GCSE AQA Chemistry- organic chemistry
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/160
Last updated 11:37 PM on 11/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
1
New cards
How is crude oil formed?
Over millions of years from the fossilised remains of plankton
2
New cards
Where is crude oil found?
In the porous rocks in the Earth's crust
3
New cards
Is crude oil renewable or non-renewable?
Non-renewable
4
New cards
What is crude oil made up of?
Hydrocarbons
5
New cards
What gives hydrocarbon molecules varying properties?
They vary in size
6
New cards
What happens to the properties of hydrocarbons as the molecules get larger?
It gets more viscous, its boiling point gets higher, the less volatile it is, the less easily it ignites
7
New cards
How are the components of crude oil separated?
Fractional distillation
8
New cards
Why does fractional distillation work?
Different sized molecules of hydrocarbons have different boiling points
9
New cards
What has been done to try and reduce the amount of sulfur released into the atmosphere?
It can be removed from fuels before combustion in motor vehicles or removed from waste gases in power stations
10
New cards
What piece of equipment does fractional distillation take place in?
Fractionating column
11
New cards
What is the effect of particulates?
They cause global dimming by reducing the amount of sun that can reach the earth's surface, they cause damage to people's lungs
12
New cards
What happens when carboxylic acids ionise in water?
They form weak acids and they do not ionise fully
13
New cards
What is an example of an amino acid?
Glycine
14
New cards
What is a hydroxyl molecule?
-OH
15
New cards
What is a nucleotide?
Half of one rung of DNA- A phospate, a sugar and a base
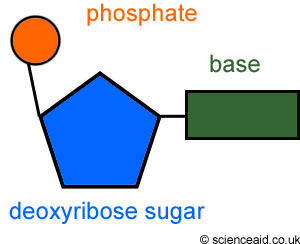
16
New cards
What happens to alcohols as they dissolve in water?
They form neutral solutions
17
New cards
What are thermosetting polymers?
Consist of polymer chains that are joined together by cross-links, do no melt when heated
18
New cards
What is DNA?
Stores the genetic material of living organisms
19
New cards
What test can be used to differentiate between alkanes and alkenes?
Shaken bromine water
20
New cards
What colour does an alkene go in the shaken bromine water test?
Colourless
21
New cards
How are nitrogen oxides produced from combustion?
When high temperatures from combustion are reaches, nitrogen in the air reacts with oxygen
22
New cards
What are alcohols used for?
As fuels and solvents
23
New cards
What is the functional group found in alcohols?
Hydroxyl
24
New cards
What do polypeptides contain?
Lots of peptide links
25
New cards
What process do amino acids go through to form larger molecules?
Condensation polymerisation
26
New cards
What is cracking?
Long chain hydrocarbons being broken down into shorter chain hydrocarbons
27
New cards
Are alkanes saturated or unsaturated?
Saturated
28
New cards
What is the formula of glycine?
NH2CH2COOH
29
New cards
What is formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with a carbonate?
Carbon dioxide
30
New cards
What are monomers?
Small molecules with a double bond that can join together to make polymers
31
New cards
What is the name of an hydrocarbon with 2 carbon molecules?
Eth(ane/ene)
32
New cards
What is DNA made of?
4 nucleotides, a phosphate and a sugar
33
New cards
What is the general formula for an alkane?
CnH2n+2
34
New cards
What type of molecules are starch, cellulose and sugars?
Carbohydrates
35
New cards
How are esters formed?
When carboxylic acids and alcohols react
36
New cards
What catalyst is used in the addition reaction used to produce alkanes from alkenes?
Nickel
37
New cards
What happens during the combustion of hydrocarbons?
Carbon and hydrogen are oxidised, energy is released, waste products are released into the atmosphere
38
New cards
What are hydrocarbons that have double bonds described as?
Unsaturated
39
New cards
What happens in incomplete combustion?
Carbon monoxide/ soot and water is produced
40
New cards
dangers of carbon monoxide
binds to the same part of haemoglobin molecule that oxygen does so less space for oxygen leading to oxygen shortage
it permanently binds to haemoglobin
it permanently binds to haemoglobin
41
New cards
dangers of soot
carbon particulates can cause global dimming and respiratory problems
42
New cards
prefixes for naming organic molecules
meth, eth, prop, but
43
New cards
complete combustion
happens in plentiful supply of oxygen
44
New cards
incomplete combustion
happens in a limited supply of oxygen
45
New cards
combustion
the process of burning something
46
New cards
What is the name of an hydrocarbon with 5 carbon molecules?
Prop(ane/ene)
47
New cards
How can ethanoic acid be produced?
By oxidising ethanol with chemical oxidation agents or by the action of bacteria from the air
48
New cards
What do the properties of a polymer depend on?
What monomer was used, the conditions under which it was made
49
New cards
What are the products of cracking?
Both alkanes and alkenes
50
New cards
The repeating unit and the monomer unit always contain what?
The same atoms
51
New cards
What are esters used for?
They are used in food flavourings and perfumes
52
New cards
What are the 4 nucleotides in DNA?
Guanine (G). cytosine (C), adenine (A), and thymine (T)
53
New cards
How are esters named?
