Chapter 13 - Intracellular Compartments and Protein Transport
1/98
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
What is Biomolecular Condensate
membraneless organelles/sub compartments
Biomolecular condensates often contain
RNA in addition to protein
perform a particular function
What is the largest biomolecular condensate
The nucleolus
An animal cell contains a basic set of__________
membrane enclosed organelles
What does each membrane compartment contain
a unique set of molecules that carry out a specialized function
Contains many metabolic pathways, protein synthesis, the cytoskeleton
Cytosol
Contains main genome, DNA and RNA synthesis
Nucleus
Synthesis of most lipids, synthesis of proteins for distribution to many organelles and to the plasma membrane
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Modification, sorting, and packaging of proteins and lipids for either secretion or delivery to another organelle
Golgi apparatus
ATP sythesis by oxidative phosphorylation
Mitochondria
Sorting of endocytosed material
Endosomes
Intracellular degradation
Lysosomes
Oxidative breakdown of toxic molecules
Peroxisomes
Surrounded by double membrane which consists of a nuclear envelope and nuclear pores
Nucleus
True or false, the outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the membrane of the ER
True
Types of ER
Smooth
Rough
ER interior is also called
ER lumen
Receives lipids and proteins from ER, modifies them and dispatched to other destinations. Also the production of vesicles
Golgi Apparatus
This compartment is surrounded by a db membrane, with is also a site for oxidative phosphorylation
Mitochondria
Digestive enzymes that degrade worn out organelles, macromolecules and particles taken into cell by endocytosis
Lysosomes
Series of compartments involved in sorting of ingested molecules. Some recycle back to PM, others deliver to lysosomes
endosomes
Enzymes that brwak down lipids and destroy toxic molecules
peroxisomes
Membrane enclosed organelles on average occupy nearly ______ of the volume of a cell
1/2
The area of the ER membrane is _________ than the ______ in a typical mammalian cell
20-30x greater
PM
True or False: In terms of area and mass, the PM is only a major membrane in most eukaryotic cells
False
To break open cells and tissues you will need
Homogenate
Extract
Lysate
How do we isolate cellular organelles when breaking open cells and tissues
differential centrifugation
differential centrifugation separates components based on
size and density
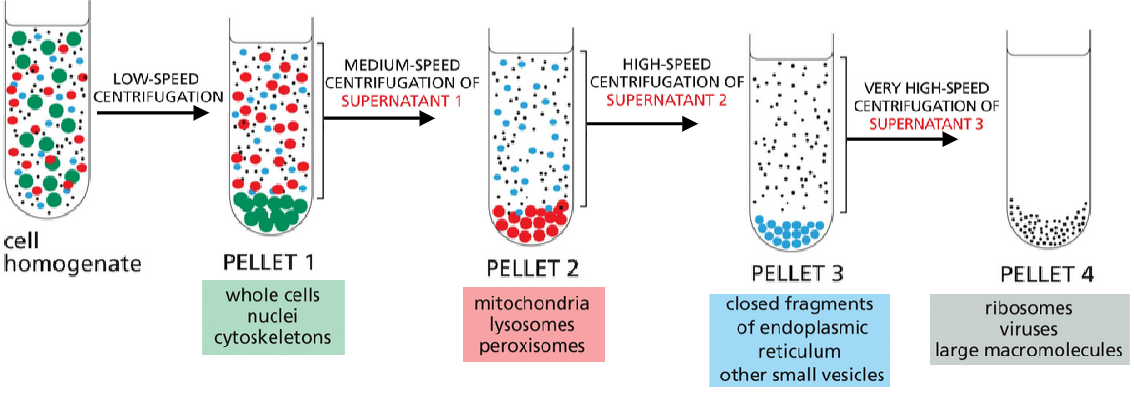
During the evolution of membrane enclosed organelles, what compartment remained isolated
Mito genome
Why is continuous protein synthesis and delivery necessary
Proper functioning of cells
For any cell to grow and divide
Newly synthesized proteins must be accurately delivered to their ____________
appropriate organelle
Direct delivery of proteins from cytosol lead into
Interior of the nucleus
mitochondria
the chloroplast
Indirect delivery of proteins via the ER leads to
Inner nuclear membrane
Golgi
lysosome
endosome
Where does protein synthesis begin
On ribosomes in the cytosol
Mitochondrial and Chloroplast protein facts
few mitochondrial and chloroplast proteins that are synthesized on ribosomes inside these organelles
most mitochondrial and chloroplast proteins are made in the cytosol and subsequently imported
protein destination after its synthesis in the cytosol is dictated by
its amino acid sequence
directs the protein to the organelle in which it is required
a sorting signal
What happens to proteins that lack a sorting signal
proteins remain permanent residents of the cytosol
Can a membrane-enclosed organelle import a water-soluble protein to its interior?
