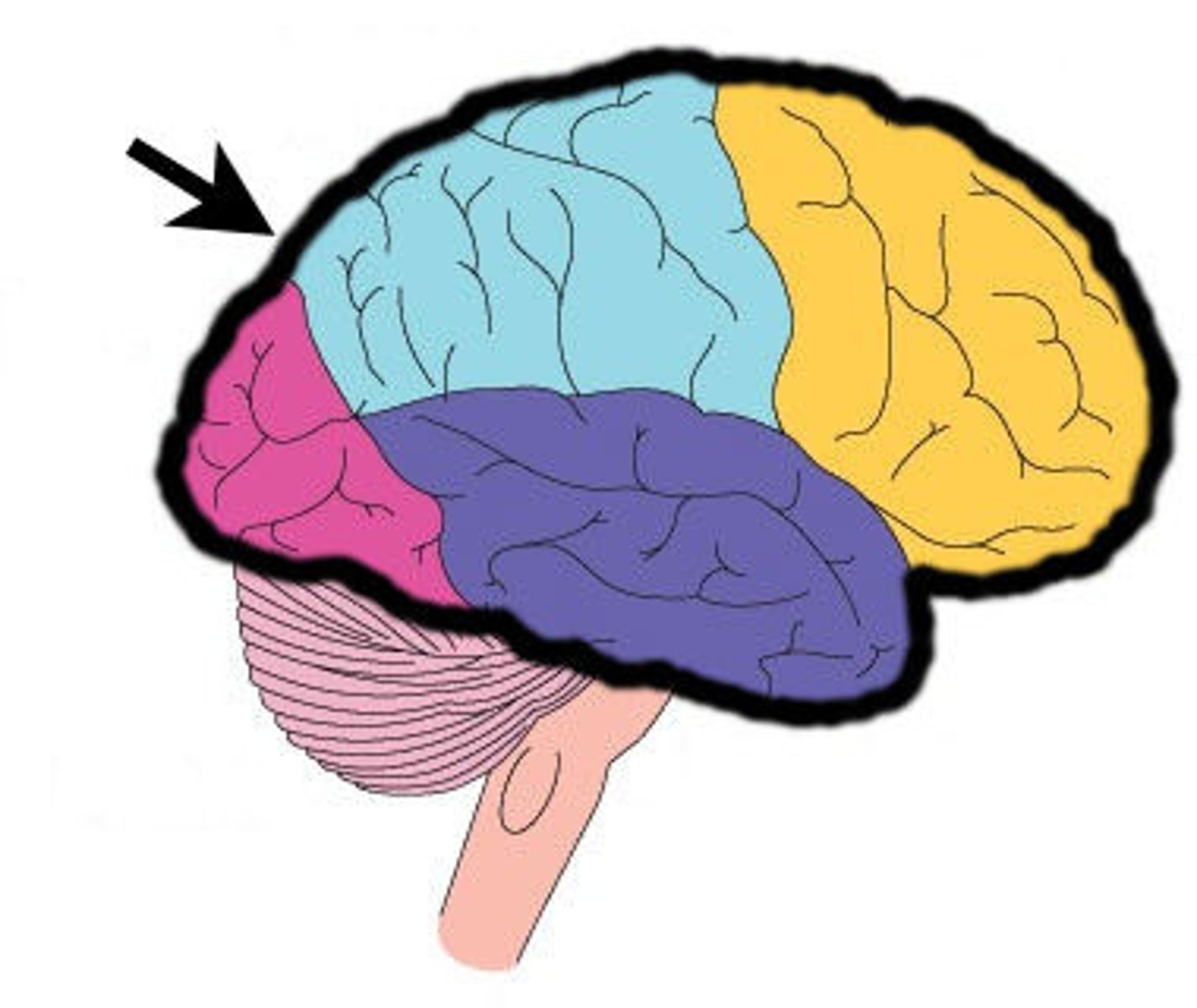
cerebellum
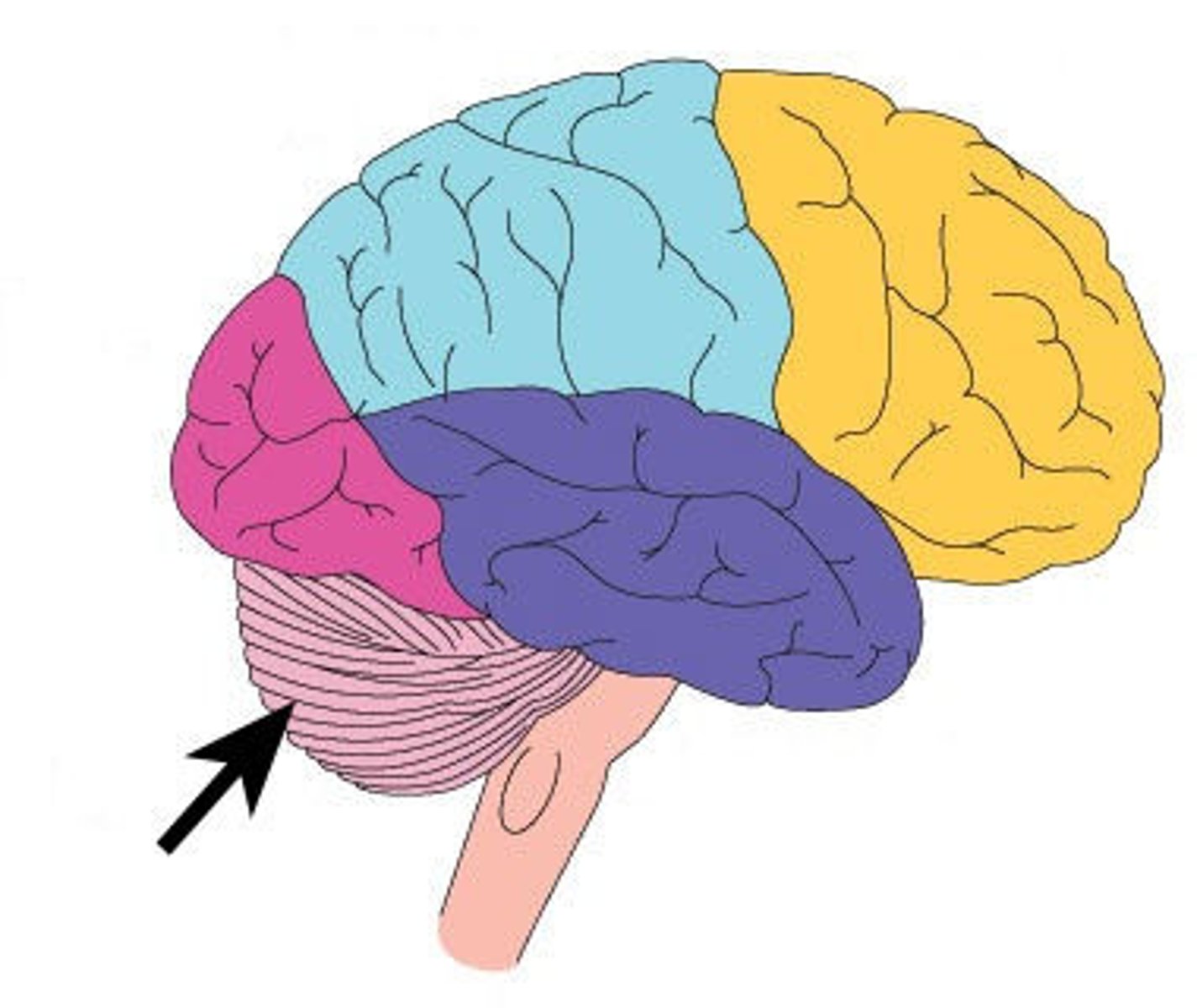
cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
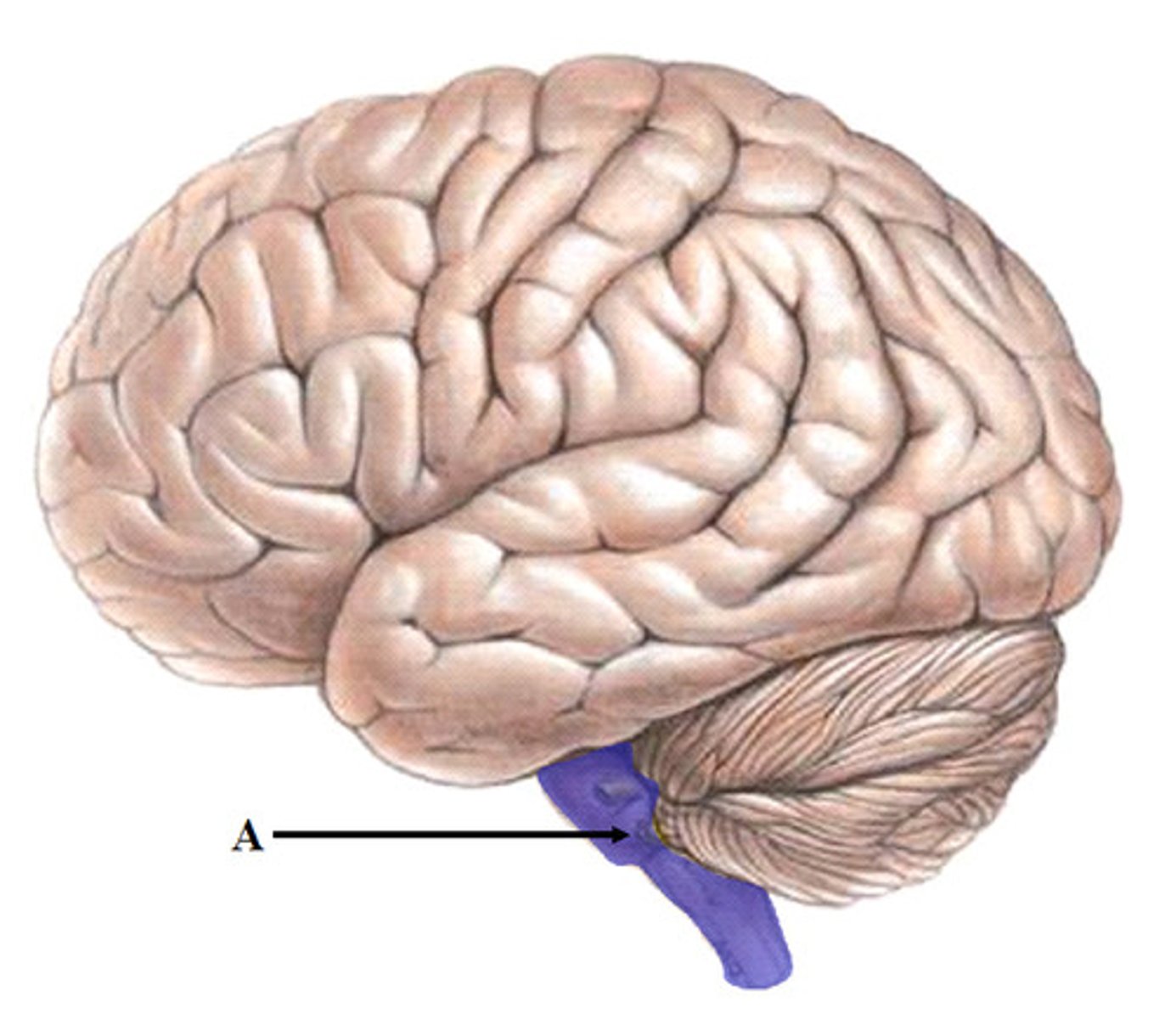
cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills
diencephalon
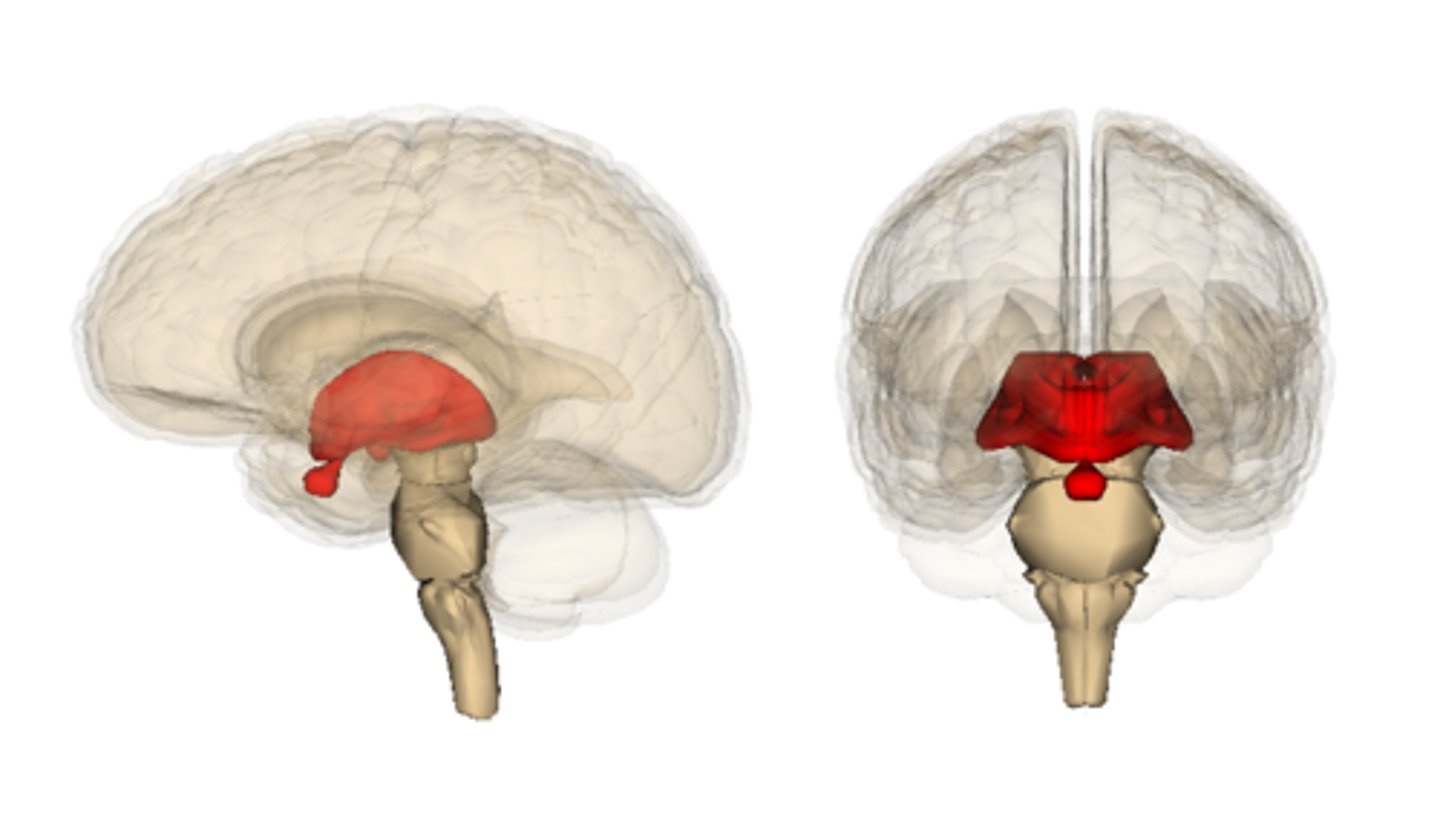
thalamus
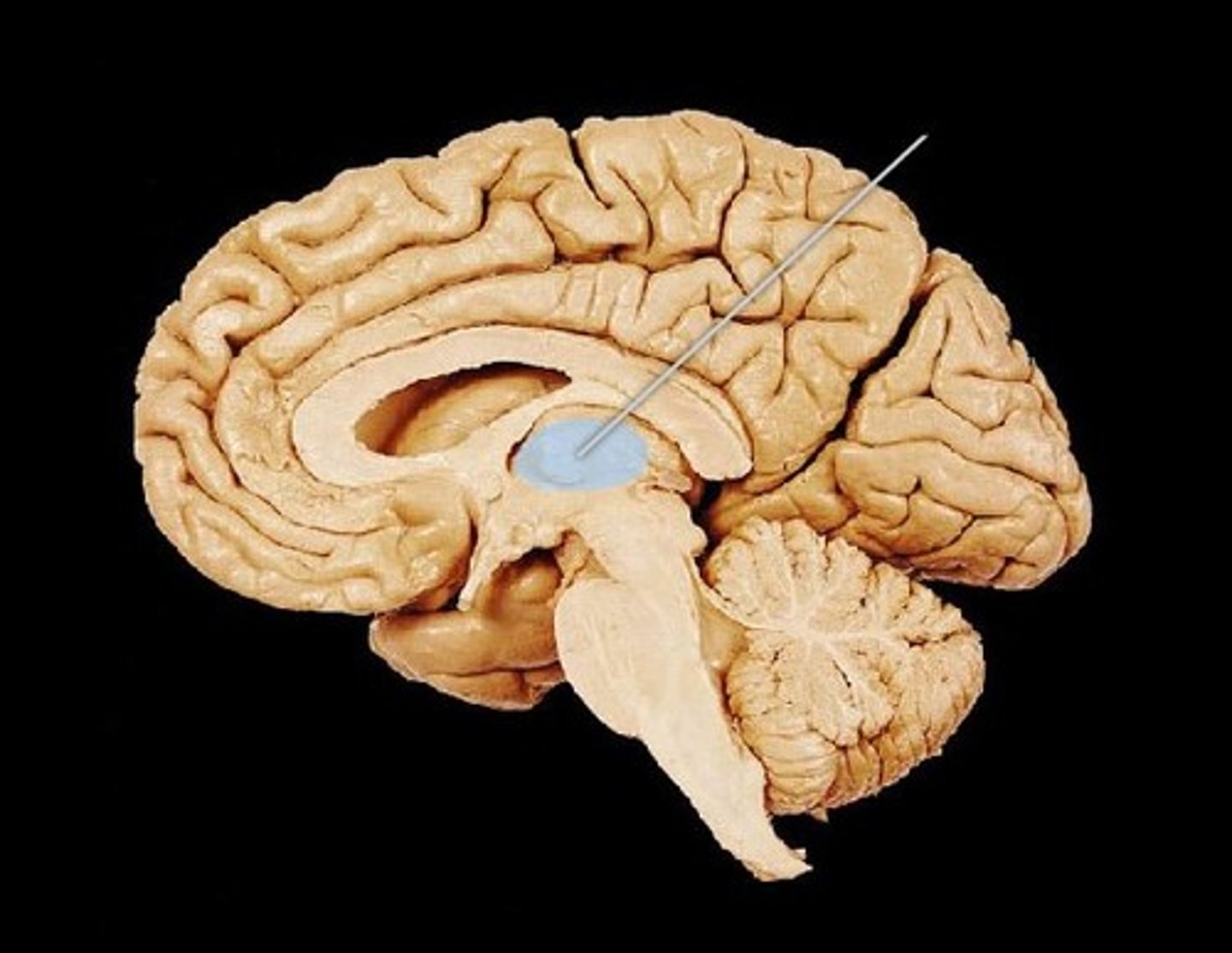
hypothalamus
diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
thalamus
the brain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
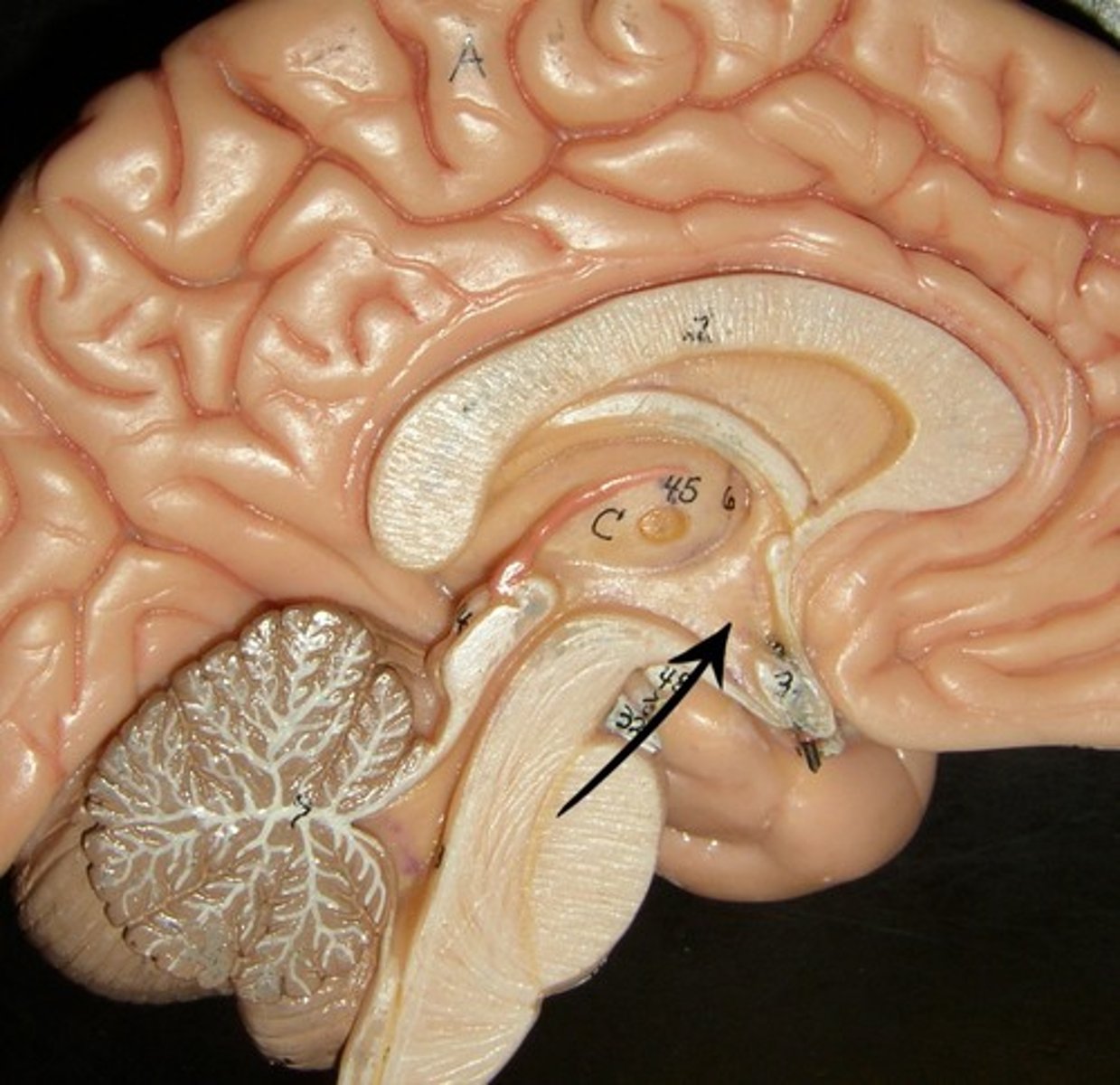
brainstem
medulla oblongata