The prefix of the alcohol with -yl as a suffix and the prefix of the acid with-oate as the suffix. For example, ethanol and ethanoic acid would react to form ethyl ethanoate
54
New cards
What is the main difference between alkenes and alkanes?
Alkenes have a double carbon-carbon bond
55
New cards
What is the name of an hydrocarbon with 1 carbon molecule?
Meth(ane/ene)
56
New cards
What type of alcohol do alcoholic drinks contain?
Ethanol
57
New cards
What do carboxylic acids form when dissolved in water?
Acidic solutions
58
New cards
What are starch and cellulose?
Polymers of sugars
59
New cards
What is the general formula for an alkene?
C(n)H(2n)
60
New cards
What are the properties of esters?
They are volatile and have distinctive smells
61
New cards
What is the balanced symbol equation for complete combustion?
C + O2 = CO2
62
New cards
What is the balanced symbol equation for the combustion of hydrogen?
2H2 + O2 = 2H2O
63
New cards
What do amino acids form when they join by condensation polymerisation?
Polypeptides and water
64
New cards
What does the process of cracking include?
1) the hydrocarbons are heated until they vaporise 2) the vapour is passed over a hot catalyst 3) thermal decomposition then takes place
65
New cards
Why are alkenes more reactive than alkanes?
Because of the C=C bond
66
New cards
What is an example of a thermosetting polymer?
Melamine
67
New cards
What can be added to alkenes to produce alkanes?
Hydrogen
68
New cards
What is the name of an hydrocarbon with 3 carbon molecules?
Prop(ane/ene)
69
New cards
Why do alkenes burn with a smokier flame than alkanes?
They go through incomplete combustion
70
New cards
How are the simplest polymers formed in a condensation reaction?
When diols (molecules containing two hydroxyl groups) join with diacarboxylic acids
71
New cards
What are the first four members of the homologous series of alcohols?
Methanol, ethanol, propanol, butanol
72
New cards
What is the ideal temperature range for the fermentation of sugar to produce ethanol?
25 degrees to 50 degrees
73
New cards
What is formed when carboxylic acids react with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst?
They form esters
74
New cards
What is the atom economy of an addition polymerisation reaction?
100%
75
New cards
What is a peptide link?
The bond formed between the carboxyl groups and the amino acid groups when amino acids join together
76
New cards
What is a condensation polymerisation reaction?
Monomers join together to form large polymer molecules and lose small molecules such as water
77
New cards
What is the balanced symbol equation for the combustion of sulfur?
S + O2 = SO2
78
New cards
What happens to alcohols when they react with sodium?
They produce hydrogen
79
New cards
What problems do nitrogen oxides cause?
Cause respiratory problems, react with rainwater to form acid rain
80
New cards
What is the name of an hydrocarbon with 4 carbon molecules?
But(ane/ene)
81
New cards
What happens to alcohols as they burn in air?
They produce carbon dioxide and water
82
New cards
What is an example of a thermosoftening polymer?
Polyethene
83
New cards
What is functional group found in esters?
-COO
84
New cards
What is an alkane?
A saturated hydrocarbon with the general formula CnH2n+2
85
New cards
What organism makes starch and cellulose?
Plants
86
New cards
Why are hydrocarbons split into shorter molecules?
There is a higher demand for short hydrocarbons as they easy to ignite and have low boiling points so are used in fuels
87
New cards
How can ethanol be produced?
By reacting ethene with steam in the presence of a catalyst- phosphoric acid
88
New cards
What are the stages of fractional distillation?
1) the crude oil is heated to about 450 C 2) and pumped into the bottom of a tall tower called a fractioning column where it vaporises 3) the column is very hot at the bottom but much cooler at the top 4) as the vaporised oil rises, it cools and condenses 5) heavy fractions (containing large molecules) have a high BP and so condense near the bottom of the column 6) lighter fractions (containing small molecules have a lower BP and so condense further up the column
89
New cards
How can aqueous solutions of ethanol can be produced?
The fermentation of sugar
90
New cards
What are carboxylic acids?
Organic compounds that contain the functional group carboxyl
91
New cards
What colour does an alkane go in the shaken bromine water test?
Stays orange
92
New cards
What is the balanced symbol equation for incomplete combustion?
2C + O2 = 2CO
93
New cards
What is carboxyl molecule?
-COOH
94
New cards
What are the properties of thermosoftening polymers?
Have individual chains of polymers that are all tangled together. Have weak intermolecular forces between chains so soften when heated
95
New cards
what is an alkene?
a hydrocarbon with a carbon-carbon double bond (unsaturated)
96
New cards
Catalytic cracking
a process in which catalysts are used to crack larger hydrocarbon molecules into smaller ones at relatively low temperature
97
New cards
what type of reaction is catalytic cracking?
thermal decomposition
98
New cards
what is a functional group of any organic compound?
the part that can undergo reactions and makes the compound "special" (i.e different from the alkane)
99
New cards
Addition reactions of alkenes
can involve H2, halogens (Br2, Cl2) , H20 (steam)
100
New cards
alkene reactions with h2
alkene + H2 > alkane