it really depends on the organelle
Ways to transport a water-soluble protein in a membrane-enclosed organelle
Nuclear pore
Protein translocators
Transport vesicles
what is a signal sequence
a sequence that directs proteins to the correct destination
In specifying the same destination, properties such as hydrophobicity and placement of charged aa appear to be more import than the aa sequence itself, True or False?
True
True or False: Properties are often not removed from the finished protein
False
____________ encloses the nuclear DNA and defines the nuclear compartment; is formed from two______________
Nuclear envelope
Concentric membranes
Inner nuclear membrane contains proteins that act as a binding site for
chromosomes
Inner nuclear membrane contains proteins that act provide anchorage for
The nuclear lamina
Finely woven meshwork of protein filaments that lines the inner face of this membrane and provides structural support to the nuclear envelope
Nuclear lamina
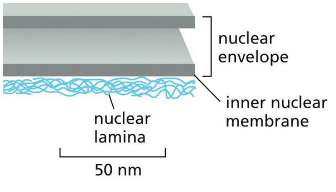
what is that nuclear lamina apart of
Inner nuclear membrane
closely resembles the membrane of the ER, with which it is continuous
Outer nuclear membrane
Outer nuclear membrane is apart of
the nuclear envelope
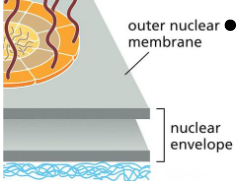
The nuclear envelope is perforated by
Nuclear Pores
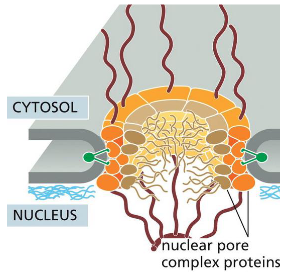
large, elaborate structure composed of a complex ~30 different proteins, each present in multiple copies
Nuclear pores
Nuclear pores are lined with
Extensive unstructured disordered regions of polypeptide chains
What do proteins to be delivered inside the nucleus require
Nuclear localization signals
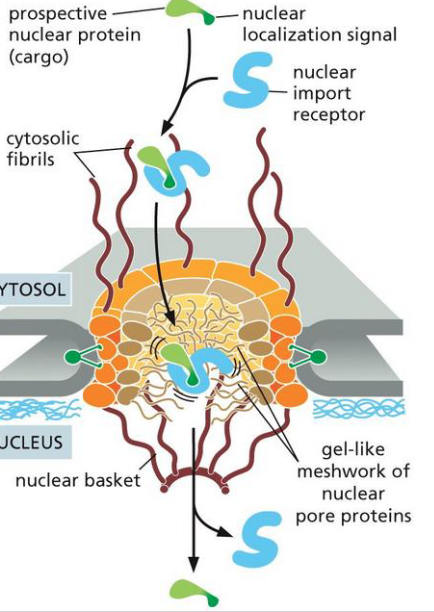
What do Nuclear localization sites consist of?
one or two short sequences containing several positively charged Lys or Arg
What are nuclear localization sites usually recognized by?
cytosolic proteins called nuclear import receptors
Directionality of nuclear import receptors is guided by what?