pons
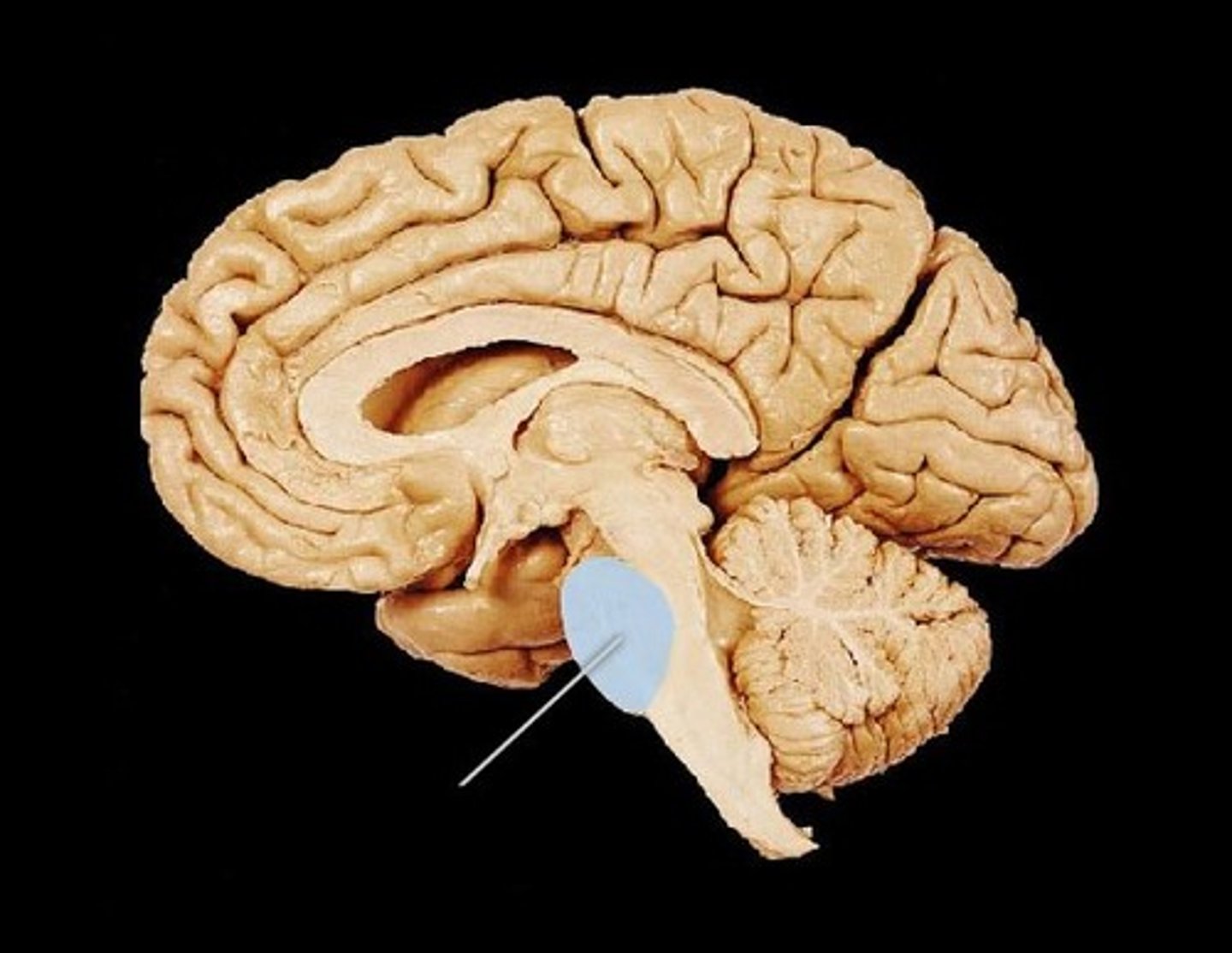
midbrain
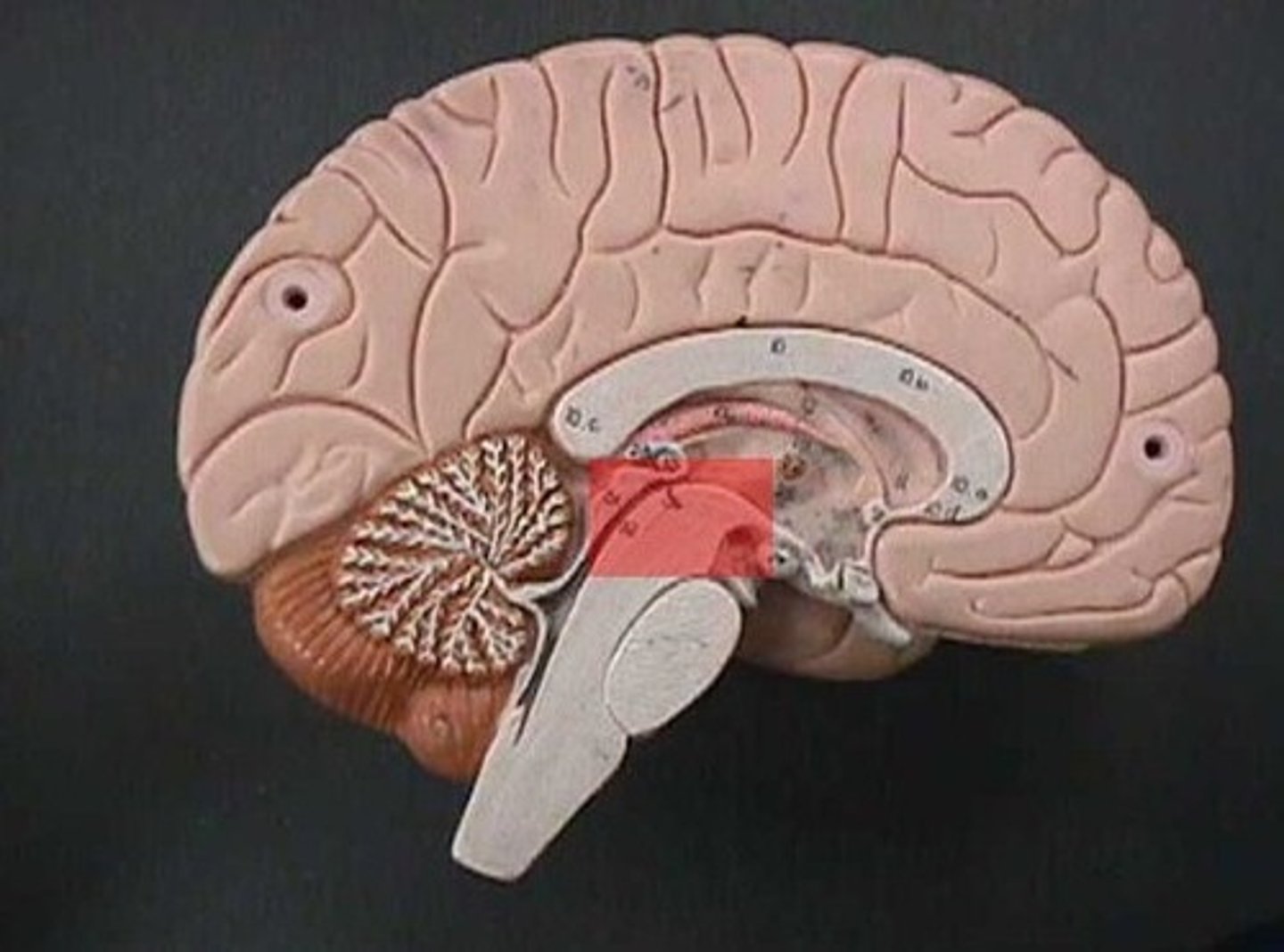
brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions
medulla oblongata
Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
postcentral gyrus
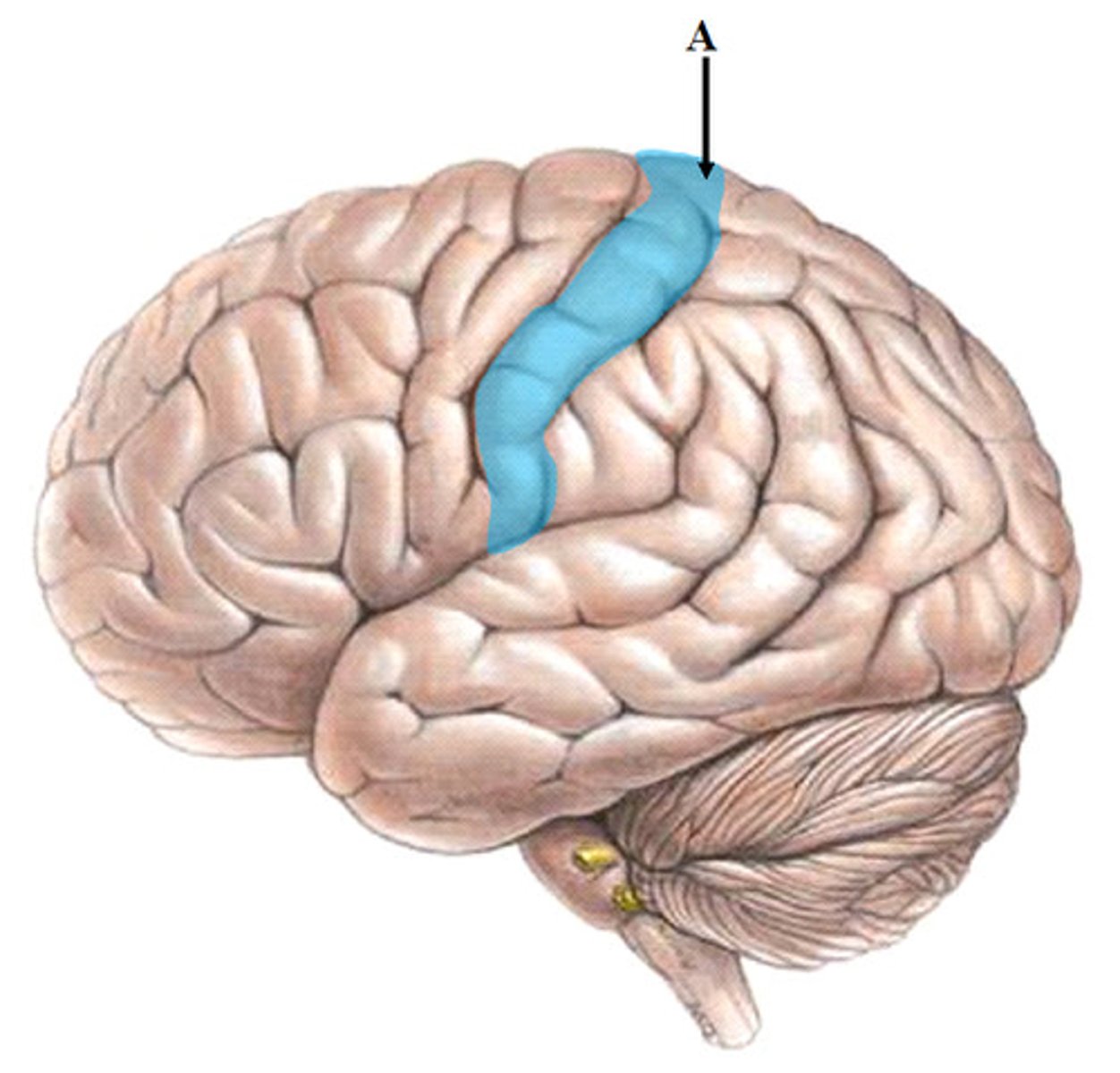
postcentral gyrus
the strip of parietal cortex, just behind the central sulcus, that receives somatosensory information from the entire body
precentral gyrus
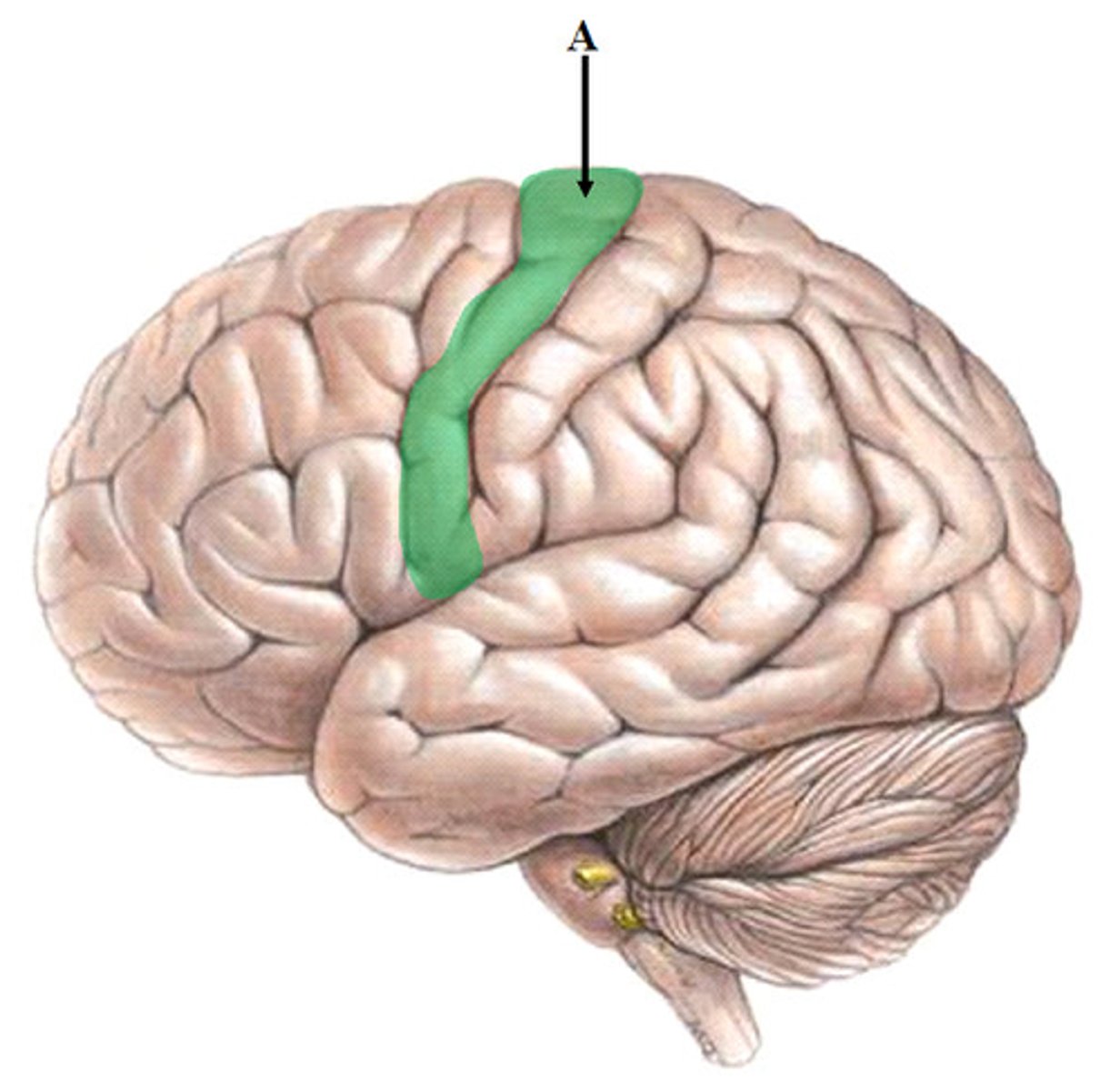
precentral gyrus
the strip of frontal cortex, just in front of the central sulcus, that is crucial for motor control
