10 Science sem 1 Exam revision
1/164
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For the semester 1 science exam for year 10 science in Australia
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
Atom
Smallest particle of an element
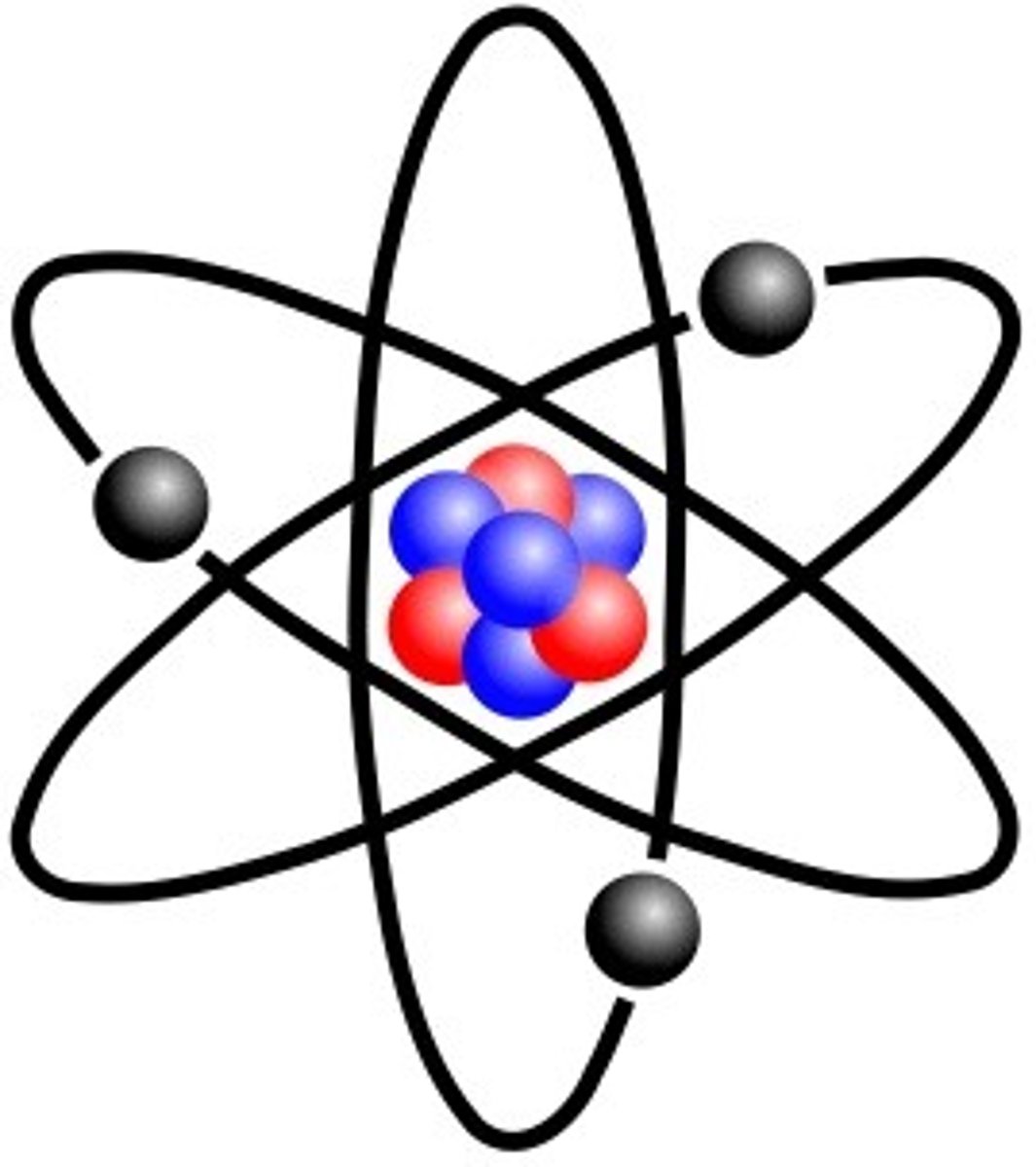
Proton
Positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom

Neutron
Particle with no charge found in the nucleus of an atom

Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom

Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds

Molecule
Two or more atoms bonded together
Atomic Number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
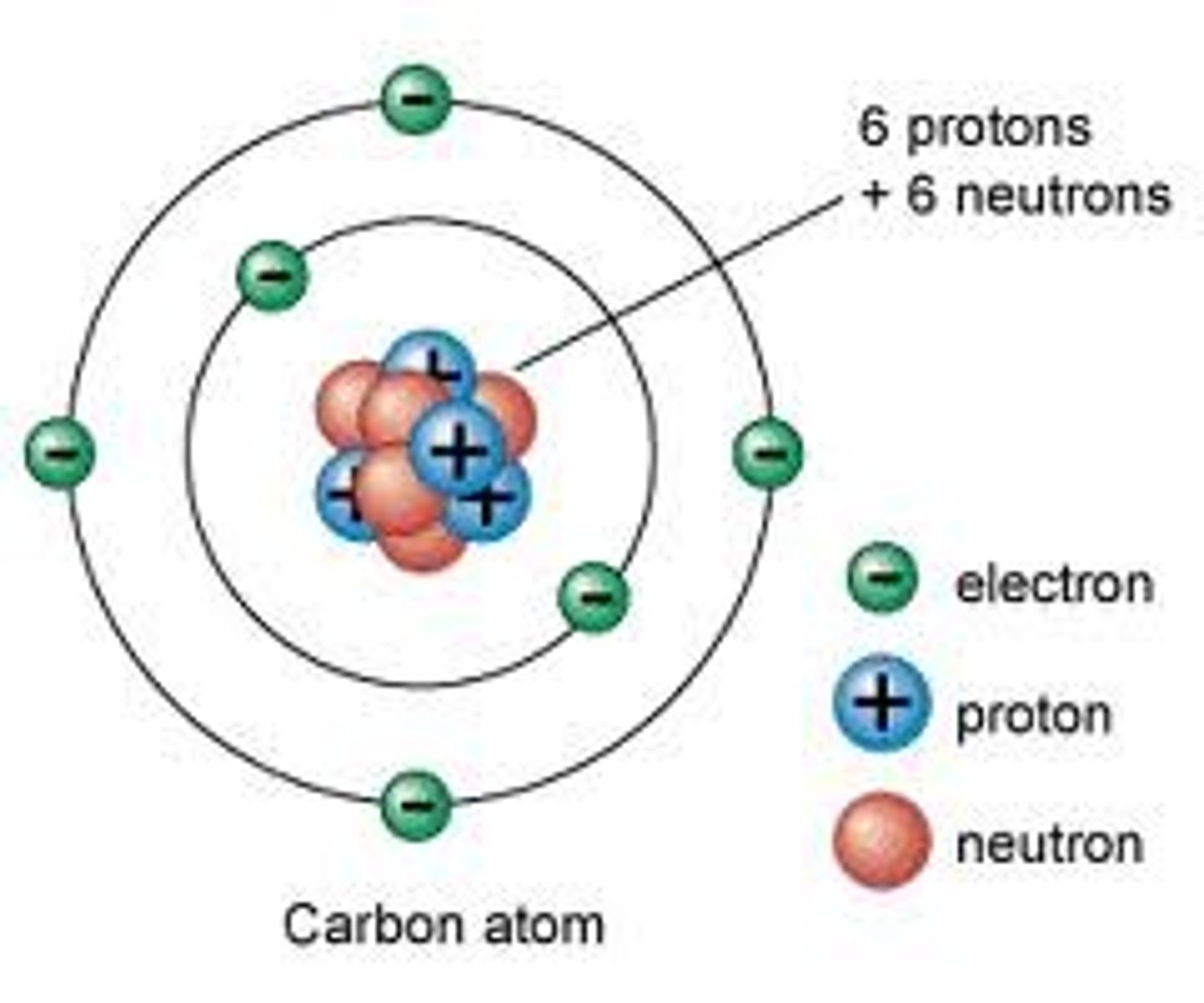
Mass Number
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
Nuclide Symbol
Symbol that indicates the atomic number, mass number, and identity of a nucleus
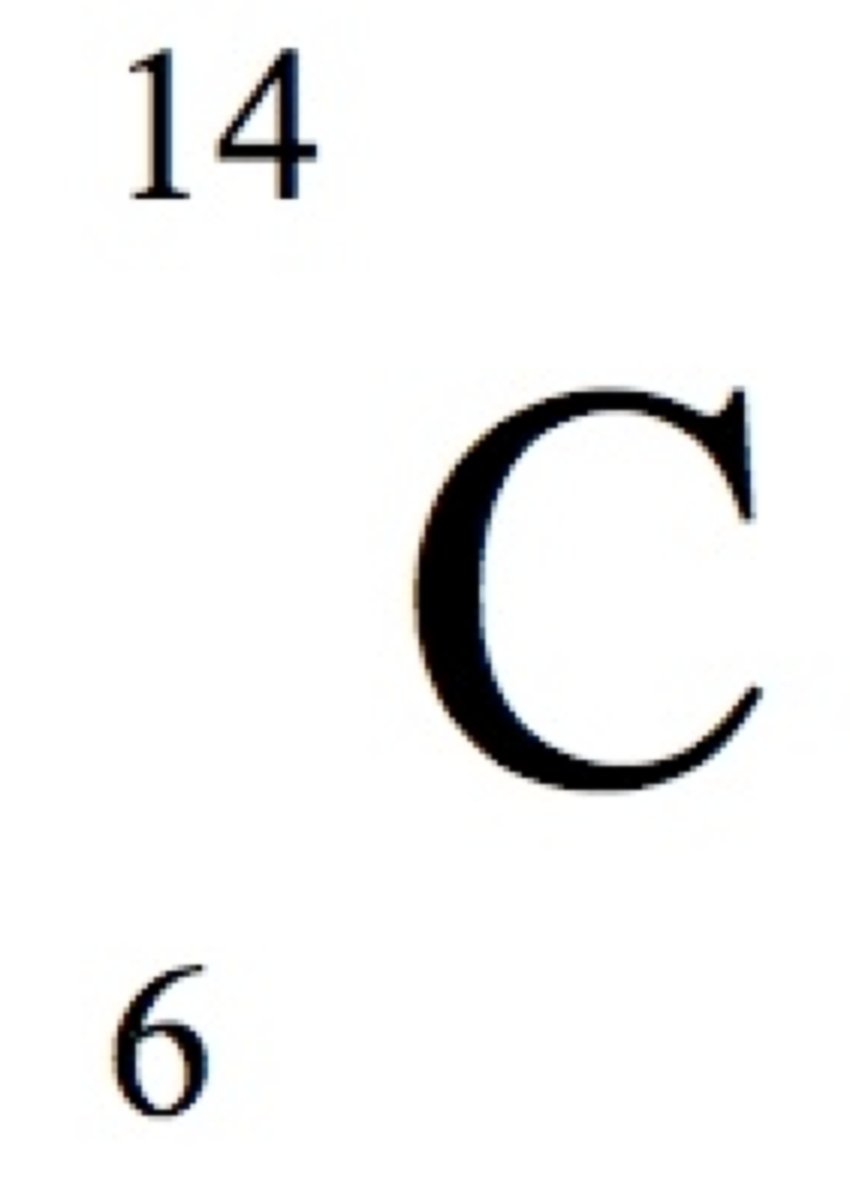
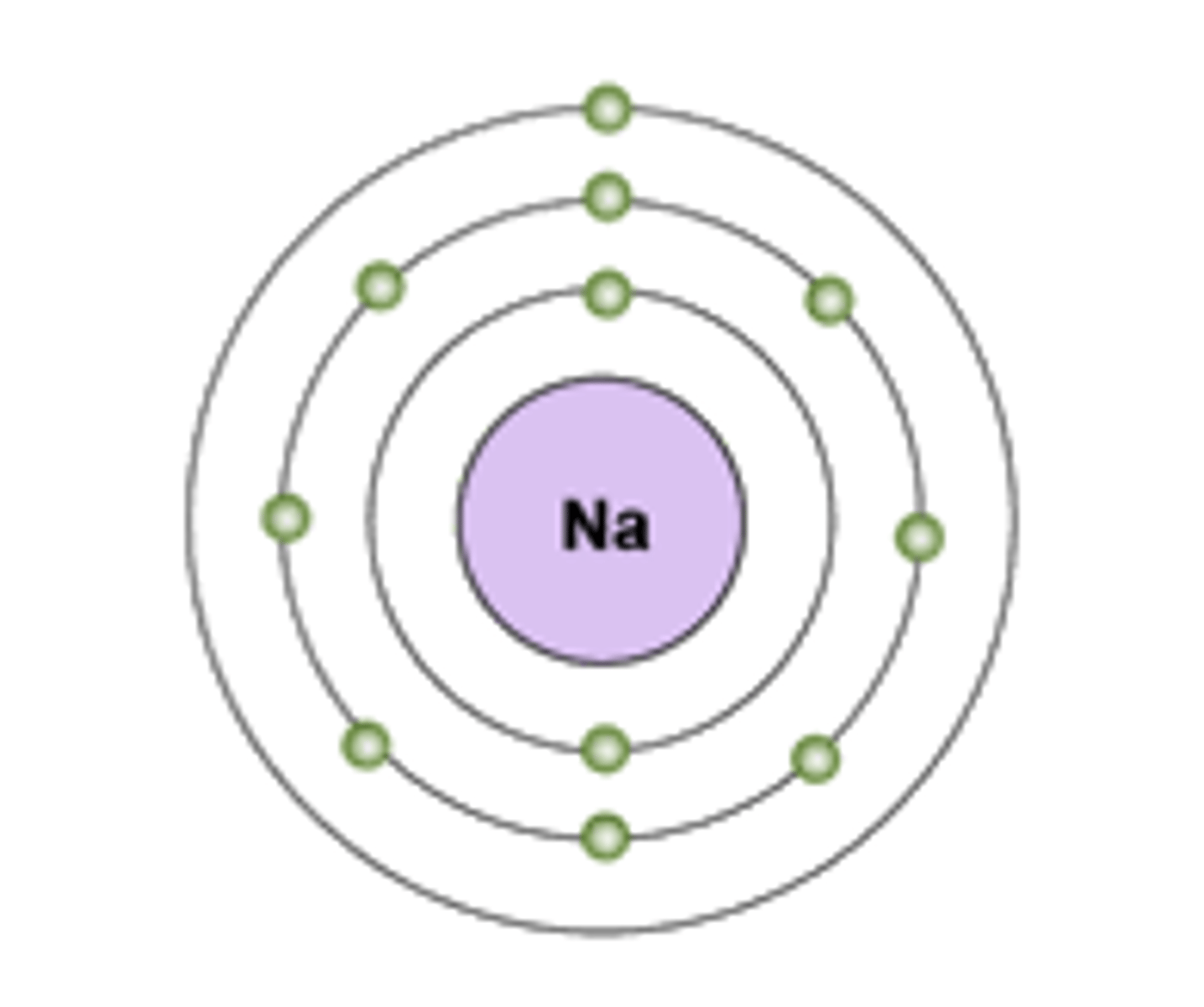
Electron Shell
A grouping of electrons surrounding the nucleus of an atom
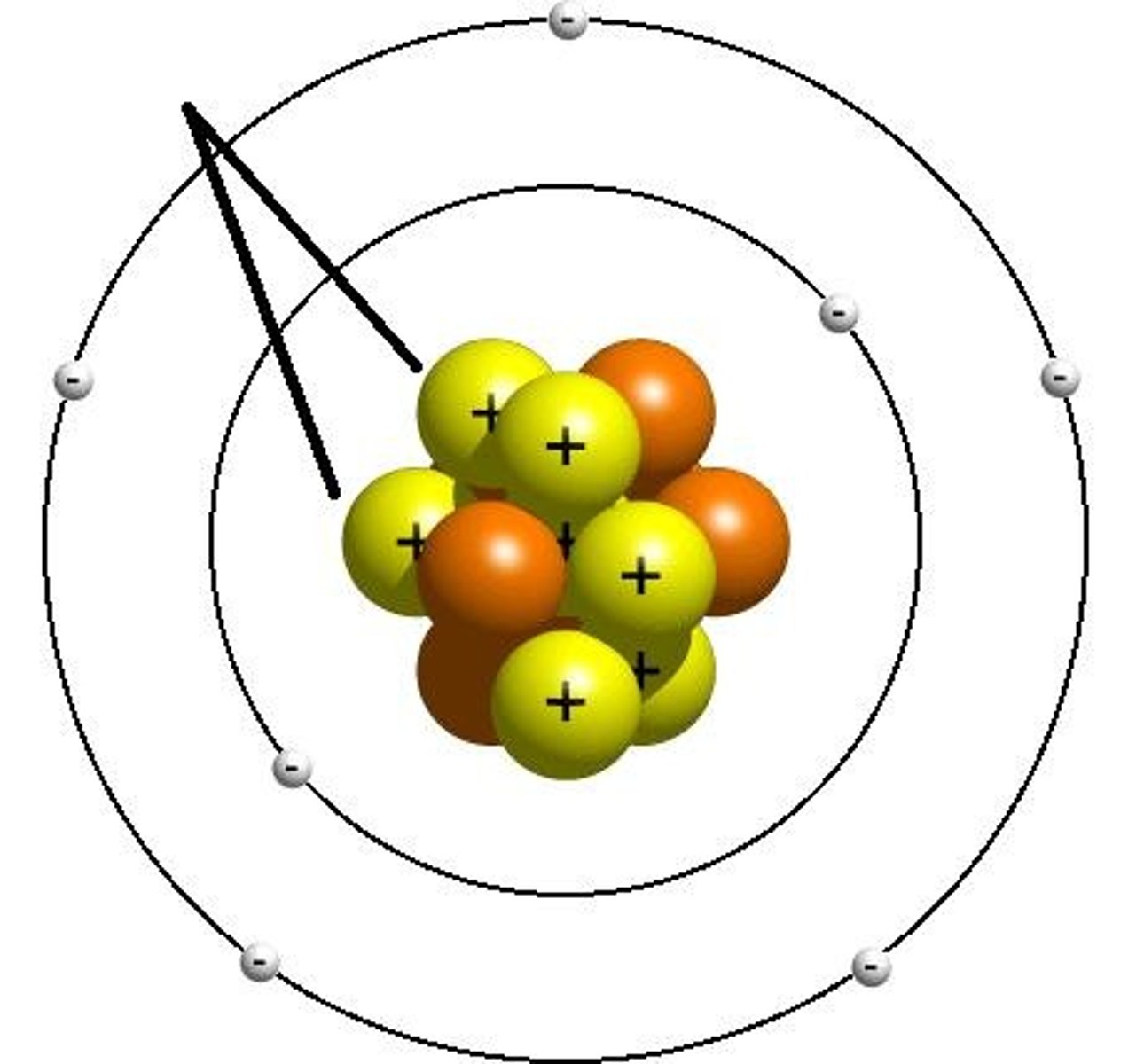
Subatomic Particle
Particles found within the atom, mainly protons, neutrons, and electrons.
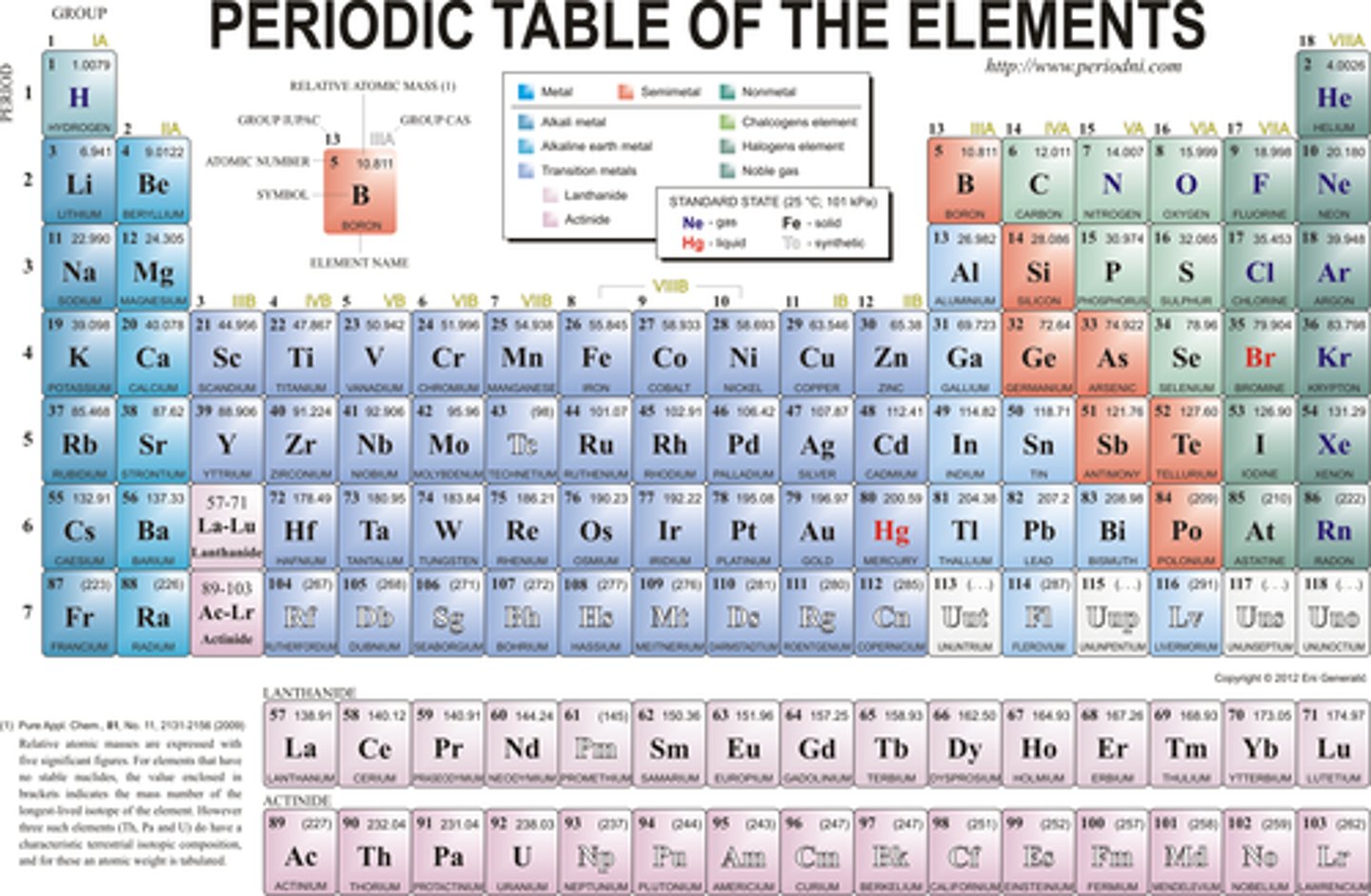
Periodic Table
A table that shows the elements, their atomic number, symbol, and average atomic mass; elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together.
Group
Vertical column in the periodic table
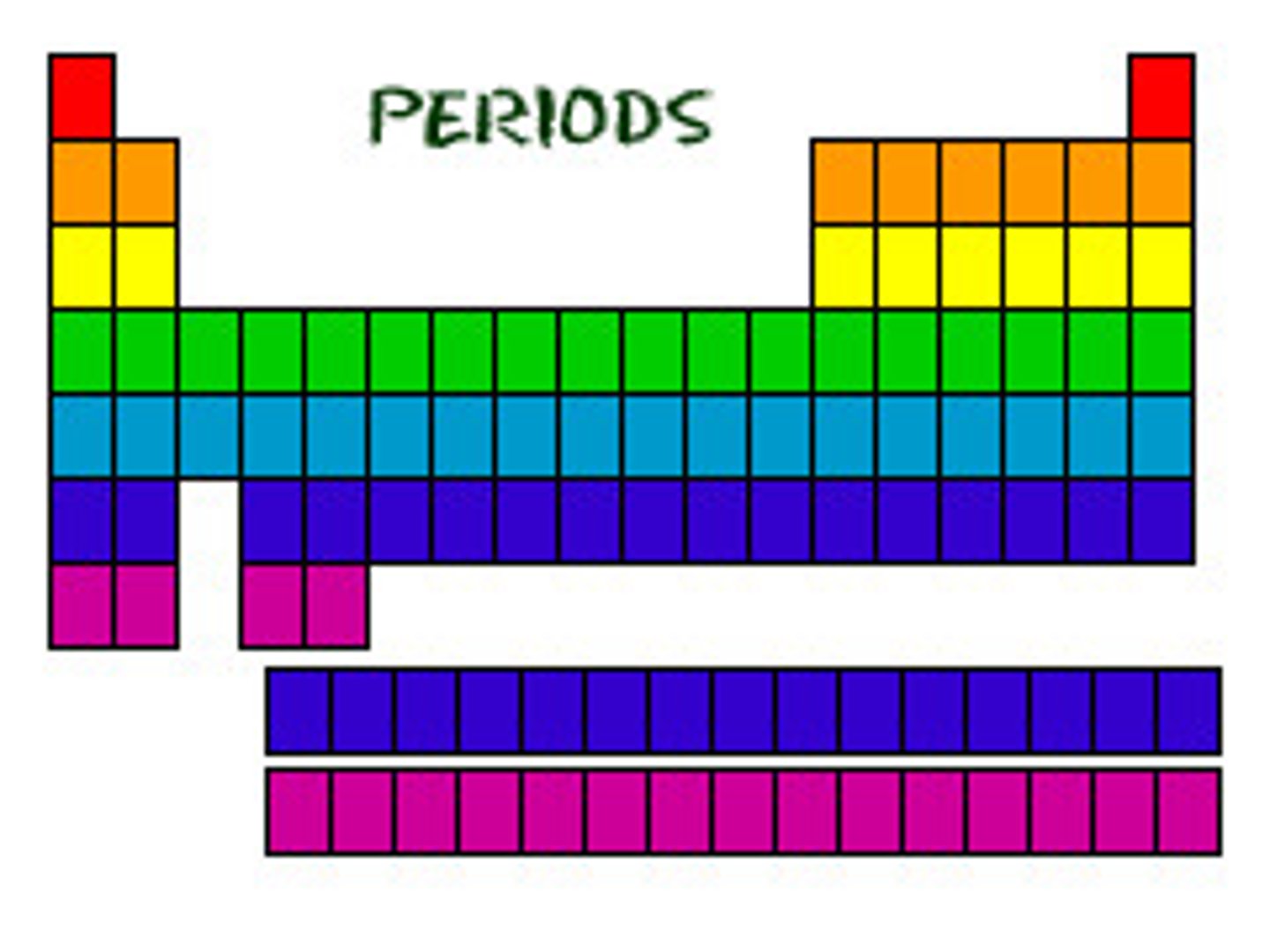
Period
A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table
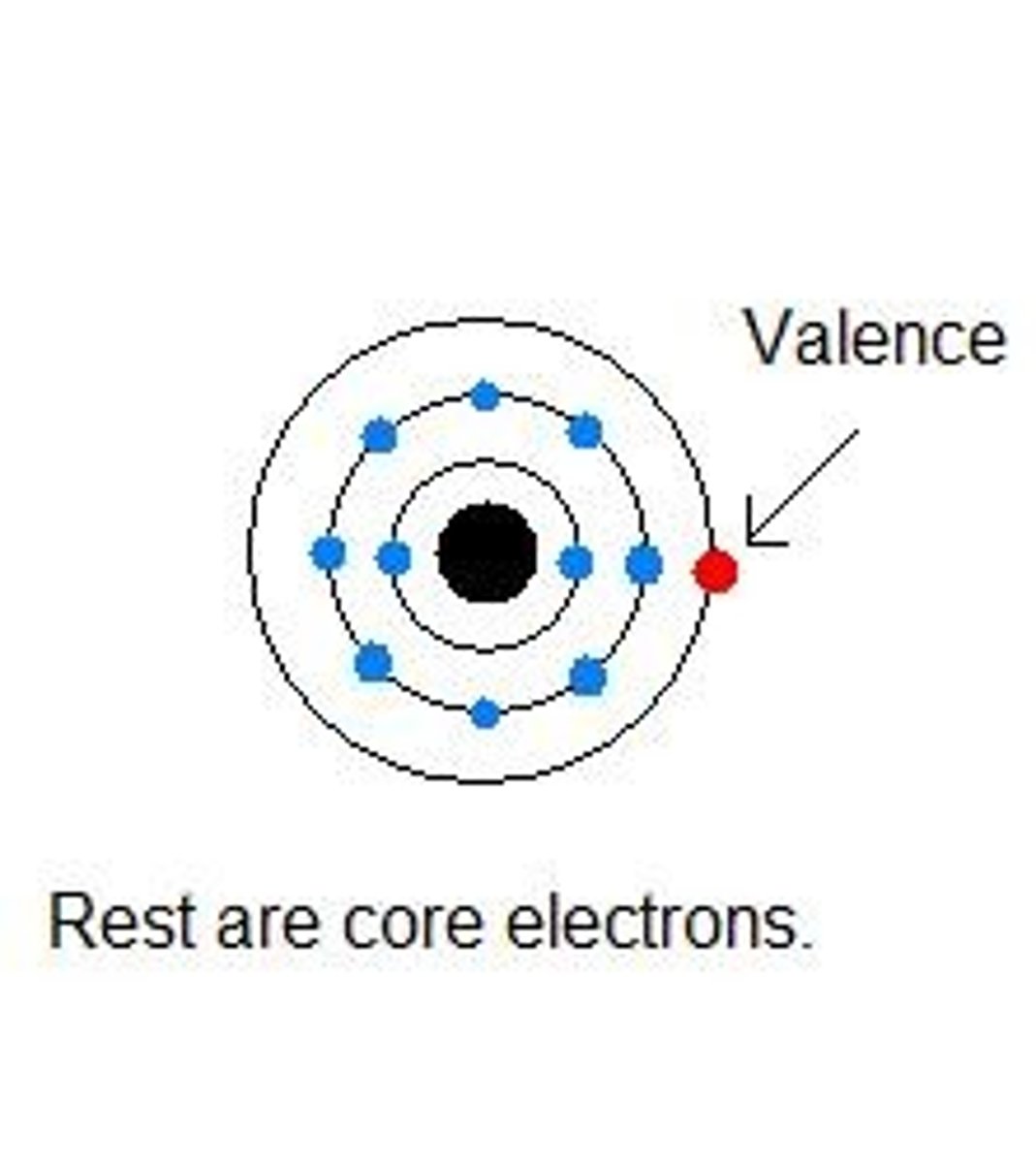
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
Metals
Elements that are good conductors of electric current and heat.
