A.1.3.2 The Respiratory System
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9VdHhD1vcDU
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Oxygen transport in the body
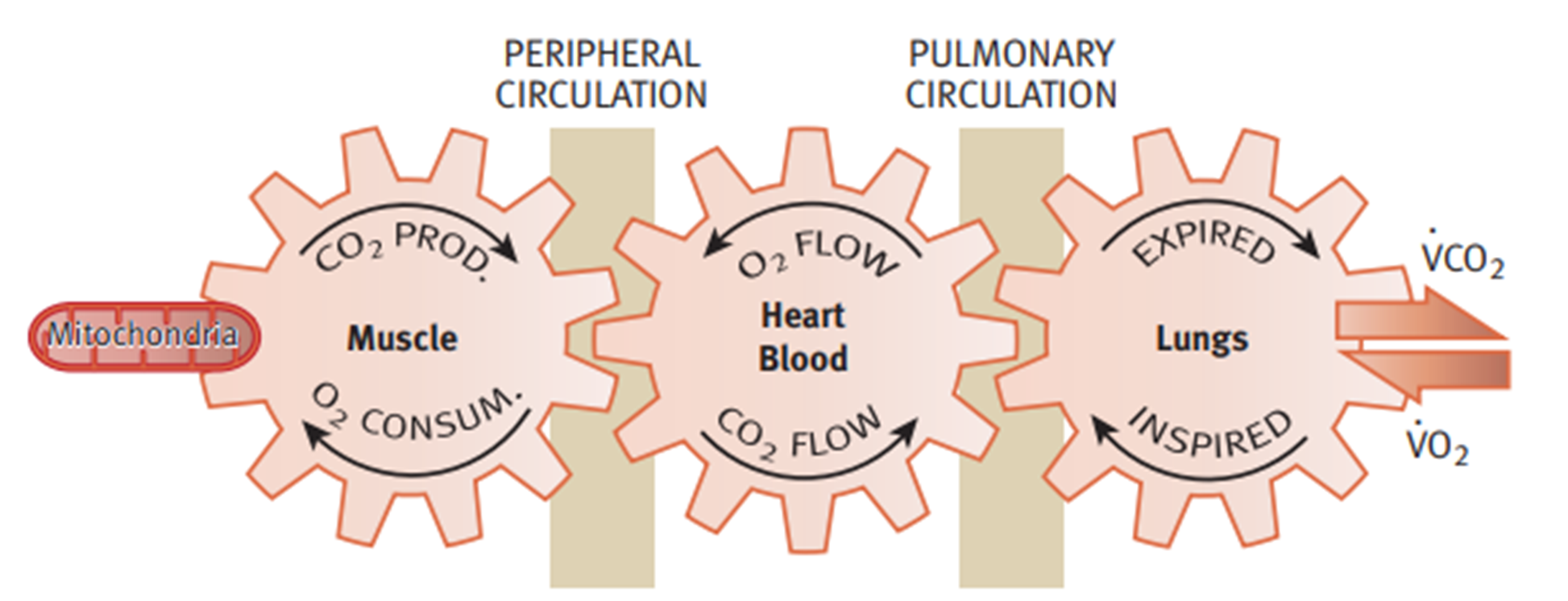
Step 1 - O2 Transport
air enters the nose/mouth, and passes the pharynx and larynx, trachea carries air down the bronchi
Step 2 - O2 Transport
bronchi is divided into bronchioles leading to clusters of alveoli
Step 3 - O2 Transport
oxygen diffuses into bloodstream while CO2 diffuses out into the alveoli
Step 4 - O2 Transport
diaphragm relaxes, pushing air out of the lungs and travles backwards
Nose and nasal cavity
entry point of air
filters incoming air
warms and humidifies air
Mouth and oral cavity
alternate entry point for air
speech and swallowing
Pharynx (throat)
connects the cavities to the trachea
epiglottis
Larynx (voice box)
tough and flexible
allows air to pass through it preventing food and drink blocking the airway
Trachea (windpipe)
wide, hollow tube , C-shaped cartilage
connects larynx to bronchi
enable airflow to and from the lungs
Bronchi
main airways to the lungs
trachea branches into bronchus in each lung
cilia
move mucus out of your lungs
Bronchioles
small branching air passages in lungs
connect larger bronchi to alveoli
Alveoli
tiny air sacs, end of bronchioles
cruical role of gas exchnage
How does gaseous exchange occur?
diffusion
Where do the gases move?
area of high partial pressure to area of lower partial pressure
What is partial pressure?
pressure exerted by a single gas (O2) within a mixture (air, blood, tissue fluid)
What happens during inhalation?
the volume of the thoracic cavity increases
so pressure decreases
diaphragm contracts (flattens)
external intercostal muscles contract
ribcage moves up and out
air is drawn in
What happens during exhalation?
the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases
so pressure increases
diaphragm relaxes (dome-shape)
external intercostal muscles relax
ribcage moves down
air is forced out
What is Fick’s law?
describes how gases diffuse across membranes
What does it state?
rate of diffusion of a gas across a membrane depends on three main factors
What are the three factors?
Surface area
Concentration (PP) gradient
Thickness of the Membrane
Surface area - Ficks Law
the larger the surface area the greater the rate of diffusion
Concentration gradient (PP) - Ficks Law
the bigger the diff in concentration of the gas on either side of the membrane, the faster the diffusion
Thickness of the Membrane - Fick’s Law
thinner membrane = faster diffusion
What is minute ventilation (VE)?
volume of air being exhaled per minute
Minute ventilation formula
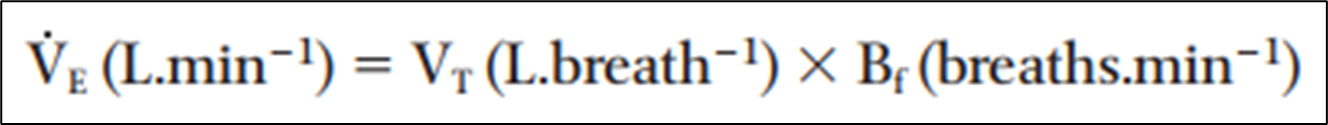
What is tidal volume (VT)?
amount of air inhaled and exhaled in a single breath during regular breathing
What is respiratory rate (BT)?
number of breaths per minute
What is vital capacity?
maximum amount of air you can exhale after taking a deep breath
What is residual volume?
amount of air that remains in your lungs after exhaling as much as you can
What is total lung capacity?
total amount of air in your lungs can hold, sum of vital capacity and residual volume
What are the inspiratory/expiratory reserve volumes?
extra amount of air you can inhale/exhale after a normal inhalation/exhalation
How do trained and untrained individuals of the same size affect lung volumes and capacities?
Trained:
larger capacites/volumes
training improves respiratory muscle strength
more efficient breathing
larger tidal volumes
How does age affect lung volumes and capacities?
Young:
larger capacities/volumes
greater elasticity in lung tissue
Old:
decline in vital capacity
increase in residual volume
reduce efficiency in gas exchange
How does fitness level affect lung volumes and capacities?
High fitness levels:
accomodate more air with each breath
higher capacites
respiratory muscles are stronger
greater expansion of lungs
How does body size affect lung volumes and capacities?
Larger/tall:
larger volumes/capacities
more space in the chest cavity
Shorter/small:
smaller capacites/volumes
lung size is small
How does gender affect lung volumes and capacities?
Males:
larger volumes/capacites
larger lung size
larger thoracic dimensions
a higher proportion of lung tissue