prefrontal cortex
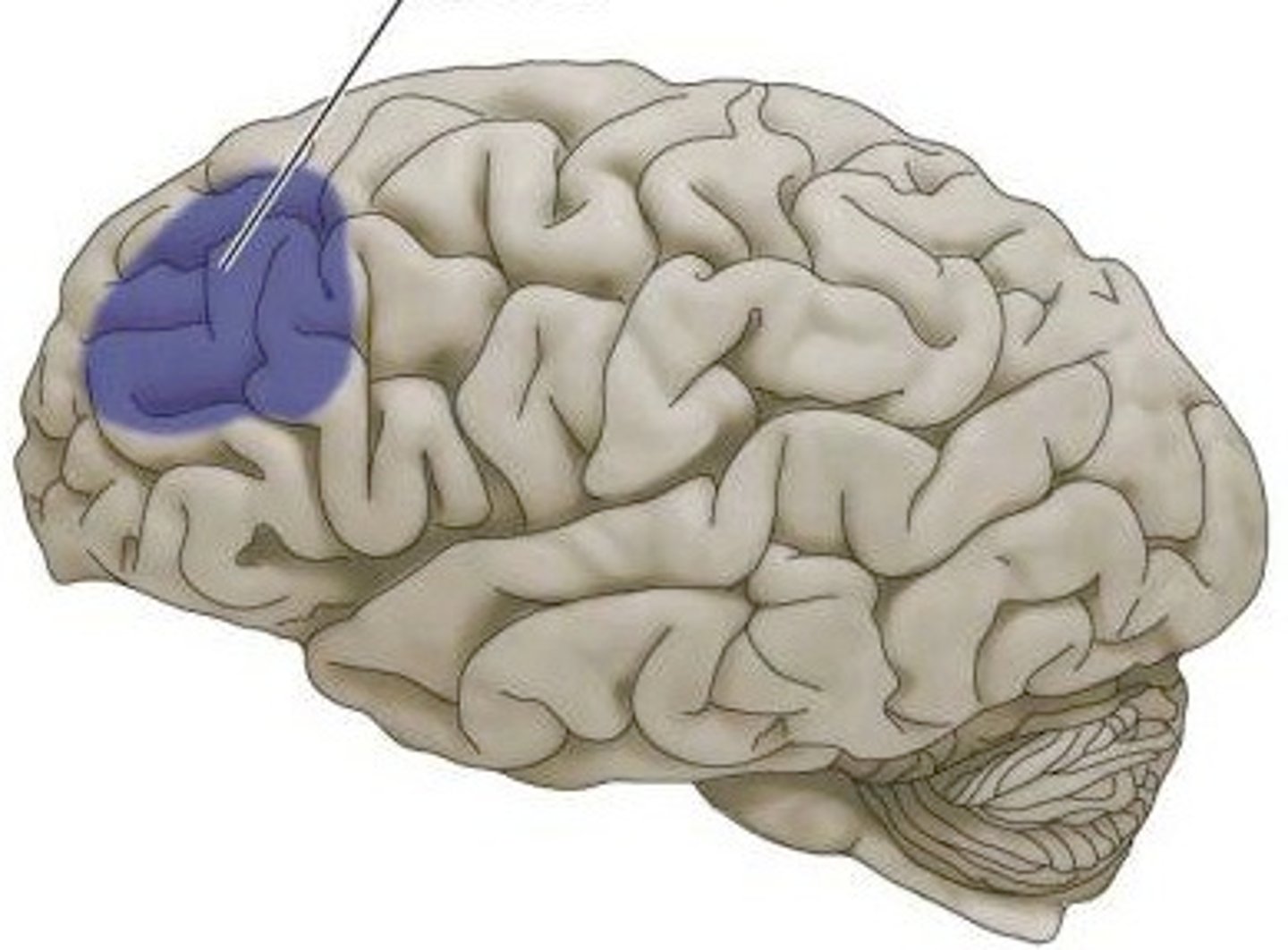
prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language
occipital lobe
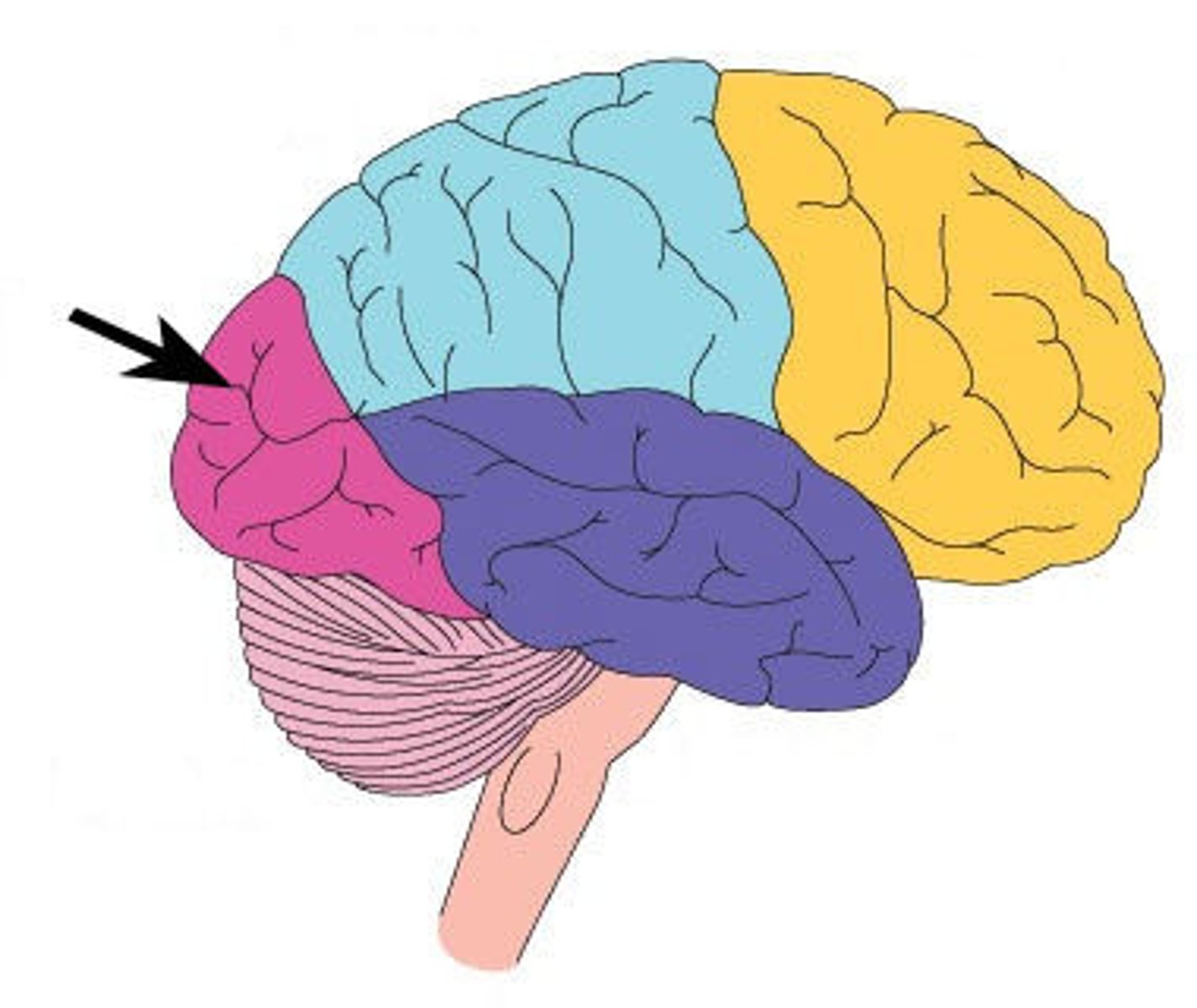
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
temporal lobe
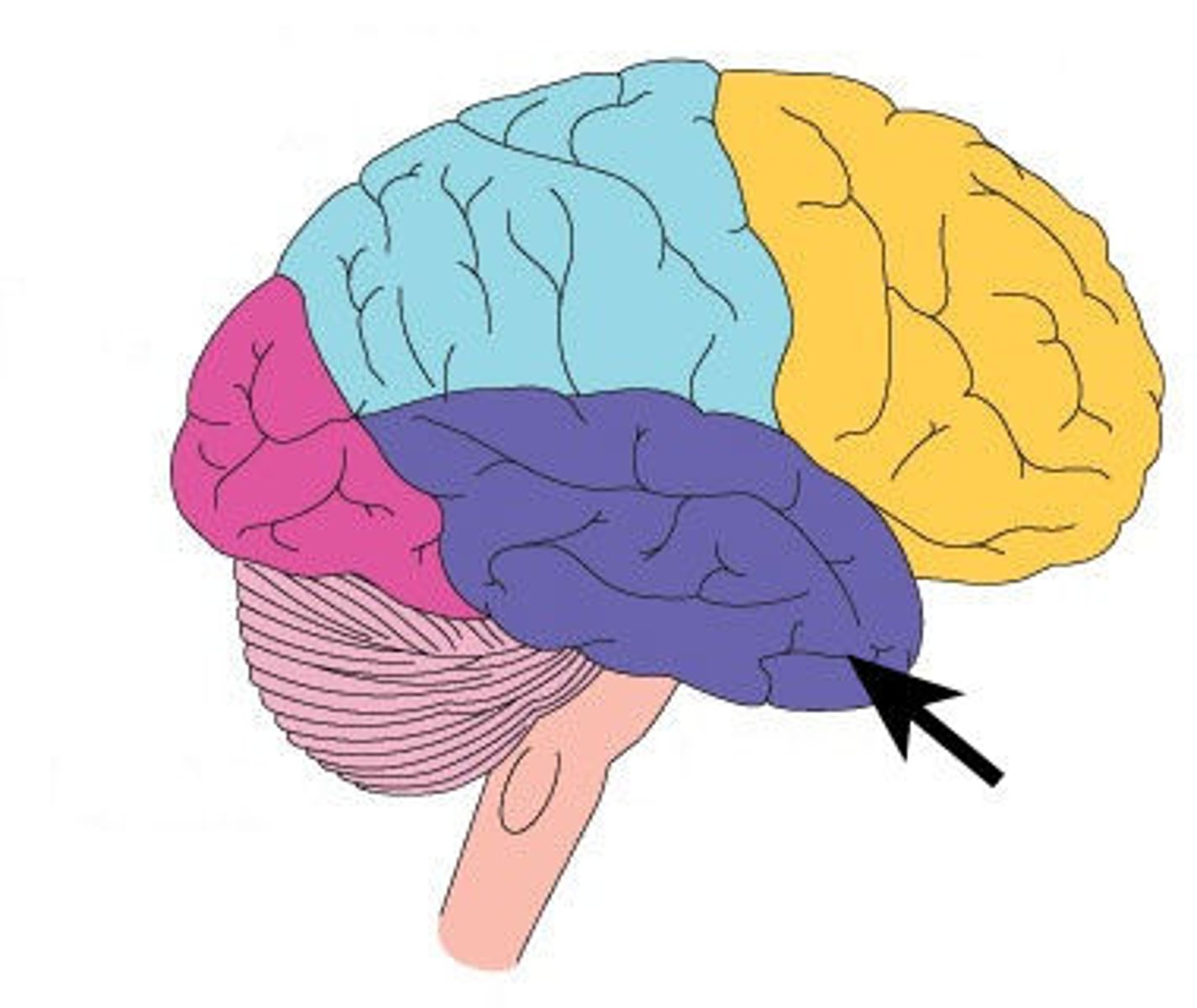
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
olfactory bulbs and tracts
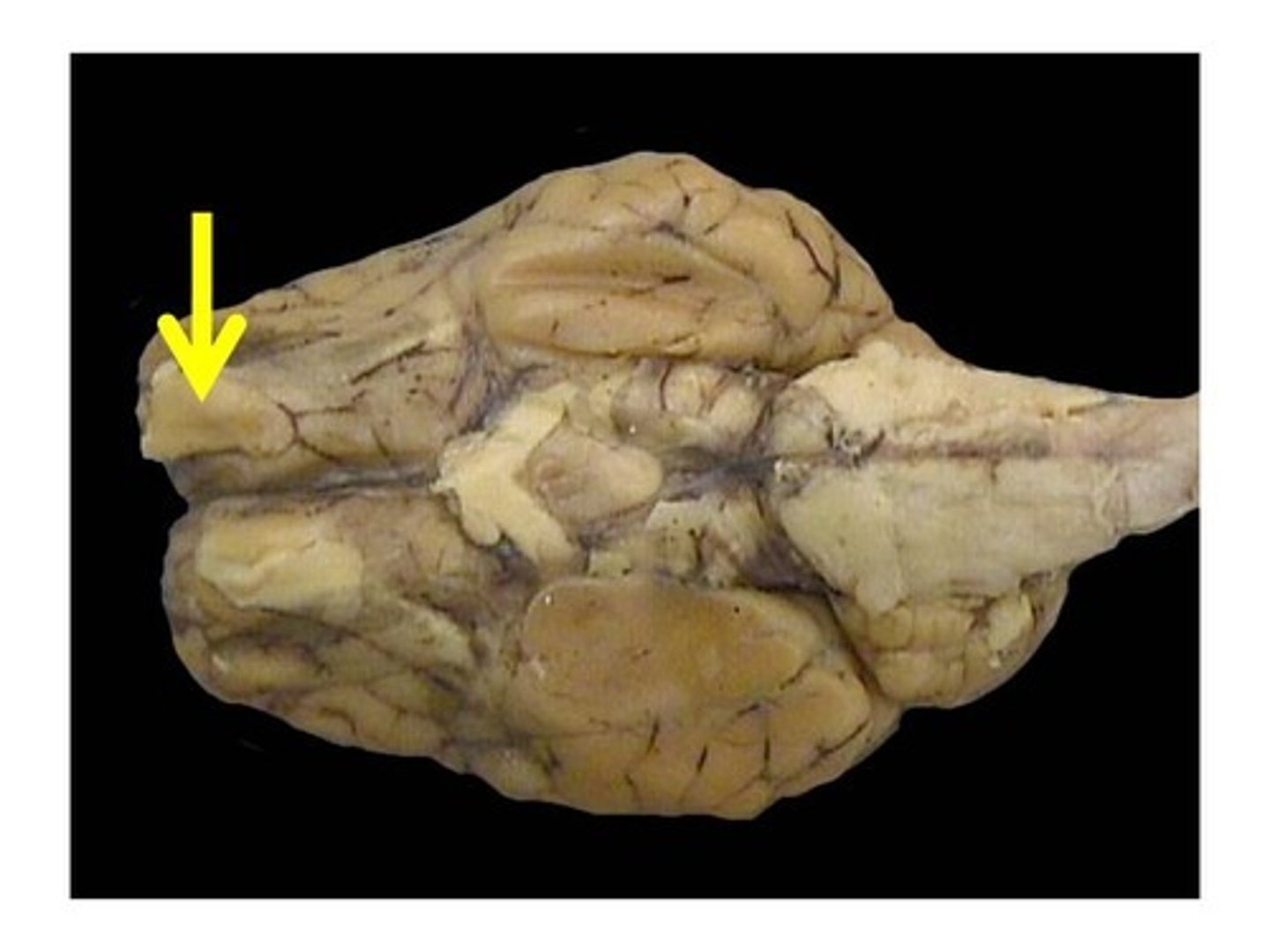
olfactory bulbs and tracts
Receive information about smells from the nose and send it to the brain.