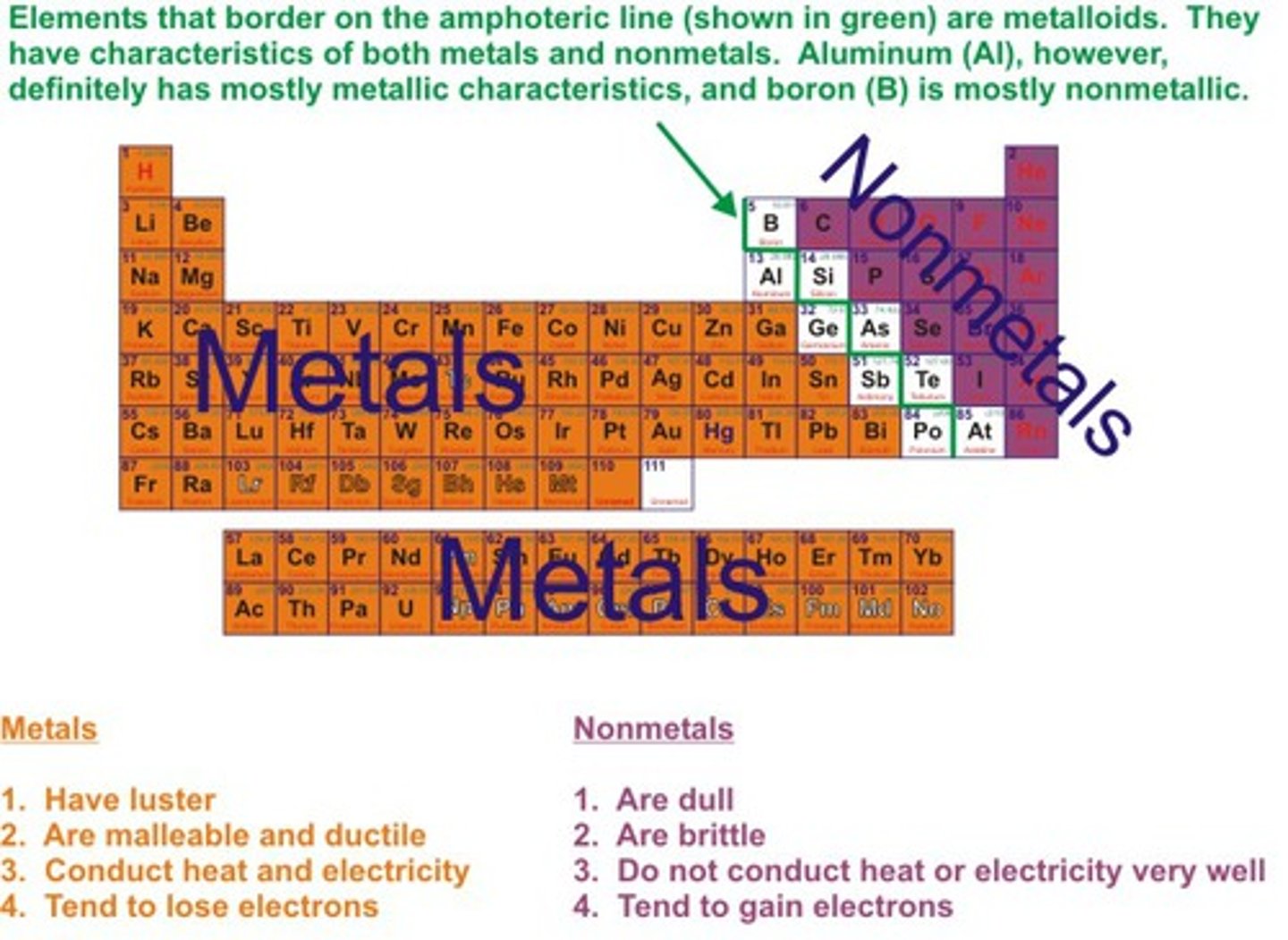
Non-metals
Elements that are usually dull in appearance, poor conductors of heat and electricity, usually gases at room temperature
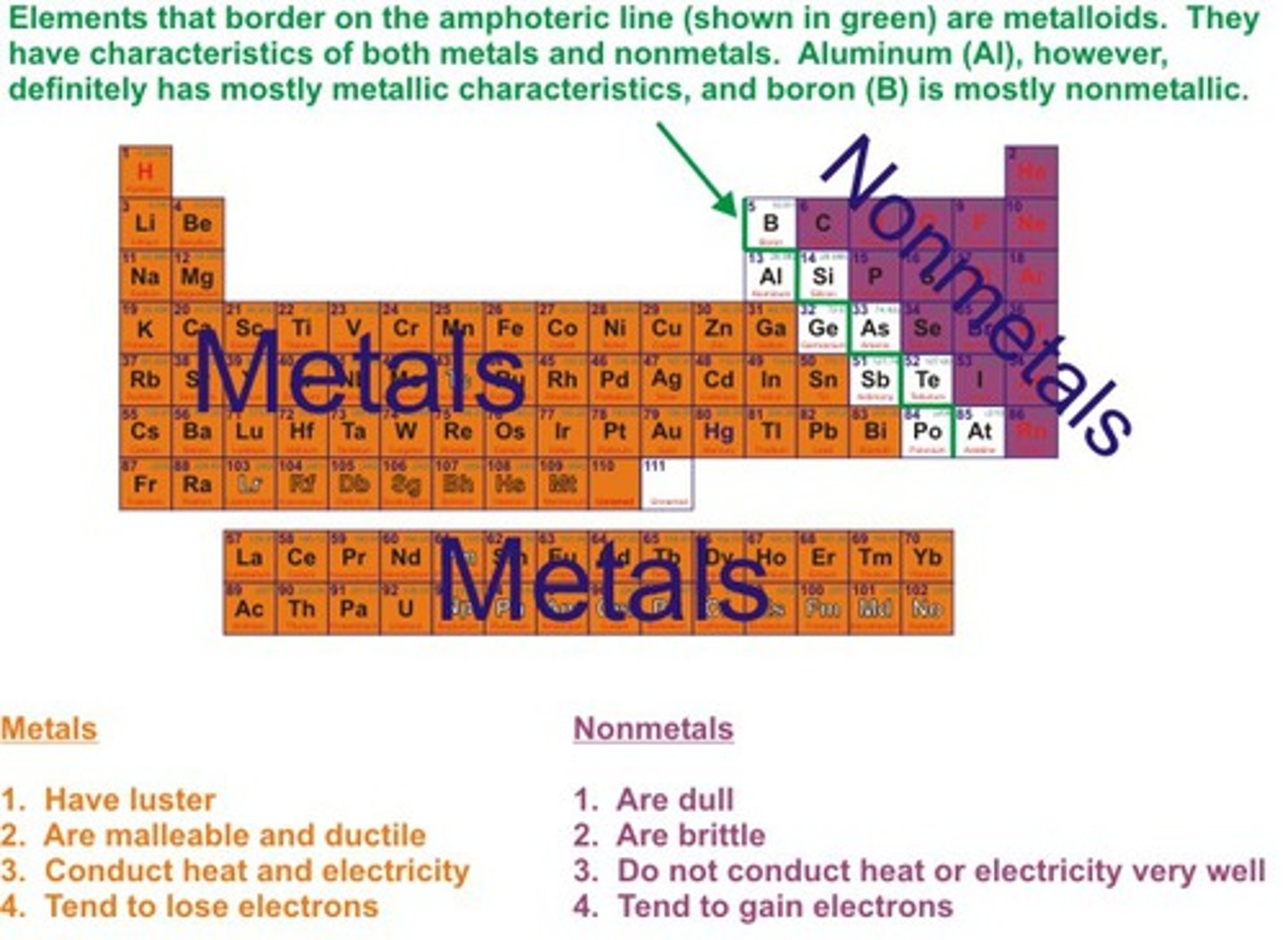
Metalloids
Elements that have properties of both metals and nonmetals.
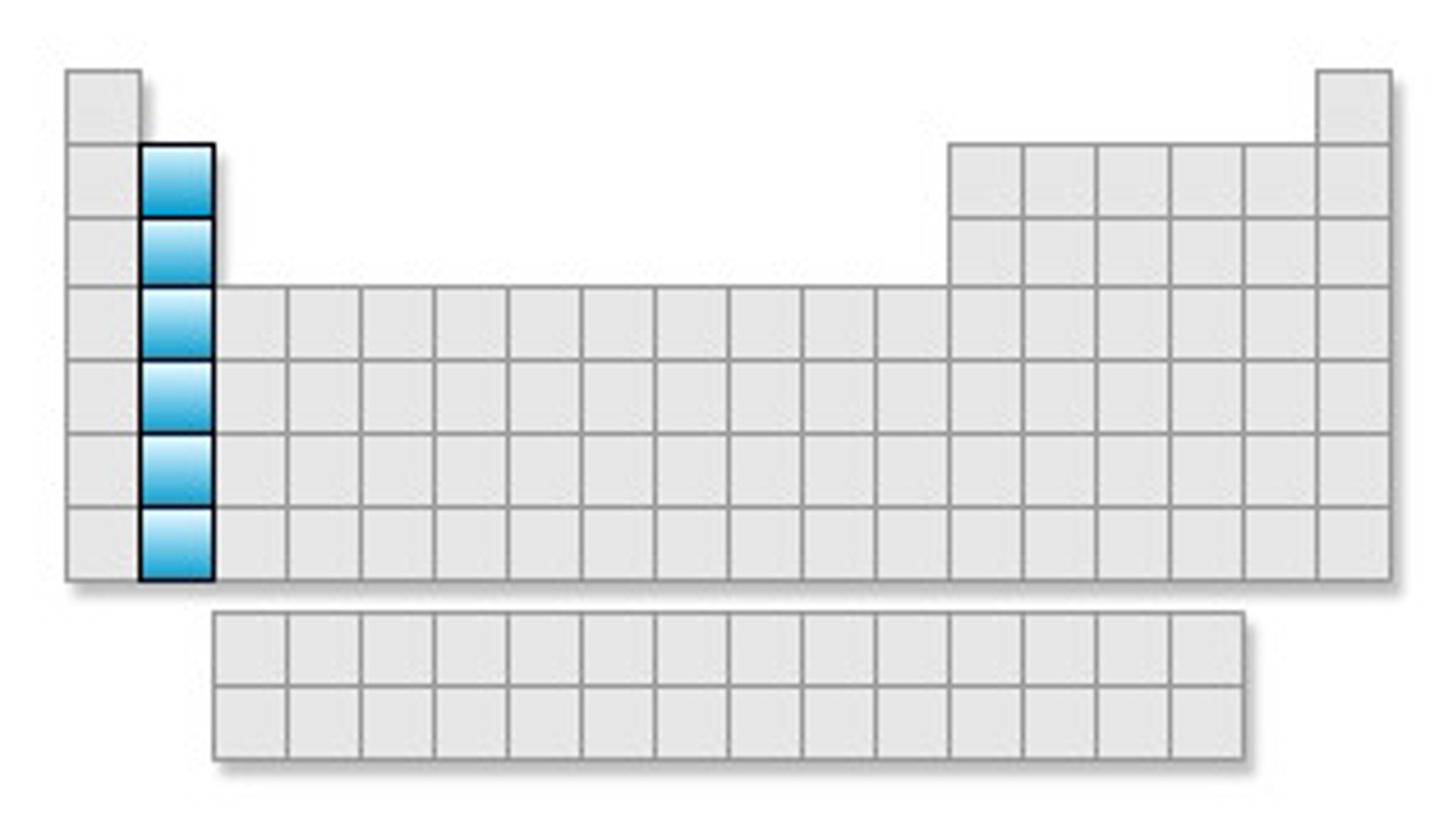
Alkali Metals
Elements found in group 1 of the Periodic Table
Alkaline Earth Metals
Elements found in group 2 of the Periodic Table
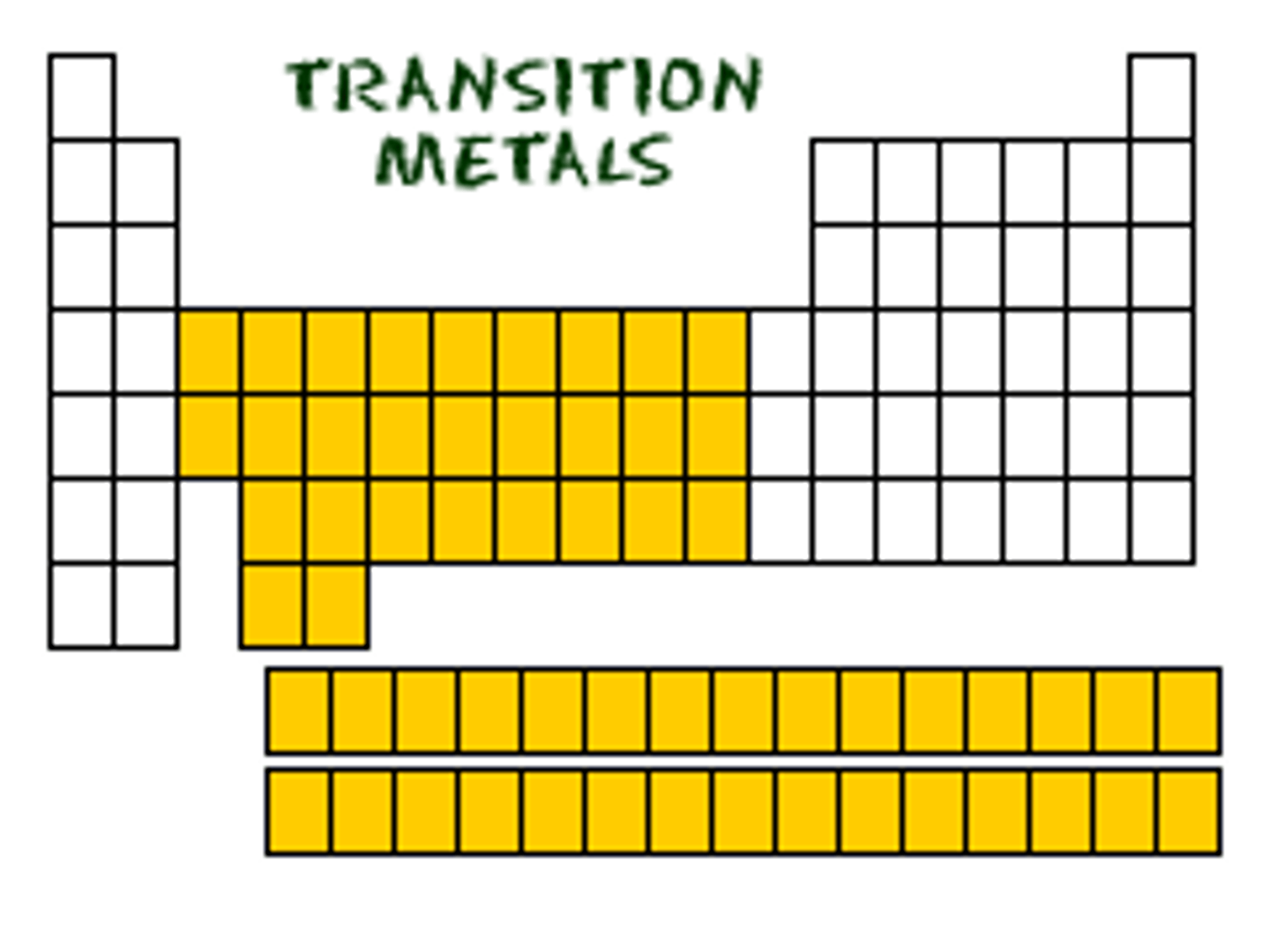
Transition Metals
Elements found in groups 3 - 12 of the Periodic Table
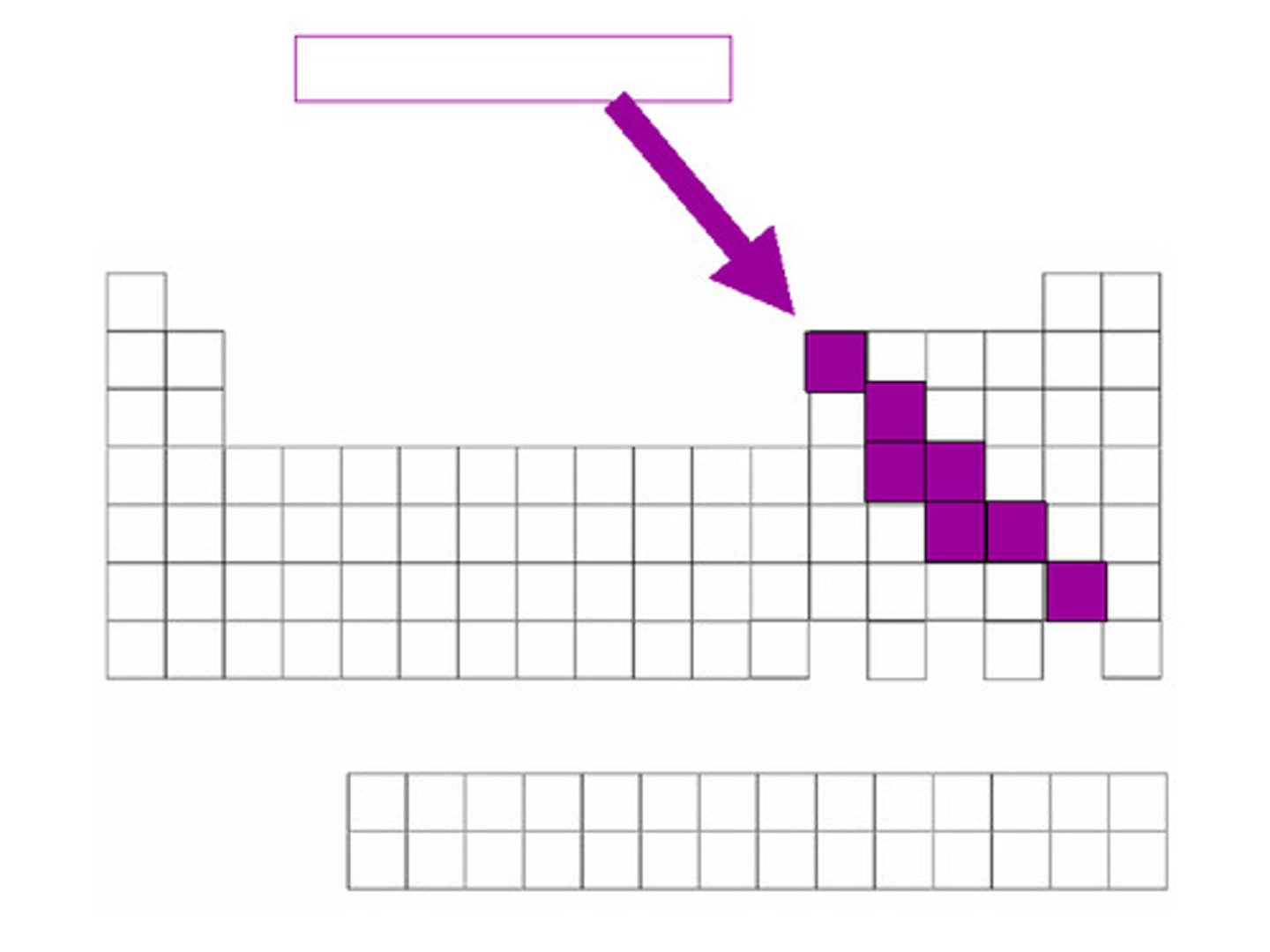
Halogens
Elements found in group 17 of the Periodic Table
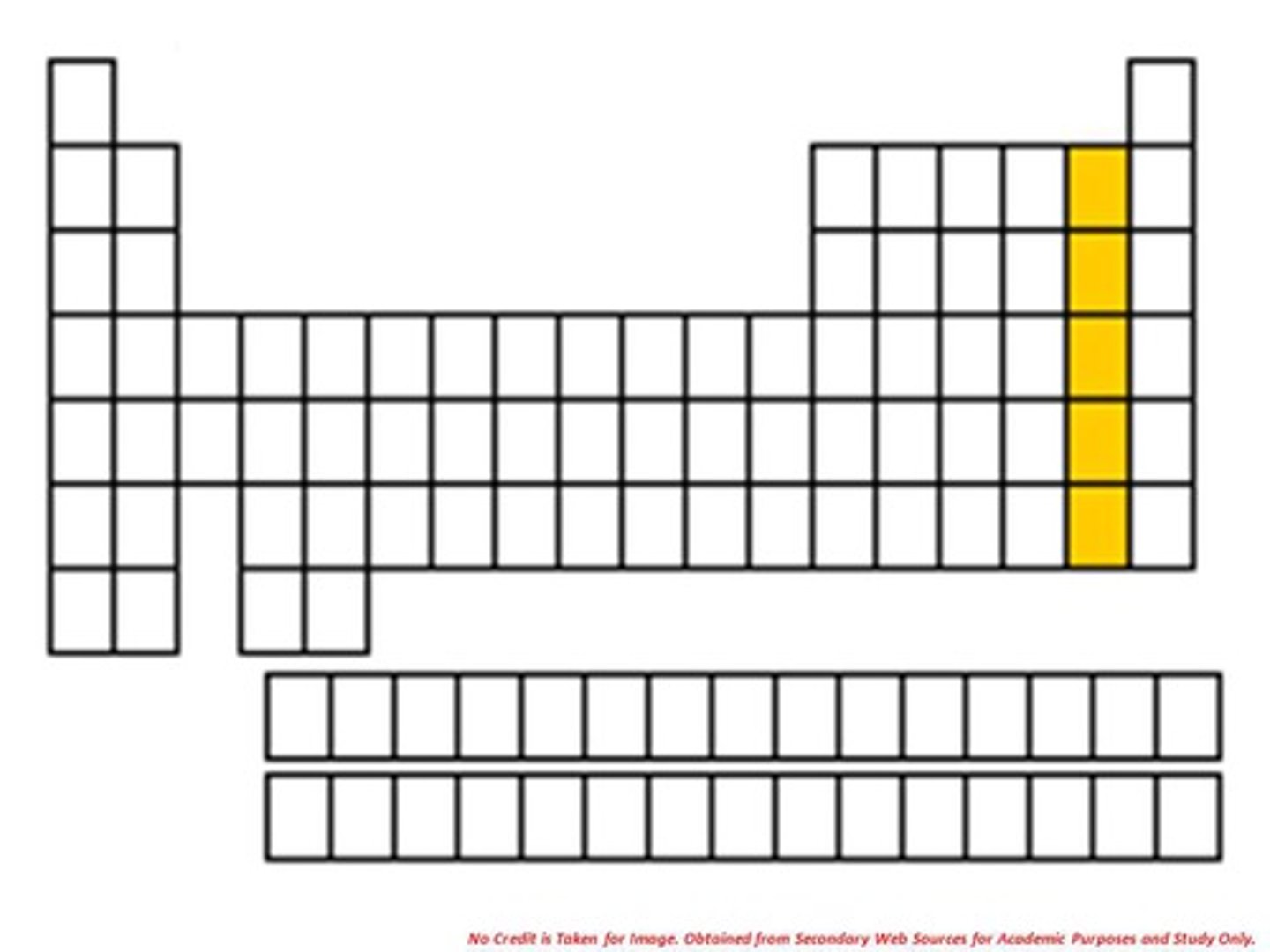
Lanthanoids
the top period of the 2 below
Conductor
A material that allows heat and electricity to pass through it.

Ductile
A term used to describe a material that can be pulled out into a long wire.

Tensile Strength
A measure of how much stress from pulling, or tension, a material can withstand before breaking.
Density
Mass per unit volume of a substance.