the hydrolysis of nucleoside triphosphate,
GTP, by monomeric GTPase named Ran
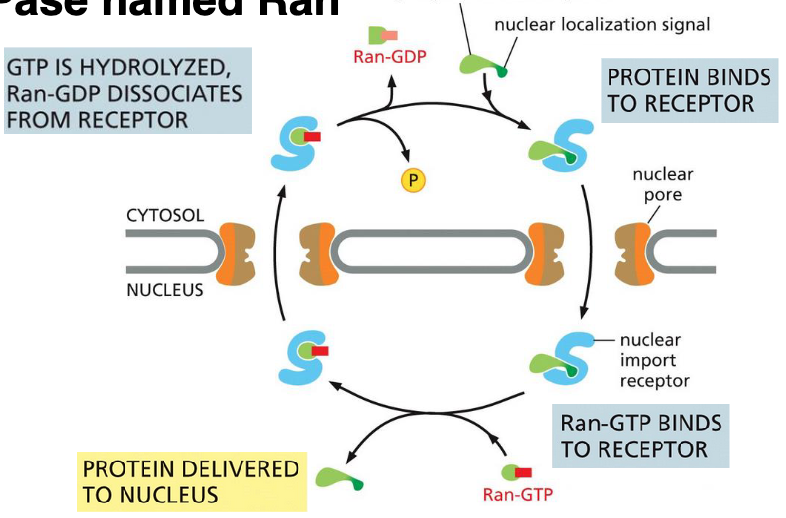
The differently localized accessory proteins that Ran converts from one form to another are
Ran - GDP - mainly in cytosol
Ran - GTP - high concentration in the nucleus
Ran - GAP - GTPase-activating protein
Ran-GEF - Guanine nucleotide exchange factor
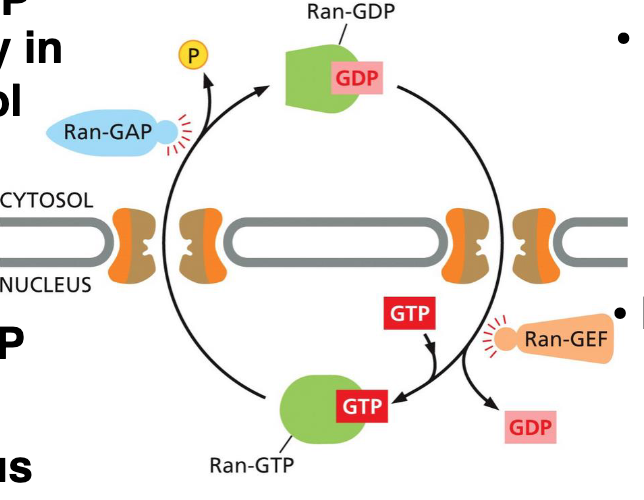
What drives protein and RNA traffic from the nucleus to the cytosol
Nuclear export receptors
What recognizes specific nuclear export signals
Nuclear export receptors
What also uses Ran to couple the transport to an energy source
Nuclear export receptors
How are proteins transported into nucleus
in their fully formed conformation
For delivery into the nucleus, nuclear pore proteins rapidly usher macromolecules in both directions through each pore
What usually has a signal sequence at their N-terminus and must cross both, the inner and the outer membranes that surround each of these organelles
Proteins to be delivered into the mitochondria
Where does translocation take place
At specialized sites where the two membranes are held closely together
Proteins being delivered to the mitochondria are _________ as it is transported
Unfolded
After proteins are delivered to the mitochondria, _______________ is removed after translocation is complete
Signal sequencing
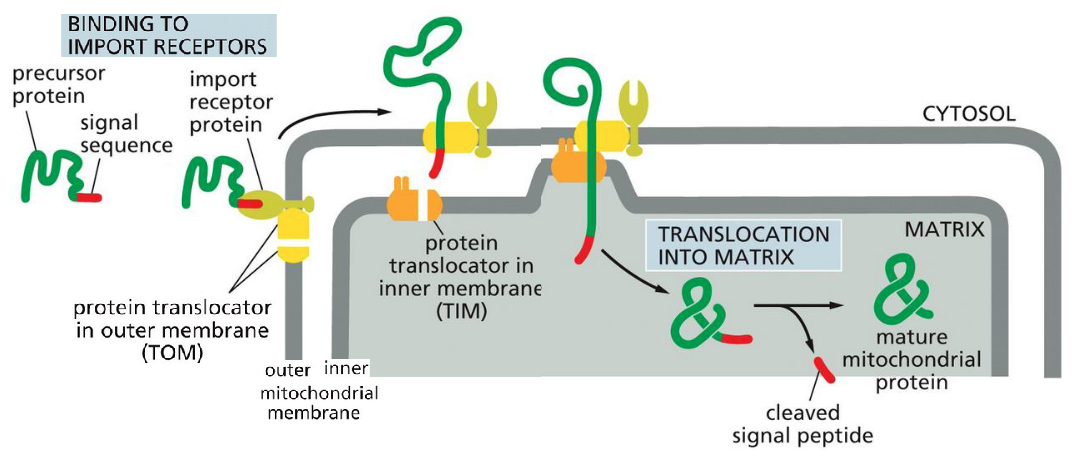
proteins inside mito help to pull the protein across the two membranes and refold it once it is inside
Chaperone proteins
How do proteins enter peroxisomes
both the cytosol and ER
a short sequence of only 3 aa serves as an import signal peroxisomes acquire the bulk of their proteins via selective transport from