- postcentral gyrus
- precentral gyrus
- prefrontal cortex
- occipital lobe
- temporal lobe
What are the functional areas?
optic nerve
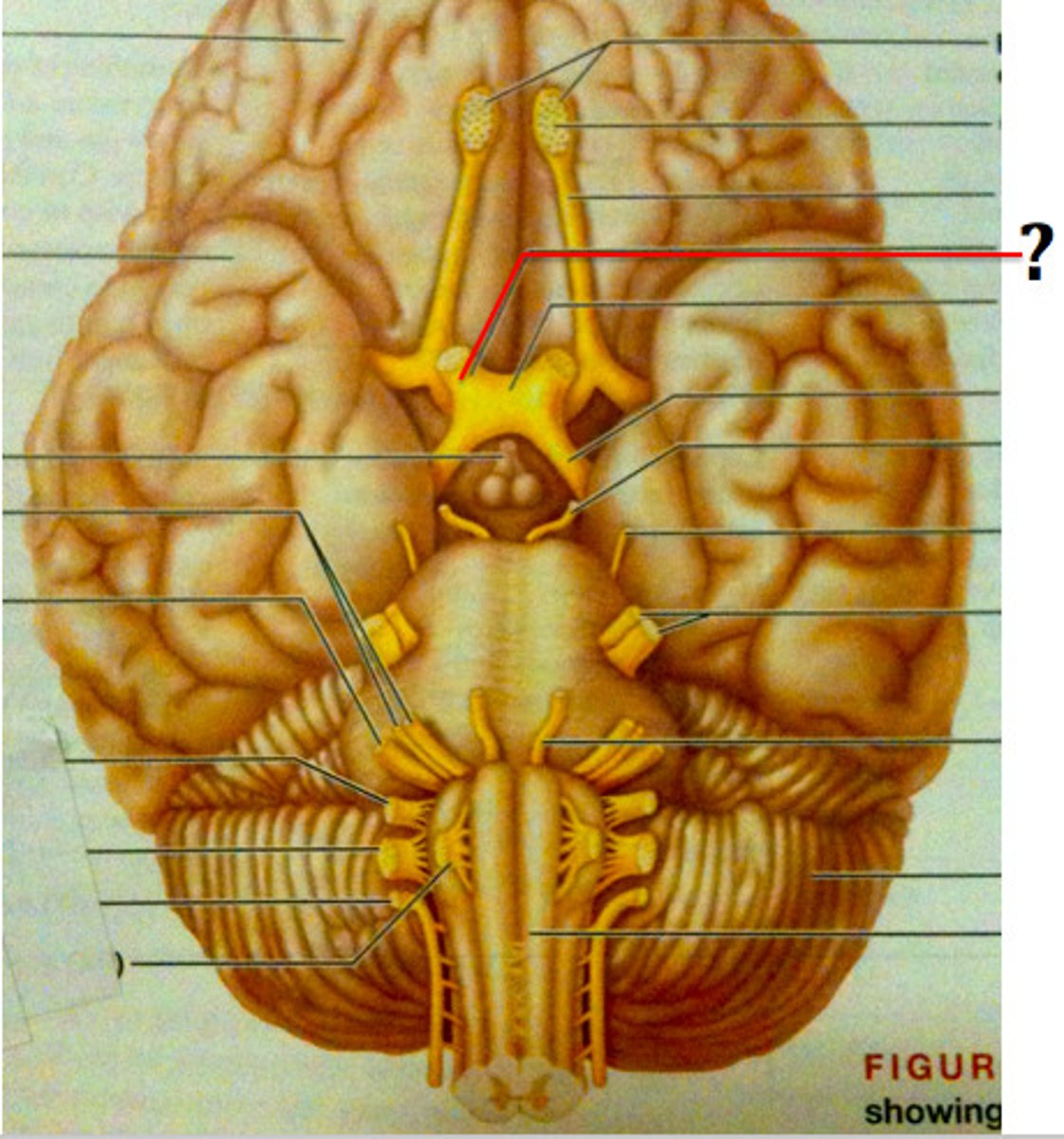
optic nerve
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
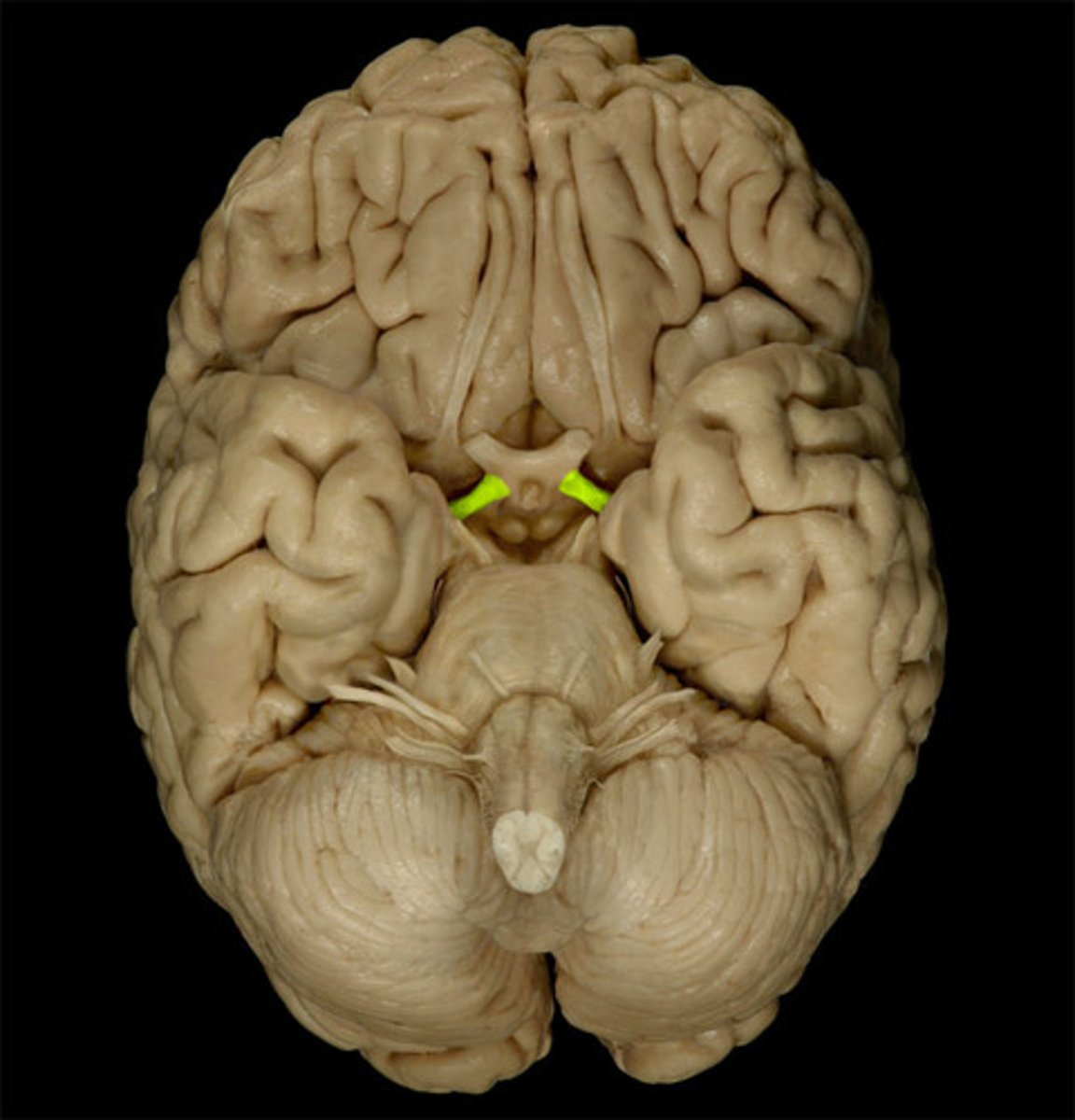
optic chiasma
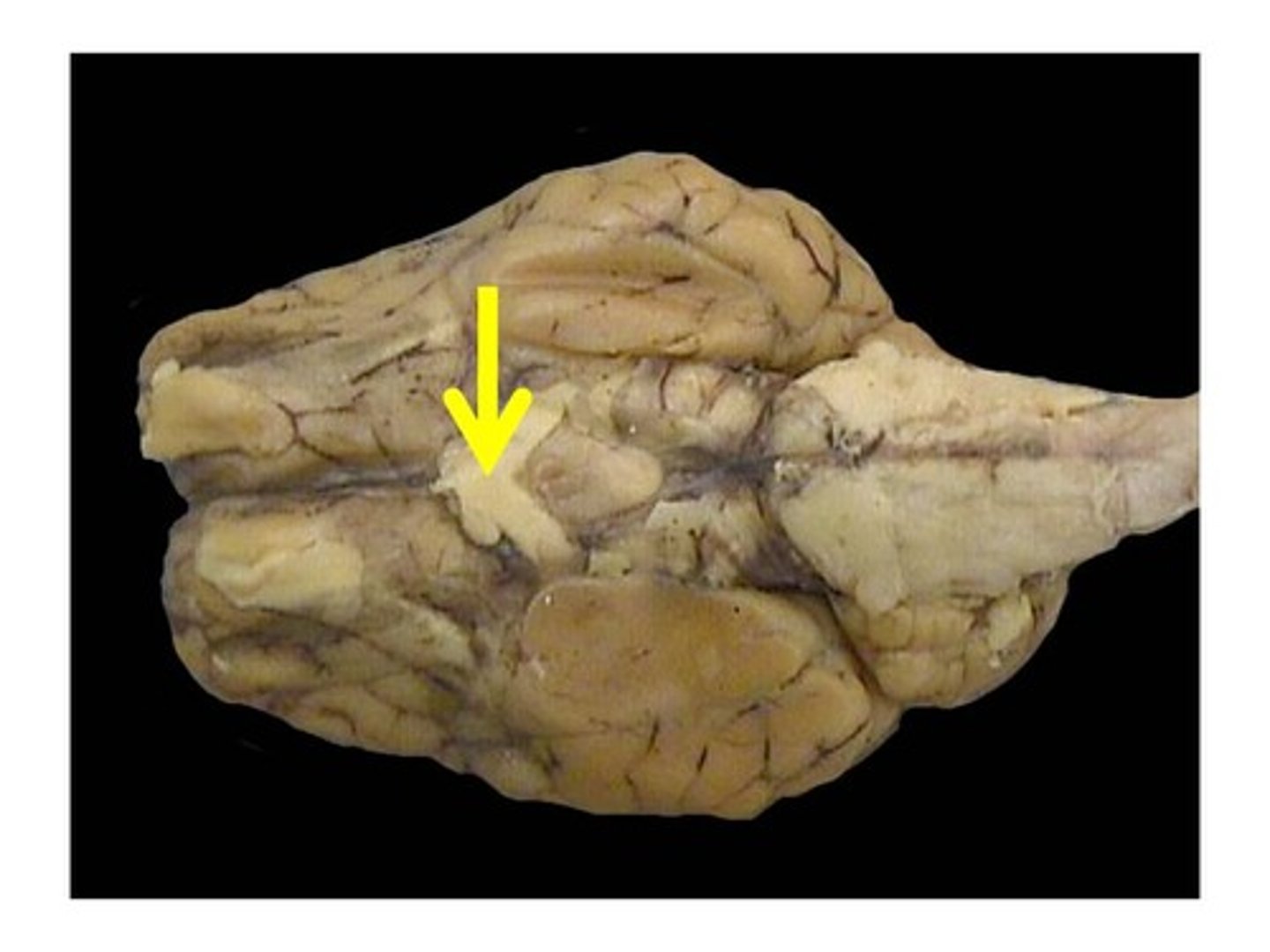
optic chiasma
the crossing of the optic nerves from the two eyes at the base of the brain
optic tract
optic tract
How information from the optic nerve travels to the thalamus
pituitary gland
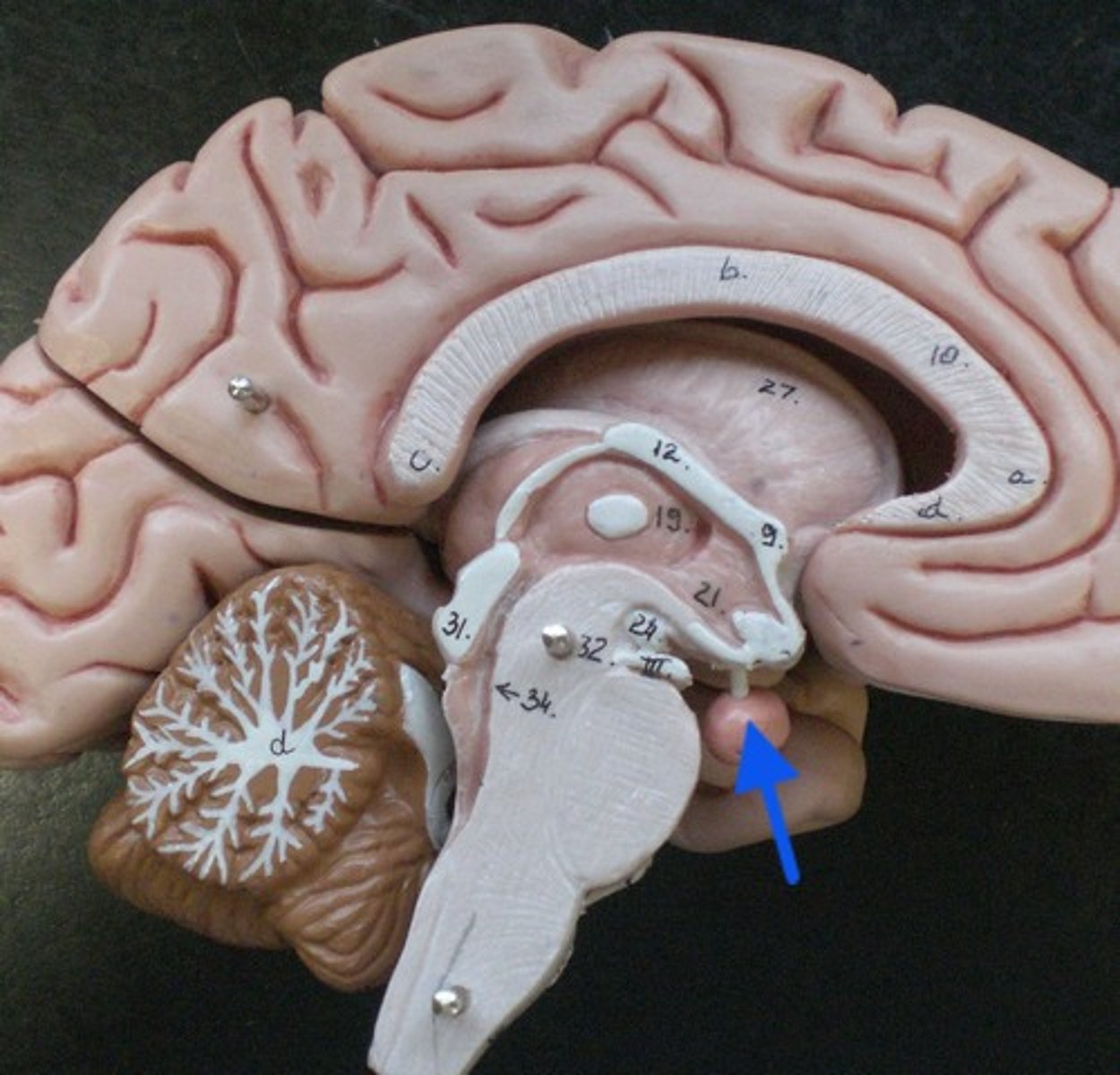
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands; only on brains with dura mater
mammillary body
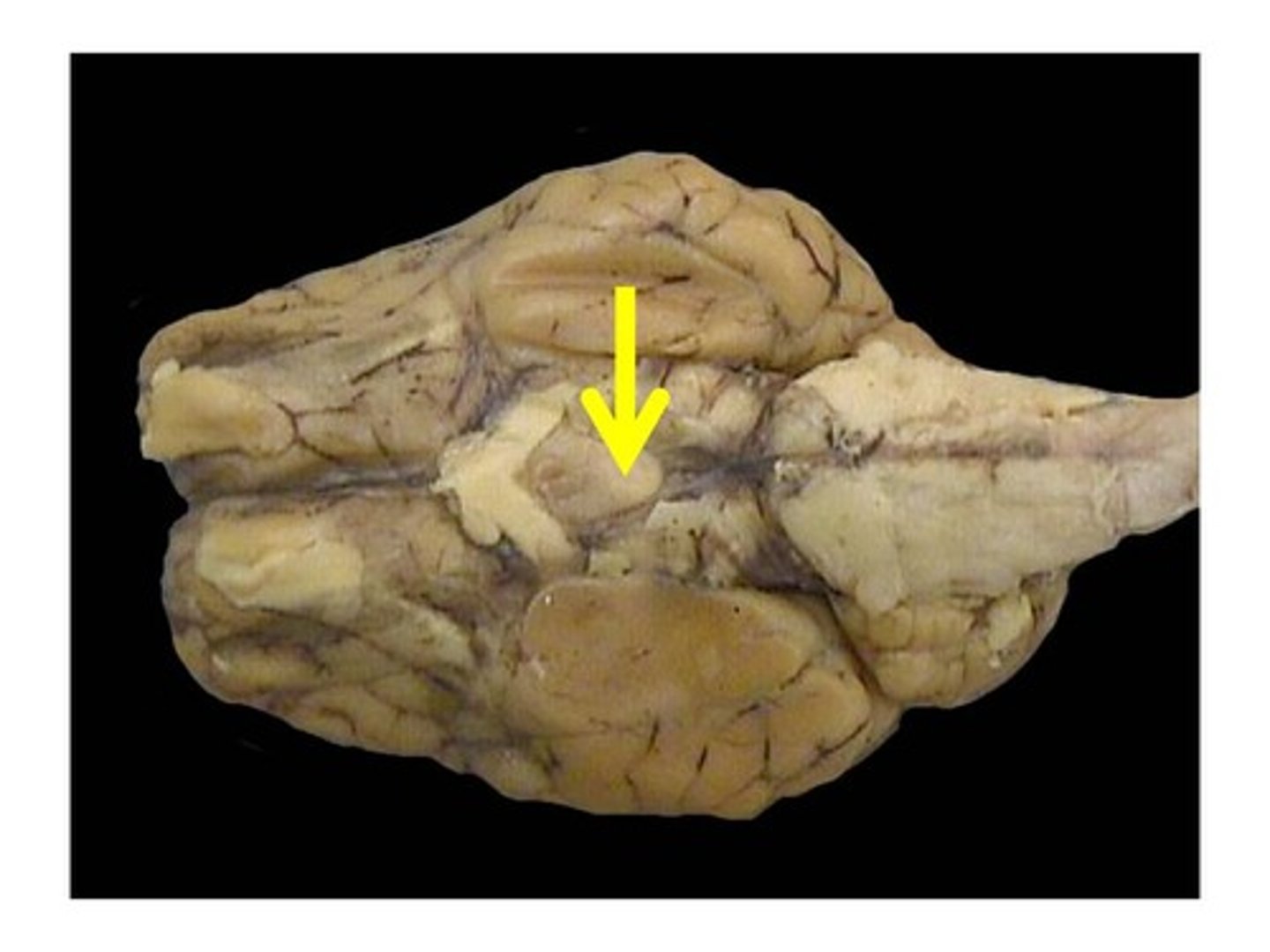
mammillary body
one of a pair of limbic system structures that are connected to the hippocampus
cerebral peduncles
cerebral peduncles
contain fibers that carry motor output from cerebrum to other regions of CNS
- olfactory bulbs and tracts
- optic nerve
- optic chiasma
- optic tract
- pituitary gland
- mammillary body
- cerebral peduncles
- pons
- medulla oblongata
- cerebellum
What are the parts on the ventral surface of the brain?