Reactivity
The property that describes how readily a substance combines chemically with other substances
Stable
Not easily changed
Electron Configuration
the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals/shells of an atom
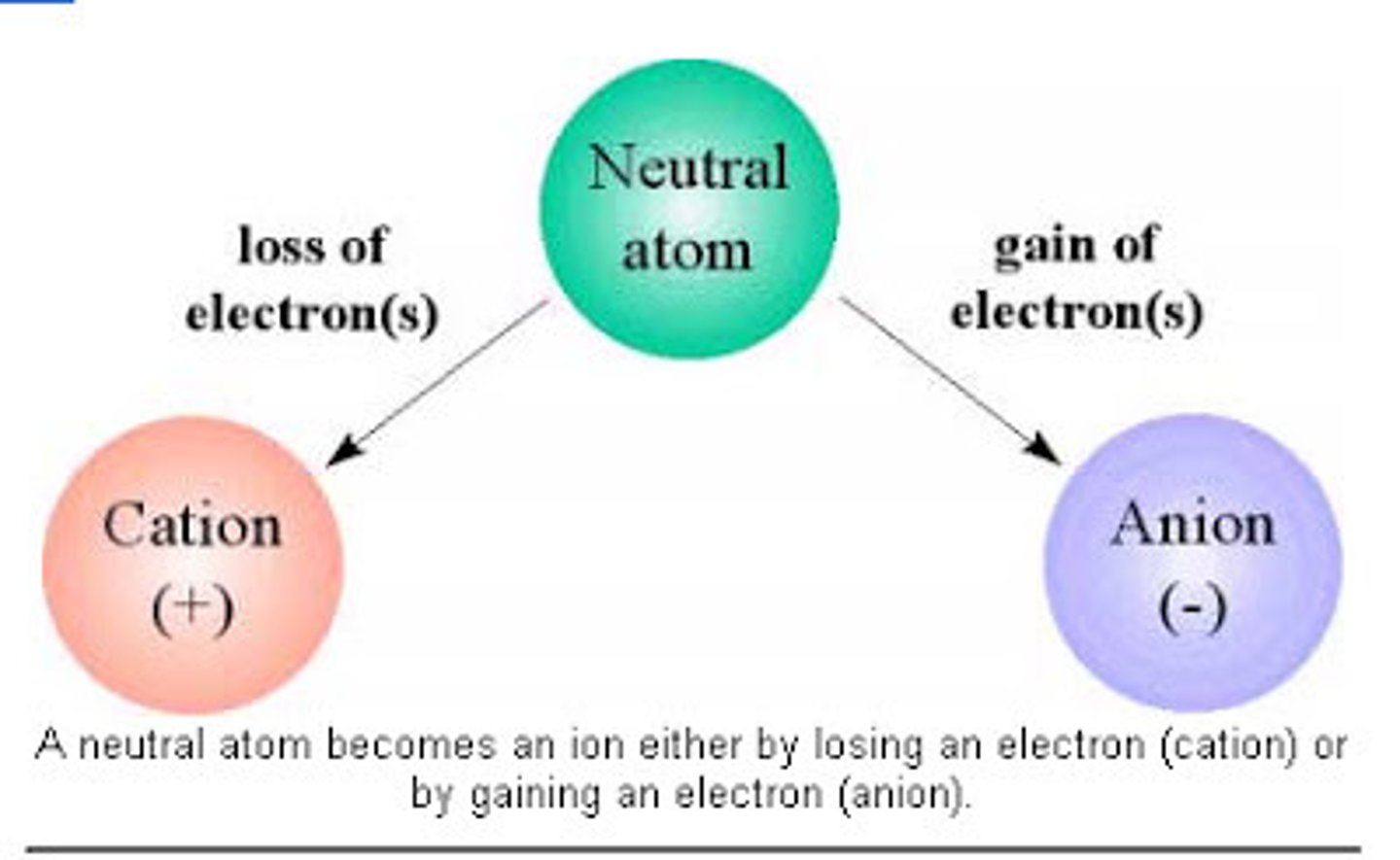
Ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge.
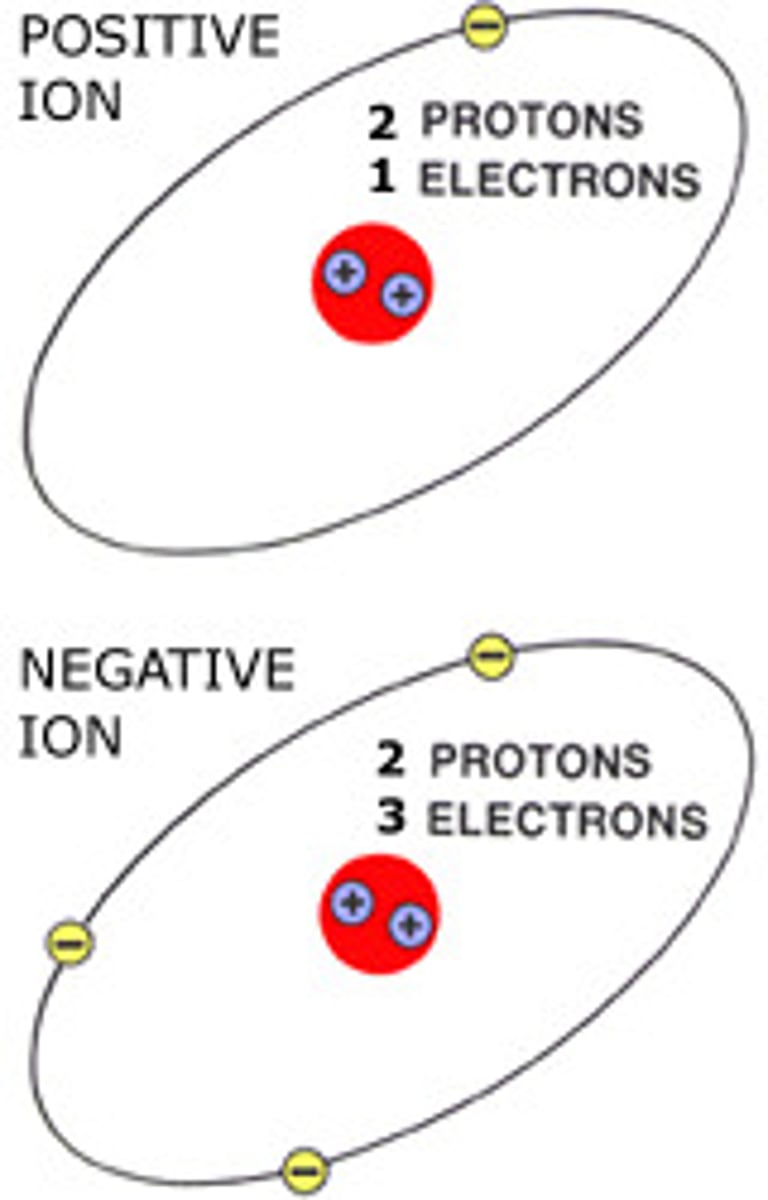
Cation
A positively charged ion (loses electrons)
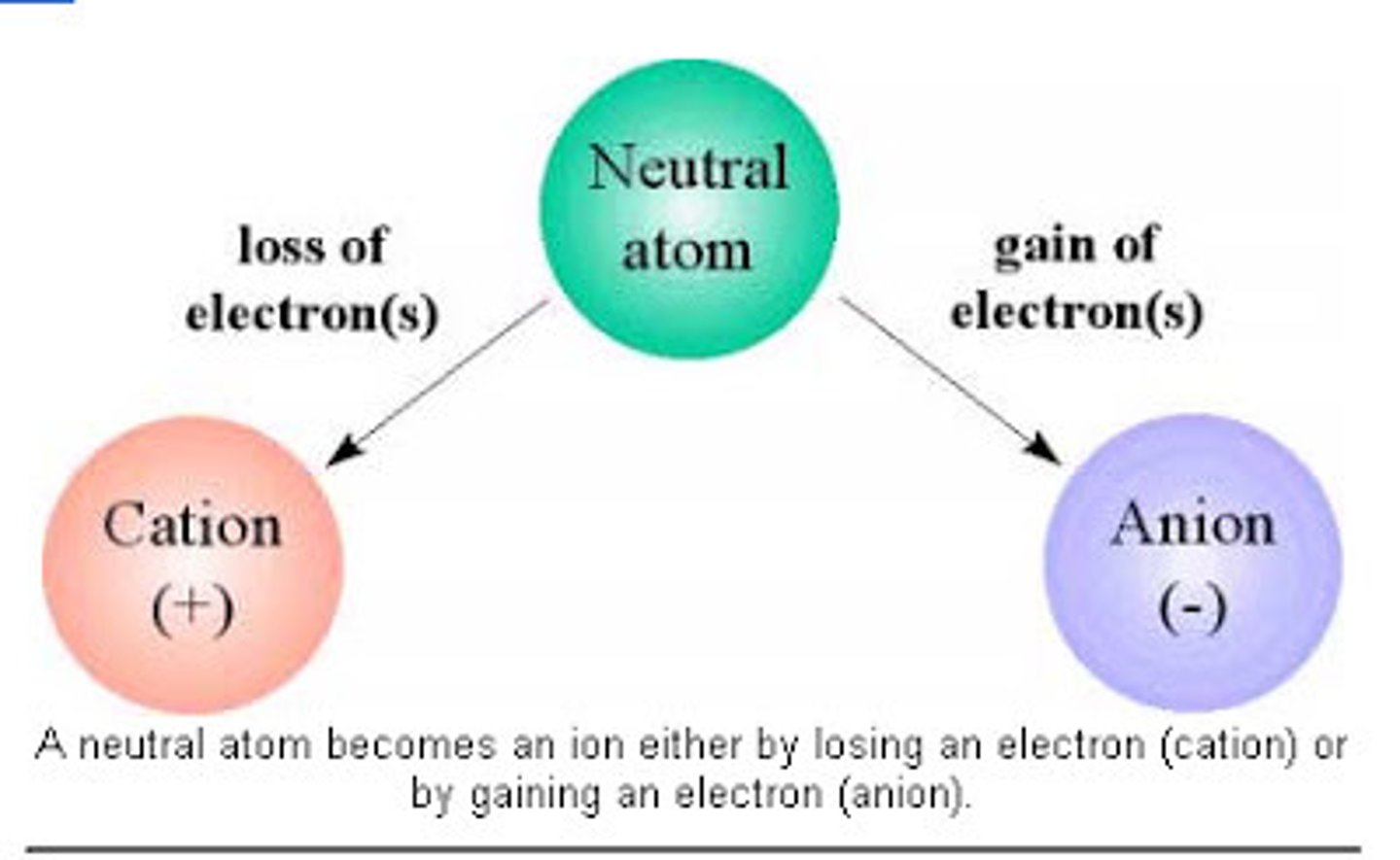
Anion
A negatively charged ion (gains electrons)
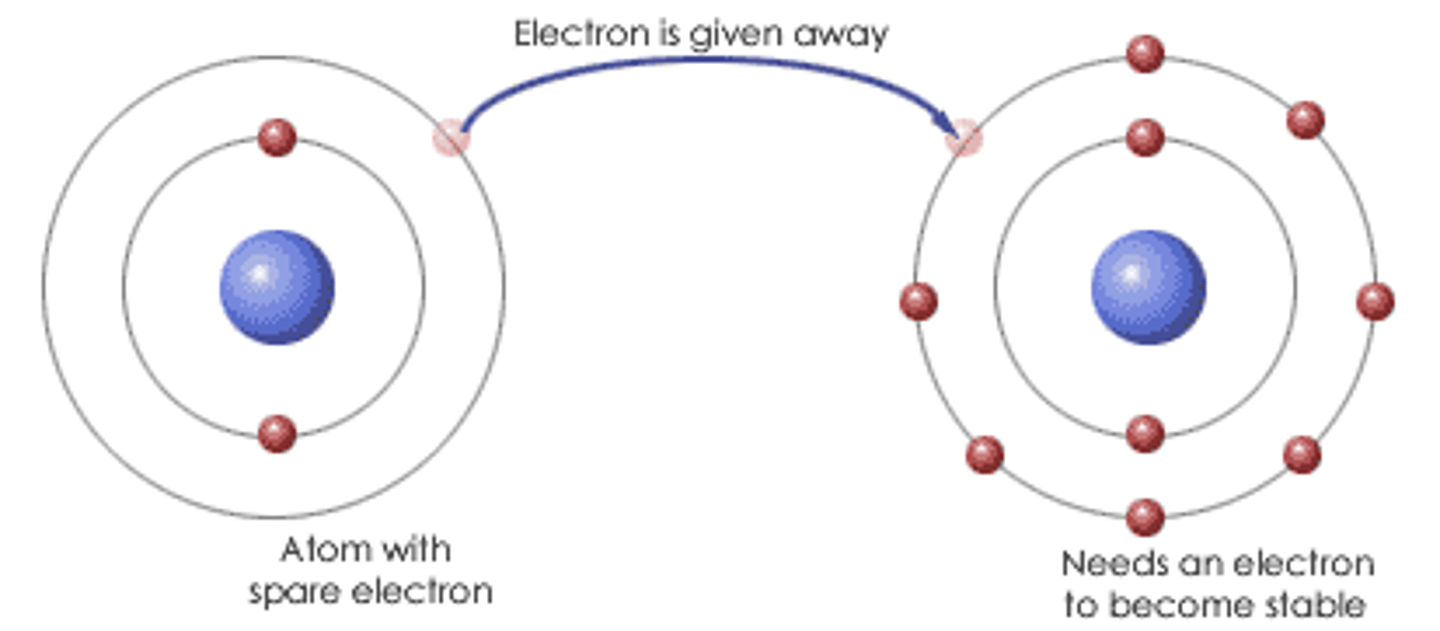
Ionic bonding
Chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between cations and anions
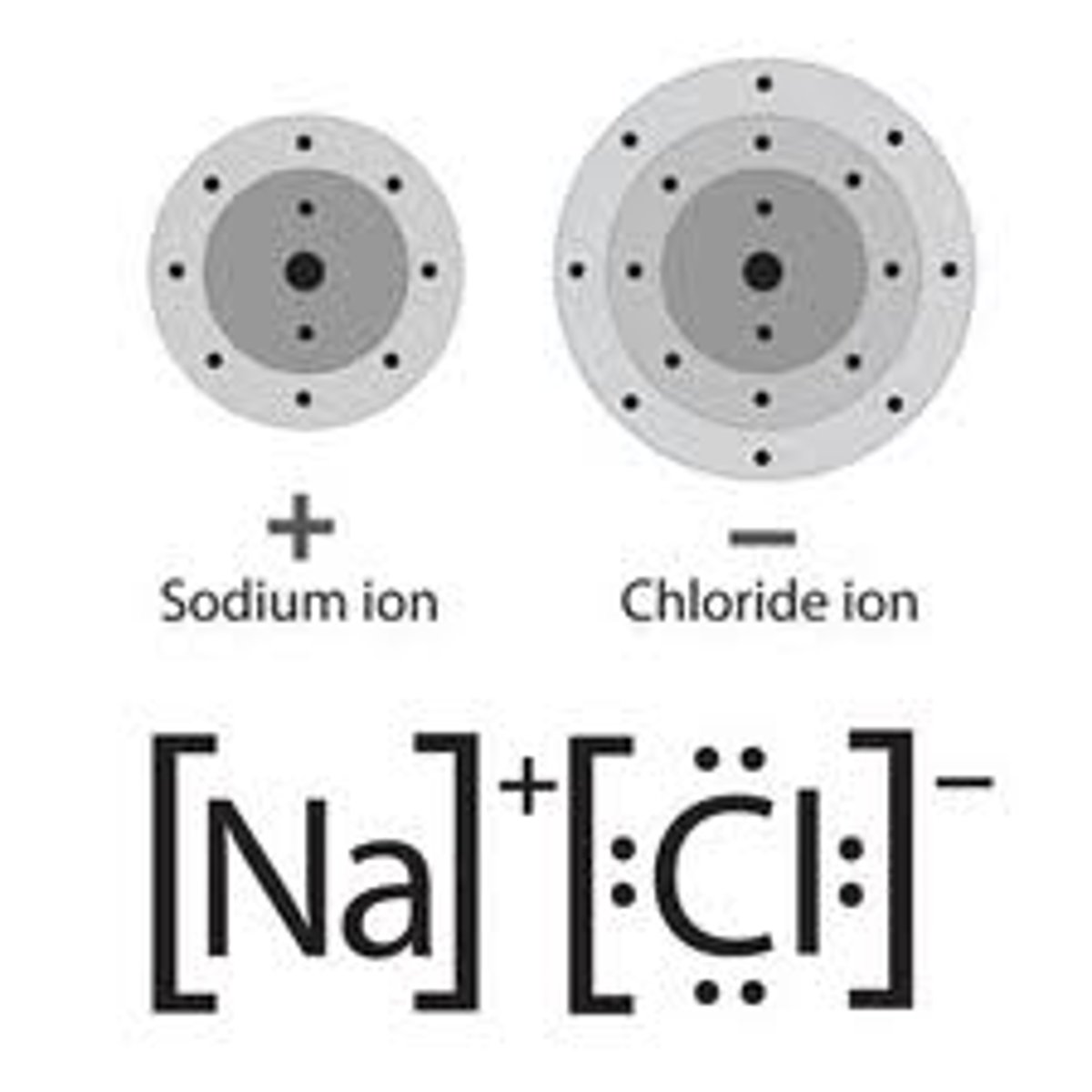
Ionic compound
composed of positive and negative ions that are combined so that the numbers of positive and negative charges are equal
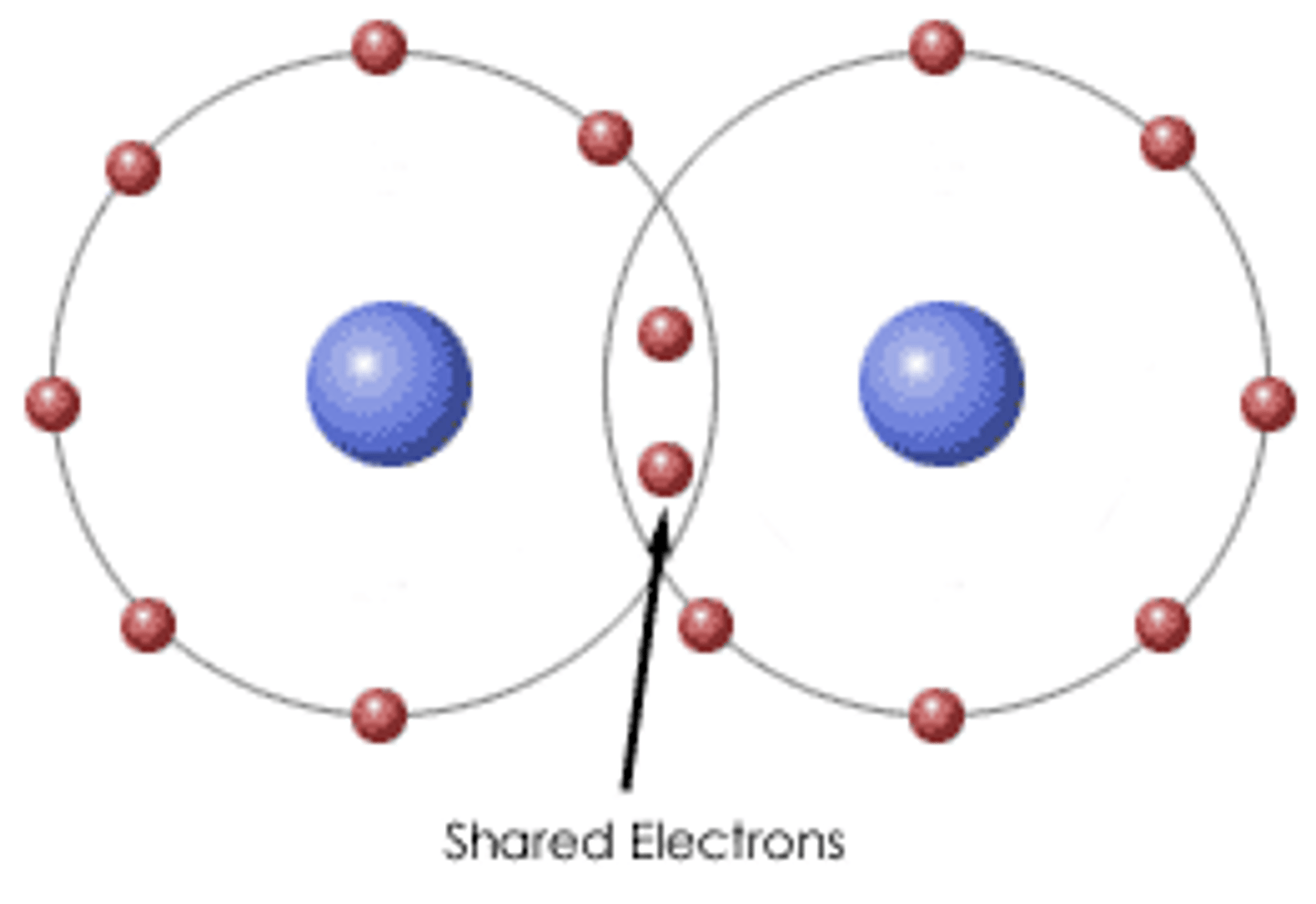
Covalent bonding
a bond formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons
Reactivity
The ease and speed with which an element combines, or reacts, with other elements and compounds.
Alkali metals
group 1
Alkaline earth metals
group 2
transition metals
the short section in the middle, excluding the lanthanides and actinides
Post transition metals
Sn, Pb to A, and group 13, excluding B and Nh
Metalloids
A set of stairs going from Te upwards to the left to B
Reactive non-metals
Above metalloids, in groups 14-16
Noble gases
Group 18
Actinides
the bottom most group
halogens
group 17
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
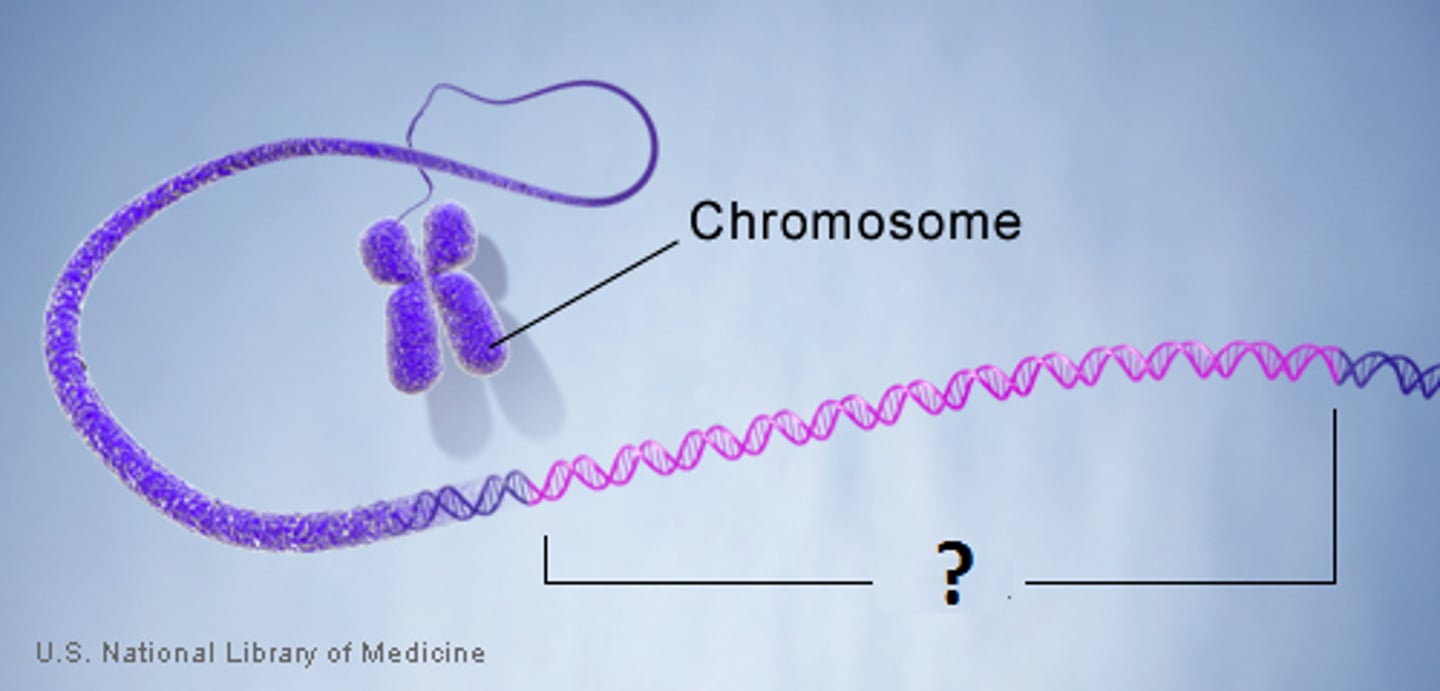
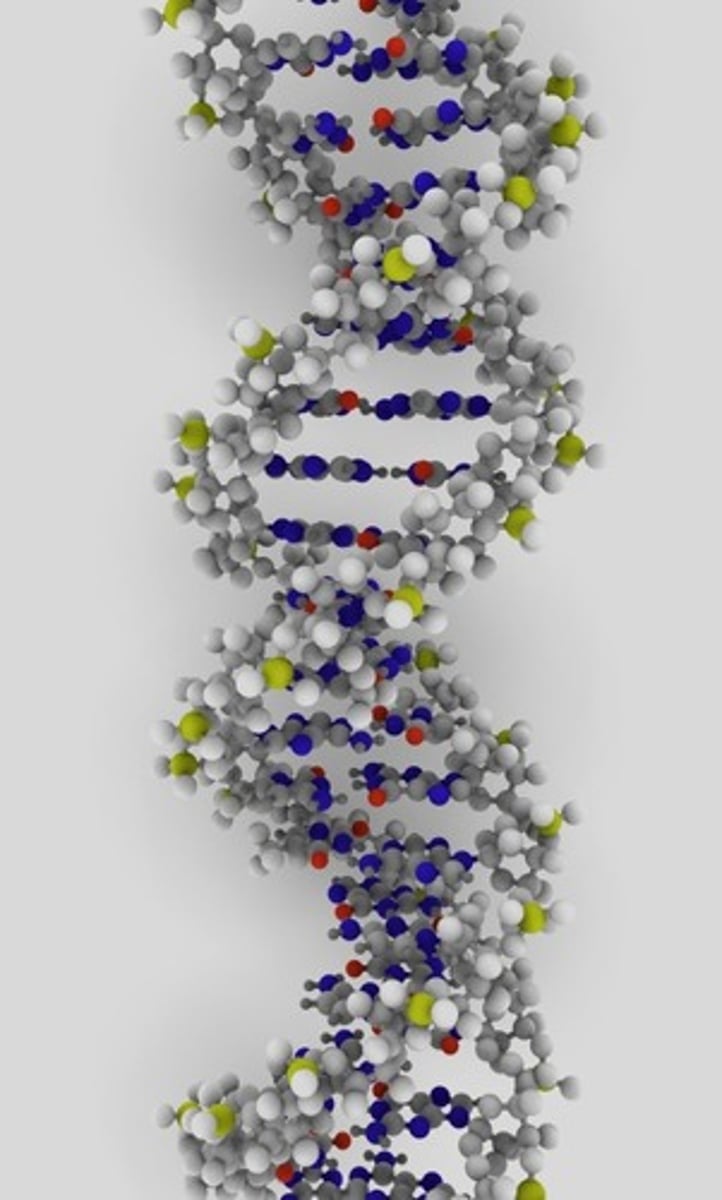
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid. A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
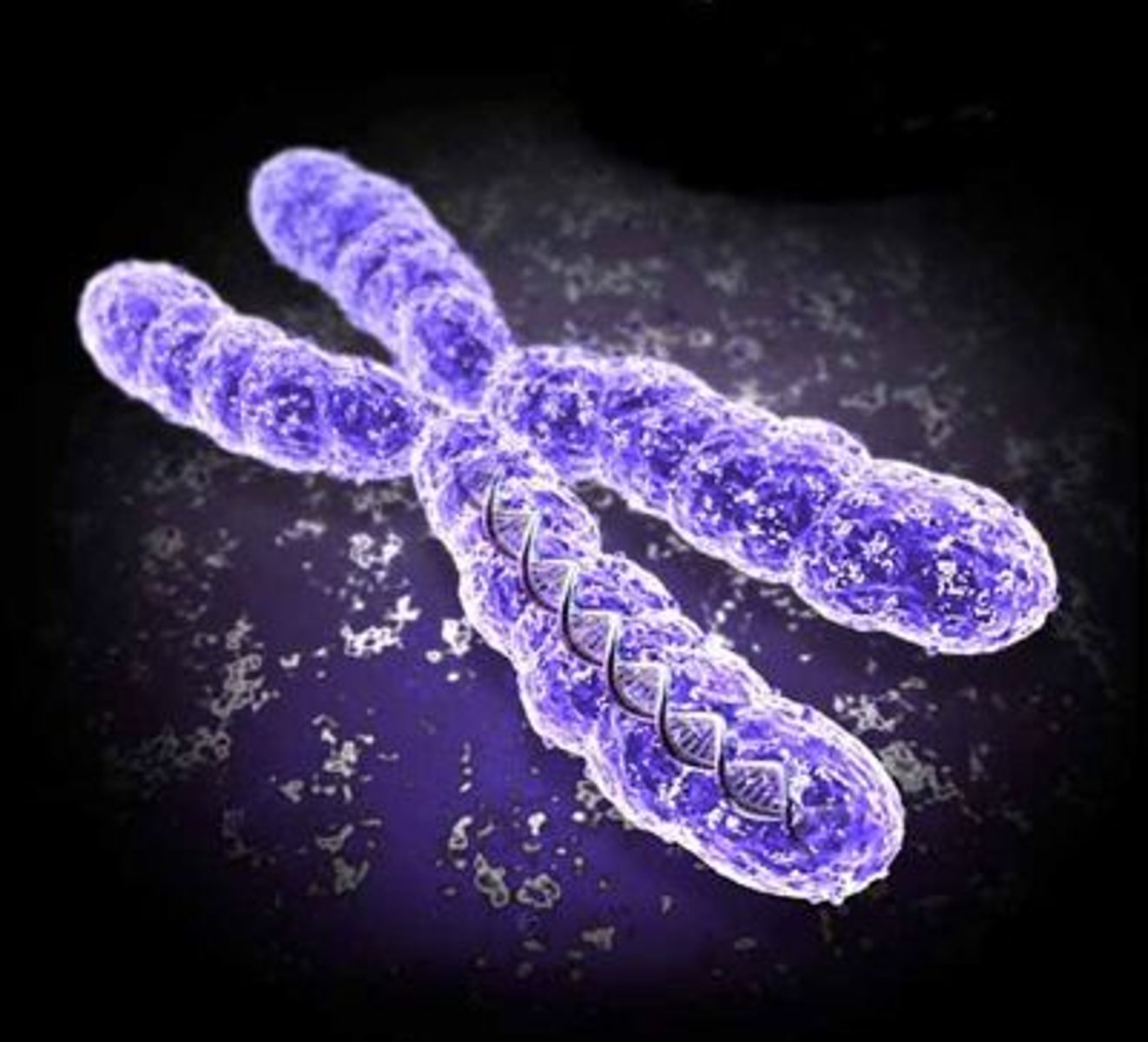
Chromosome
A thread-like structure made of DNA and proteins, found within the nucleus of a cell
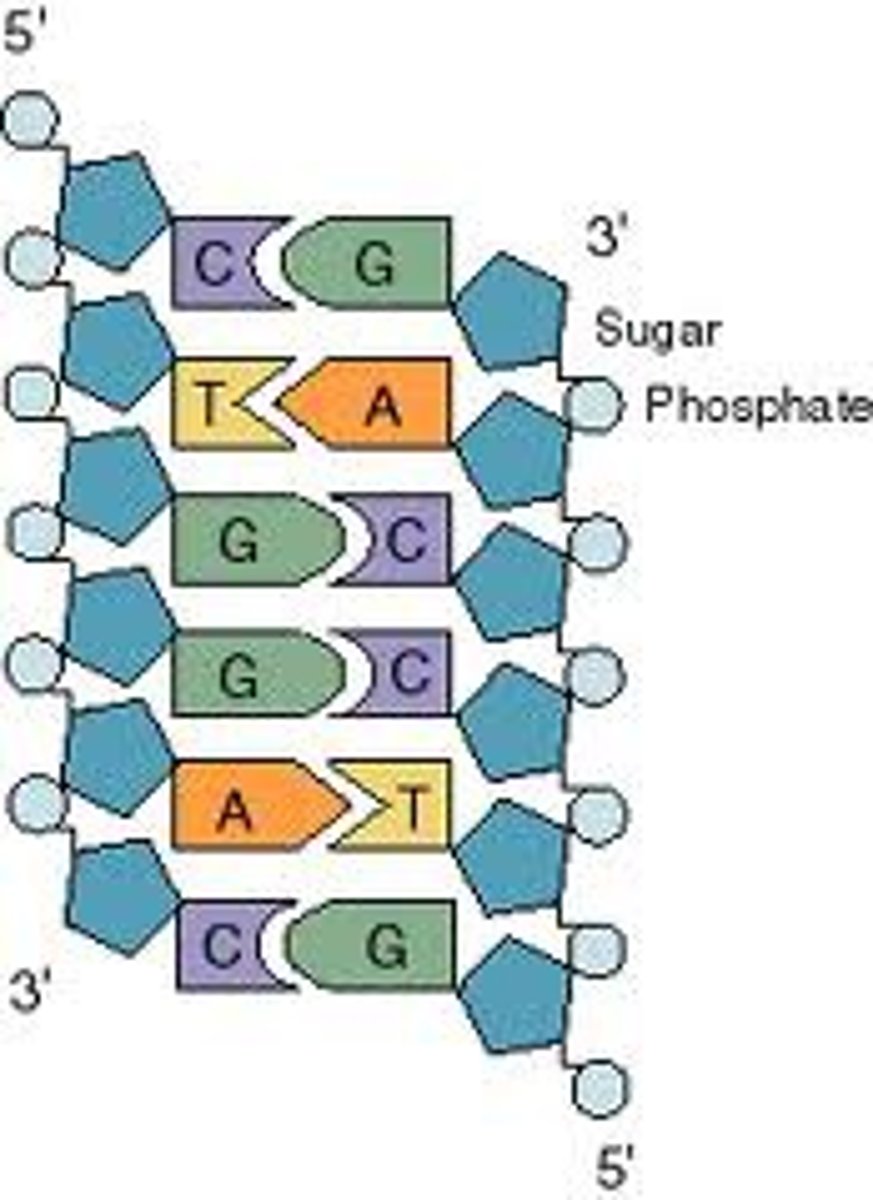
Nucleotide
A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogenous base and a phosphate group.