the cytosol
few proteins arrive via vesicles that bud from the ER true or false
True
Entry point for proteins designed for ER and other organelles
Golgi
Endosomes
Lysosomes
Cell surface
One proteins enter the ER, they will not re-enter what?
The cytosol
How do proteins that enter the ER while being synthesized reach their destination
by transport vesicles
Proteins translocated into ER
Water-soluble proteins
TM proteins
completely translocated across the ER membrane and release into ER lumen
Water-soluble proteins
only partially translocated across the ER membrane and become embedded in it
TM proteins
ER signal sequence consists of
a segment of 8 or more hydrophobic aa
also involved in the process of translocation across the membrane
True or False: proteins are threaded across the ER membrane before the polypeptide chain has been completely synthesize
True
True or False: ribosome synthesizing the protein does not have to be attached to the ER membrane
False
How do free and bound ribosomes differ
The proteins they make
What happens when a ribosome is making a protein with an ER signal sequence
The signal sequence directs the ribosome to the ER membrane
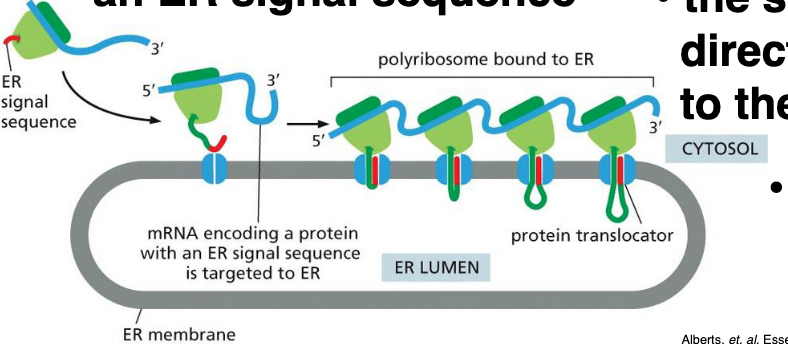
proteins with an ER signal are translocated as they are being made, additional energy is required for their import: True or False
False
proteins with an ER signal are translocated as they are being made, no additional energy is required for their import, this is because
the elongation of each polypeptide provides the thrust needed to push the growing chain through the ER membrane
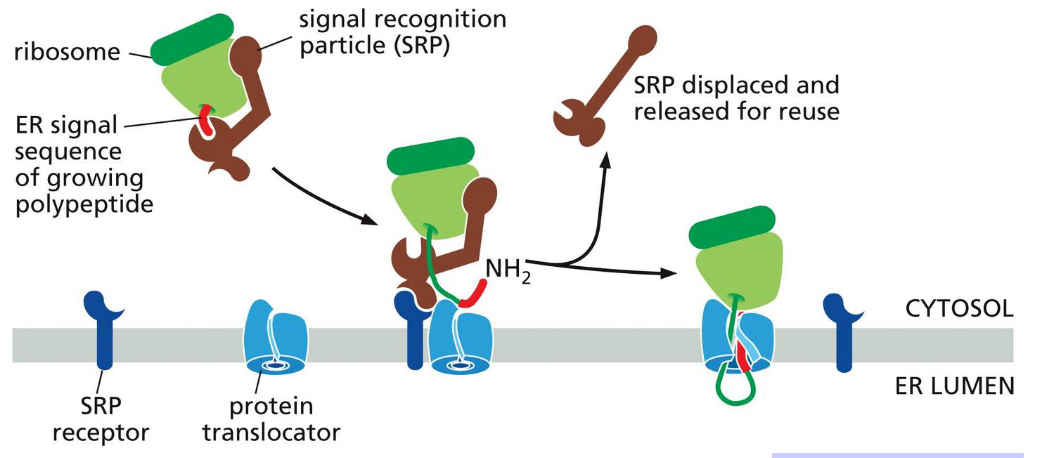
Signal-recognition particles bind to both?
