Consciousness, Sleep and Learning
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
fMRI
Measured ‘BOLD’
Blood Oxygen Level Dependent Signal
fMRI strengths
Functional, in real-time
Good spatial resolution
No radiation
fMRI limitations
Poor temporal resolution
Subject is very restricted
Aversive environment
Resting state
State against which activation of brain regions is compared in imaging research
At rest
Brain is the most energy-hungry organ
2% of body weight
20% of energy use in adults
40% in children
Constant consumption of energy
Active only adds 10% max
Redistribution of activity, rather than net changes in total activity
Default mode network
Medial Cortical Regions
Frontal, Temporal and parietal
Becomes more active when we are not focused on a task
Stimulus Independent Thought
Introspection, Daydreaming
Self-referential
Includes regions associated with ‘theory of mind’
Creativity?
Paradoxical Function Facilitation
Turning down A, enhances B
Damage to A, enhances B
Damage to, or turning off of the prefrontal cortex
Creativity
Default mode network (medial cortical regions) are inhibited by prefrontal regions when engaged in a task
Especially language
This top-down inhibition weakens with aging
Can be severely impaired in certain dementias
Frontotemporal dementia (Picks disease)
Primary Progressive Aphasia
Rare, early, unrecognised sign is a sudden, intense, repetitive creativity
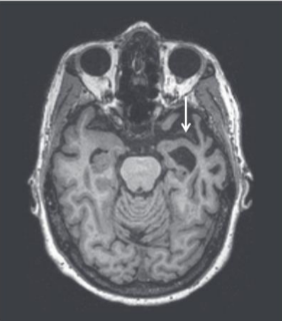
Frontotemporal dementia
Most common form of dementia in patients under 65
20% have known familial cause
40% have strong family history
Poor outlook - limited treatment and slow progression
Often restricted to one hemisphere
Lots of variance in presentation
Presentation of frontotemporal dementia
Progressive deterioration of behaviour/cognition
Behavioural disinhibition
Apathy/inertia
Loss of sympathy/empathy
Decline of executive function
Memory is largely spared
Contrast with Alzheimer’s Dementia
Verbal/language impairment
Changes in diet
Not psychiatric
Anne Adams
Cell biologist
Quit science in mid 40s and decided to become a painter
Painted obsessively, with repetitive motifs
Eventually diagnosed with a form of frontotemporal dementia
57% of people with bvFTD have committed a crime
Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex
Decision making based on
Moral judgements
Emotions
Values
Integration of ‘gut’ and ‘logic’
Self-referential
Impulse
Disorders of consciousness
Coma
Vegetative State
Delirium
Hallucinations
Dementia
Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
Epilepsy
Synchronous (abnormal) firing of large groups of neurons
Electroencephalography (EEG)
Measures electrical activity in the cerebral cortex
Groups of neurons firing together
Does not really measure action potentials
Characteristic ‘waves’
Oscillations
Temporal, rather than spatial
Temporal lobe epilepsy
Simple partial seizures - not loss of consciousness - auras
Emotional
Auditory, olfactory, gustatory
Deja vu
Complex partial seizures - most common type of seizure in TLE - impaired consciousness
Unusual behaviour
Automatisms (e.g., lip smacking)
Secondarily generalised to tonic-clonic seizures
Extends beyond the temporal lobe
‘Full blown’ seizures
Hypergraphia
Writing copiously (not necessarily in a creative way) and keep voluminous diaries
Hypo-sexuality
Decreased interest in sexual matters often resulting in marital disharmony
Emotional viscosity or stickiness
Anxiety, obsessional, dwells on minor matters, experiences difficulty in terminating conversations
Increased interest in spiritual or ideational issues in the absence of pragmatic interests
Turbulent emotions
Irritability, agitation, restlessness, paranoia etc.
Mood swings
More commonly depression or dysphoria with occasional elation
Psychotic and quasi-psychotic phenomena
Intermittent hallucinations, delusional thinking etc.
Hyper-religiosity
Very religious, often ritualistically so, out of sync with family/cultural background
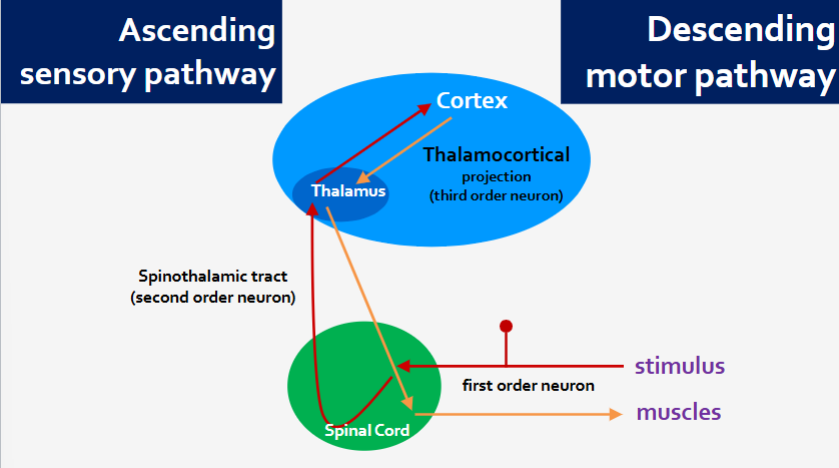
Sensory and motor pathways
Ascending- sensory
Descending - motor
Stages of sleep
Rapid eye movement (REM sleep)
Non-REM sleep
Stage 1
Stage 2
Stage 3
More NREM early in the night, more REM later
Non-REM sleep
Processing the days experience
Consolidating memories
Especially declarative memories
Clear out the hippocampus
Long term memories eventually stored in the cortex
REM sleep
Integrating new memories with existing
Emotional processing of new memories
Dreaming
Cognitively acting out memories and experiences
Brain is very active, body is notThalamus prevents outgoing motor commands
Muscle atonia
What happens when you sleep
Thalamic gate is closed, in and out
(In) we don’t attend to external stimuli
(Out) we don’t (really) act out our dreams
Repeated cycles of (re)consolidation
Integration of new knowledge with
Prior knowledge
Prior emotions
Modifying connections between neurons
Clearing of ‘temporary store’ in the hippocampus
Sleep deprivation leads to
Drastically impaired learning
Failure to ‘clear’ the temporary store in the hippocampus
Atrophy
Smaller hippocampus
Smaller prefrontal cortex
All sorts of other problems
Sleep deprivation can also lead to
Death
Fatal Familial Insomnia
Rare genetic disorder
Progressive neurodegeneration of the thalamus
Symptoms develop mid-adulthood
Die from lack of sleep
Alcohol impairs sleep
Initially causes sedation
Quicker to fall asleep
Quicker to reach NREM3
Reduces REM sleep
Over-relaxes certain muscles
Snoring, resulting in waking up more often
Rebound effects of alcohol metabolism cause wakefulness
Impairs memory