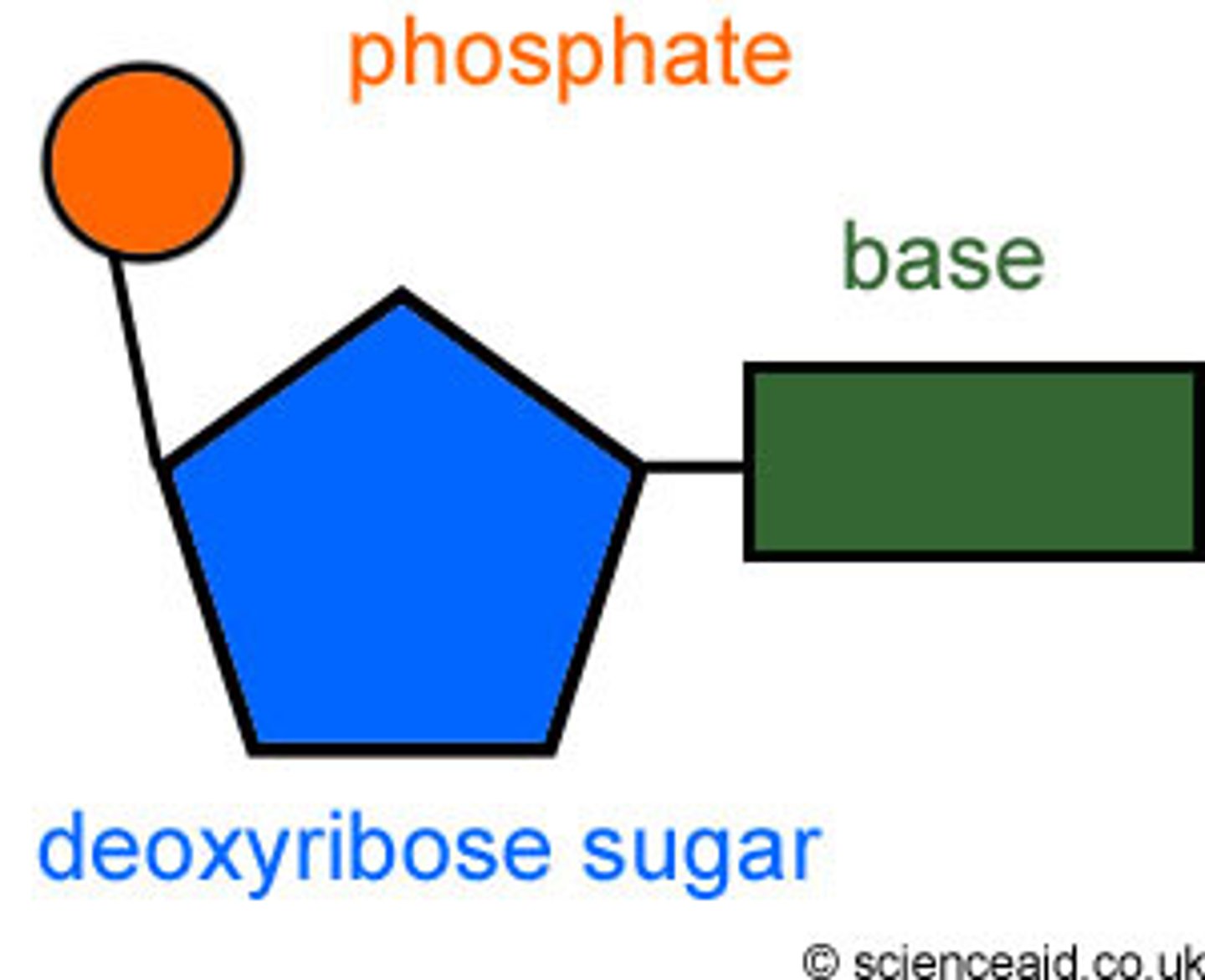
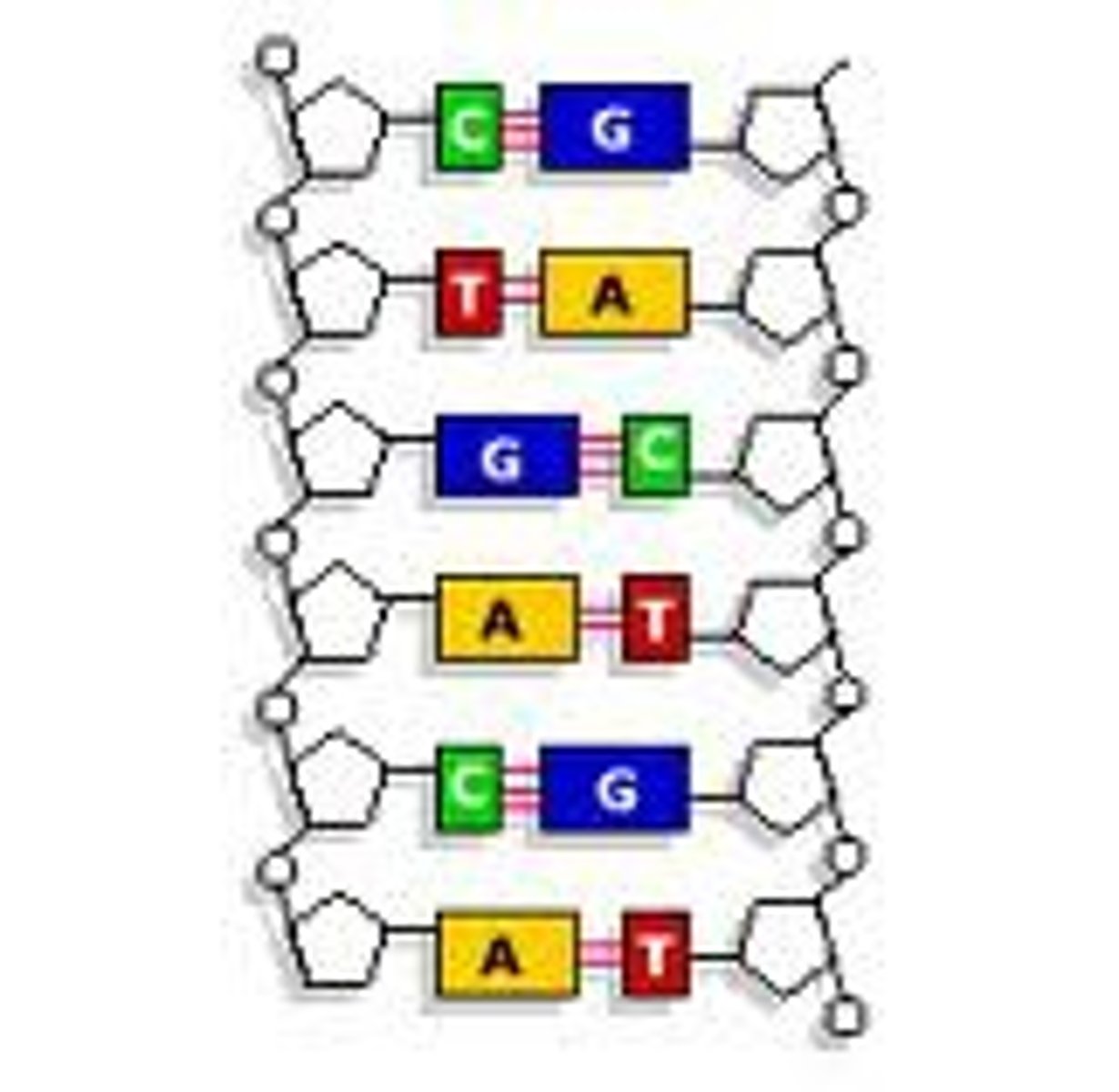
sugar-phosphate backbone
The alternating chain of sugar and phosphate to which the DNA nitrogenous bases are attached
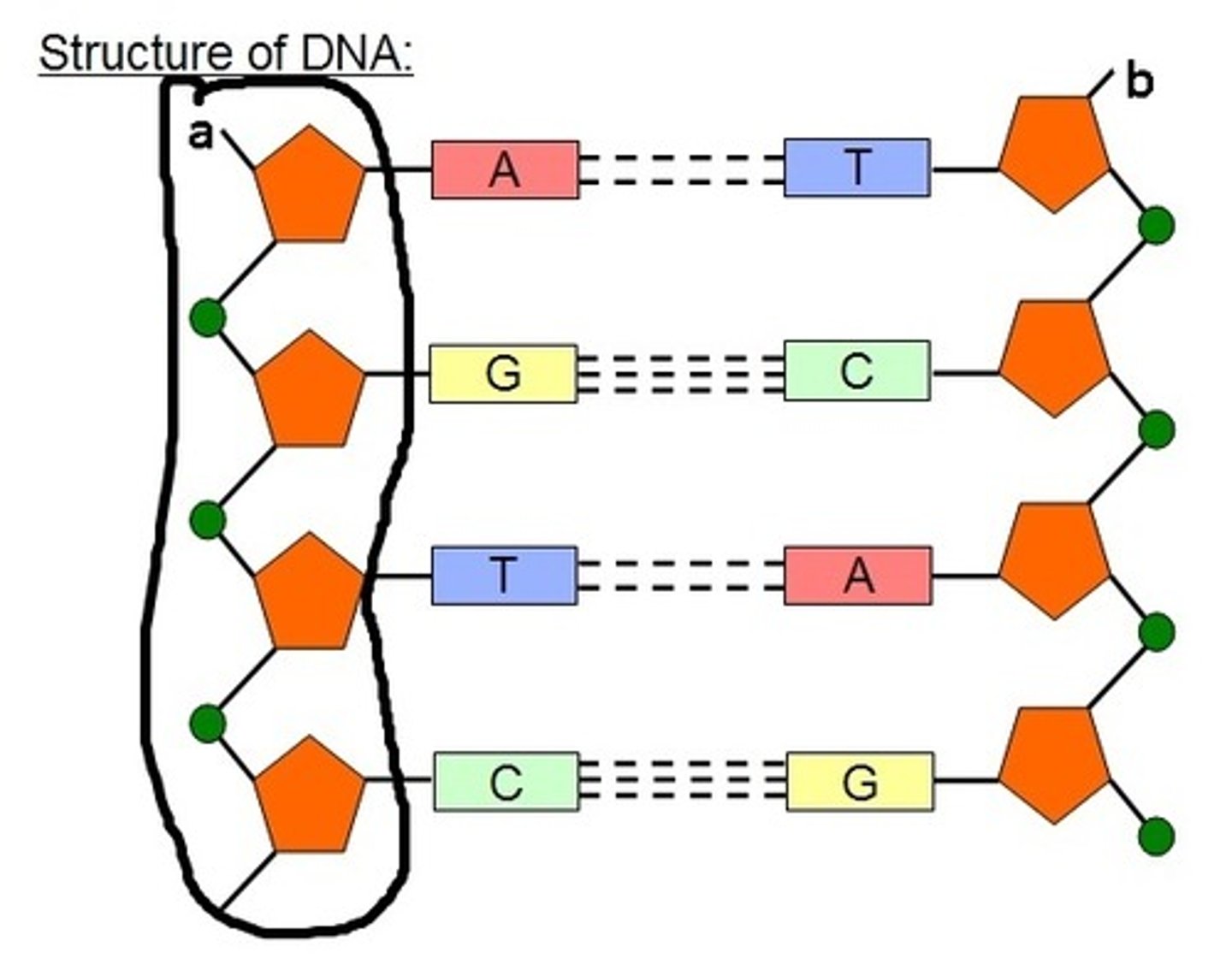
Nitrogenous base
An organic base that contains nitrogen, such as a purine or pyrimidine; a subunit of a nucleotide in DNA
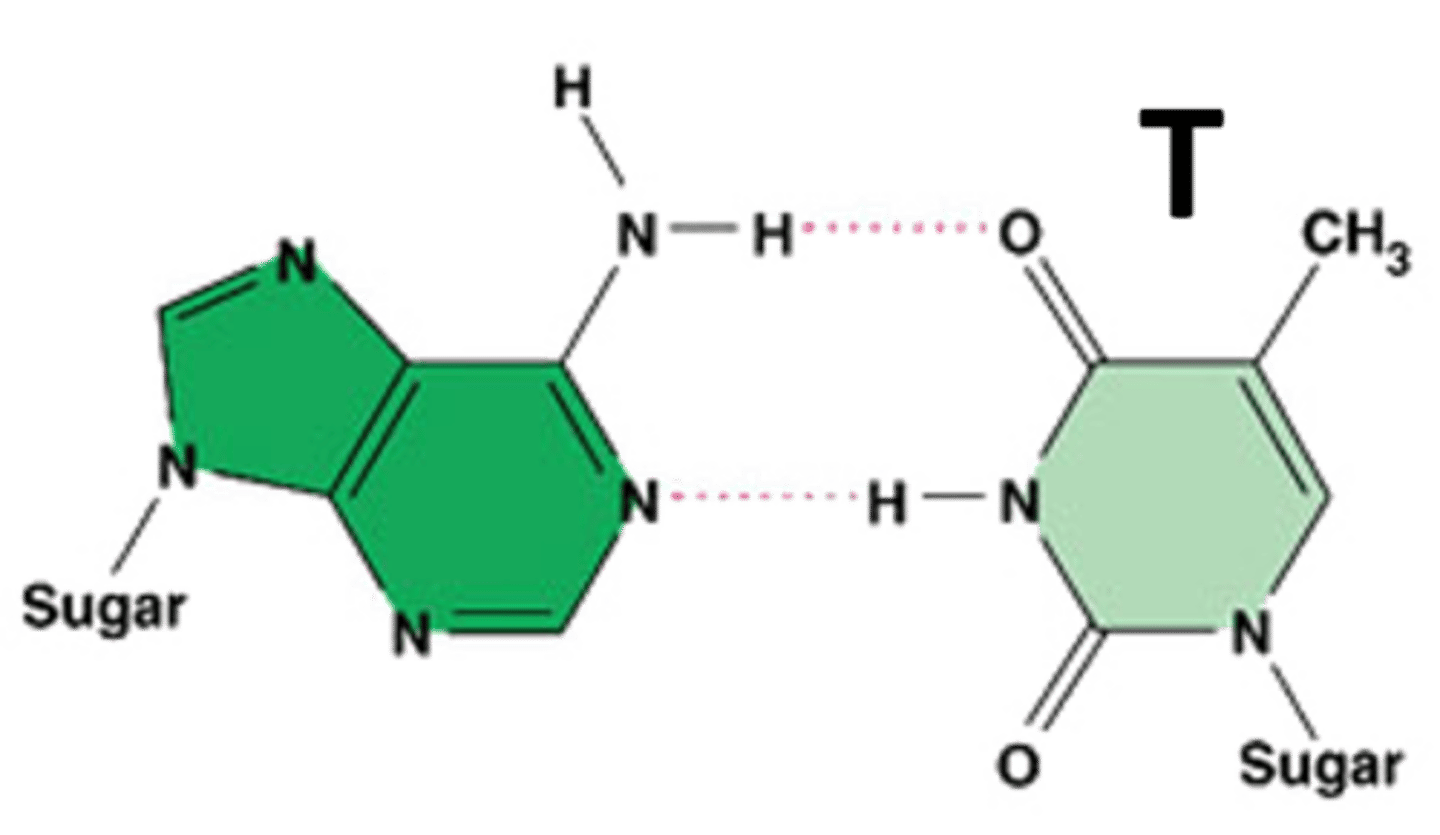
Thymine
A component of nucleic acid that carries hereditary information in DNA in cells. Chemically, it is a pyrimidine base.
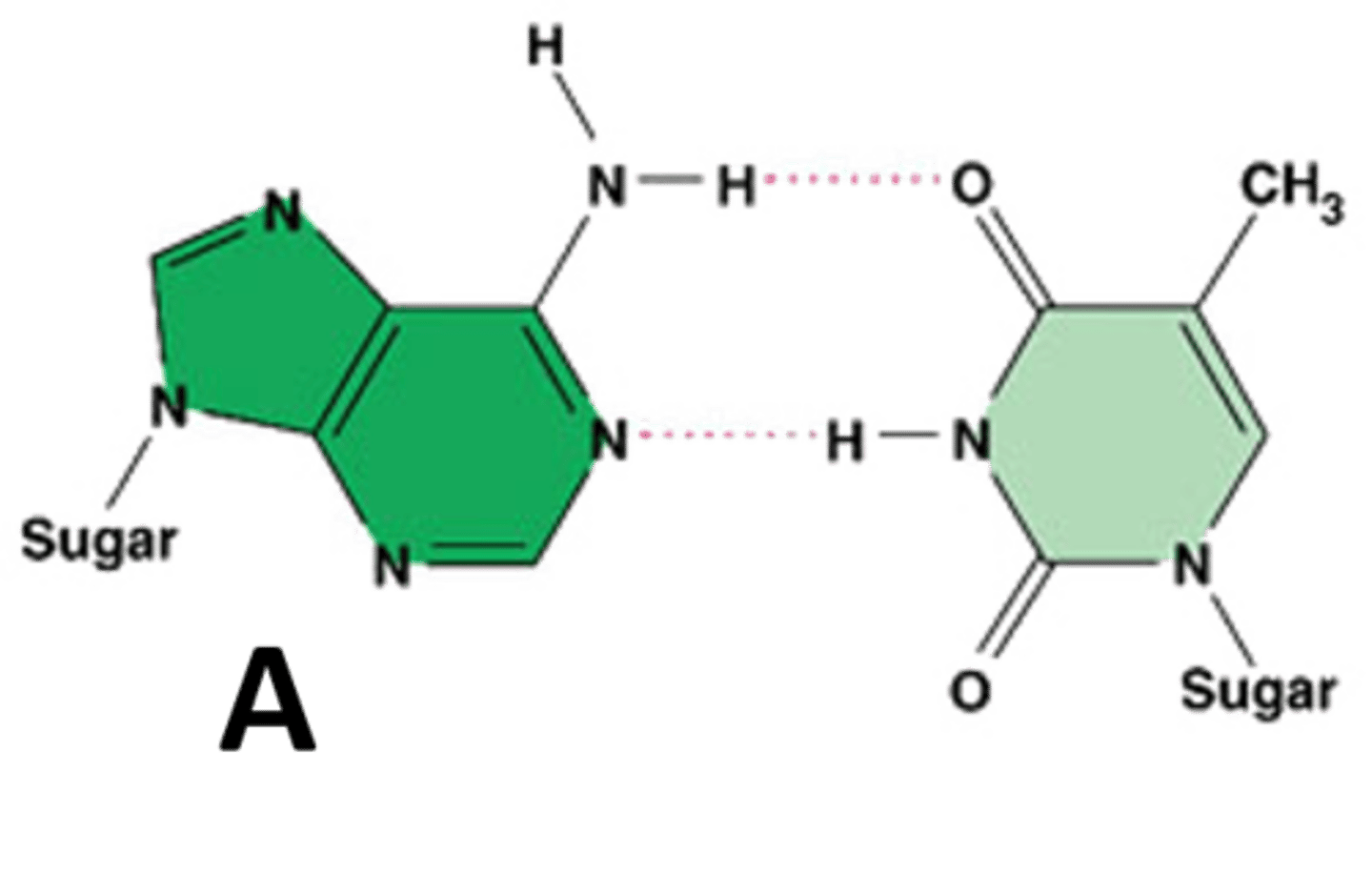
Adenine
A nitrogenous base that pairs with thymine
Guanine
A nitrogenous base that pairs with cytosine.