The exposed ER signal sequence and the ribosome
What does the SRP receptor do?
Recognizes the SRP embedded in the ER membrane
One SRP binds to SRP receptors what happens?
SRP is released
receptor passes on the ribosome to a protein translocator in the ER membrane
When an ER signal and an SRP direct a ribosome to the ER membrane, what happens to the growing polypeptide
it is threaded across the ER membrane through a channel in the translocator
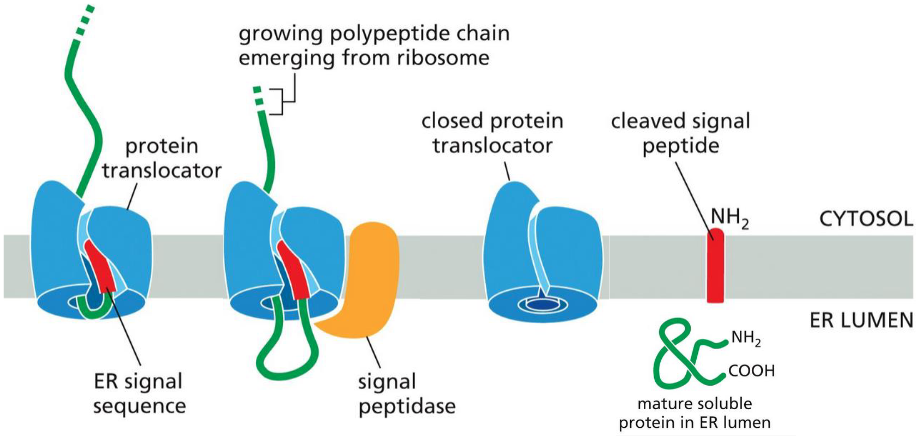
An ER signal sequence for soluble proteins
is almost always at N-terminus
functions to open the translocator
remains bound to the translocator
removed by TM signal peptidase
What is a single pass transmembrane protein
TM protein with a single alpha-helical membrane- spanning segment
Describe the single pass transmembrane protein process
N-term signal sequence initiates translocation
process is halted by additional sequence of hydrophobic aa, stop-transfer sequence
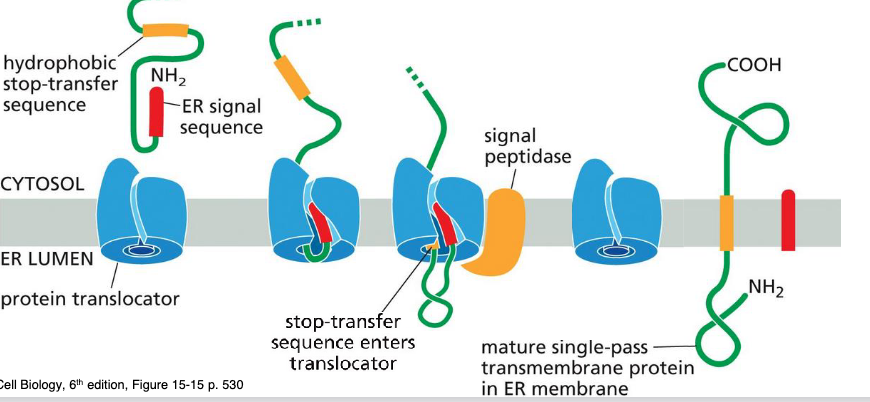
What do db pass membrane proteins do