corpus callosum
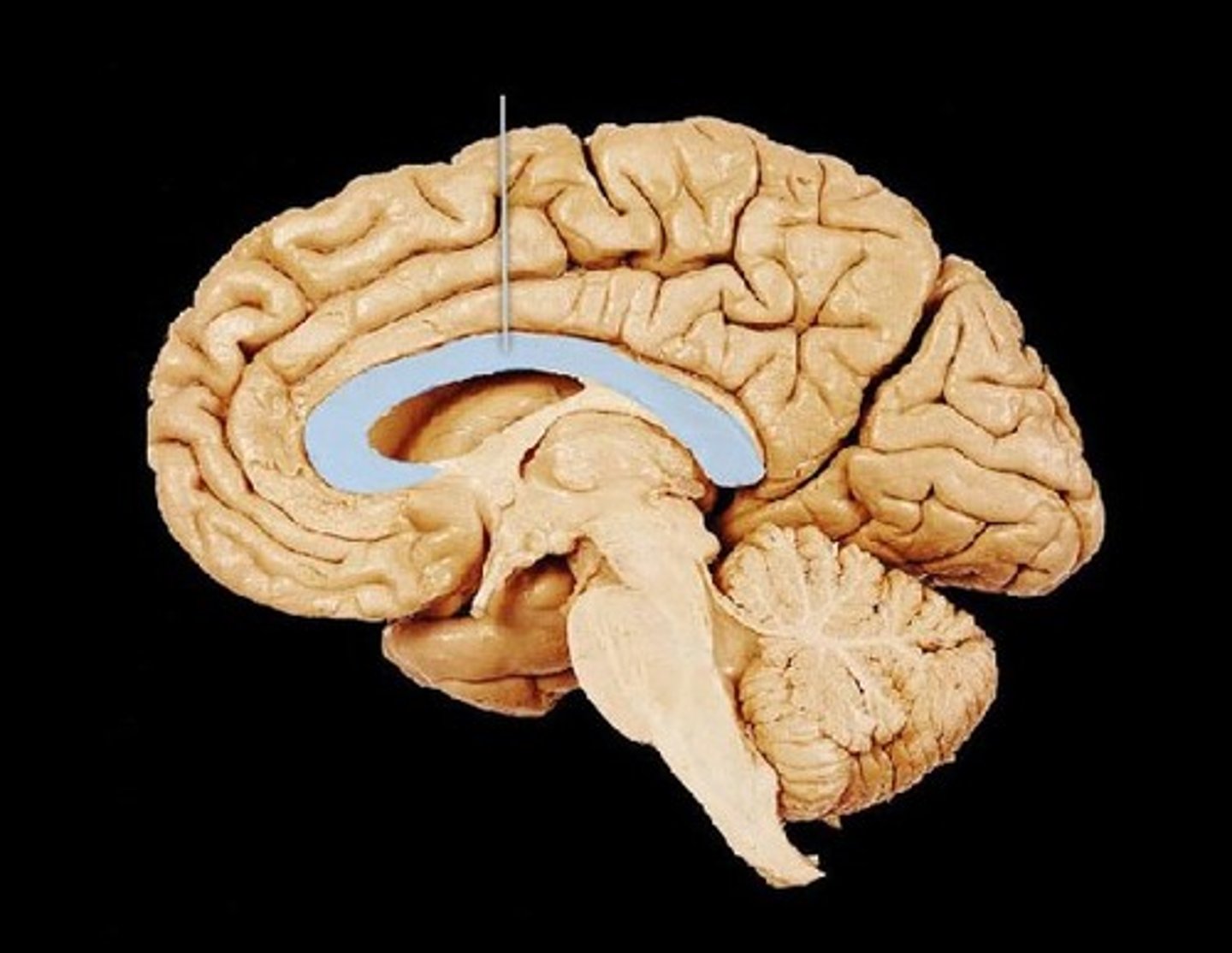
corpus callosum
the large band of neural fibers connecting the two brain hemispheres and carrying messages between them
lateral ventricle
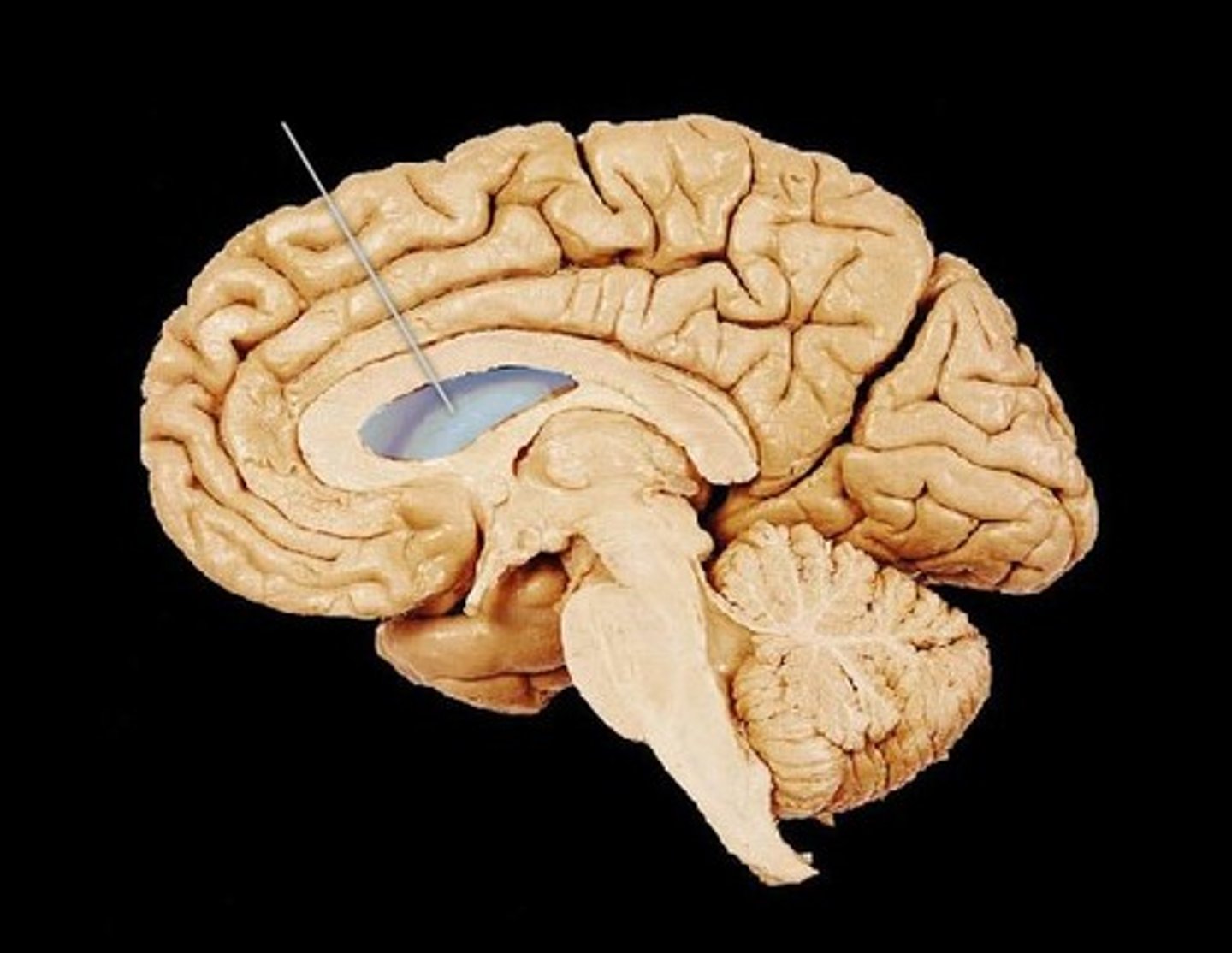
lateral ventricle
A complexly shaped lateral portion of the ventricular system within each hemisphere of the brain.
choroid plexus
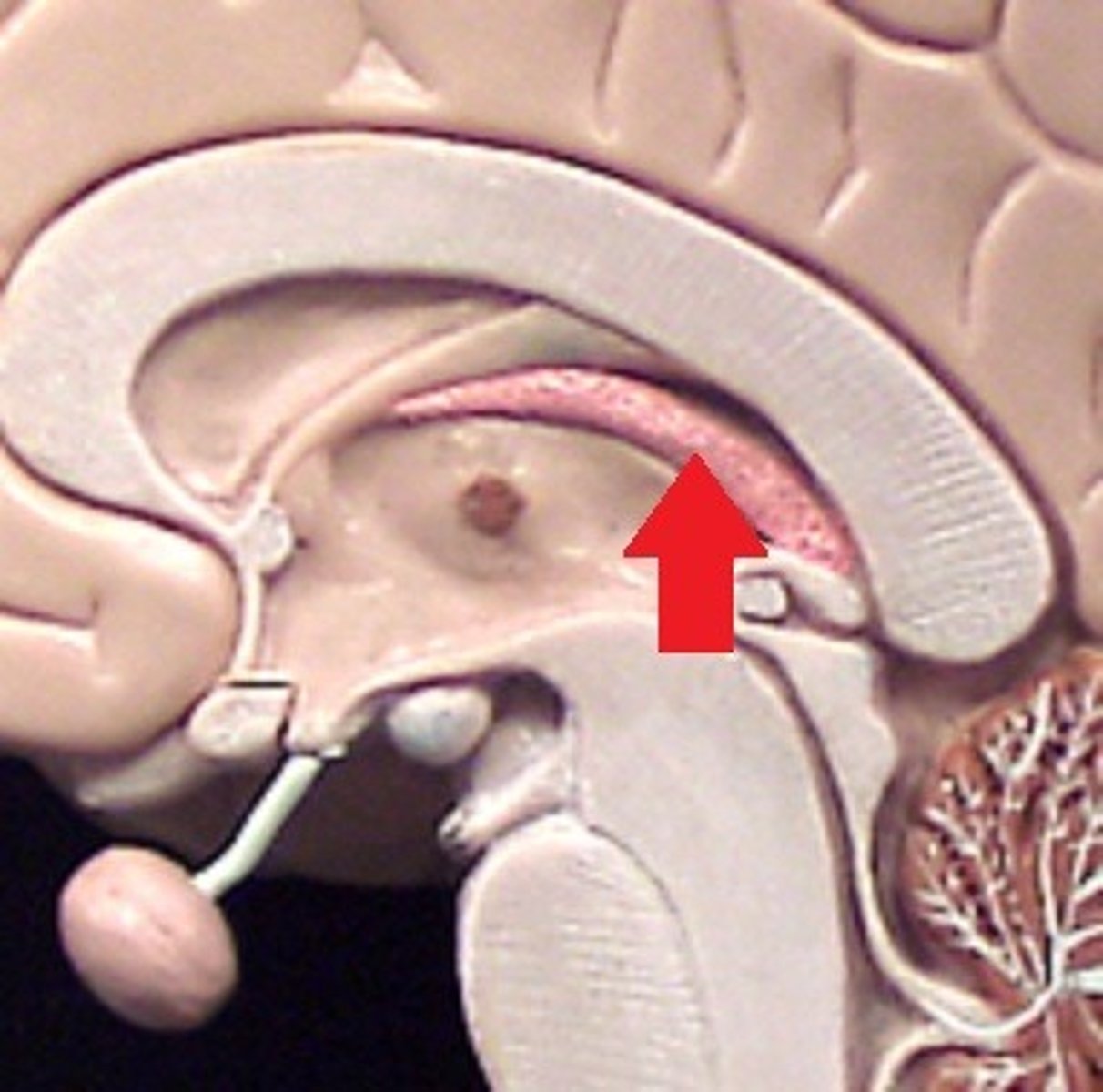
choroid plexus
A highly vascular portion of the lining of the ventricles that secretes cerebrospinal fluid.