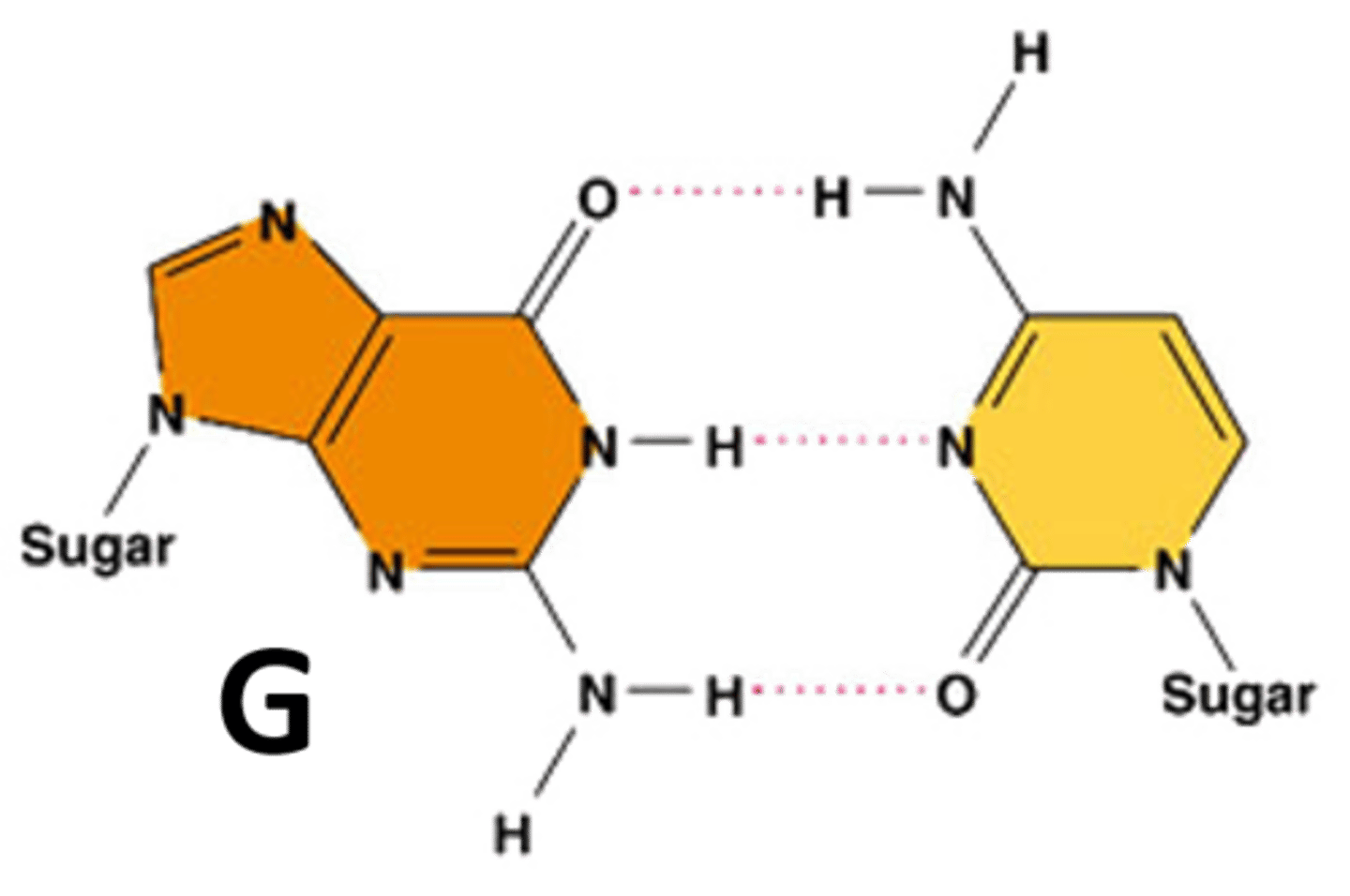
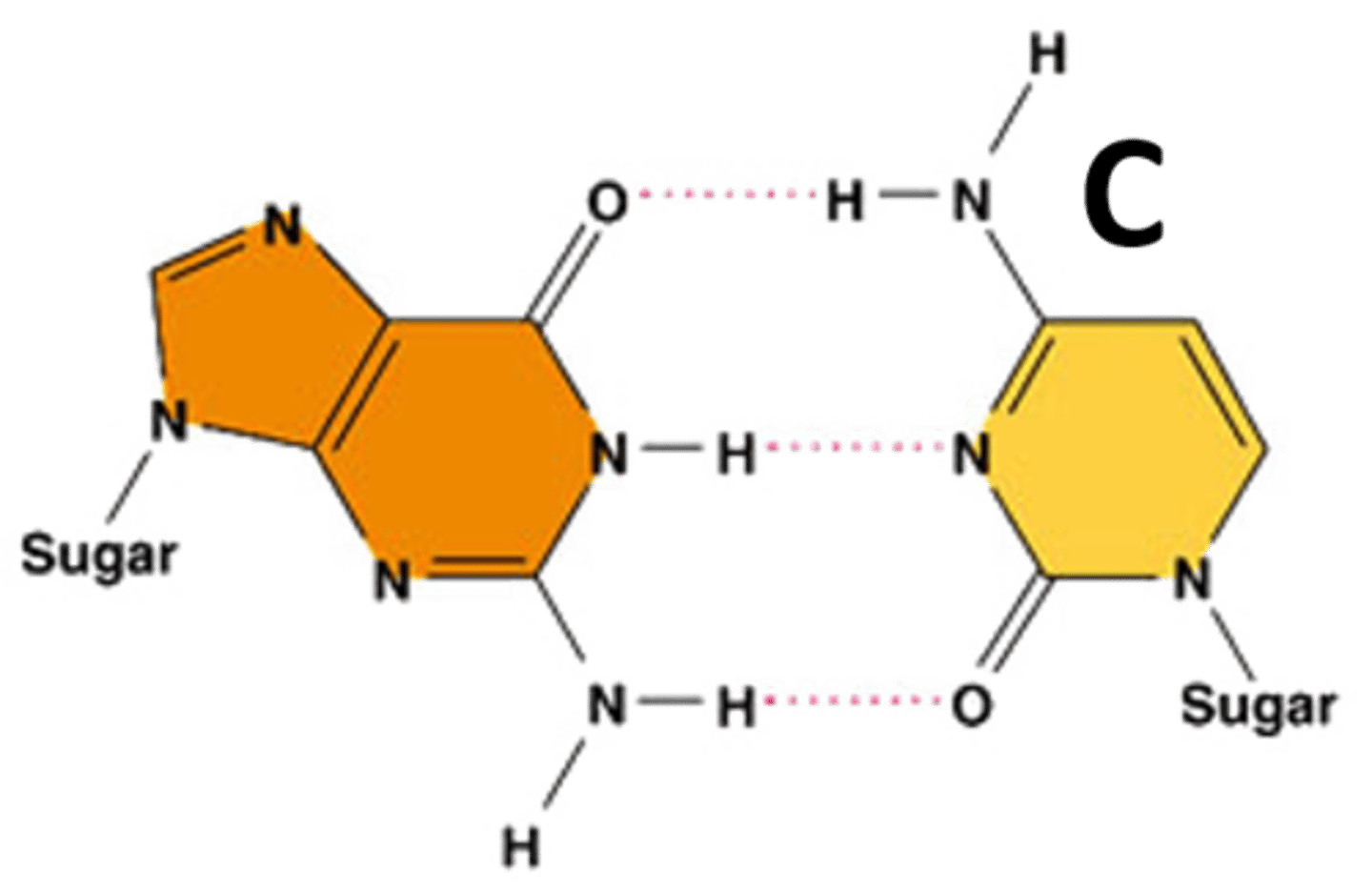
Cytosine
A nitrogenous base that pairs with Guanine
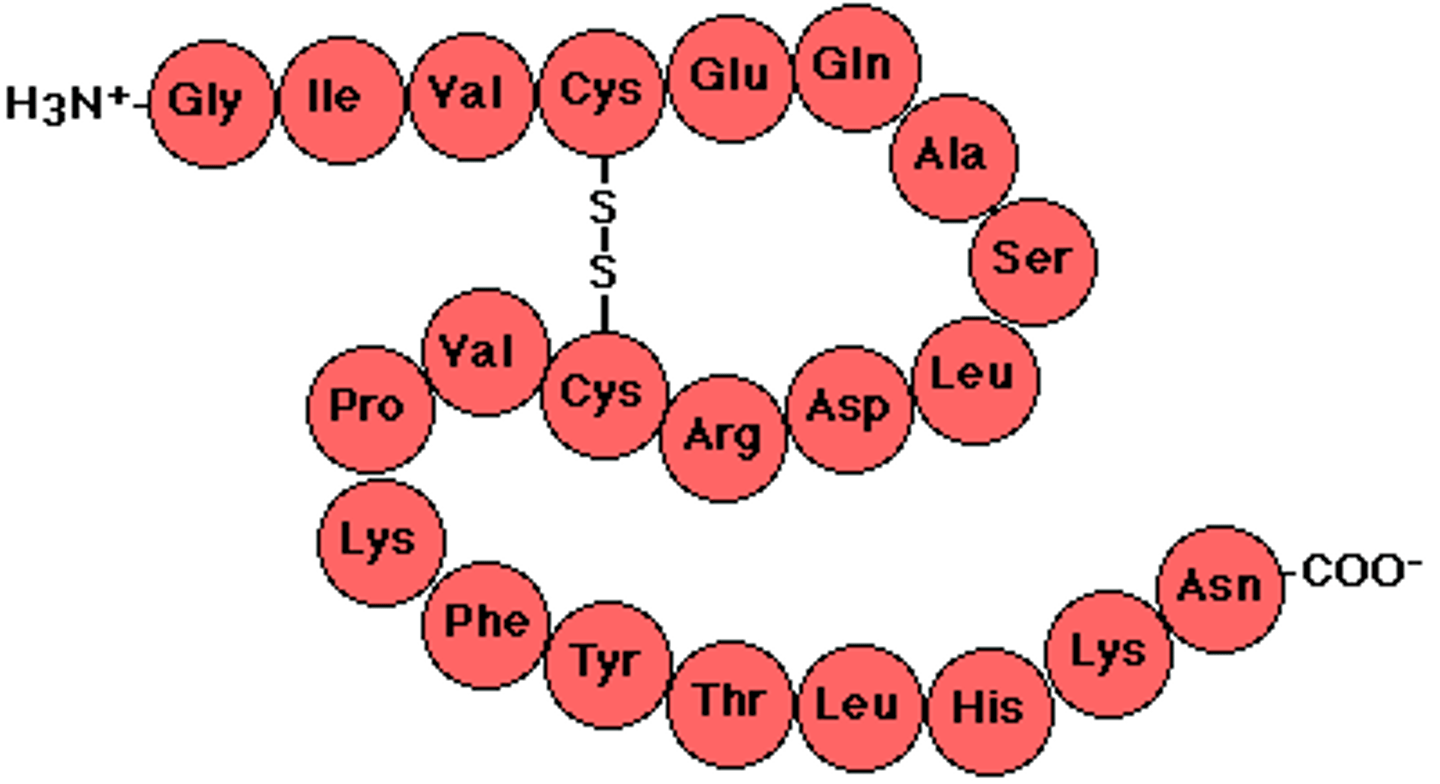
Amino Acid
Building blocks of protein
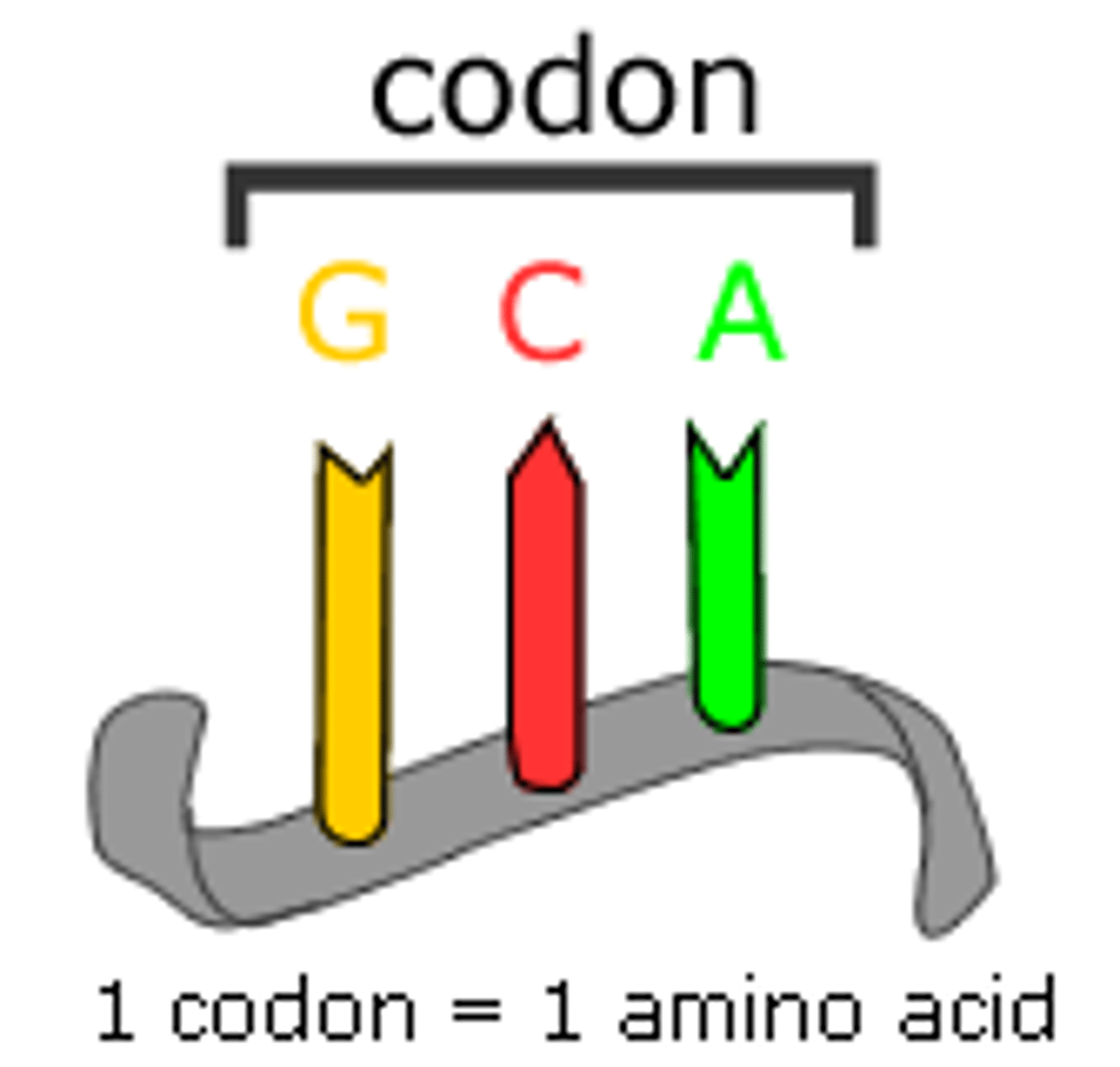
Codon
A specific sequence of three adjacent bases on a strand of DNA or RNA that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid
Protein
A three dimensional polymer made of monomers of amino acids. Genes code for proteins.
Base pairs
Any of the pairs formed between complimentary bases in the two nucleotide chains of DNA, such as A-T and C-G
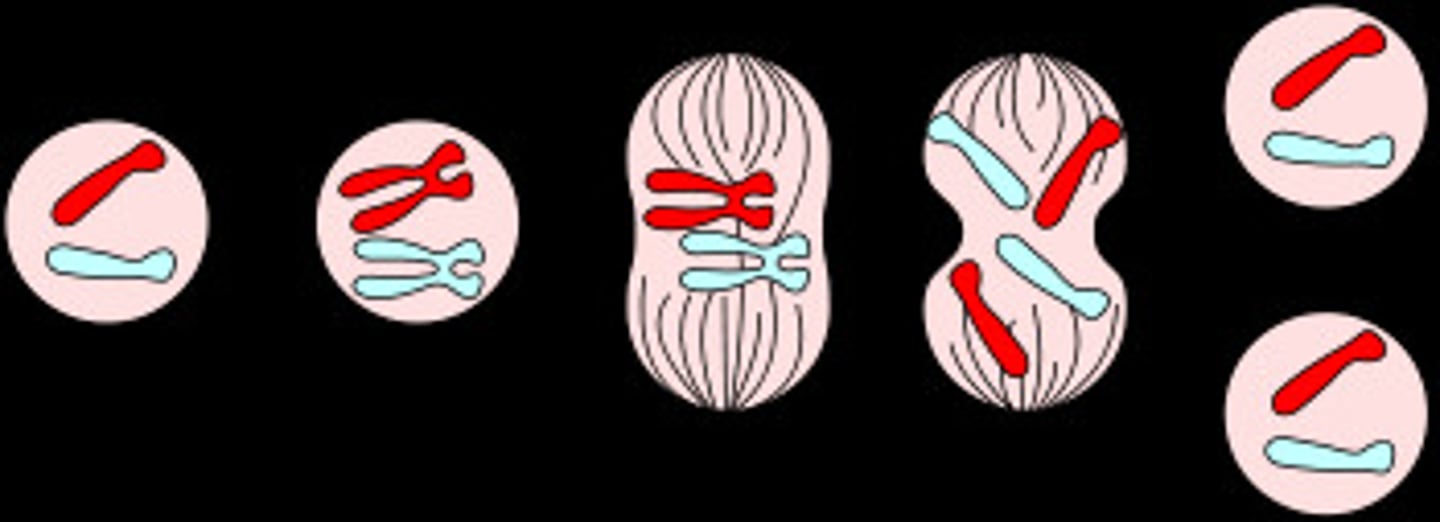
Mitosis
Cell division in which the nucleus divides into two nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
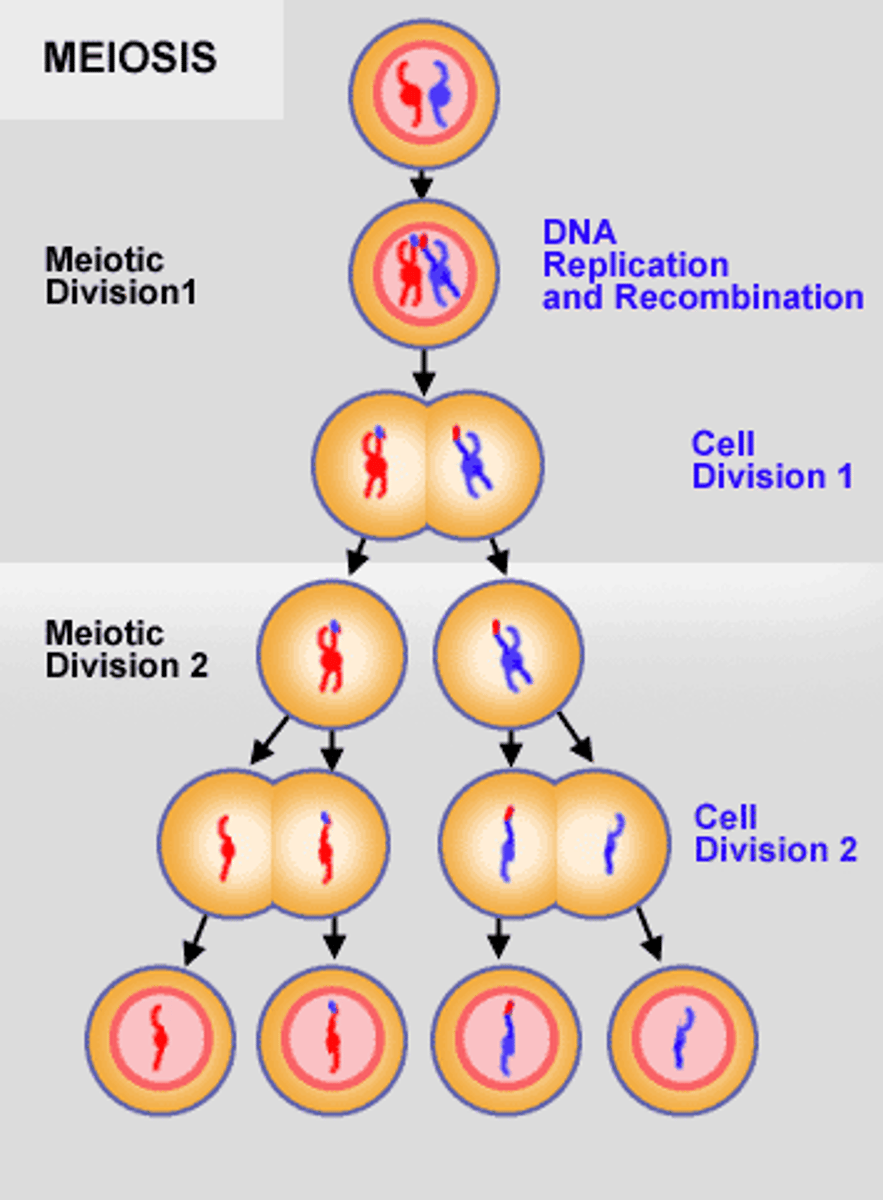
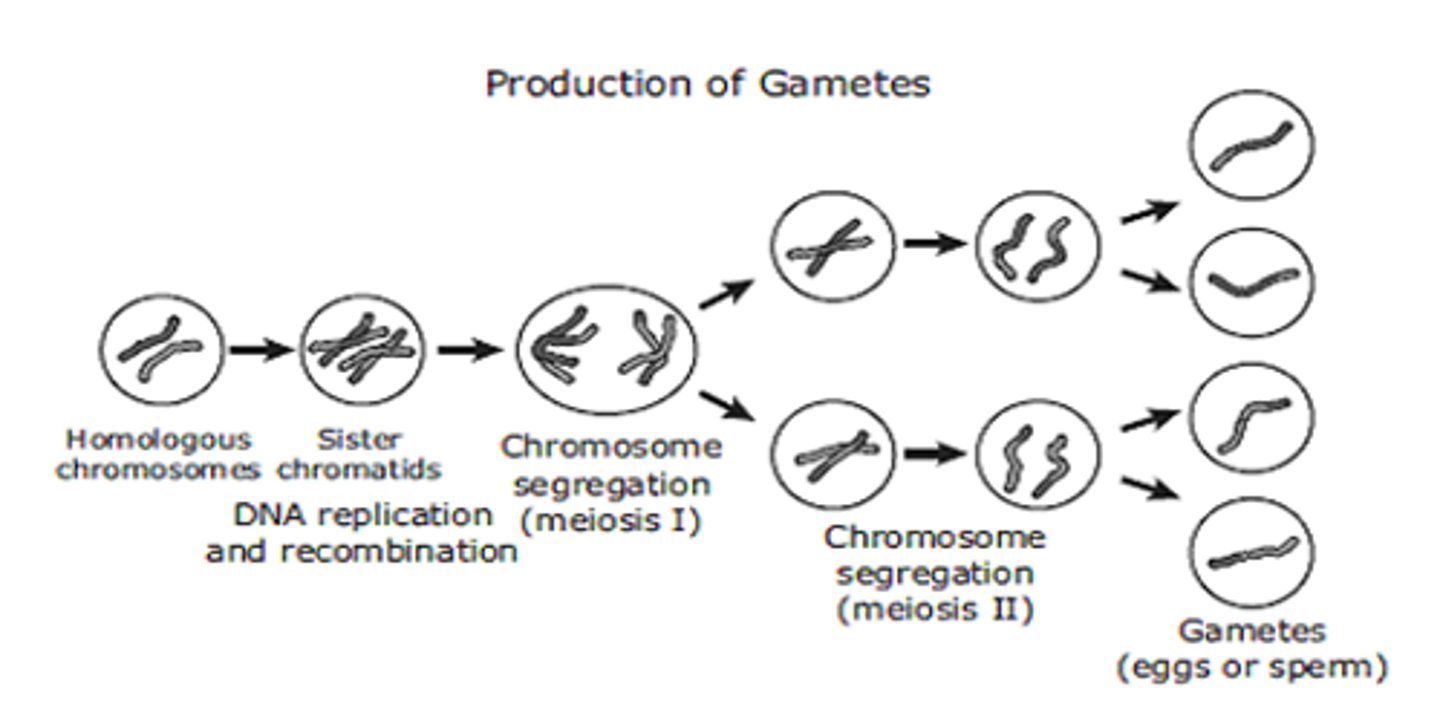
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms. They contain only one copy of each chromosome (haploid).
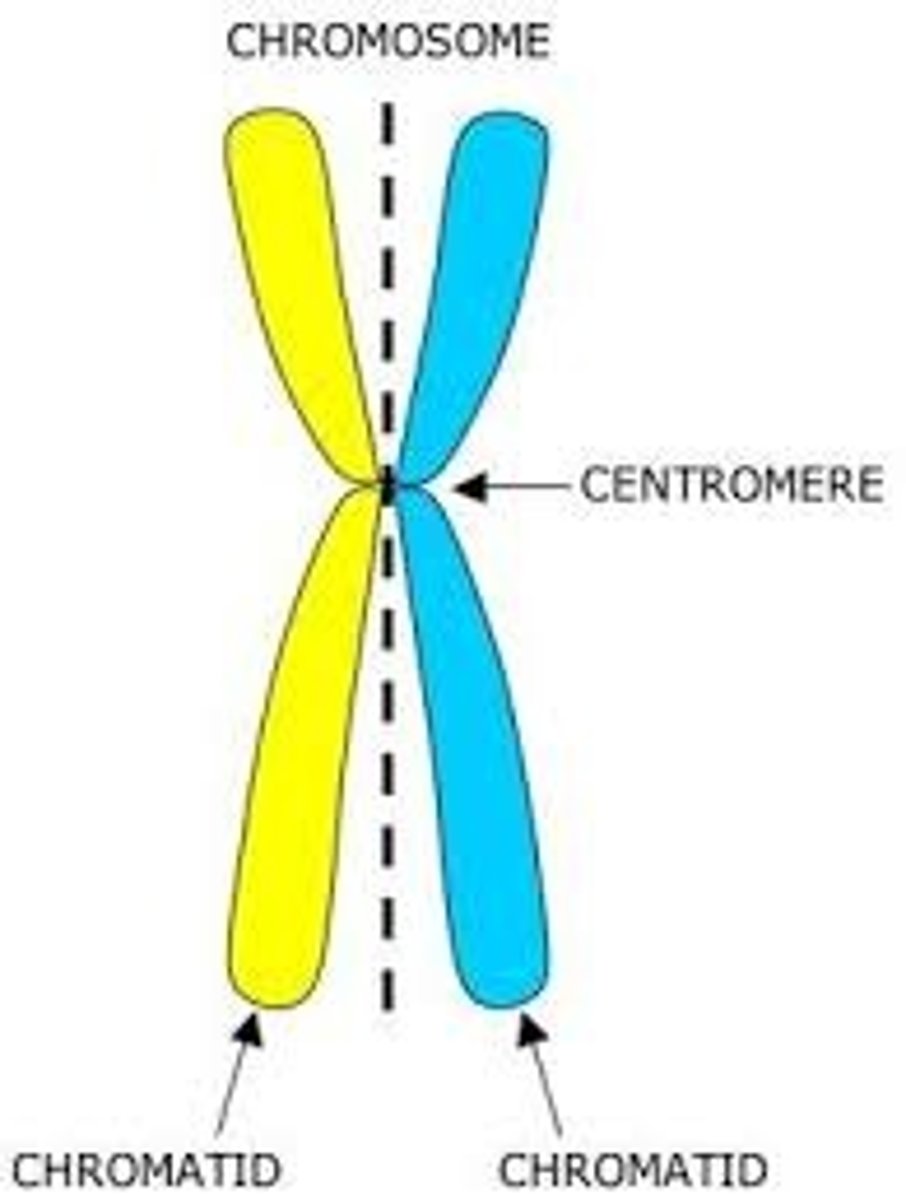
Sister chromatids
Replicated forms of a chromosome joined together by the centromere and eventually separated during mitosis or meiosis II.