Start-transfer sequence
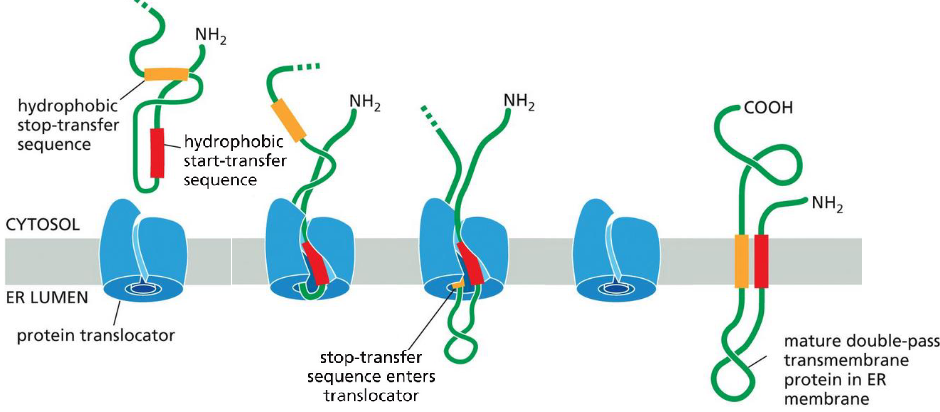
What are multi-pass transmembrane proteins
when many hydrophobic alpha helices span the bilayer
Name the properties of multipass TM proteins
additional pairs of start- and stop-sequences
even # of transmembrane alpha helices
both N- and C-terminus oriented toward the same side of the membrane
odd # of transmembrane alpha helices
opposite orientation of N- and C-terminus
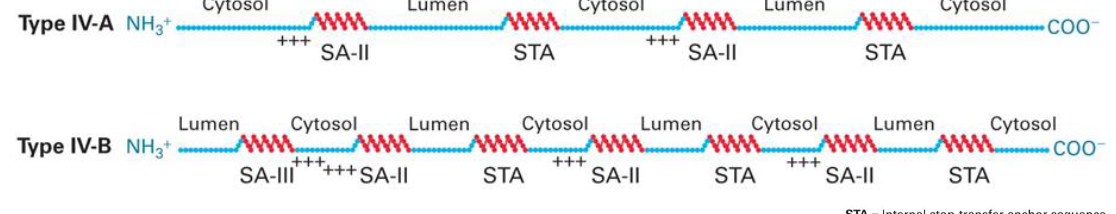
________________ direct insertion and orientation of various classes of integral proteins into ER membranes
Topogenic sequences
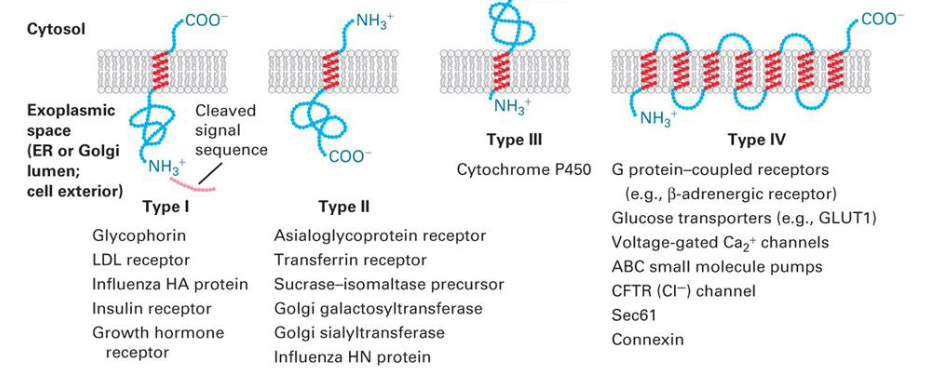
_________________ requires not only import of new proteins, but also incorporation of new lipids into the organelle membranes
Growth and maintenance of organelles
phospholipids are manufactured
by enzymes bound to the cytosolic surface of ER
True or False: organelles that are part of endomembrane system can receive lipids via transport vesicles
True