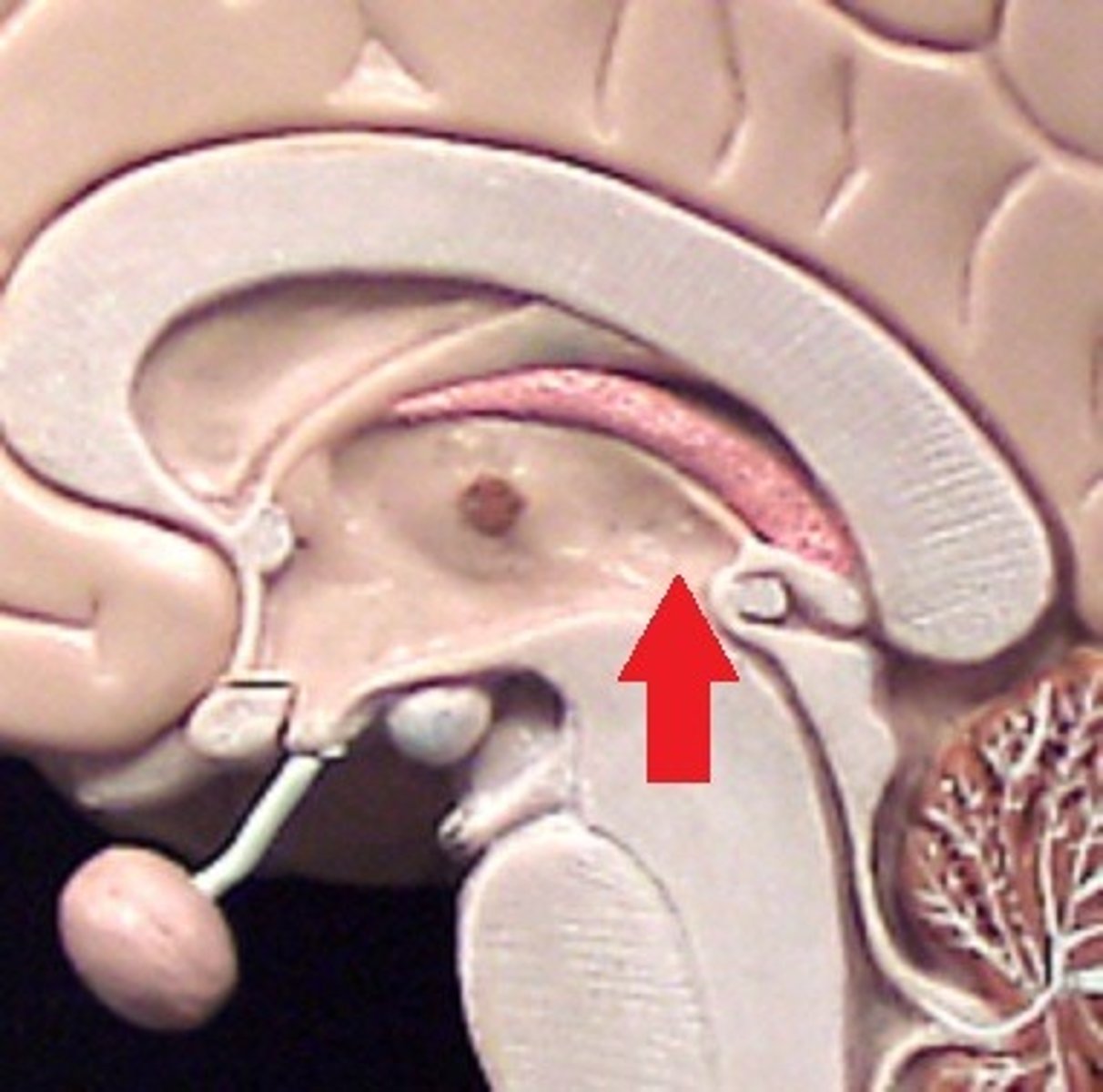
fornix
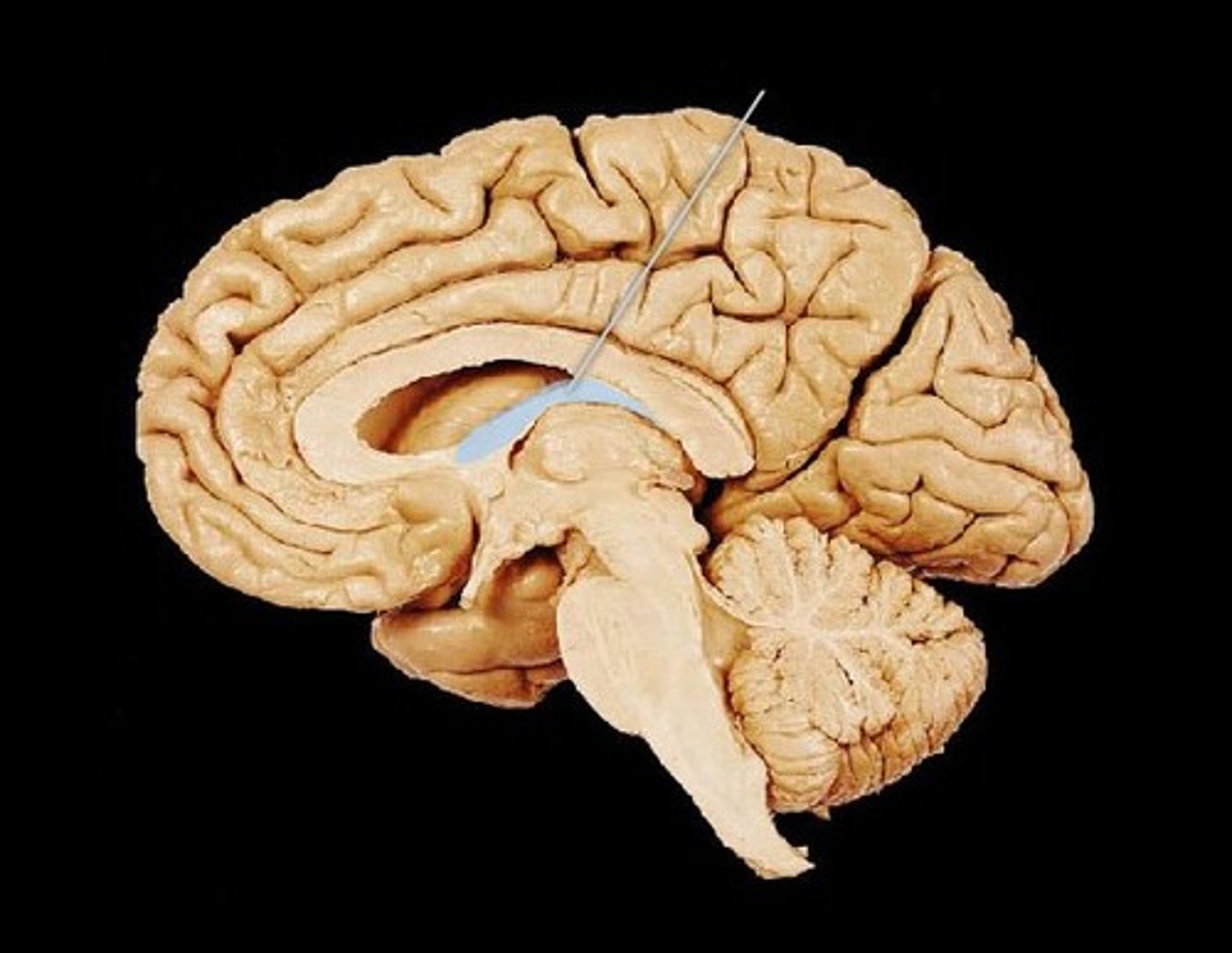
fornix
a fiber tract that extends from the hippocampus to the mammillary body
septum pellucidum
third ventricle
septum pellucidum
thin membrane that separates lateral ventricles
third ventricle
the ventricle located in the center of the diencephalon
pineal body
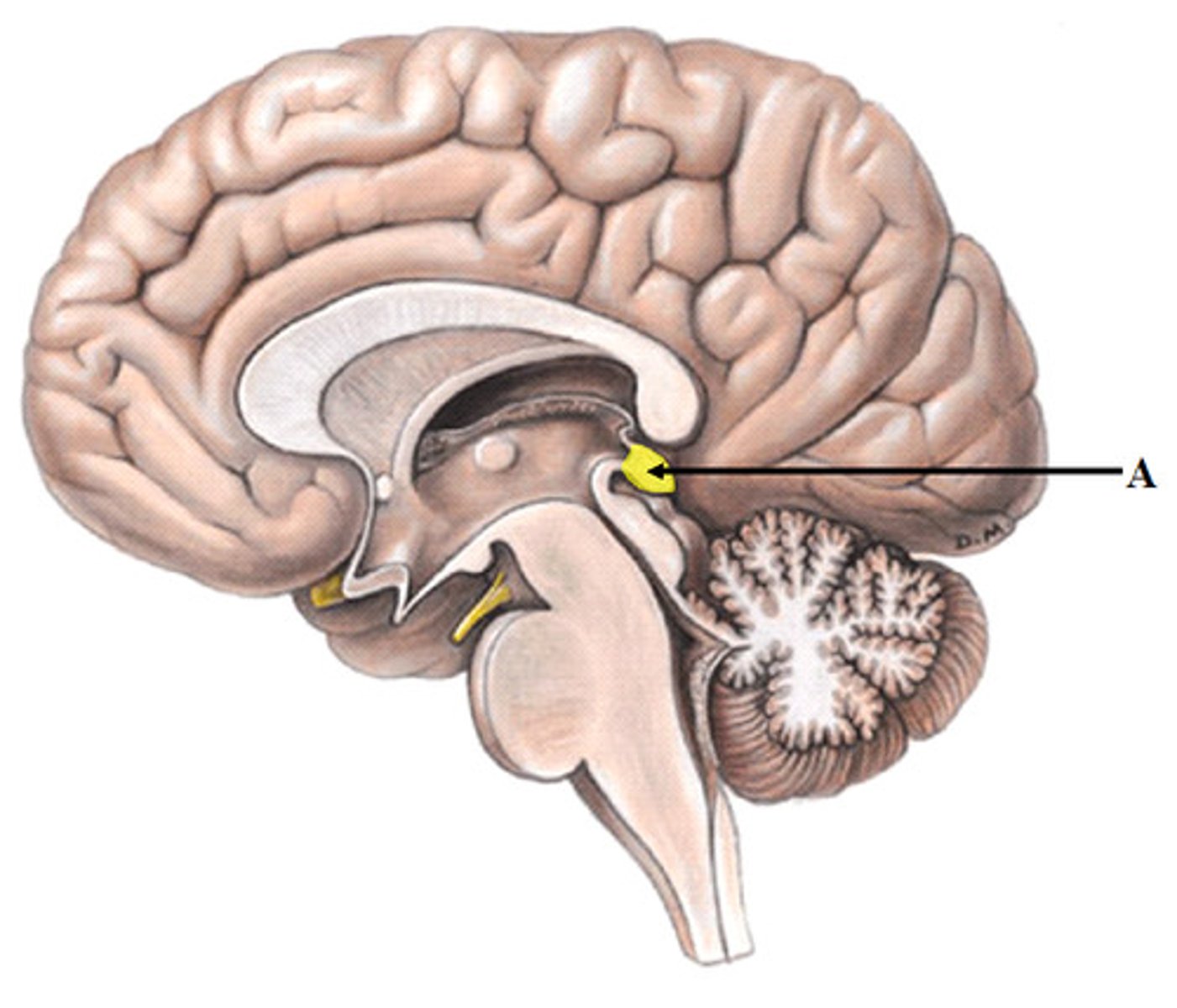
pineal body
a structure found between the cerebral hemispheres of vertebrates; secretes melatonin
superior colliculi
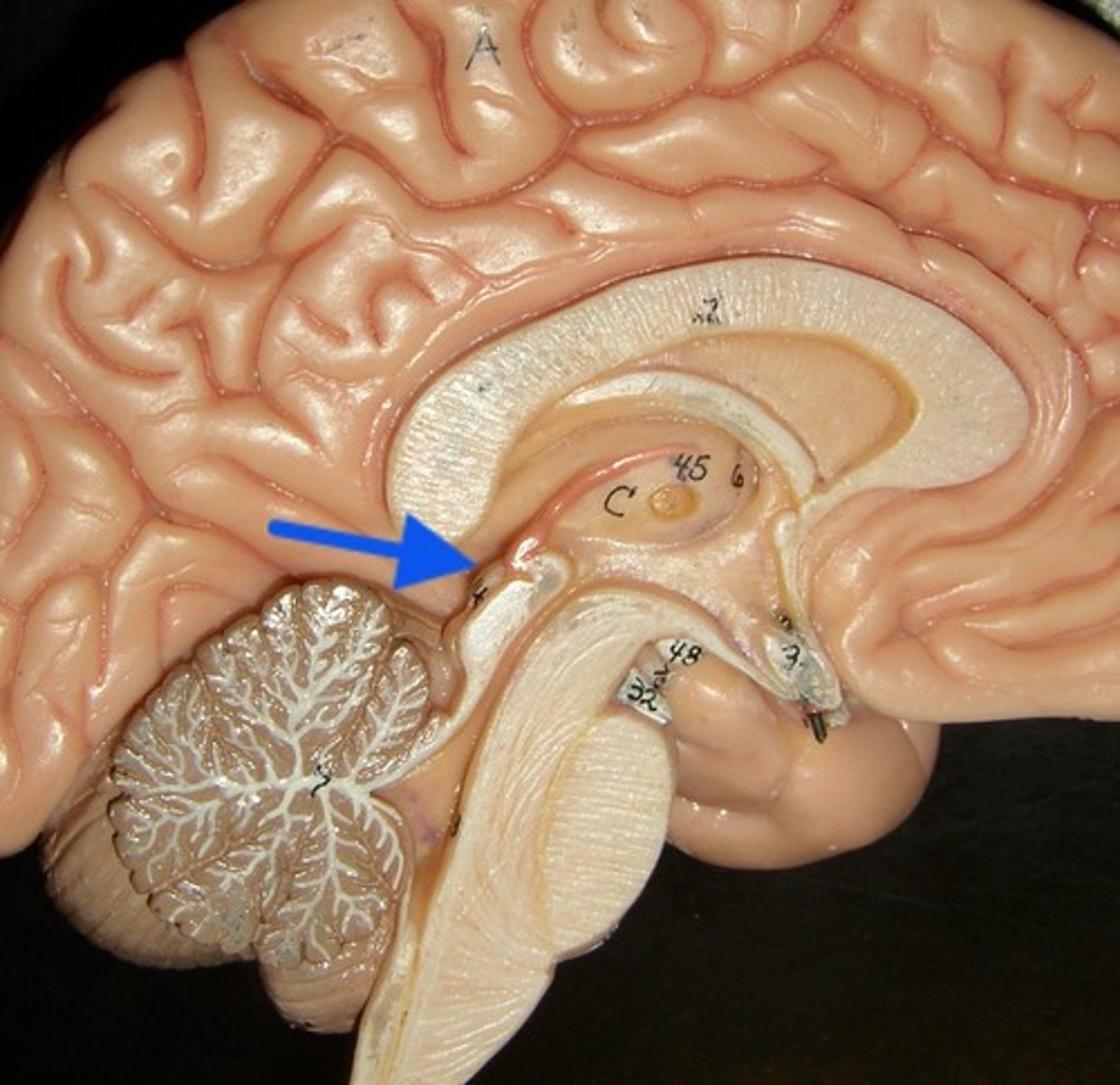
superior colliculi
visual reflexes
