Chapter 7: Flexible Budgets, Direct-Cost Variances, and Management Control
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Predetermined manufacturing overhead rate
budgeted manufacturing overhead/ budgeted allocation base
Flexible Budget formula
AO x SP x SQ
Actual Budget formula
AQ X AP
Middle column formula
AQ x SP
standard costing
targets or standards are established for direct material and direct labor. the standard costs are recorded in the accounting system. actual price and usage amounts are compared to the standard and variances are recorded.
- apply costs on the standard units, not actual
standard costing formula
actual output x standard quantity (of the input) x standard cost.
what we think it should cost!
static (master) budget
based on the output planned at the start of the budget period
variance
difference between an actual and an expected (budgeted) amountma
management by exception
the practice of focusing attention on areas not operating as expected (budgeted)
static budget variances
the difference between the actual result and the corresponding amount in the static budget
static budget formula
budgeted output x SP
favorable variance
increases operating income
unfavorable variance
decreases operating income
flexible budget
budget that is adjusted (flexed) to recognize the actual output level
- proportionately increase variable costs, keep fixed costs the same
- prepared at the end of the period
- it is what we would have prepared if we had known the actual output
budgeted contribution margin per unit
budgeted selling price - budgeted fixed cost per unit. "fixed" from budgeted amount to actual amount
1. identify actual output
2. calculate flexible budget for revenue based on budgeted selling price and actual quantity
3. calculate flexible budget for costs based on budgeted variable cost per unit, actual quantity, and budgeted fixed costs
sales-volume variance
difference between flexible budget and static budget amounts
flexible budget variance
difference between actual and flexible budget amount. much better measure than static budget variance
selling price variance
(actual selling - budgeted) x actual units
variance for variable costs
(actual variable costs/unit - budgeted) x actual units
price variance formula
(actual price of input - budgeted price of input) x actual quantity of input
efficiency variance formula
(actual quantity of input used - budgeted quantity of input allowed for actual output) x budgeted price of input
WIP
we cost at standard cost. allocation will always be SP x SQ x AO (standard cost x actual output)
- we will need to record variances from standard using variance accounts (otherwise JEs won't balance)
- variance accounts are generally closed into cost of goods sold at the end of the period, if material
- useful to report variances on COGS statement (for internal use)
JE to record purchase of materials
DR direct materials
CR accounts payable
DR/CR DM price variance
JE to record use of materials
DR work in process
CR direct materials
DR/CR DM efficiency variance
JE to record direct labor
DR work in process
CR wages payable
DR/CR DL price variance
DR/CR DL efficiency variance
JE to write off variances to COGS
DR/CR COGS
DR/CR DM price variance
DR/CR DM efficiency variance
DR/CR DL price variance
DR/CR FL efficiency variance
cost of goods sold statement
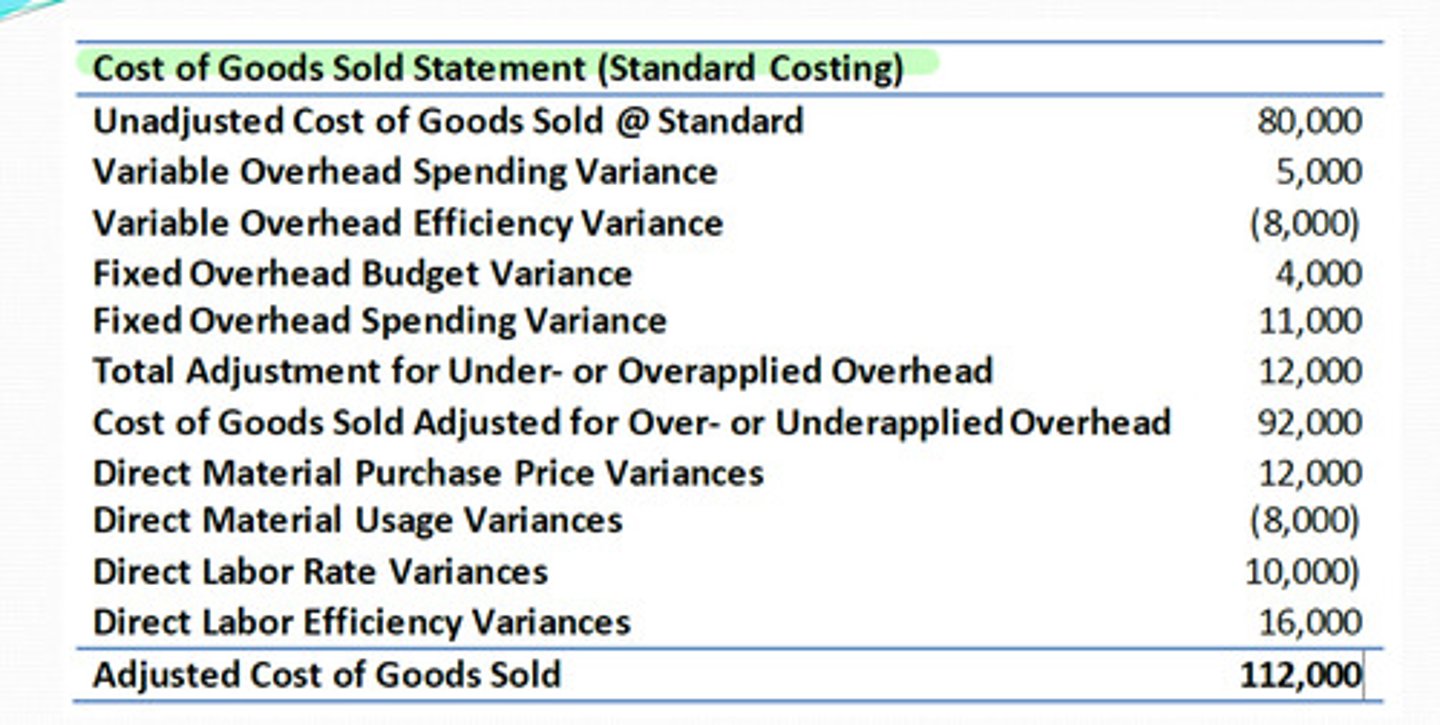
variances
- price and efficiency variances provide feedback to initiate corrective actions (management by exception)
- standards are used to control costs
- part of a continuous improvement program
important note on variances
it is important to note that a favorable variance is not necessarily a good thing, do not assume favorable = good!