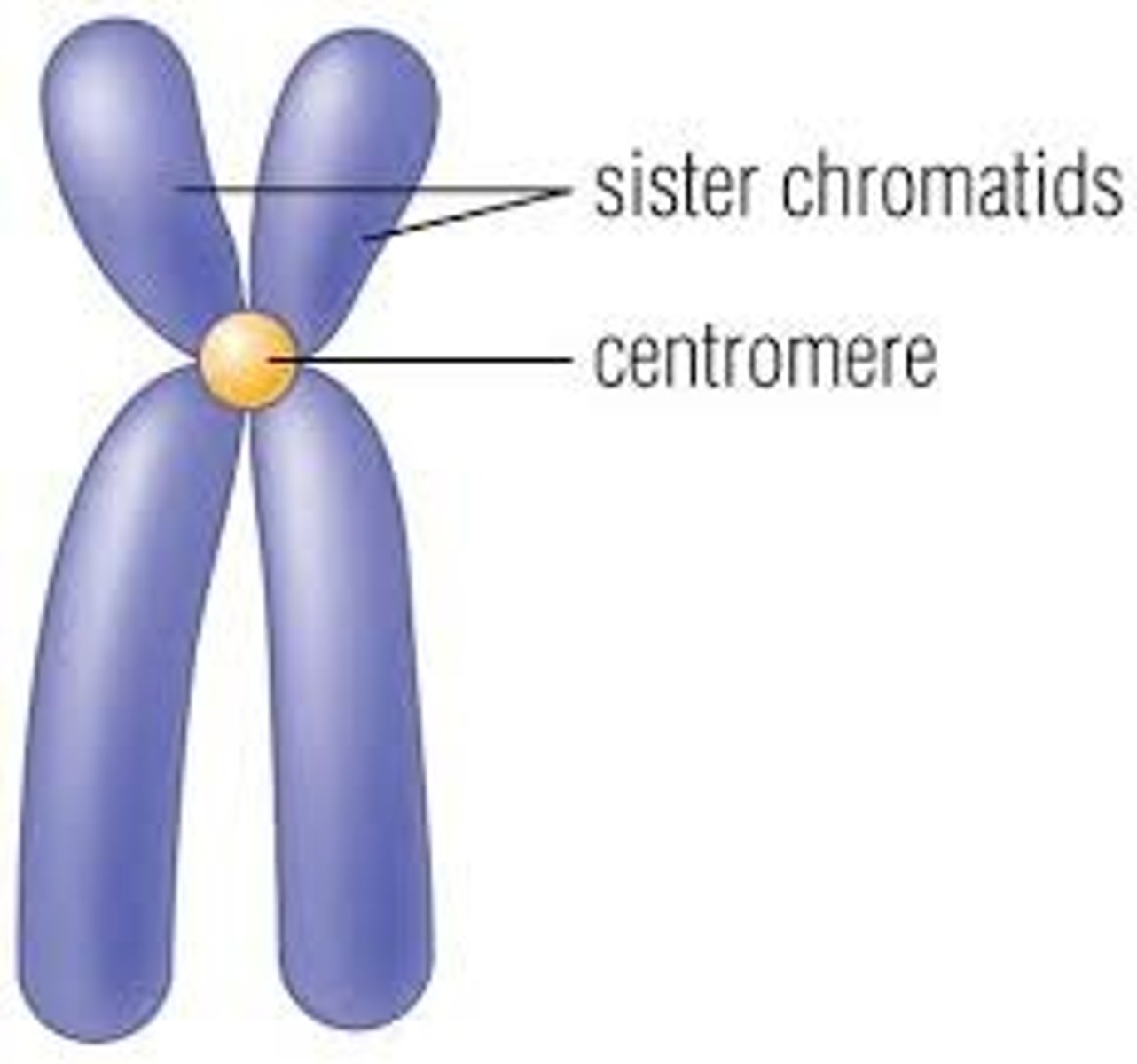
Centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
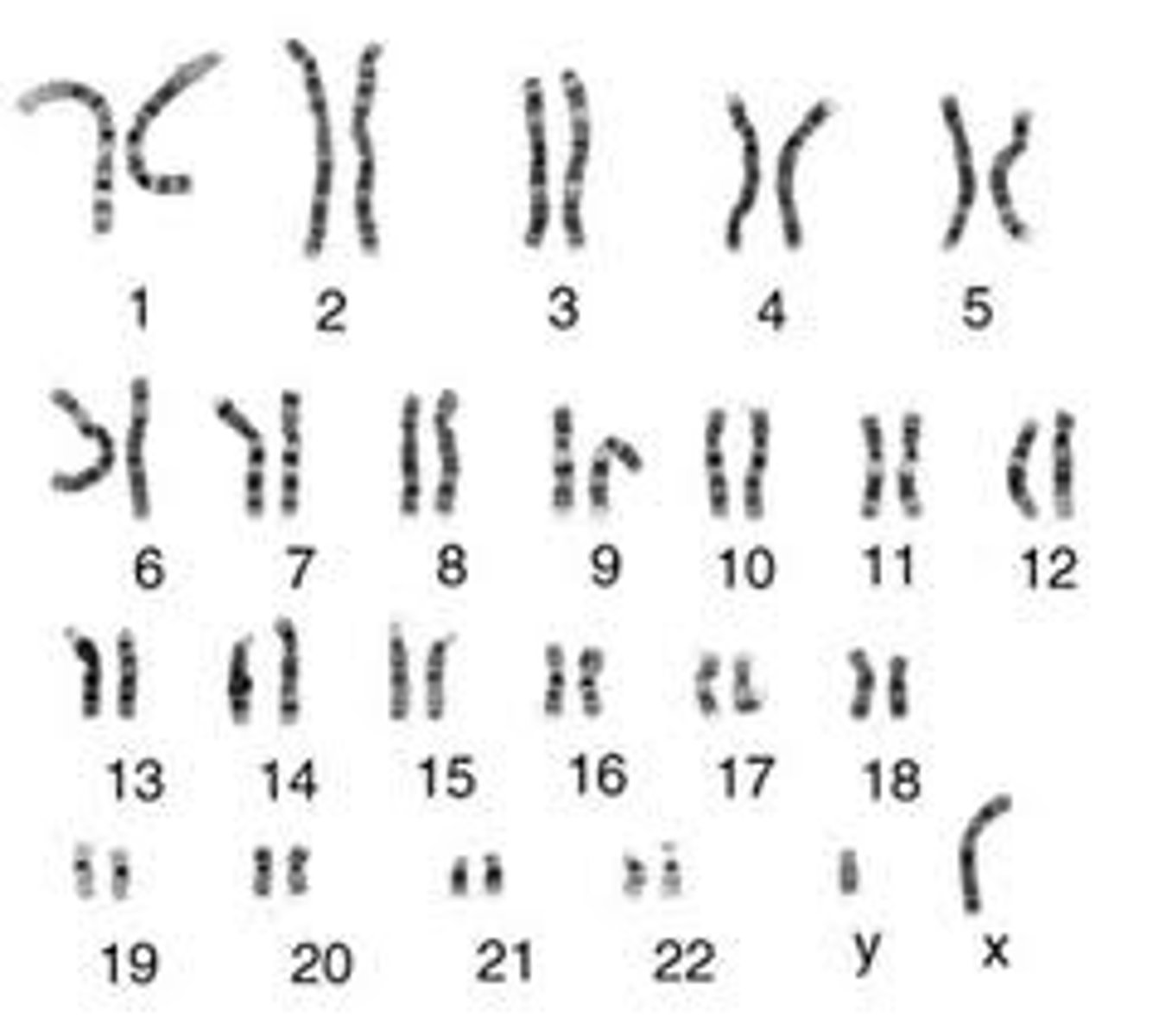
Homologous chromosome
Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes and the same structure
Somatic Cells
Any cells in the body other than reproductive cells
Gamete
sex cell
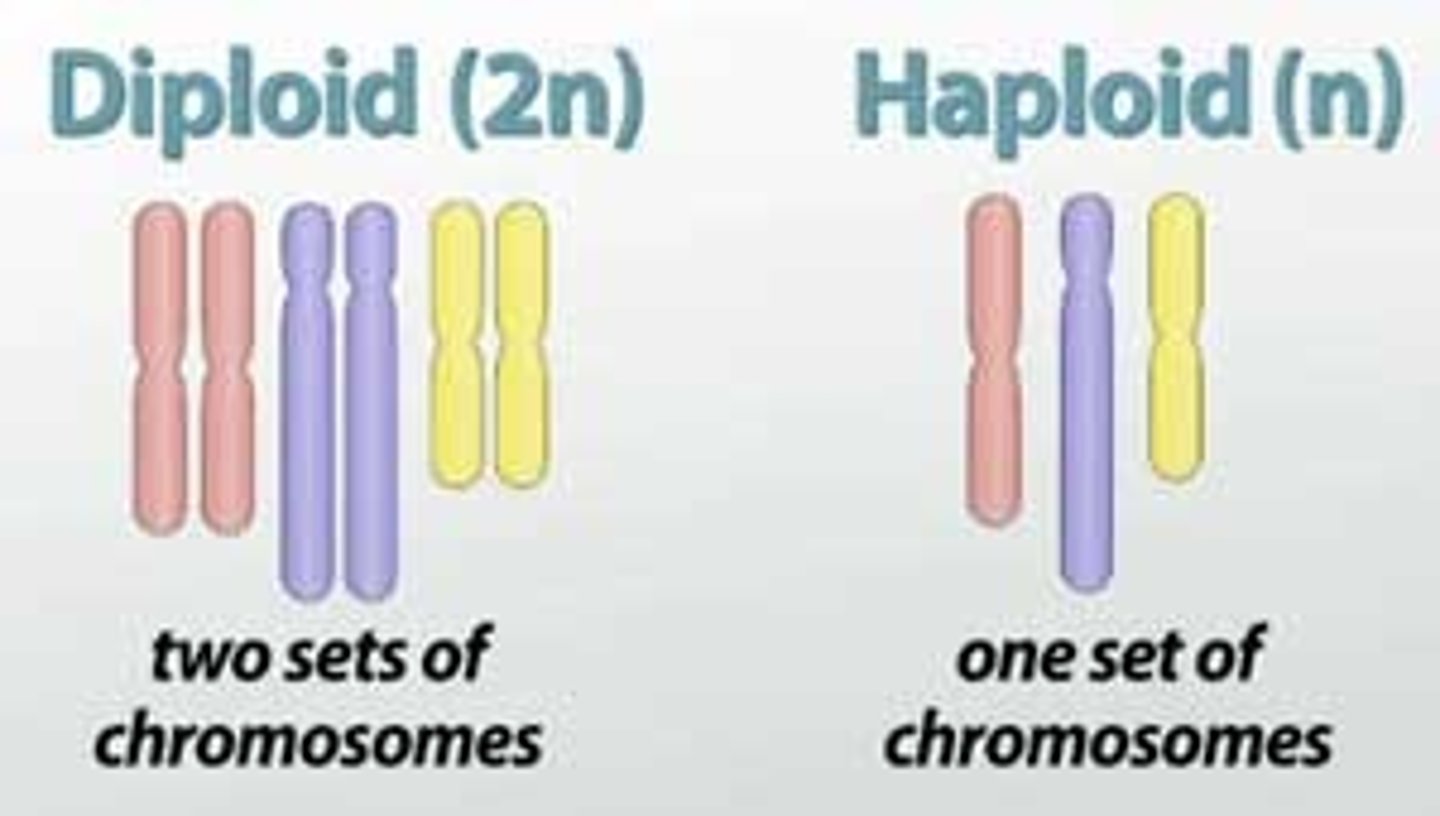
Diploid
2 sets of chromosomes
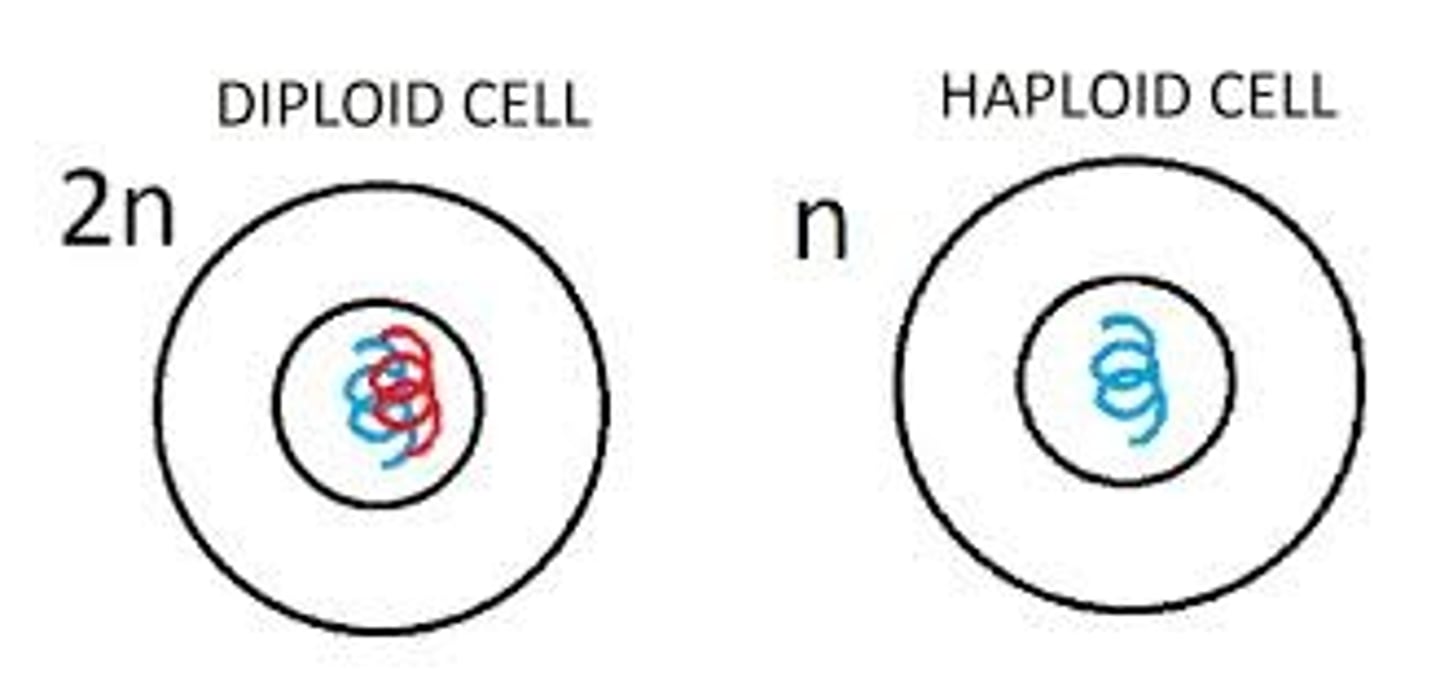
Haploid
having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
DNA replication
Process of copying DNA before cell division.

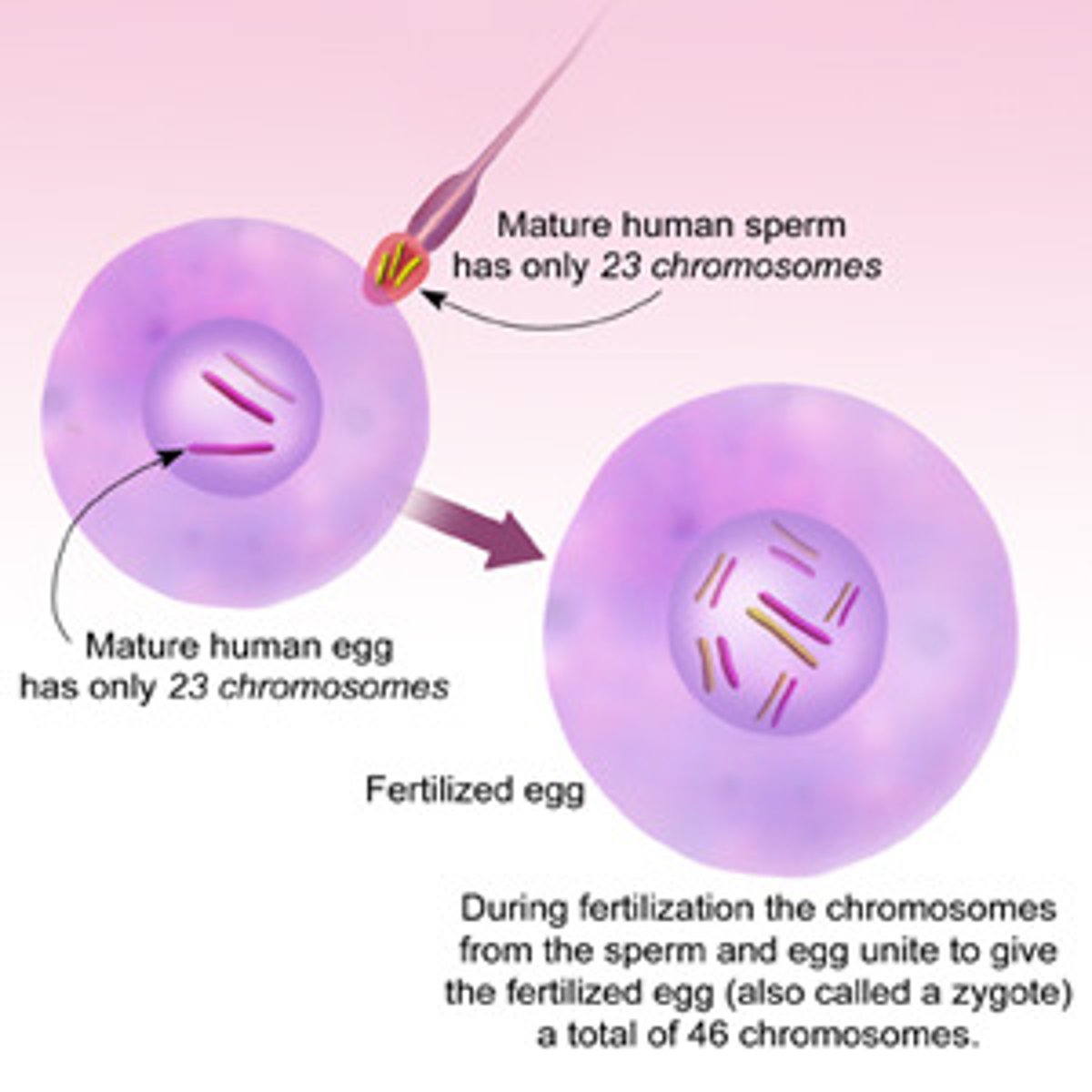
Zygote
a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; an egg and sperm cells joining.
Mutation
A change in the DNA sequence of a gene or chromosome.
Mutagen
chemical or physical agents in the environment that interact with DNA and may cause a mutation
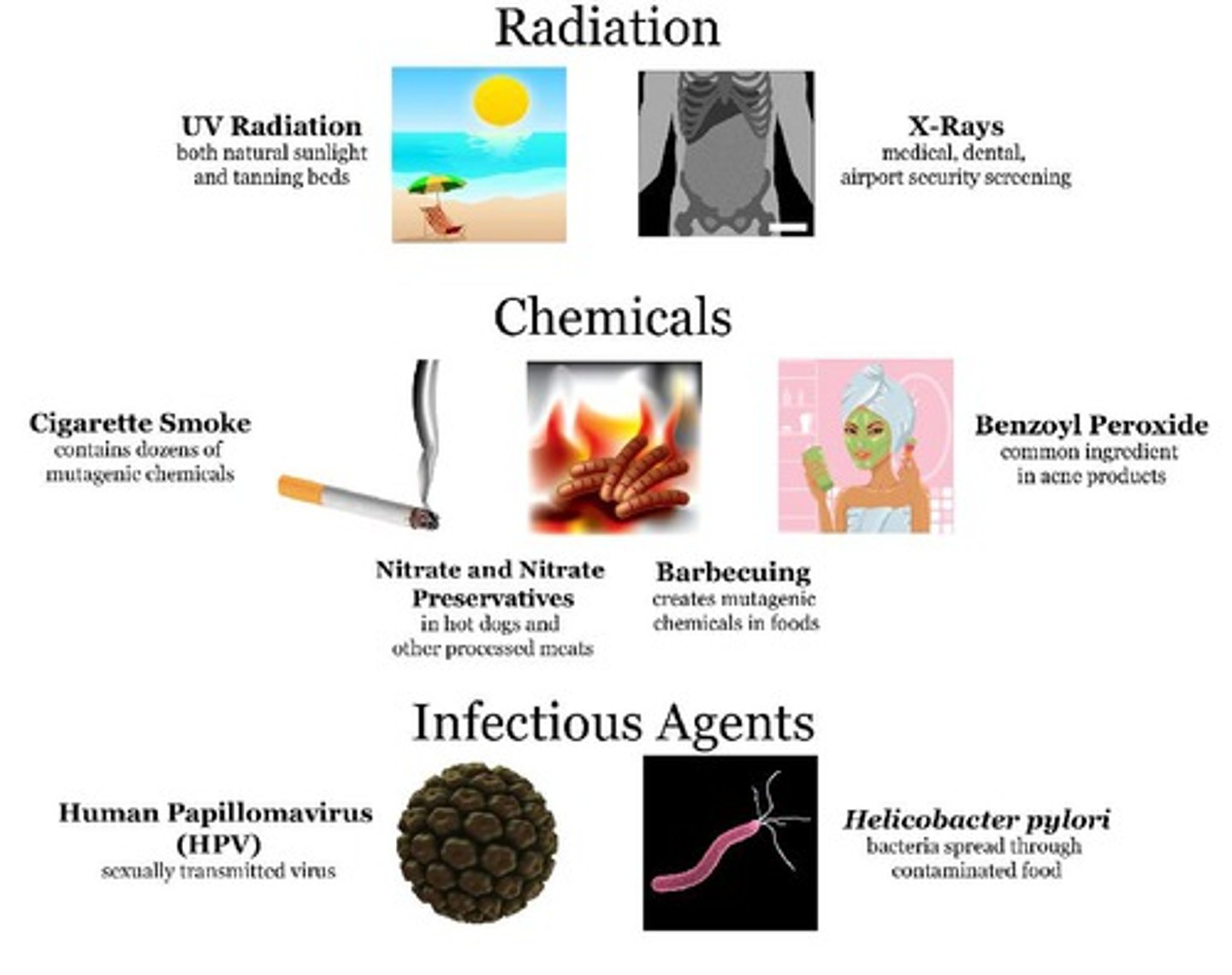
Induced mutation
a mutation caused by external agents such as mutagenic chemicals or radiation
Spontaneous mutation
a random change in the DNA arising from errors in replication that occur randomly
Germline mutation
DNA alteration occurring in gametes that can be transmitted to offspring
Beneficial mutation
A mutation that enhances the survival or reproductive success of an organism
deleterious mutation
A mutation that causes a change in DNA that negatively affects an individual
Neutral mutation
a mutation that has no effect on survival or reproduction
Point mutation
gene mutation in which a single base pair in DNA has been changed
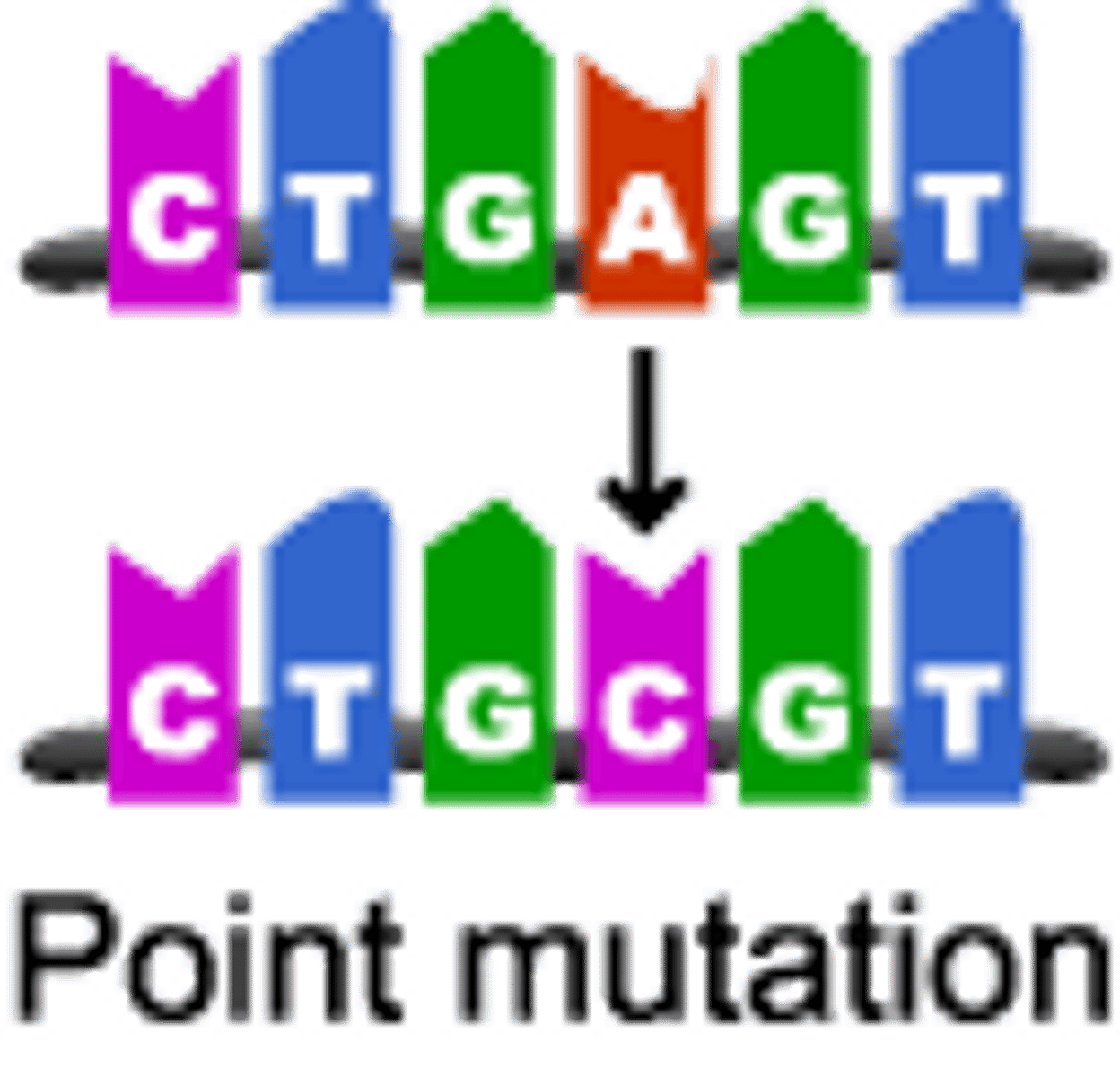
Substitution mutation
Mutation in which a single base is replaced, potentially altering the gene product.