inferior colliculi
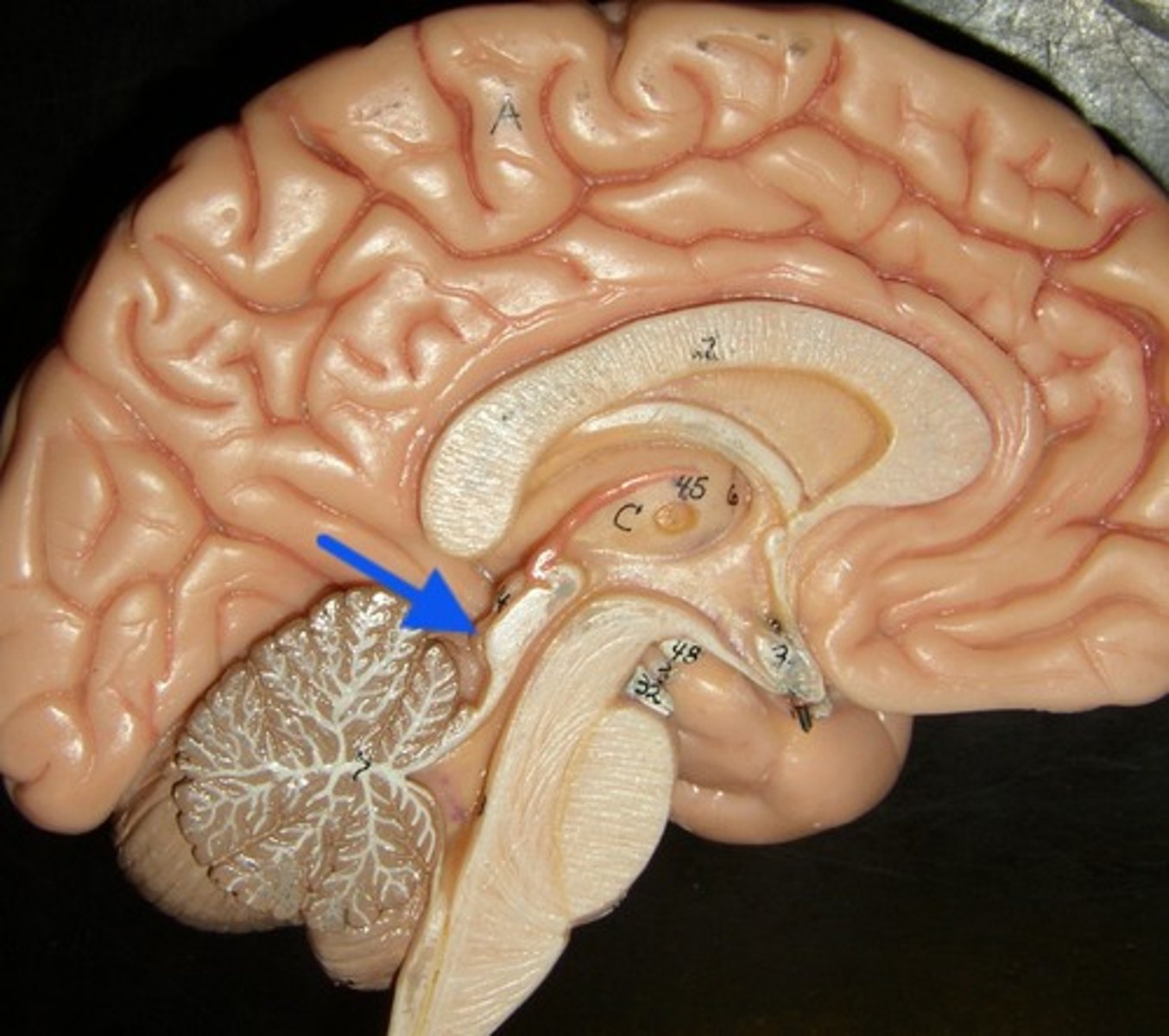
inferior colliculi
auditory reflexes
cerebral aqueduct
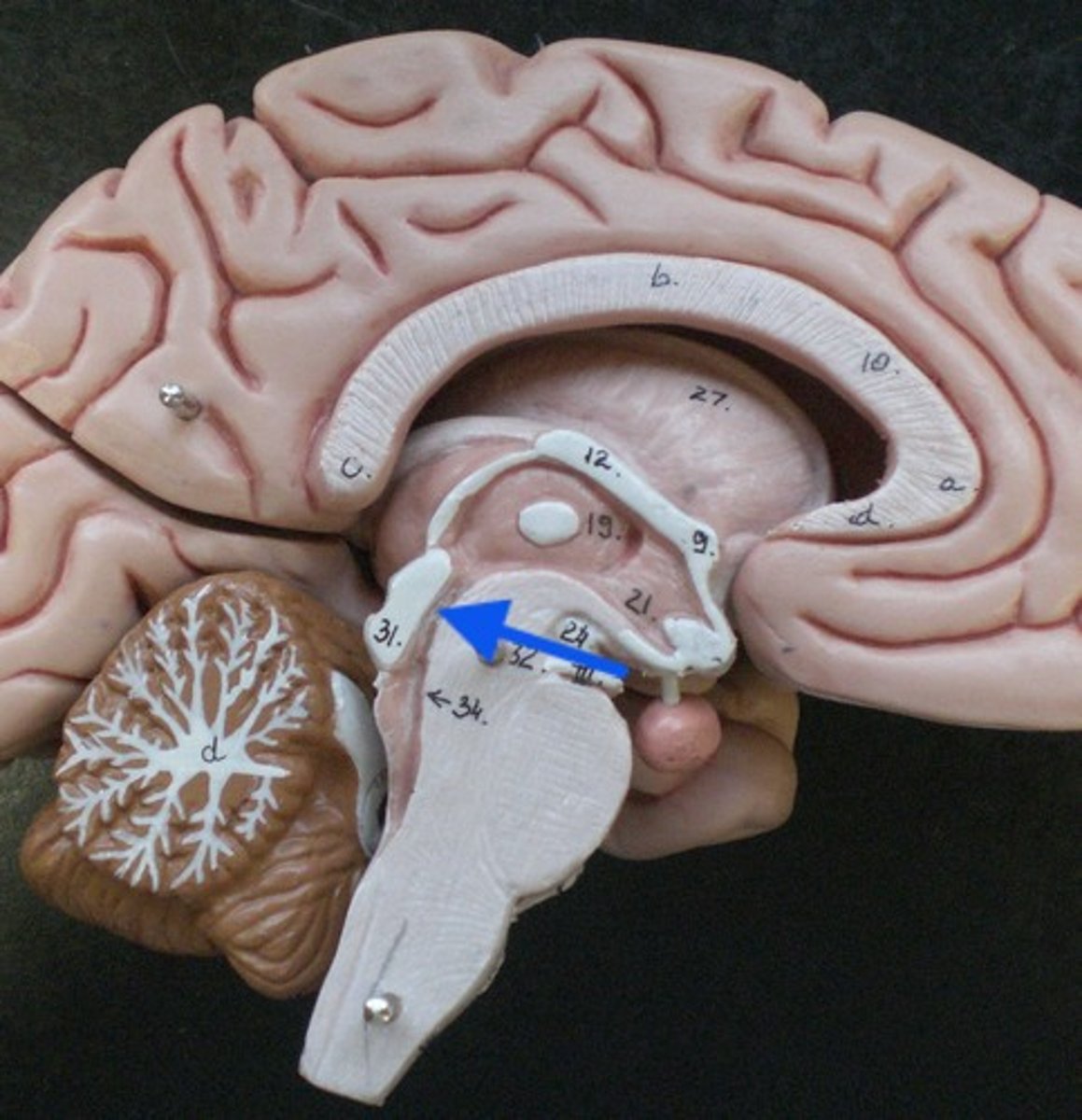
cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
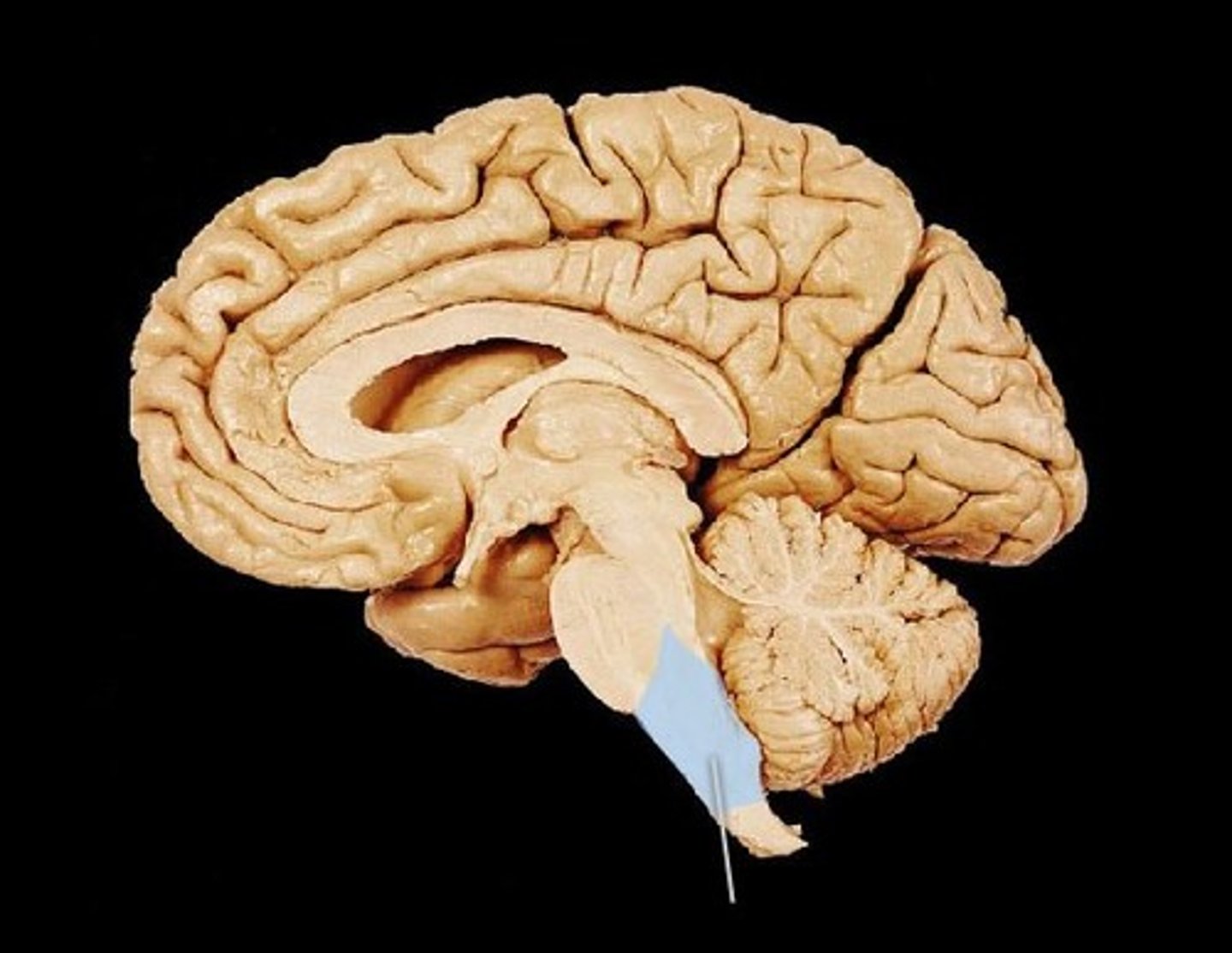
arbor vitae of the cerebellum
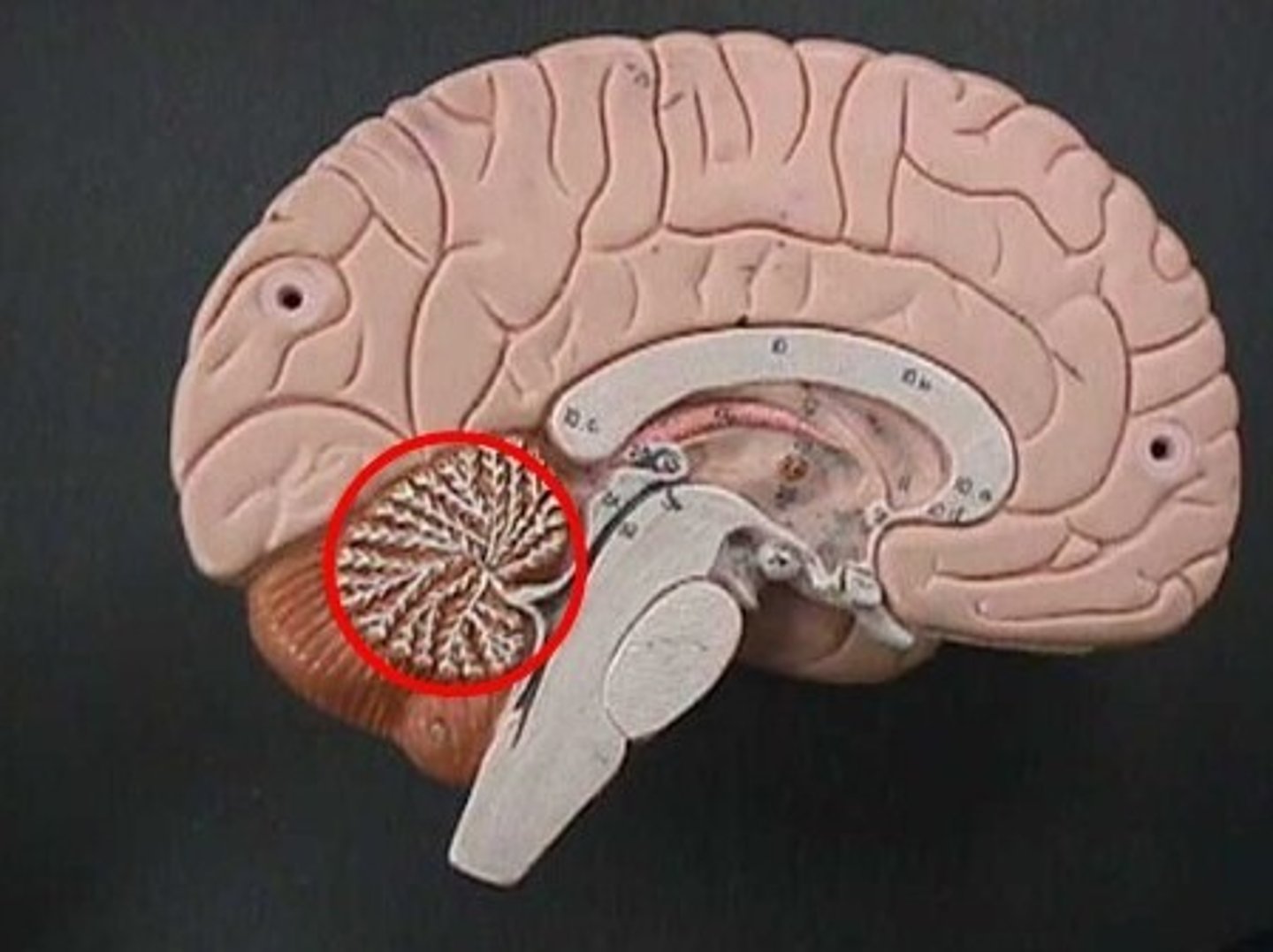
arbor vitae of the cerebellum
tree like arrangement of white matter
dura mater
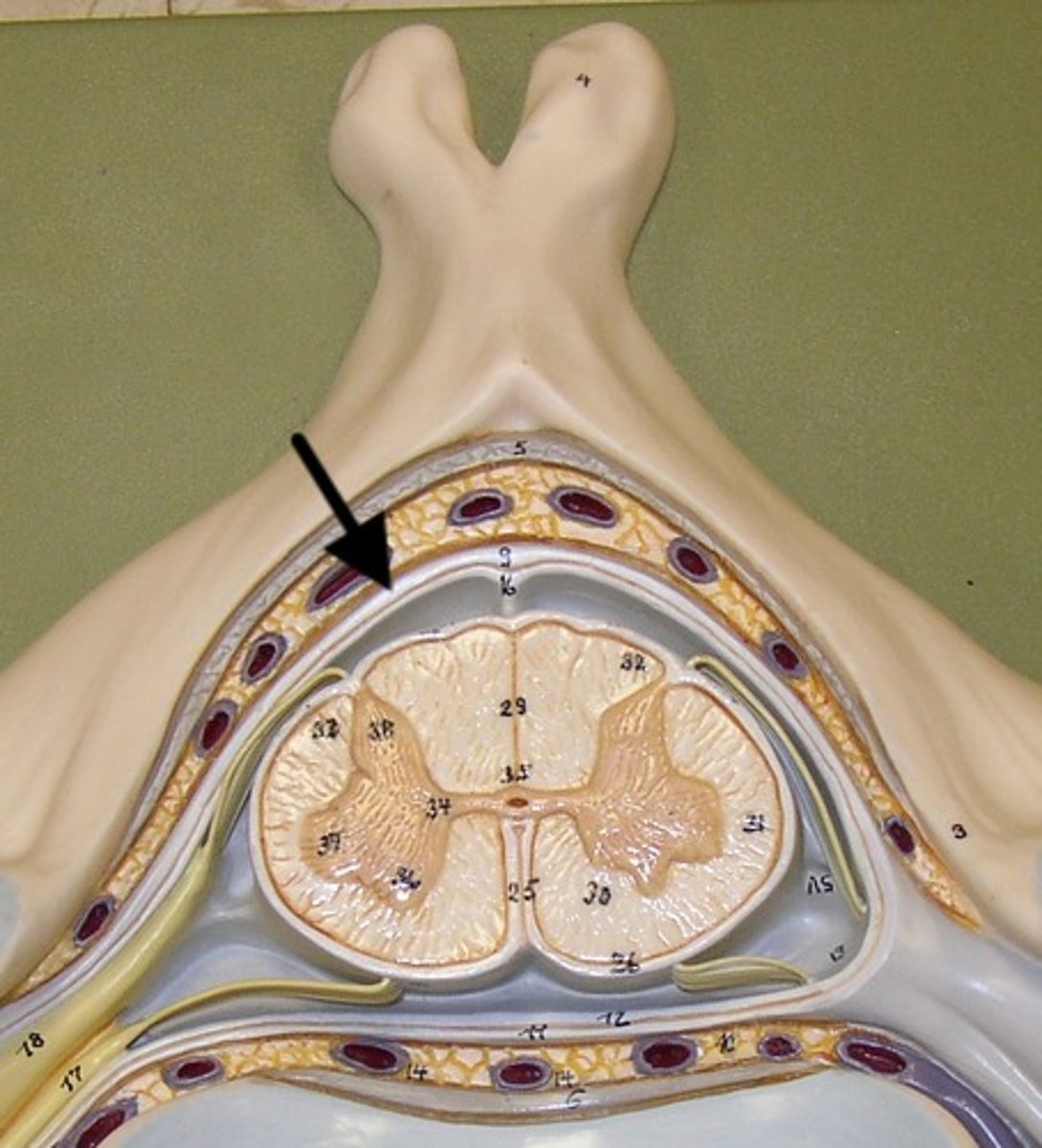
dura mater
thick, outermost layer of the meninges surrounding and protecting the brain and spinal cord
arachnoid mater
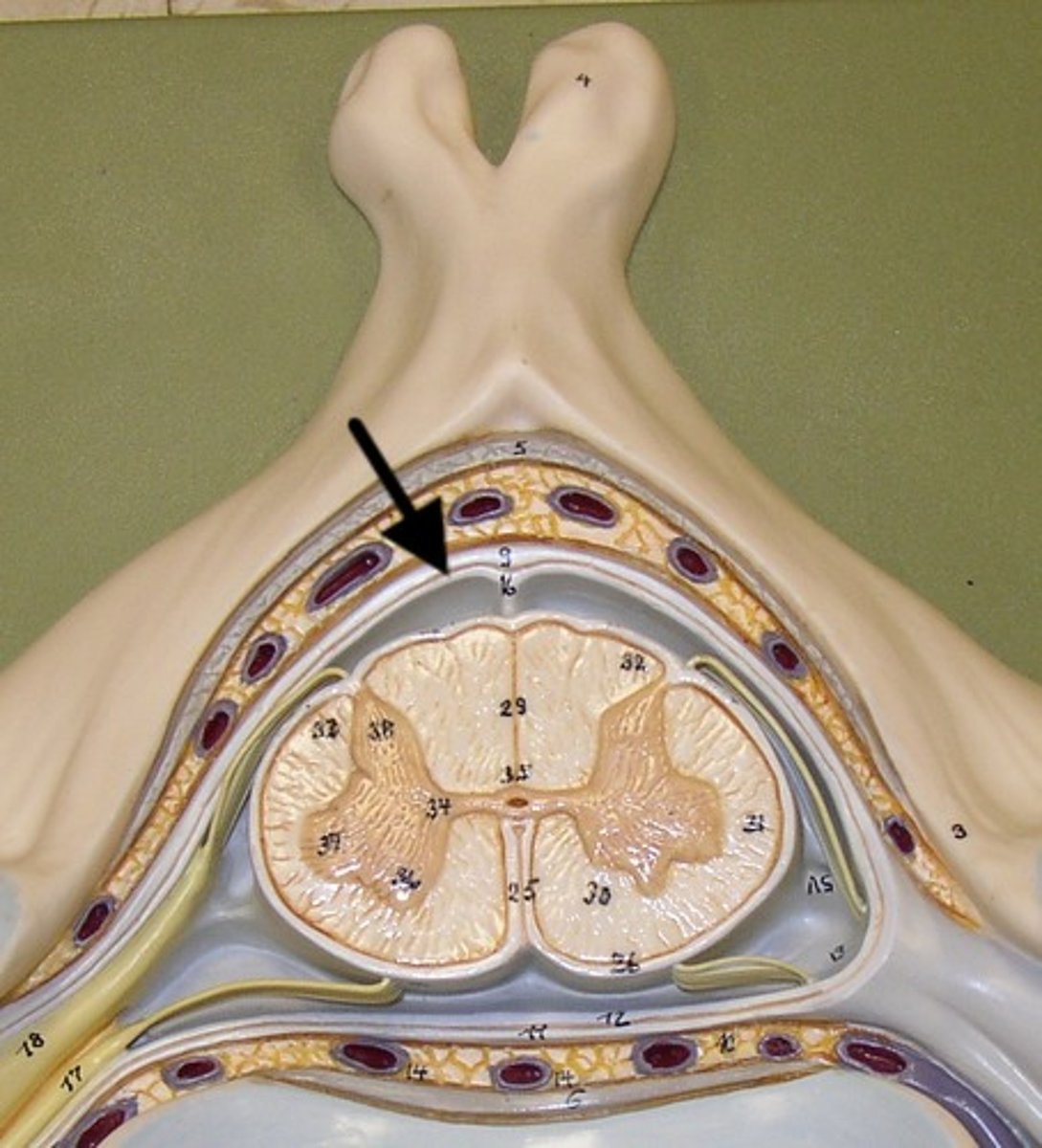
