Population Growth
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Population Growth Rate
Population Growth Rate: How fast a population changes in size over time.
Dispersal
Dispersal: The movement of offspring away from their parents, which affects population size and growth.
Migration
Migration: Seasonal movement of individuals or populations, also impacting population size.
Immigration = the movement of an organism into a new area
Leads to an increase in population size
Emigration = the movement of an organism out of a population or area
Leads to a decrease in population size
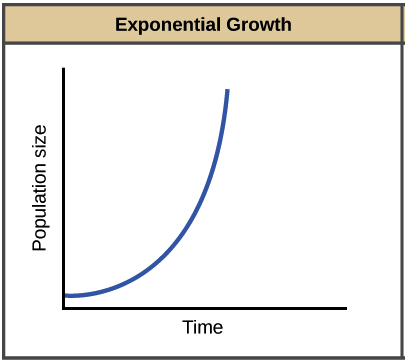
Exponential Growth
Exponential Growth:
Happens when resources are unlimited.
Population size increases quickly over time.
Shown as a J-shaped curve on a graph.
Example: Bacteria growing rapidly in a petri dish with unlimited nutrients.
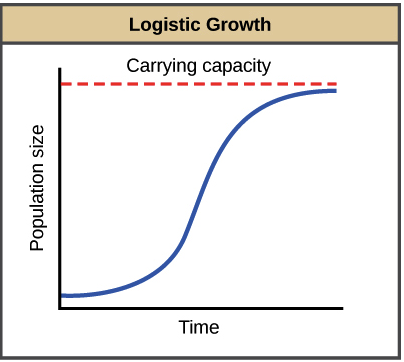
Logistic Growth
Logistic Growth:
Happens when resources are limited.
Growth slows as it reaches the carrying capacity (maximum number an environment can support).
Shown as an S-shaped curve on a graph.
Example: Deer population in a forest with limited food and space.
Biodiversity
Biodiversity: The variety of life in an area, including different species, genetic differences, and the ecosystems they form.
Richness
Richness: Number of different species in an ecosystem.
Example: A forest with 20 different tree species has a richness of 20.
Evenness
Evenness: How evenly the individuals are spread among species.
Example: Garden A has 10 flower species with equal numbers; Garden B has 10 flower species, but one dominates. Garden A has higher evenness.
Biomass
Biomass: Organic material from plants and animals used as a renewable energy source.
Examples: Wood, agricultural crops, animal waste.
Uses of Biomass
Uses:
Direct Combustion: Burning biomass to produce heat.
Biofuels: Converting biomass into liquid fuels like ethanol.
Biogas: Decomposing organic material without oxygen to produce methane for heating or electricity.
Pros and Cons of Biomass Use
Benefits: Renewable, reduces waste, and is carbon neutral.
Challenges: Requires land and may not be very efficient.