Insertion mutation
the addition of one or more nucleotide base pairs into a DNA sequence

Deletion mutation
a mutation in which one or more pairs of nucleotides are removed from a gene

Frameshift mutation
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide (changes the codons)
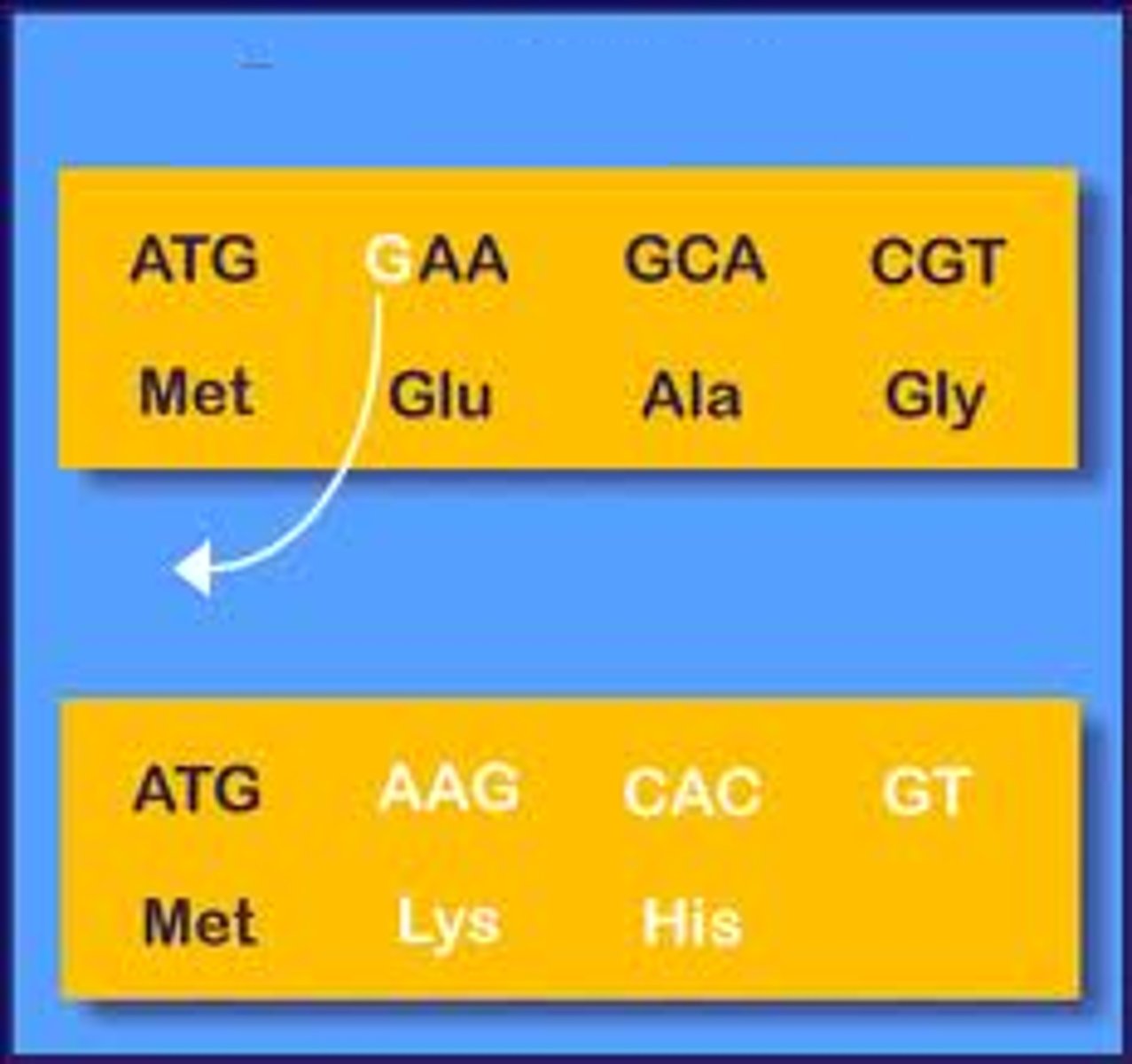
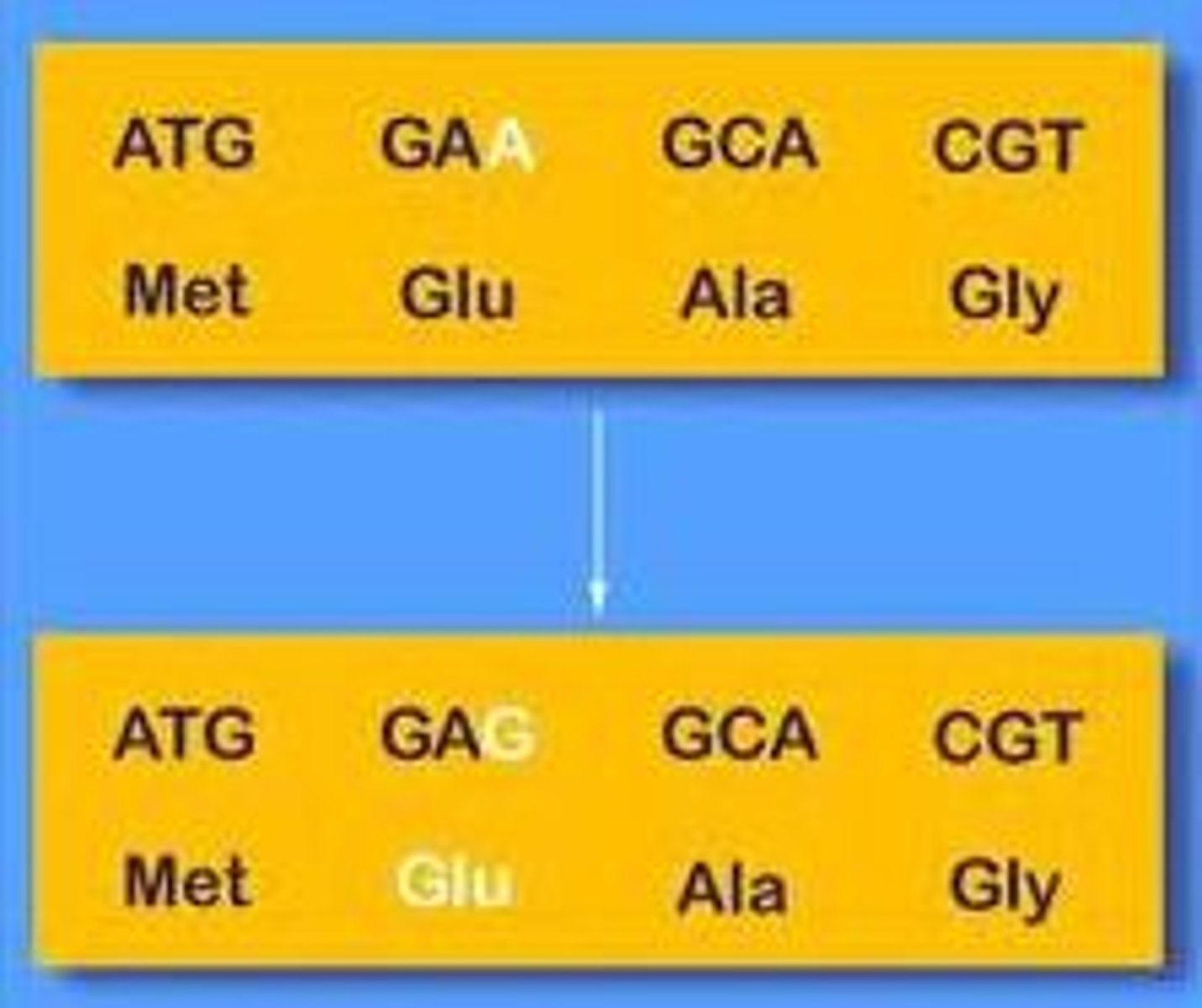
Silent mutation
A mutation that changes a single nucleotide, but does not change the amino acid created.
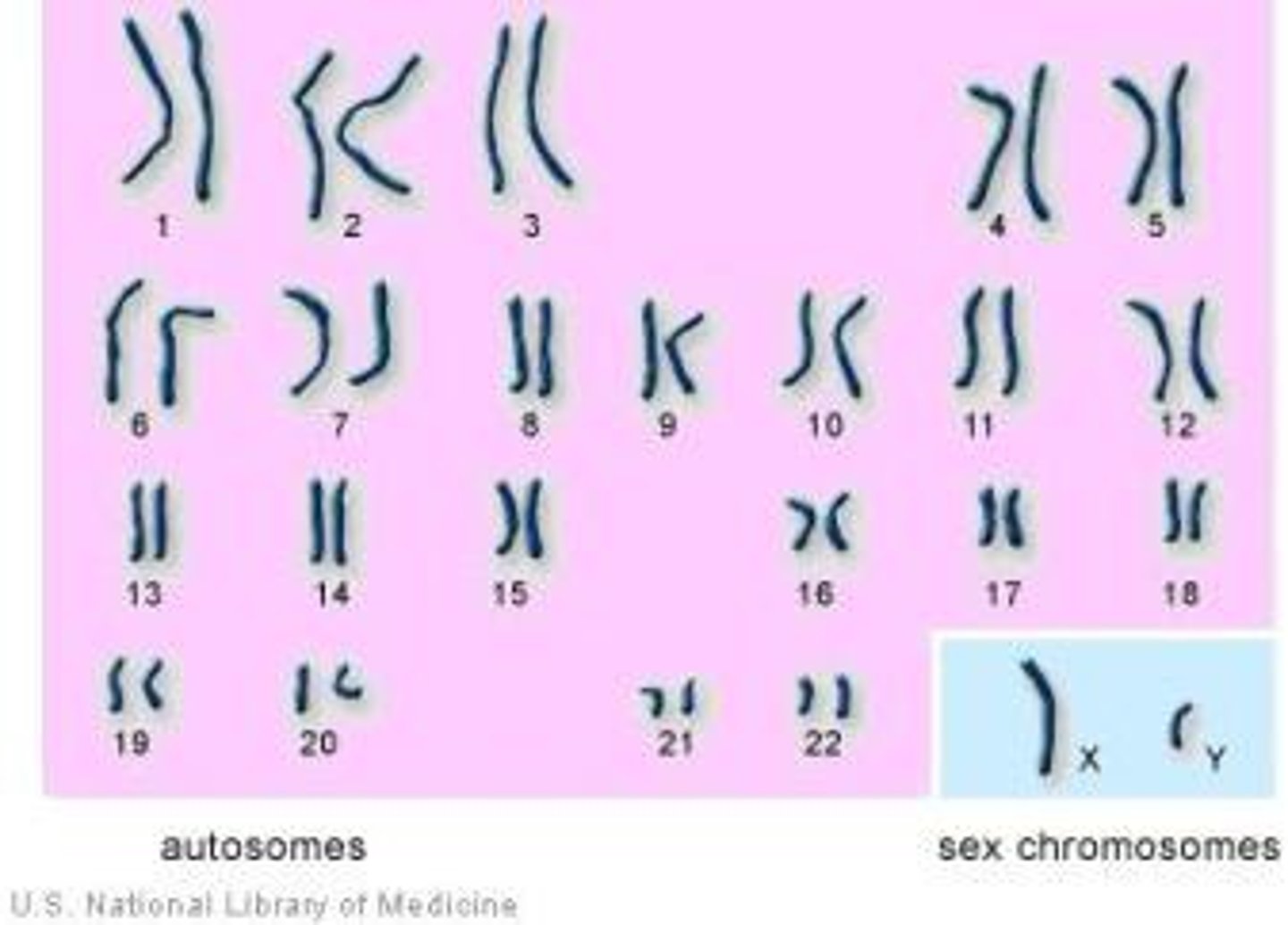
Sex chromosomes
Chromosomes that determine the biological sex of an individual
Autosomes
Any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome (humans have 22 pairs)
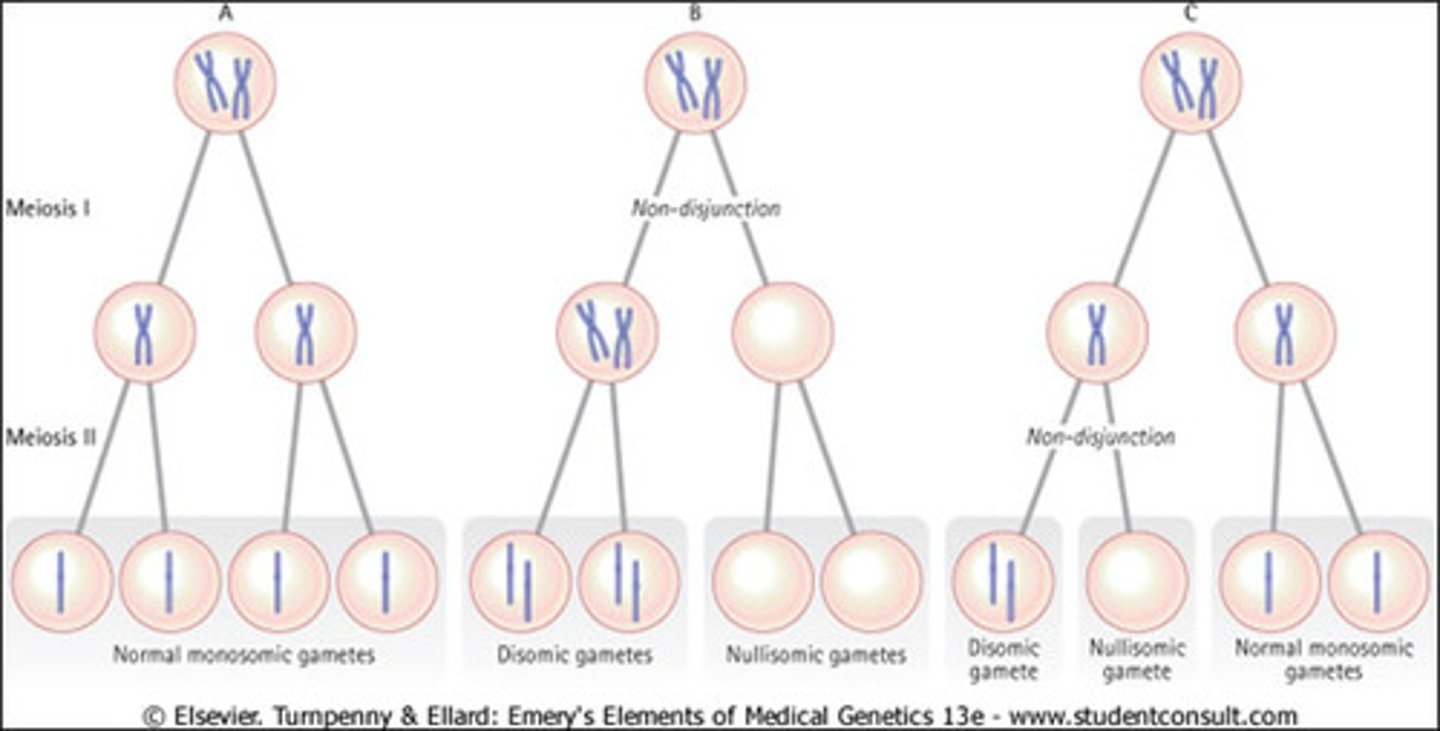
Non-disjunction
Error in meiosis in which homologous chromosomes fail to separate.
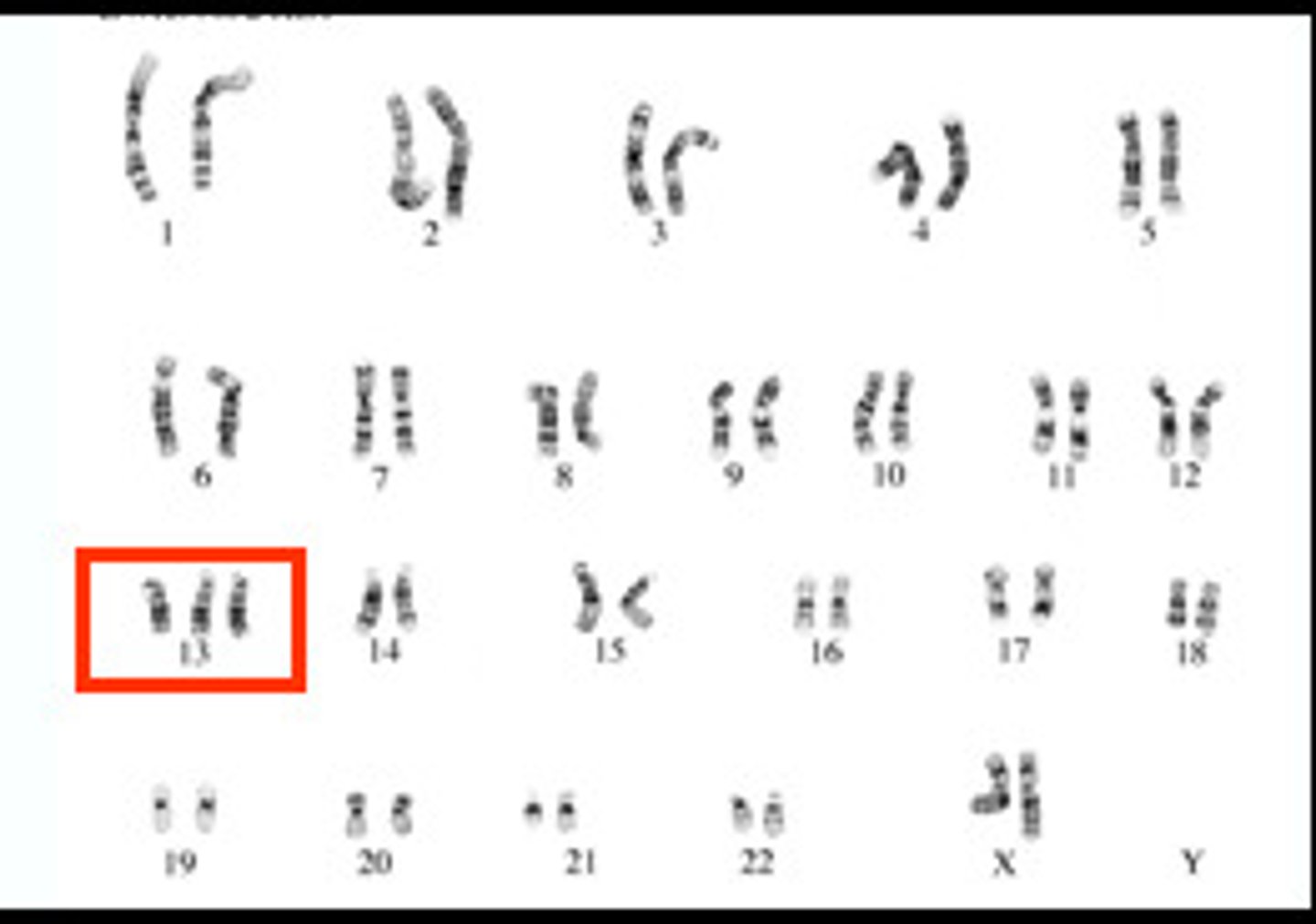
Trisomy
3 copies of a chromosome
Monosomy
missing a chromosome
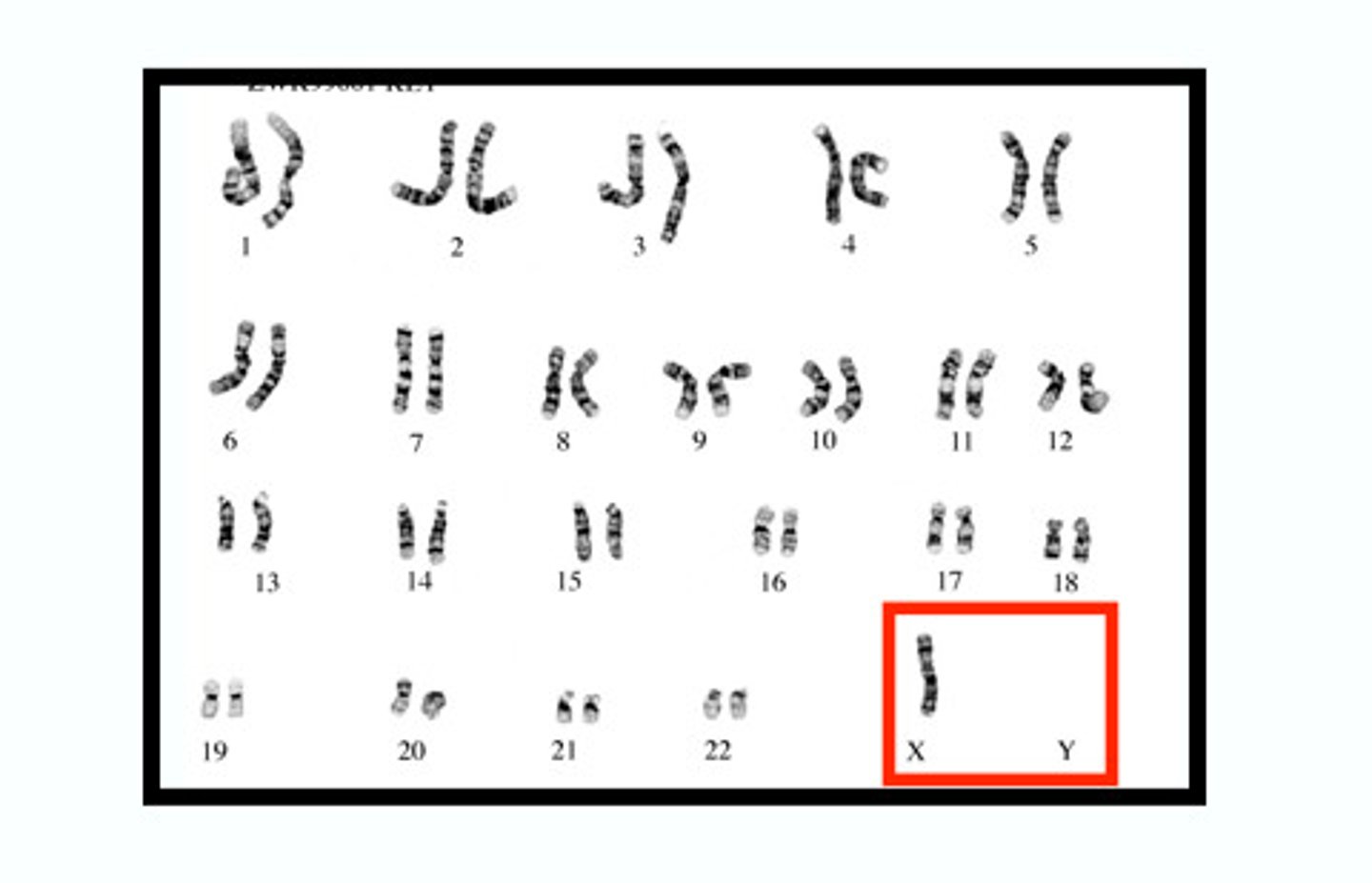
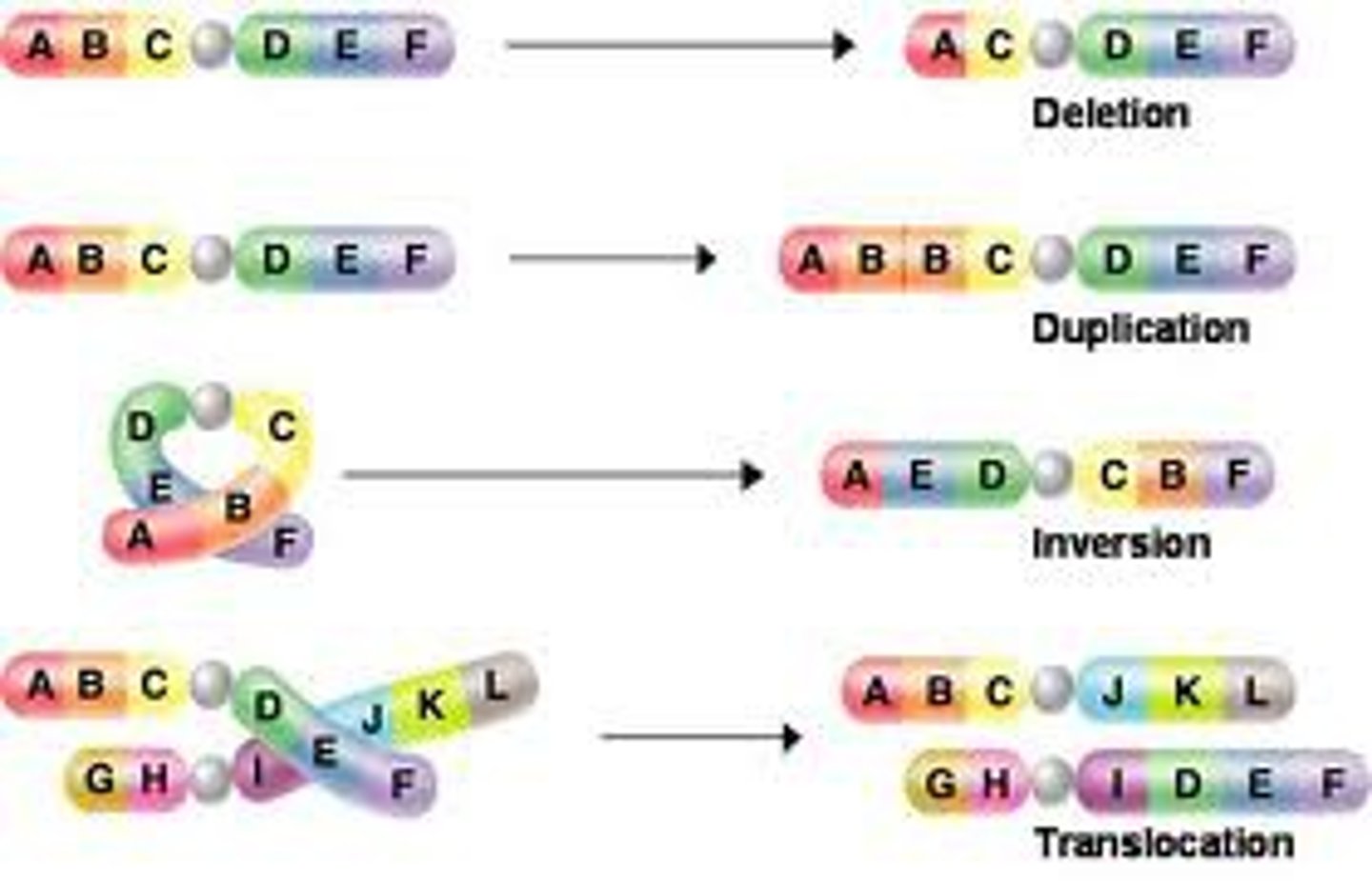
Chromosomal mutation
A change in the structure of a chromosome