arachnoid mater
weblike middle layer of the three meninges
pia mater
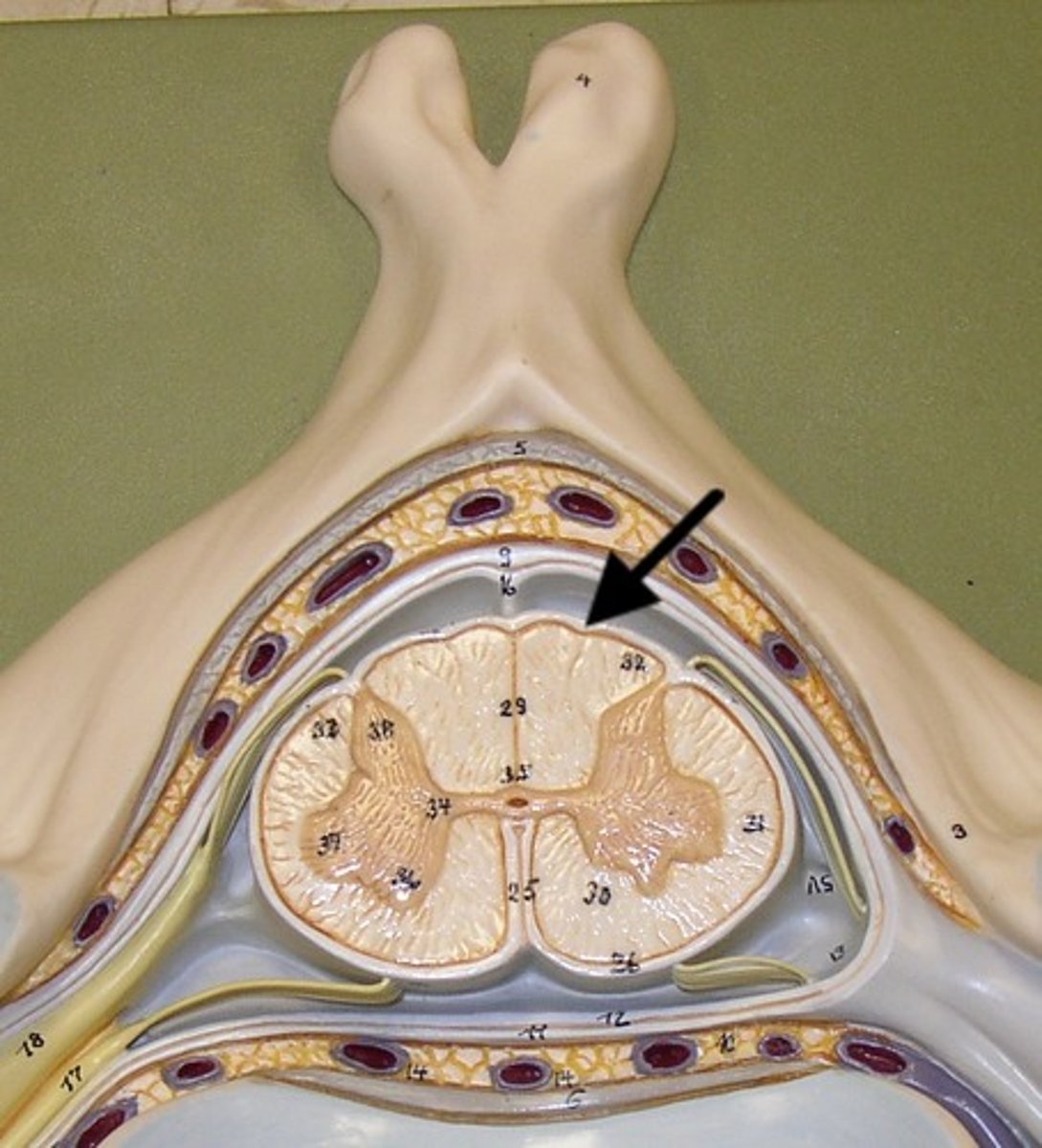
pia mater
thin, delicate inner membrane of the meninges
1. Olfactory
2. Optic
3. Oculomotor
4. Trochlear
5. Trigeminal
6. Abducens
What are the 6 cranial nerves?
olfactory nerve
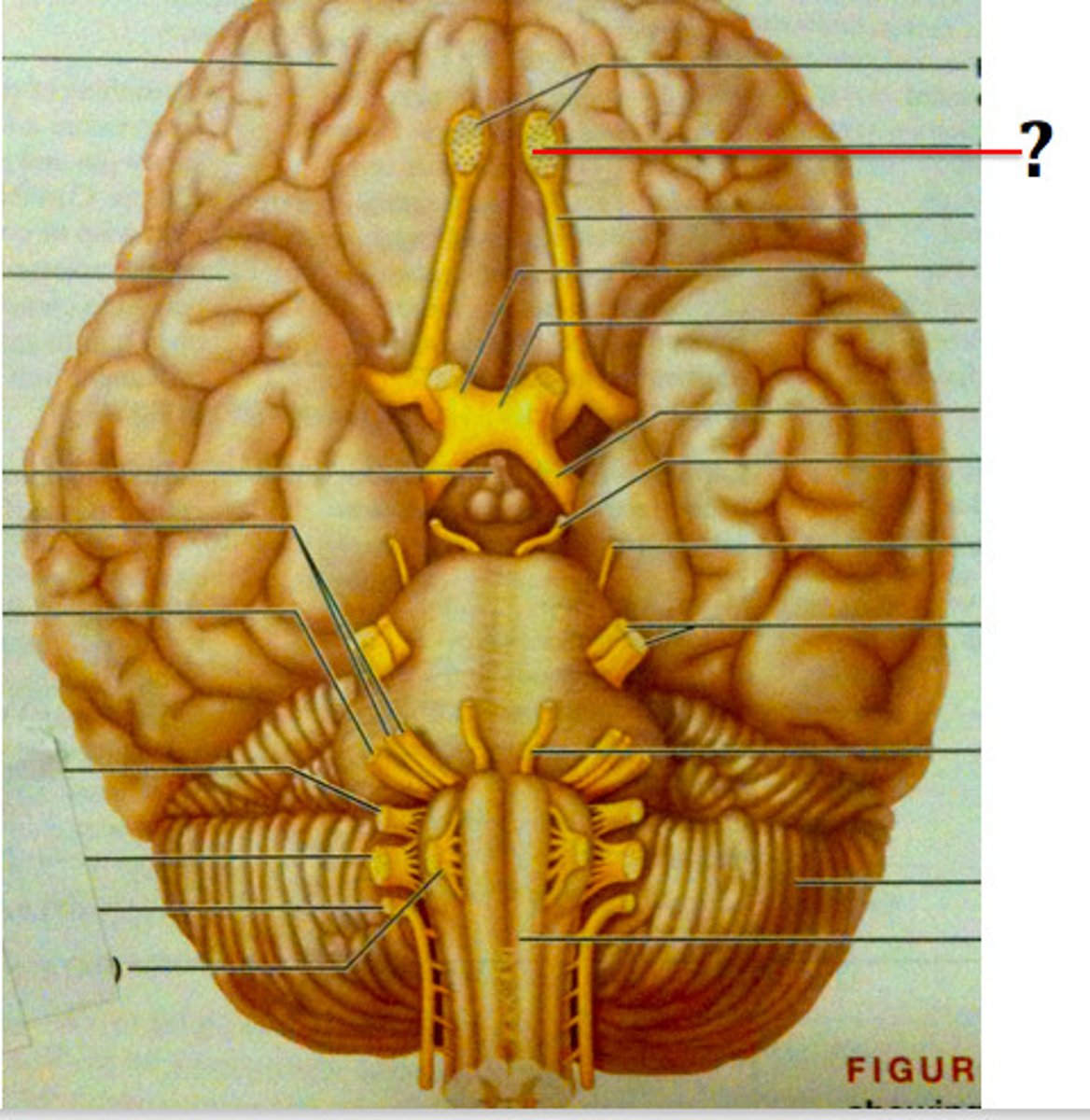
olfactory nerve
the nerve that carries smell impulses from the nose to the brain
oculomotor nerve
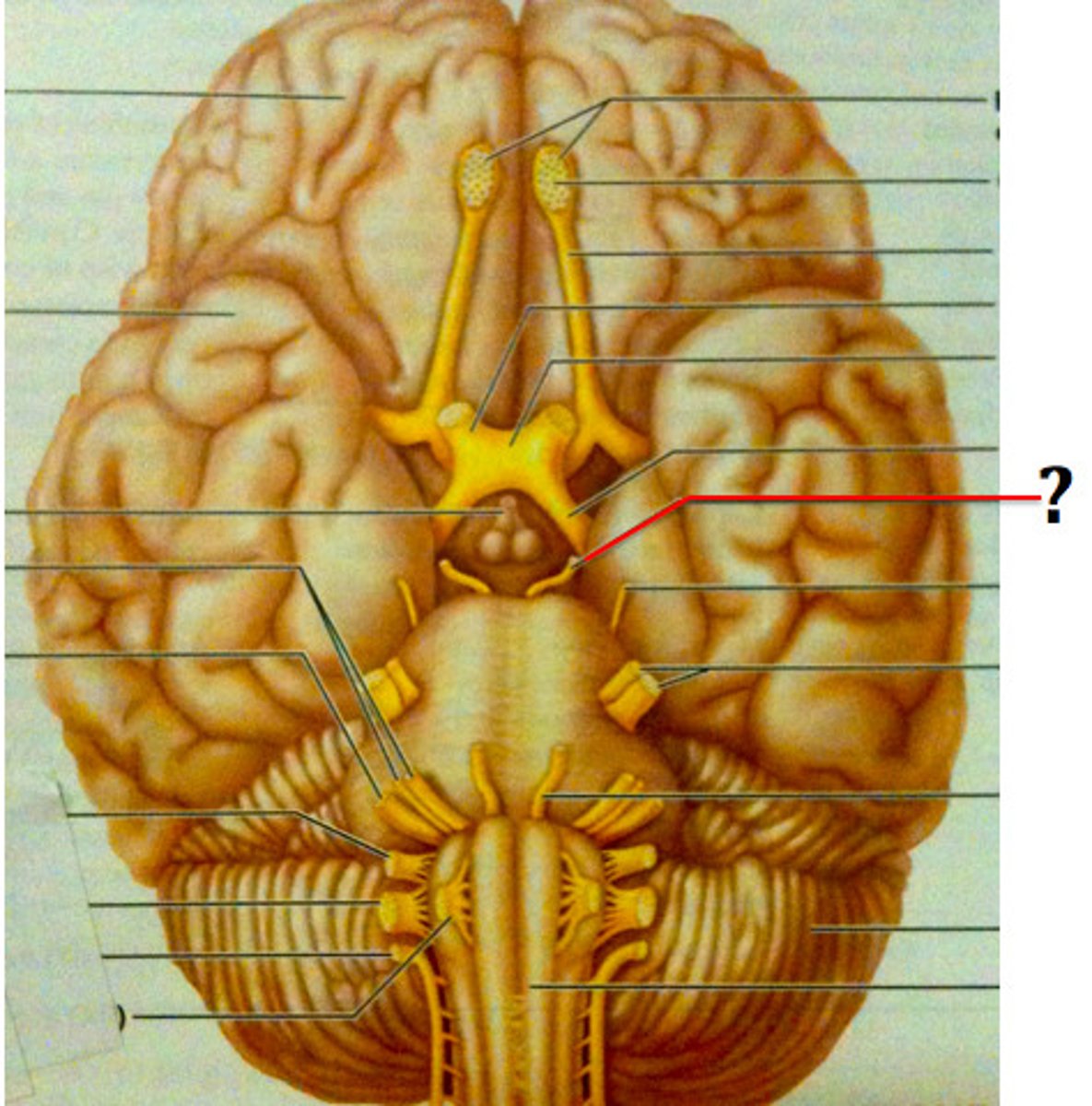
oculomotor nerve
eye movement
trochlear nerve
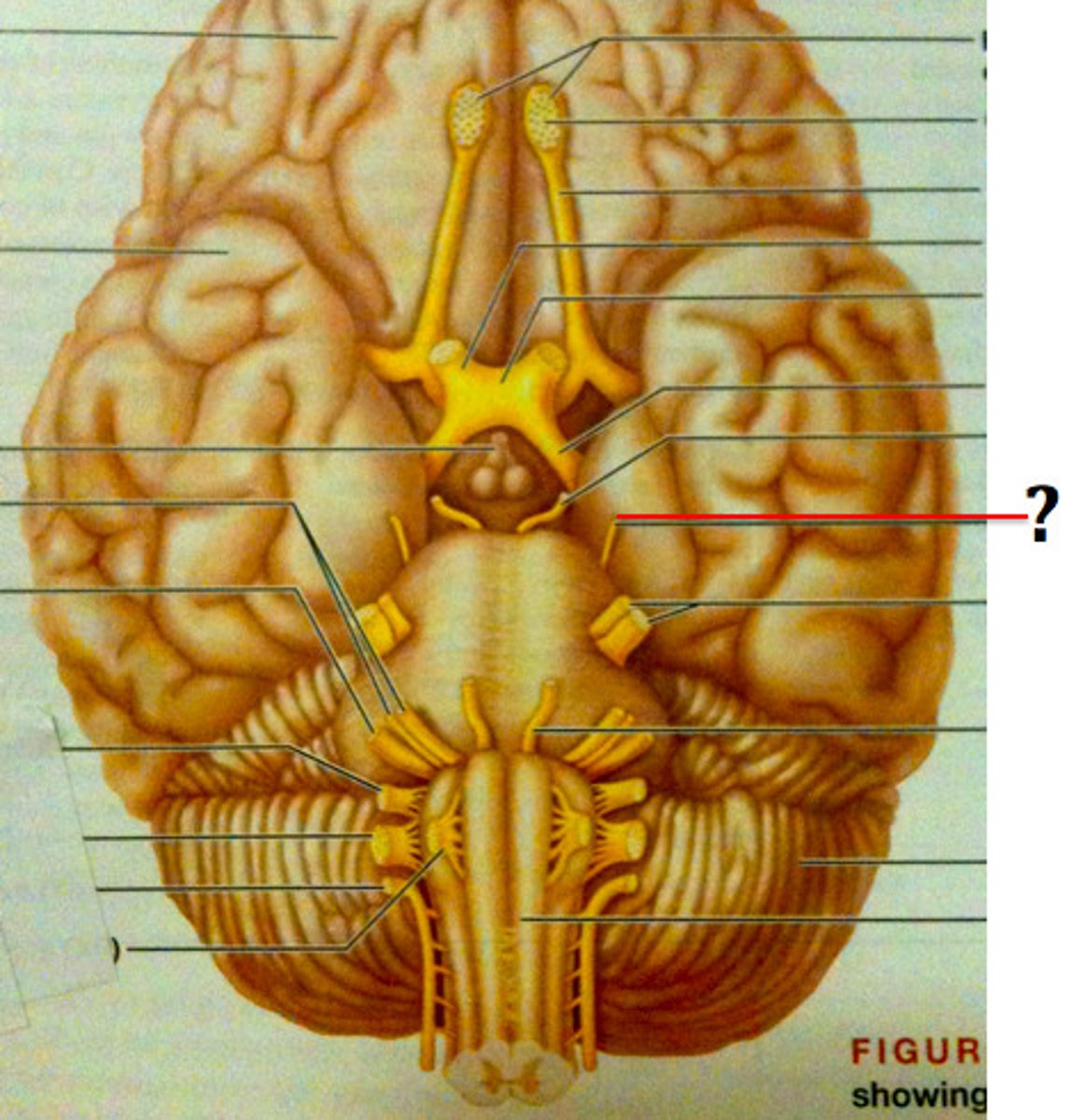
trochlear nerve
eye movement (2)