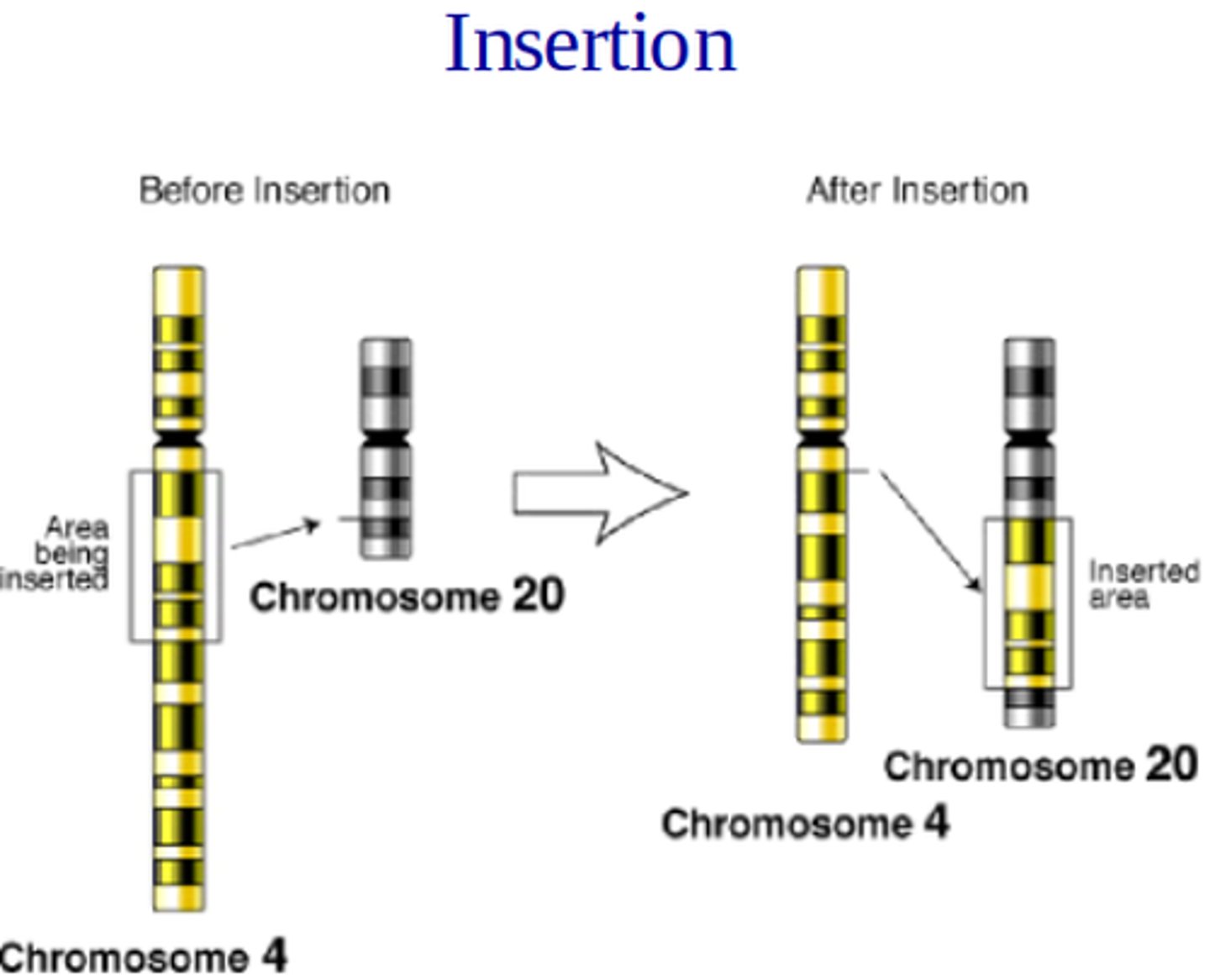
Insertion Chromosomal Mutation
section of a chromosome gets inserted into another chromosome
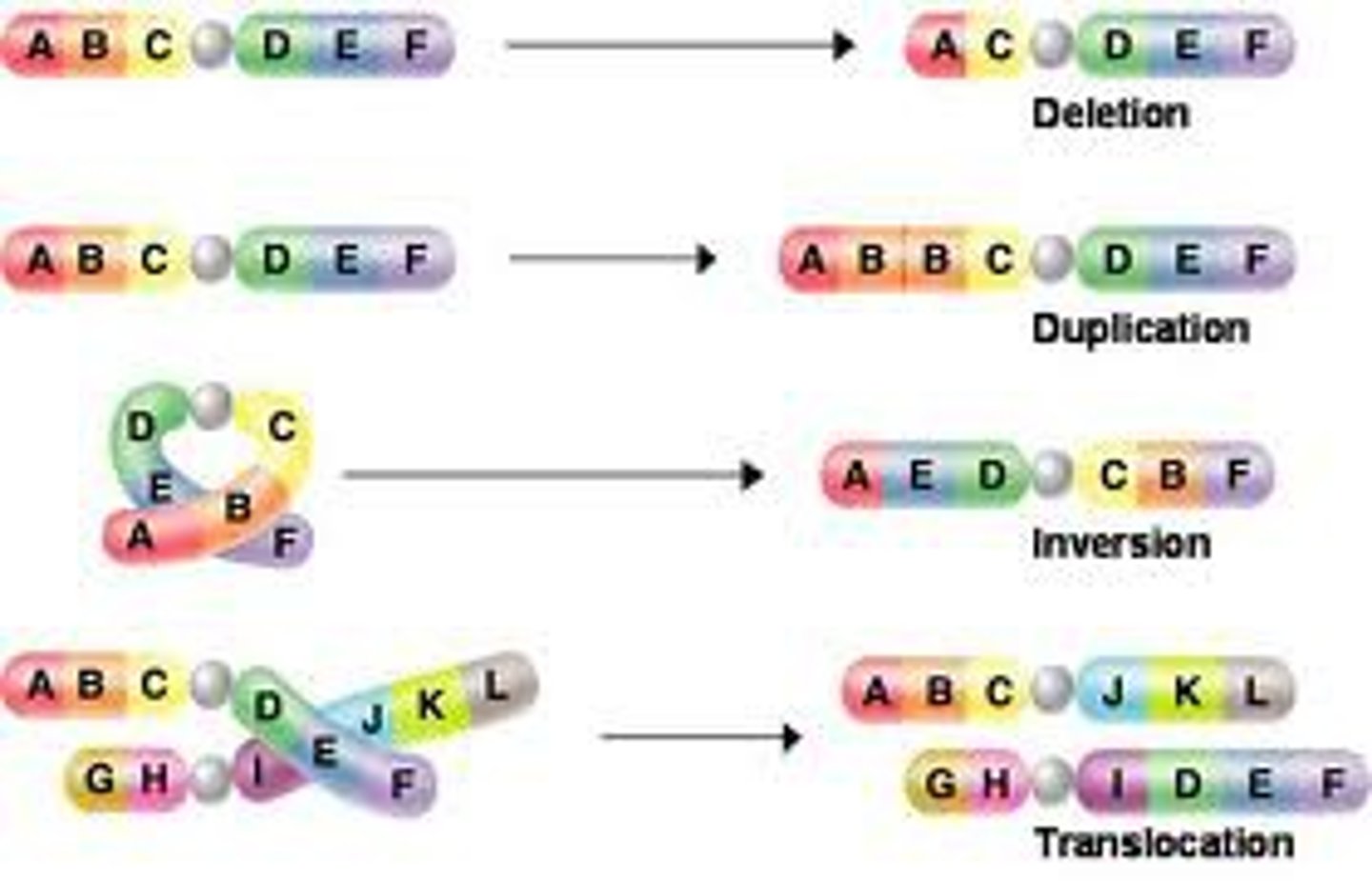
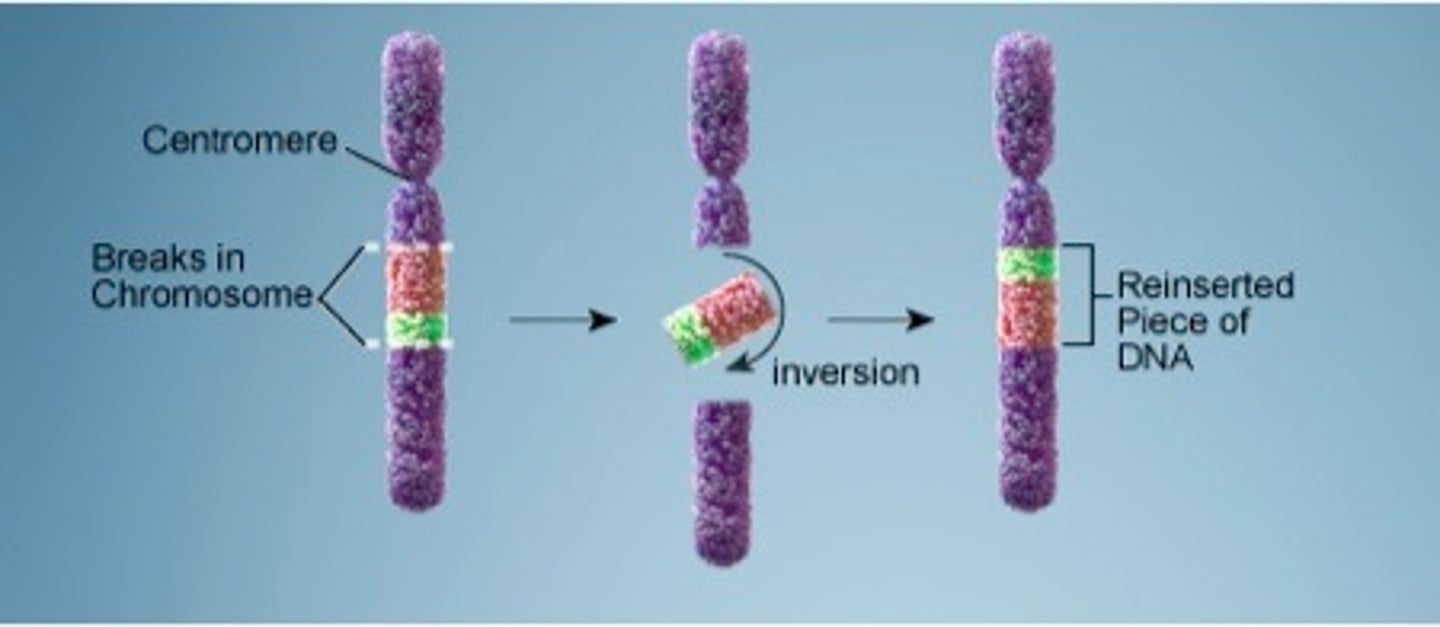
Inversion Chromosomal Mutation
a mutation that reverses the direction of parts of a chromosome
Duplication Chromosomal Mutation
a mutation that produces extra copies of parts of a chromosome
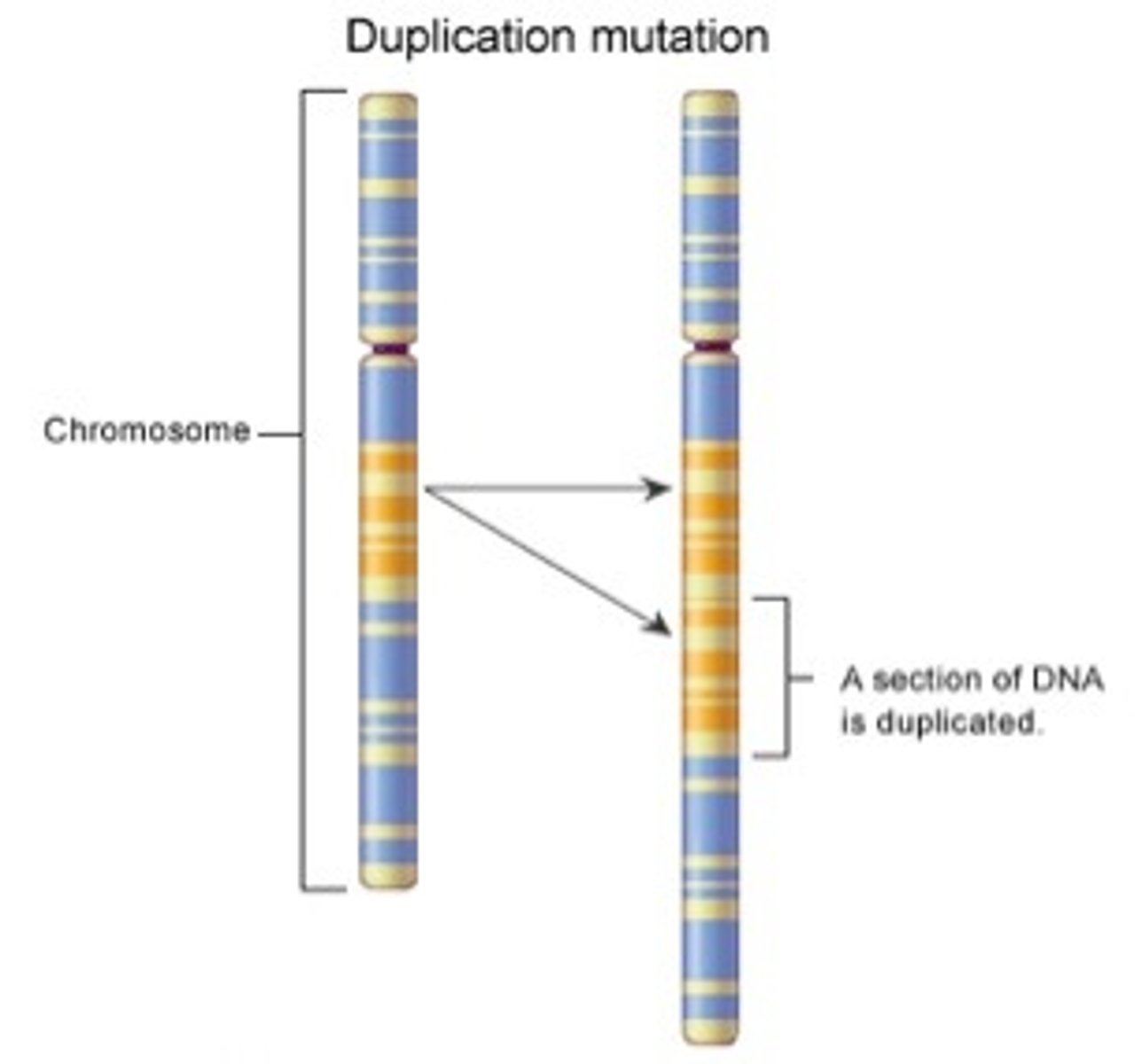
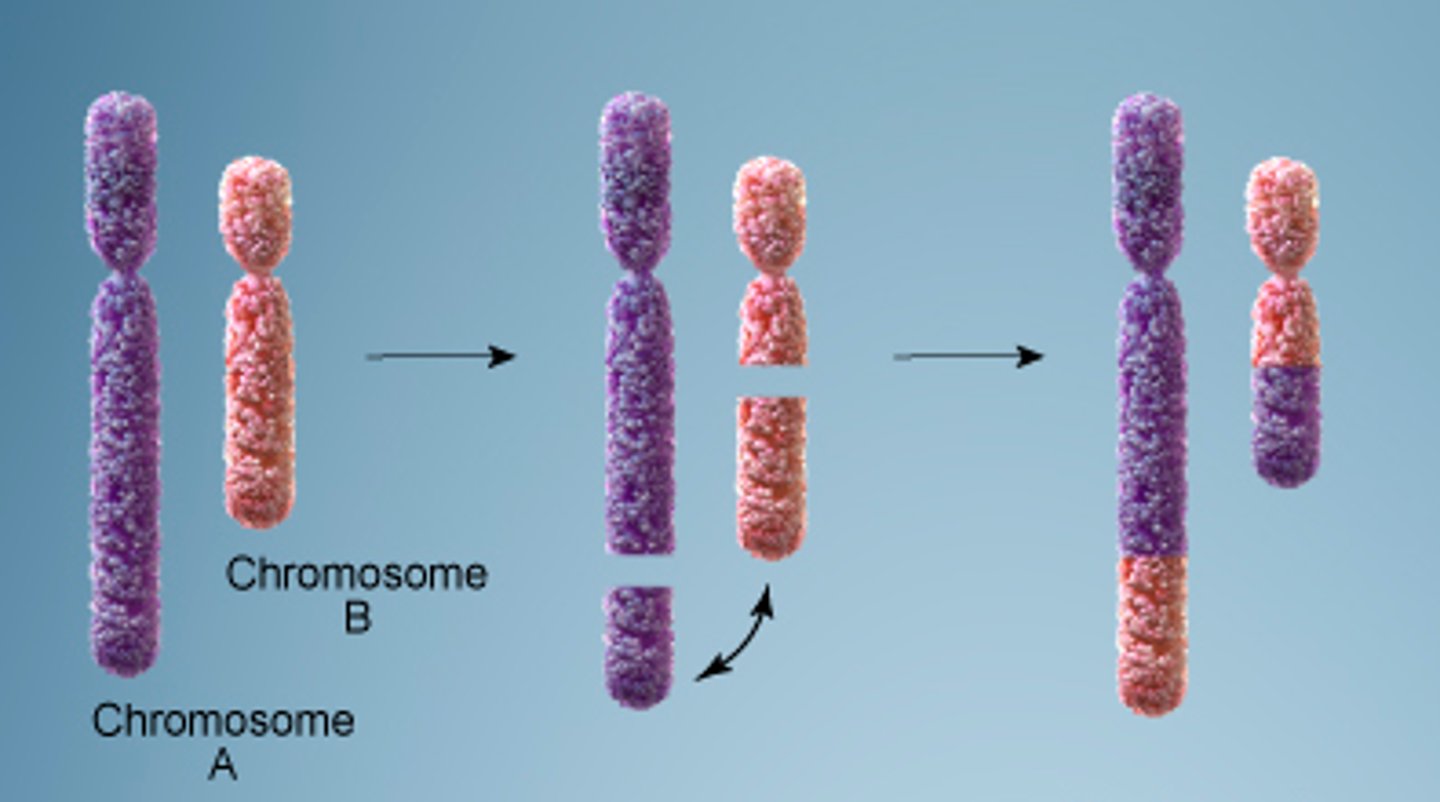
Translocation Chromosomal Mutation
Part of a chromosome is swapped with a part of a different chromosome
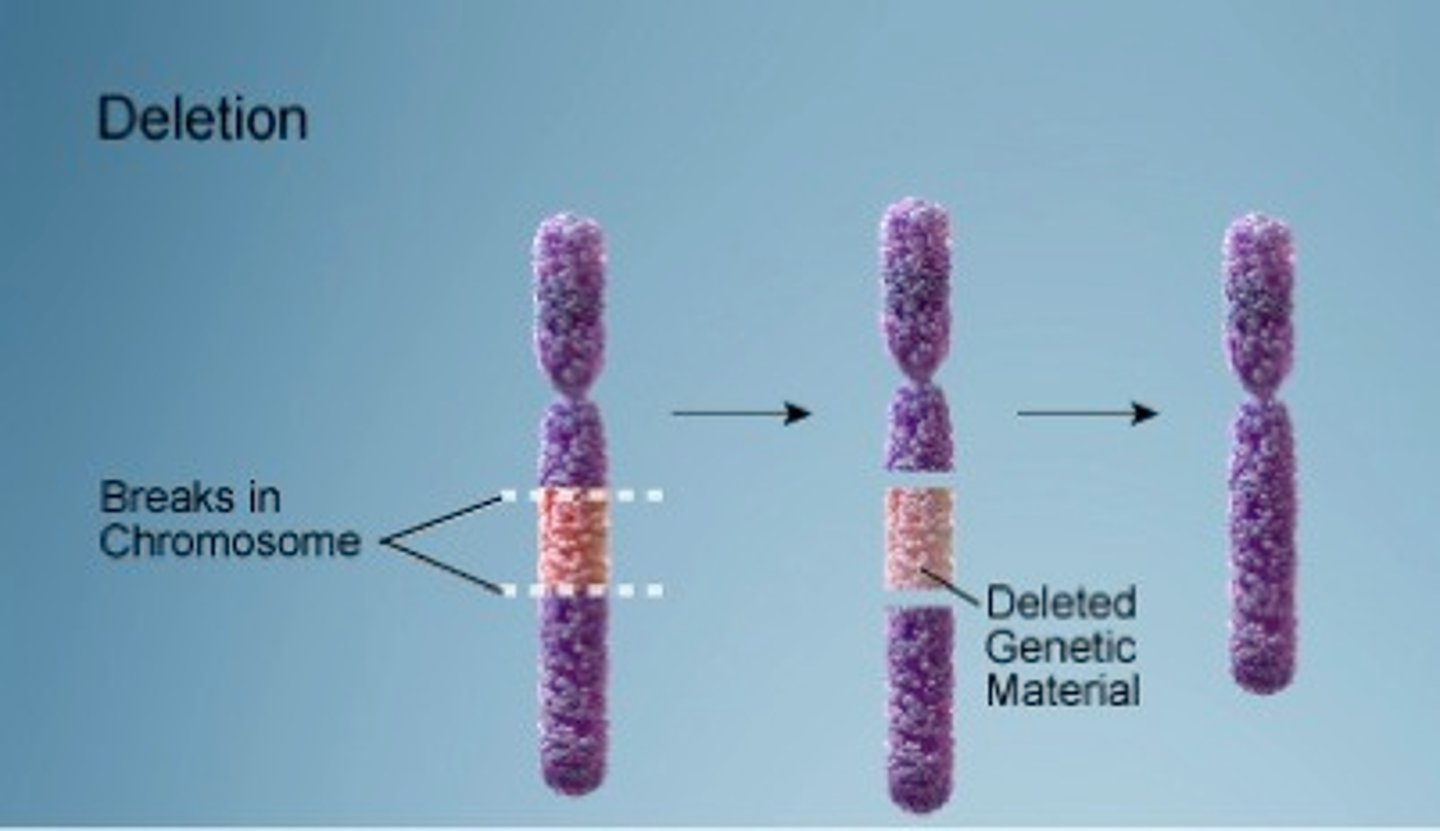
Deletion Chromosomal Mutation
A segment of a chromosome breaks off and is lost.
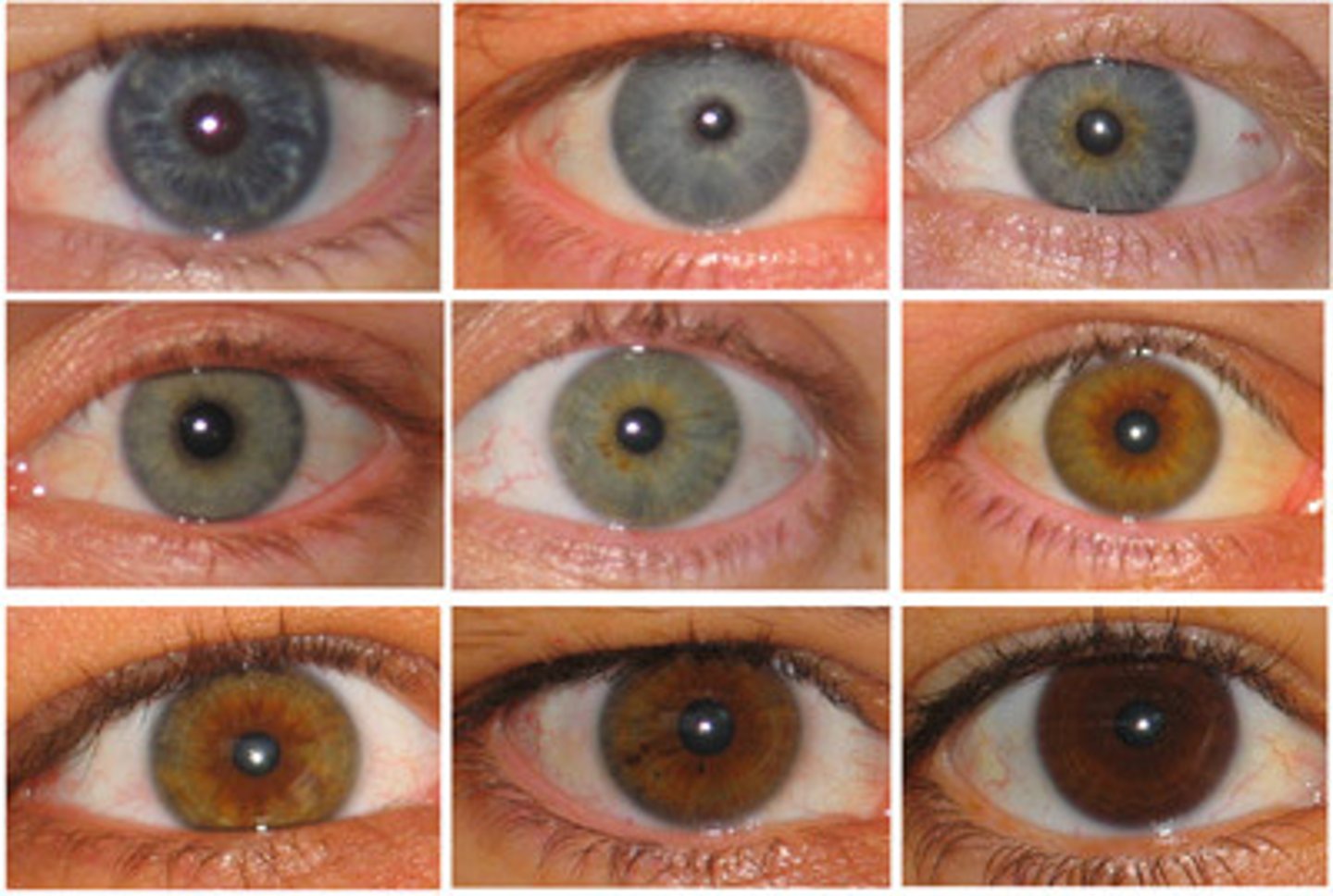
Inheritance
The process in which genetic material is passed from parents to their offspring.
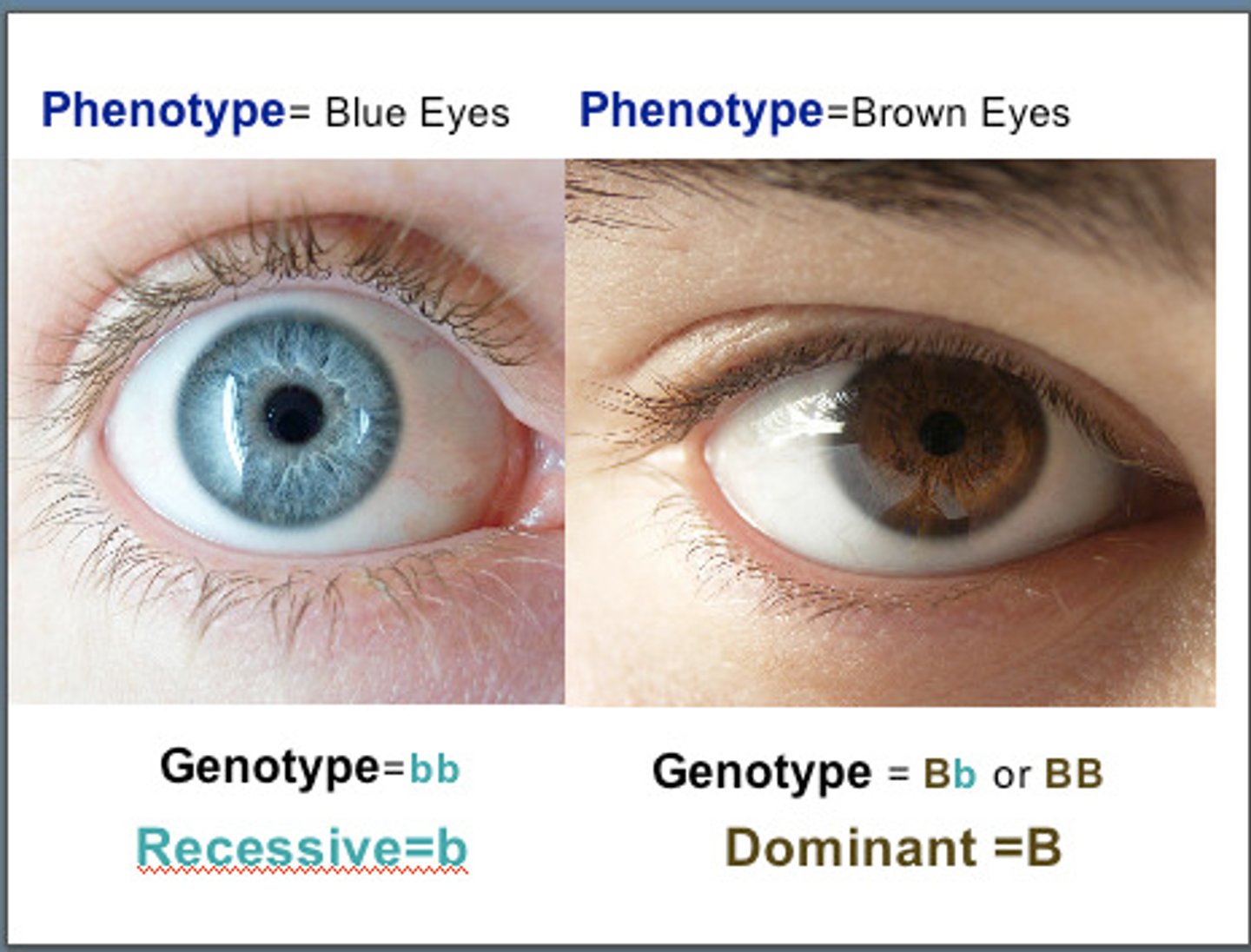
Dominant
An allele that is always expressed
Recessive
An allele that is masked/hidden when a dominant allele is present
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.